For services with high queries per second (QPS) such as image services, enabling VPC direct connection can significantly enhance access performance and reduce latency. But this does not grant load balancing capabilities among multiple instances. If you already have microservices using Nacos, you can use Nacos to implement access control. This topic describes how to call an Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) service by mounting a Nacos instance.
Prerequisites
A virtual private cloud (VPC), a vSwitch, and a security group have been created. The vSwitch must have a sufficient number of available IPs. EAS will register the IP addresses of your service instance on the elastic network interface (ENI). For more information, see Create and manage a VPC and Manage security groups.
ImportantSecurity groups manage both inbound and outbound traffic for ECS instances, as well as network interactions with EAS service instances. By default, instances within the same basic security group can interact over the VPC. When configuring VPC direct connection, select the appropriate security group for the ECS instance that requires access to the EAS service to facilitate inter-instance communication. To enable communication between different security groups, you must configure the security group rules accordingly.
VPC direct connection has been enabled for EAS. For more information, see Configure network connectivity.
A Nacos instance is available, see Create an instance.
The VPC and vSwitch where the Nacos instance is deployed are the same as those configured for VPC direct connection.
How it works

Create a Nacos instance within a VPC and a vSwitch, which are the same as those configured for VPC direct connection.
When you deploy an EAS inference service, ensure you specify the Nacos to be mounted.
EAS registers the pods associated with the inference service to your Nacos instance.
The client initiates a Nacos service registration listener.
Nacos pushes updates to the IP list of the EAS service to clients.
The client uses the SDK to select an instance (The SDK includes a load balancing algorithm: weighted round-robin).
The client uses the IP and port of the service instance provided by the SDK to access the service and initiate the call.
Mount Nacos
To associate a Nacos instance, include the following key parameters in the JSON configuration file when deploying or updating a service. This configuration supports arrays, allowing registration with multiple Nacos instances simultaneously for scenarios like disaster recovery. Sample:
{ "cloud": { "networking": { "security_group_id": "sg-*****", "vpc_id": "vpc-***", "vswitch_id": "vsw-****" } }, "networking": { "nacos": [ { "nacos_id": "mse_regserverless_cn-****" } ] } }Parameter | Description | ||
cloud | networking | vpc_id | Enable VPC direct connection by configuring the VPC, vSwitch, and security group. Important
|
vswitch_id | |||
security_group_id | |||
networking | nacos | id | The ID of the created Nacos instance. |
Check Nacos service registration
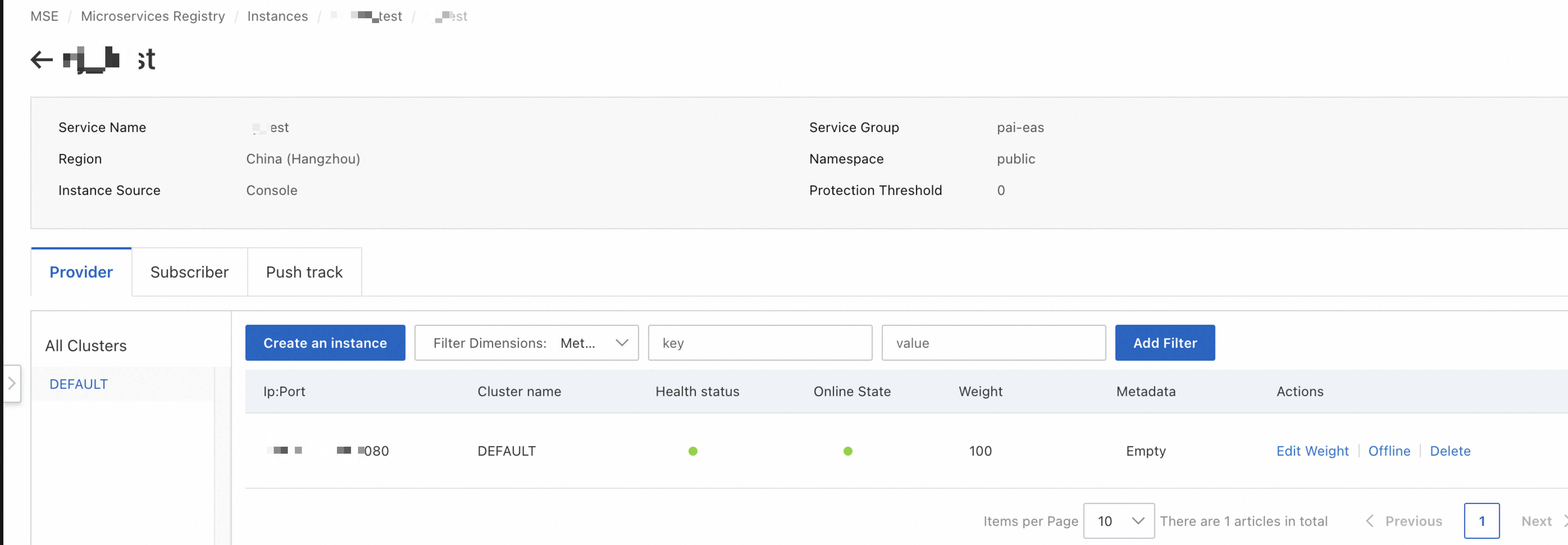
After successful service deployment, EAS will register it with your Nacos instance. Registration details:
cluster: The DEFAULT cluster
namespace: The default public namespace
serviceName: Your service name
groupName: System-generated static field, pai-eas
Verify the accuracy of the created service information:
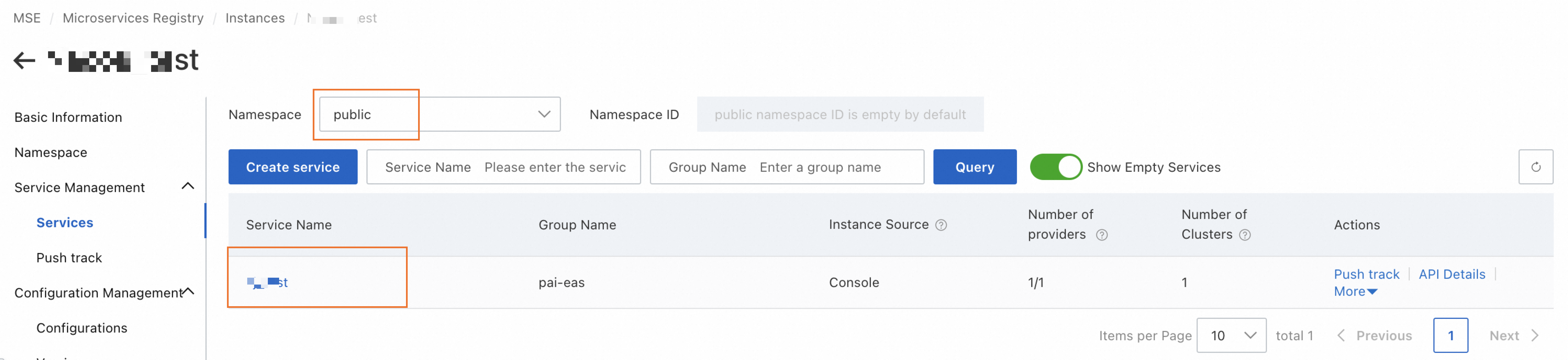
Confirm the number and status of instances within the service:
Client invocation
Go
package main import ( "fmt" "github.com/nacos-group/nacos-sdk-go/v2/clients" "github.com/nacos-group/nacos-sdk-go/v2/clients/naming_client" "github.com/nacos-group/nacos-sdk-go/v2/common/constant" "github.com/nacos-group/nacos-sdk-go/v2/model" "github.com/nacos-group/nacos-sdk-go/v2/util" "github.com/nacos-group/nacos-sdk-go/v2/vo" "strconv" "testing" "time" ) var Clients = make(map[string]NacosClientManager) type NacosClientManager struct { userId string endPoint string client naming_client.INamingClient } func NewAndGetNacosClient(userId string, endPoint string) (*NacosClientManager, error) { key := generateKey(userId, endPoint) client, exists := Clients[key] if exists { return &client, nil } client, exists = Clients[key] if exists { return &client, nil } newClient, err := clients.NewNamingClient( vo.NacosClientParam{ ClientConfig: constant.NewClientConfig( constant.WithNamespaceId(""), constant.WithTimeoutMs(5000), constant.WithNotLoadCacheAtStart(true), constant.WithLogDir("/tmp/nacos/log"), constant.WithCacheDir("/tmp/nacos/cache"), constant.WithLogLevel("debug"), ), ServerConfigs: []constant.ServerConfig{ *constant.NewServerConfig(endPoint, 8848, constant.WithContextPath("/nacos")), }, }, ) if err != nil { return nil, err } nacosClient := NacosClientManager{ userId: userId, endPoint: endPoint, client: newClient, } Clients[key] = nacosClient return &nacosClient, nil } func (p *NacosClientManager) SelectOneHealthyInstance(param vo.SelectOneHealthInstanceParam) (*model.Instance, error) { instance, err := p.client.SelectOneHealthyInstance(param) if err != nil { return nil, fmt.Errorf("SelectOneHealthyInstance failed: %v", err) } fmt.Printf("SelectOneHealthyInstance success, param: %+v\n", param) return instance, nil } func (p *NacosClientManager) Subscribe(service string, group string) error { subscribeParam := &vo.SubscribeParam{ ServiceName: service, GroupName: group, SubscribeCallback: func(services []model.Instance, err error) { fmt.Printf("callback return services:%s \n\n", util.ToJsonString(services)) }, } return p.client.Subscribe(subscribeParam) } func generateKey(userId string, endPoint string) string { return userId + fmt.Sprintf("-%s", endPoint) } func Test(t *testing.T) { nacosClient, err := NewAndGetNacosClient("yourAliyunUid", "yourNacosEndpoint") if err != nil { panic(err) } nacosClient.Subscribe("your_service", "pai-eas") params := vo.SelectOneHealthInstanceParam{ ServiceName: "your_service", GroupName: "pai-eas", } instance, err := nacosClient.SelectOneHealthyInstance(params) fmt.Println(instance) // check your own invoke info on console and replace host by ip:port url := fmt.Sprintf("http://%s:%s/api/predict/xxxxxxx", instance.Ip, strconv.FormatUint(instance.Port, 10)) fmt.Println(url) //todo invoke service by url } Python
The official Python SDK for Nacos does not include a load balancing algorithm. You need to implement weighted round-robin by your self.
Install dependencies
pip install nacos-sdk-pythonInitiate invocation
# -*- coding: utf8 -*- import nacos # Nacos server configuration SERVER_ADDRESSES = "yourNacosEndpoint" NAMESPACE = "" # Use default namespace if empty SERVICE_NAME = "your_service" GROUP_NAME = "pai-eas" # Create Nacos client client = nacos.NacosClient(SERVER_ADDRESSES, namespace=NAMESPACE) def callback(args): print(args) if __name__ == '__main__': # Correctly pass the callback function as a list client.add_config_watchers(SERVICE_NAME, "pai-eas", [callback]) # Fetch and print naming instance details b = client.list_naming_instance(SERVICE_NAME, None, None, GROUP_NAME, True) print(b) if b"hosts": print("ip", b["hosts"][0]["ip"]) ip = b["hosts"][0]["ip"] port = b["hosts"][0]["port"] # check your own invoke info on console and replace host by ip:port url = f"http://{ip}:{port}/api/predict/xxxxxxx" print(url) #todo invoke service by url Java
Add Maven dependencies
<dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.nacos</groupId> <artifactId>nacos-client</artifactId> <version>2.3.2</version> </dependency>Initiate invocation
package test; import java.util.concurrent.Executor; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import com.alibaba.nacos.api.NacosFactory; import com.alibaba.nacos.api.exception.NacosException; import com.alibaba.nacos.api.naming.NamingService; import com.alibaba.nacos.api.naming.listener.AbstractEventListener; import com.alibaba.nacos.api.naming.listener.Event; import com.alibaba.nacos.api.naming.listener.EventListener; import com.alibaba.nacos.api.naming.listener.NamingEvent; import com.alibaba.nacos.api.naming.pojo.Instance; public class NacosTest { public static void main(String[] args) { try { String serverAddr = "yourNacosEndpoint:8848"; NamingService namingService = NacosFactory.createNamingService(serverAddr); ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1); EventListener serviceListener = new AbstractEventListener() { @Override public void onEvent(Event event) { if (event instanceof NamingEvent) { System.out.println(((NamingEvent) event).getServiceName()); System.out.println(((NamingEvent) event).getGroupName()); } } @Override public Executor getExecutor() { return executorService; } }; namingService.subscribe("your_service", "pai-eas", serviceListener); Instance instance = namingService.selectOneHealthyInstance("your_service", "pai-eas"); System.out.println(instance.getIp()); System.out.println(instance.getPort()); // check your own invoke info on console and replace host by ip:port String url = String.format("http://%s:%d/api/predict/xxxxxxx", instance.getIp(), instance.getPort()); System.out.println(url); //todo invoke service by url } catch (NacosException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }