This topic describes common issues and troubleshooting methods for data replication, including same-account, cross-account, same-region, and cross-region replication.
Does the OSS region replication feature support custom destination Bucket paths/prefixes?
No, it does not. Same-region and cross-region replication do not support custom storage paths for the destination Bucket. The destination path is determined by the source Bucket's data path that is configured in the replication rule.
Does OSS region replication support synchronization based on a specified file modification time?
No, it does not. The data replication feature does not support configuring synchronization based on a specified range of file modification times. However, you can use the File Modification Time feature of Data Online Migration. If you specify a file modification time range, only files within that time period are migrated.
Why can't I create a data replication rule?
Check whether the required permissions are granted.
The RAM user lacks the required permissions
In the console, a RAM user cannot click OK to create a data replication rule.
Cause: The oss:PutBucketReplication permission is missing.
Solution: Grant the oss:PutBucketReplication permission to the RAM user.
When a RAM user creates a data replication rule in the console, a custom-created role is not displayed in the authorization role list.
Cause: The ram:ListRoles permission is missing.
Solution: Grant the ram:ListRoles permission to the RAM user.
For more information, see Grant custom access policies to a RAM user.
The RAM role lacks the required permissions
Replication within the same account
For replication within the same account, you must grant the role permissions to perform replication operations between the source and destination Buckets. For more information about how to create and grant permissions to a RAM role, see Role types.
Cross-account replication
For cross-account replication, Account A must grant a role the permissions to replicate data from the source Bucket, and Account B must grant a role the permissions to receive replicated objects in the destination Bucket. For more information about creating and authorizing RAM roles, see Role authorization.
Check whether the versioning status of the Buckets is consistent.
The versioning status of the source and destination Buckets must be the same. This means that versioning must be either enabled or disabled for both Buckets.
Check whether the Endpoint or AccessKey information is correct.
When you create a data replication rule using an SDK or ossutil, check the following configurations:
Check whether the Endpoints of the regions where the source and destination Buckets are located are correct. For more information, see OSS regions and endpoints.
Check whether the AccessKey used to establish the replication relationship is correct. For more information, see View the AccessKey pair of a RAM user.
Why is data not replicated to the destination Bucket?
If object replicas do not appear in the destination Bucket after you configure a data replication rule for the source Bucket, troubleshoot the issue based on the following possible causes.
Check whether the source Bucket is correctly configured.
Check whether the data replication status is Enabled.
Check whether the prefix is correct.
Replicate specified objects: To replicate only specified objects from the source Bucket, set the Prefix parameter to the prefix of the target files. For example, if you set Prefix to log, only objects with names that start with log, such as log/date1.txt and log/date2.txt, are replicated. Objects that do not match the specified prefix, such as date3.txt, are not replicated.
NoteThe prefix cannot end with an asterisk (*) or contain the Bucket name.
Replicate all objects: To replicate all objects from the source Bucket, leave the Prefix parameter empty.
Confirm whether historical data replication is configured and if historical files are not being synchronized.
Confirm whether the files in the source Bucket are replicated from another Bucket using same-region or cross-region replication.
If an object in a Bucket is a replica from another replication rule, OSS does not replicate this object again. For example, if you configure replication from Bucket A to Bucket B and from Bucket B to Bucket C, the object replicas from Bucket A are not replicated from Bucket B to Bucket C.
Confirm whether the files are encrypted using KMS. If they are, you must select the Replicate KMS-encrypted objects option.
If the source object or destination Bucket is encrypted with server-side encryption with KMS-managed keys (SSE-KMS) and a customer master key (CMK) ID is specified, you must select Replicate and configure the following parameters:
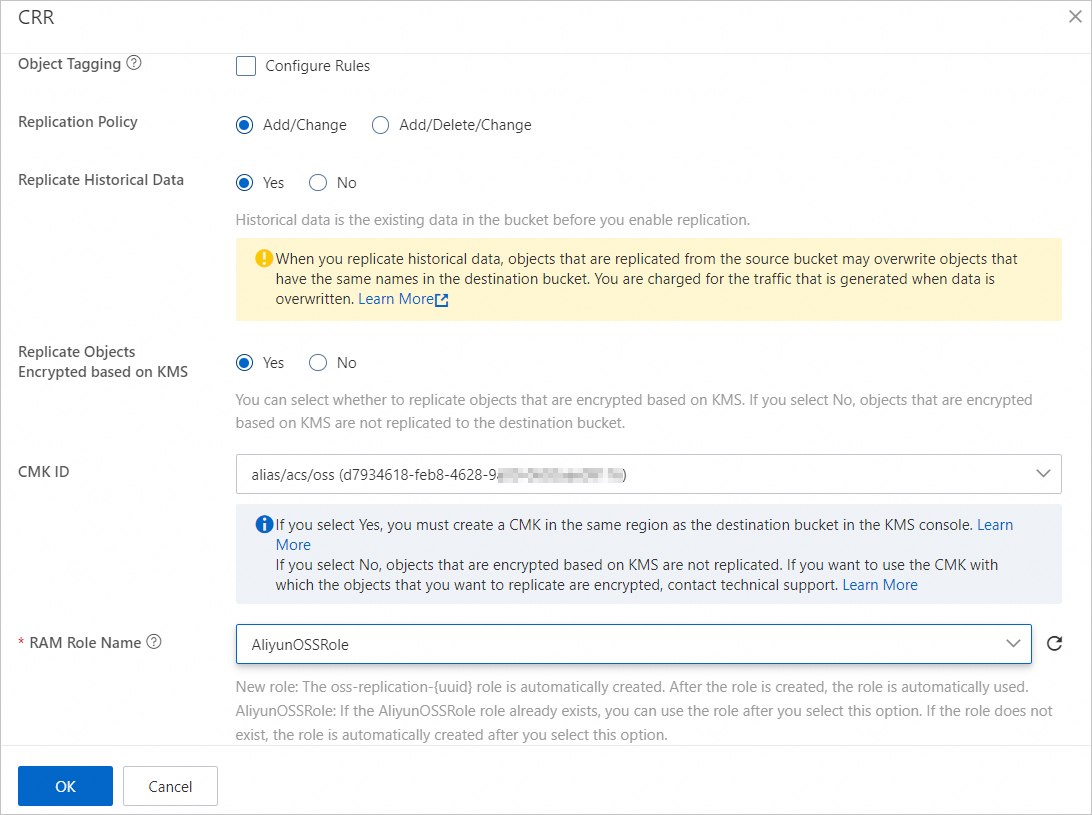
KMS Key To Use: Specifies the KMS key used to encrypt the destination object.
You must first create a KMS key in the same region as the destination Bucket on the KMS platform. For more information, see Create a key.
Authorization Role: The RAM role authorized to perform KMS encryption on the destination object.
Create Role: Creates a RAM role to encrypt destination objects using KMS. The role name must use the format
kms-replication-SourceBucketName-DestinationBucketName.AliyunOSSRole: A role used to encrypt the destination object with KMS. If this role does not exist, OSS automatically creates it when you select this option.
NoteIf you create a role or modify the permissions of a role, ensure that the
AliyunOSSFullAccesspermission is granted to the role. Otherwise, data replication may fail.
You can call the HeadObject and GetBucketEncryption operations to query the encryption status of the source object and the destination Bucket, respectively.
Check whether the replication progress is 100%.
Data replication is asynchronous and occurs in near real-time. The time required to replicate data to the destination Bucket can range from several minutes to several hours, depending on the data size. If the object to be replicated is large, wait for the replication to complete. After you confirm that the data replication progress is 100%, check whether the object is in the destination Bucket.
Why is data not deleted from the destination Bucket synchronously?
Cause 1: A Write-Once-Read-Many (WORM) retention policy is configured for the destination Bucket.
Before the retention period specified in the policy expires, no user, including the resource owner, can delete objects in the Bucket.
Cause 2: Whether data is deleted from the destination Bucket depends on the versioning status of the source Bucket and the configured data replication policy.
Versioning status of the source Bucket
Request method
Data replication policy
Result
Versioning disabled
A Delete request is initiated
Replicate created/modified data
Only objects in the source Bucket are deleted. Objects in the destination Bucket are not deleted.
Replicate created/deleted/modified data
Objects in the source and destination Buckets are deleted synchronously.
Versioning enabled
A Delete request is initiated without specifying an object version ID
Replicate created/modified data
Objects in the source and destination Buckets are not deleted. OSS creates a delete marker in the source Bucket, and the delete marker is replicated to the destination Bucket.
Replicate created/deleted/modified data
A Delete request is initiated with an object version ID specified
Replicate created/modified data
Only objects in the source Bucket are deleted. Objects in the destination Bucket are not deleted.
Replicate created/deleted/modified data
Objects in the source and destination Buckets are deleted synchronously.
How do I verify the data consistency between the source and destination Buckets after replication is complete?
You can use the following code to verify the data consistency between the source and destination Buckets after replication is complete.
import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClient; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.*; import com.aliyun.oss.model.*; import com.aliyun.oss.OSSException; import com.aliyuncs.exceptions.ClientException; public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClientException { // Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run this sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are set. EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = CredentialsProviderFactory.newEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider(); // Set srcEndpoint to the Endpoint of the region where the Bucket is located. String srcEndpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com"; OSSClient srcClient = new OSSClient(srcEndpoint , credentialsProvider); // Specify the name of the source Bucket. String srcBucketName = "src-replication-bucket"; // Set destEndpoint to the Endpoint of the region where the Bucket is located. String destEndpoint = "https://oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com"; OSSClient destClient = new OSSClient(destEndpoint, credentialsProvider); // Specify the name of the destination Bucket. String destBucketName = "dest-replication-bucket"; // If versioning is disabled for the source and destination Buckets, call the listObjectsV2 operation to list the replicated files in the source Bucket. // If versioning is enabled or suspended for the source and destination Buckets, call the listVersions operation to list the replicated files in the source Bucket. ListObjectsV2Result result; ListObjectsV2Request request = new ListObjectsV2Request(srcBucketName); do { result = srcClient.listObjectsV2(request); for (OSSObjectSummary summary : result.getObjectSummaries()) { String objectName = summary.getKey(); ObjectMetadata srcMeta; try { // Obtain the metadata of the replicated file in the source Bucket. srcMeta = srcClient.headObject(srcBucketName, objectName); } catch (OSSException ossException) { if (ossException.getErrorCode().equals("NoSuchKey")) { continue; } else { System.out.println("head src-object failed: " + objectName); } continue; } ObjectMetadata destMeta; try { // Obtain the metadata of the file replicated to the destination Bucket. destMeta = destClient.headObject(destBucketName, objectName); } catch (OSSException ossException) { if (ossException.getErrorCode().equals("NoSuchKey")) { System.out.println("dest-object not exist: " + objectName); } else { System.out.println("head dest-object failed: " + objectName); } continue; } // Check whether the CRC values of the replicated files in the source and destination Buckets are the same. Long srcCrc = srcMeta.getServerCRC(); String srcMd5 = srcMeta.getContentMD5(); if (srcCrc != null) { if (destMeta.getServerCRC() != null) { if (!destMeta.getServerCRC().equals(srcCrc)) { System.out.println("crc not equal: " + objectName + " | srcCrc: " + srcCrc + " | destCrc: " + destMeta.getServerCRC()); } continue; } } // Check whether the MD5 values of the replicated files in the source and destination Buckets are the same. if (srcMd5!= null) { if (destMeta.getContentMD5() != null) { if (!destMeta.getContentMD5().equals(srcMd5)) { System.out.println("md5 not equal: " + objectName + " | srcMd5: " + srcMd5 + " | destMd5: " + destMeta.getContentMD5()); } continue; } } // Check whether the ETags of the replicated files in the source and destination Buckets are the same. if (srcMeta.getETag() == null || !srcMeta.getETag().equals(destMeta.getETag())) { System.out.println("etag not equal: " + objectName + " | srcEtag: " + srcMeta.getETag() + " | destEtag: " + destMeta.getETag()); } } request.setContinuationToken(result.getNextContinuationToken()); request.setStartAfter(result.getStartAfter()); } while (result.isTruncated()); } } Is transitive replication supported?
No, it is not. For example, if a data replication rule is configured from Bucket A to Bucket B and another rule is configured from Bucket B to Bucket C, data from Bucket A is replicated only to Bucket B, not to Bucket C.
If you want to replicate data from Bucket A to Bucket C, you must also configure a data replication rule from Bucket A to Bucket C.
If historical data replication is enabled for both Bucket A and Bucket B, new data written to Bucket A may be scanned by the historical replication task and replicated to Bucket C before the historical data replication is complete.
Is there a risk of replication loops in two-way synchronization for OSS Buckets?
No, there is not. After a bidirectional replication relationship is configured between Bucket A and Bucket B, data replicated from Bucket A to Bucket B is not replicated back to Bucket A. This applies to both new and historical data. Similarly, data replicated from Bucket B to Bucket A is not replicated back to Bucket B.
If files in the source Bucket are deleted based on a lifecycle rule, are these files also deleted from the destination Bucket?
If the data replication policy for the source Bucket is set to Replicate Created/modified Data, files deleted from the source Bucket by a lifecycle rule are not also deleted from the destination Bucket.
If the replication policy for the source Bucket is set to Replicate Created/deleted/modified Data, files deleted from the source Bucket by a lifecycle rule are also deleted from the destination Bucket.
NoteIf you find files in the destination bucket that were deleted from the source bucket by a lifecycle rule, it does not necessarily mean that the Replicate Created/deleted/modified Data policy is ineffective. This can happen if you have manually written files with the same names to the destination bucket.
Why does the historical data replication progress remain at 0% for a long time?
The replication progress is not updated in real time
The historical data replication progress is not updated in real time. The progress is updated only after all files are scanned. If your Bucket contains many files, such as hundreds of millions, you may need to wait several hours for the progress to update. A progress bar that has not updated does not mean that historical data is not being replicated to the destination Bucket.
You can check the changes in the storage capacity of the destination Bucket and the replication traffic to confirm whether historical data from the source Bucket is being replicated. For more information about how to view the storage capacity and replication traffic of a Bucket, see Query the usage of a bucket.
The authorization policy for the source Bucket is incorrect
When you create a data replication rule, the authorization policy of the source Bucket is not checked. As a result, the rule can be created, but data is not replicated to the destination Bucket, and the replication progress remains at 0%.
To configure a correct access policy, see Data replication permissions.
What do I do if data replication is slow?
Increase bandwidth
Data replication is asynchronous and occurs in near real-time. It may take several minutes to several hours to transfer data from the source Bucket to the destination Bucket, depending on the data size. If the replication process takes too long, check whether the replication task is delayed due to bandwidth limits. If the issue is caused by insufficient bandwidth, we recommend that you contact Technical Support to request a bandwidth upgrade to optimize replication efficiency.
Enable replication time control (RTC)
After you enable RTC, OSS replicates most objects that you upload within seconds and replicates 99.99% of objects within 10 minutes. After you enable RTC, you are charged for the data replication traffic that is generated by the replication rule for which RTC is enabled. For more information, see Use replication time control (RTC).
How do I know which data replication operations are performed on the source and destination Buckets?
You can obtain information about changes in the source and destination Buckets during data replication, such as object creation, updates, deletion, and overwriting. To do this, configure an event notification rule and set the event type to ObjectReplication:ObjectCreated, ObjectReplication:ObjectRemoved, and ObjectReplication:ObjectModified. For more information, see Use event notifications to process OSS object changes in real time.
Is data replication supported for Buckets for which versioning is suspended?
No, it is not. You can enable data replication only for two Buckets that both have versioning either disabled or enabled.
If the destination Bucket is encrypted using KMS, am I charged for the API calls of the KMS encryption algorithm?
Yes, you are. If the destination Bucket is encrypted using KMS, you are charged for the API calls of the KMS encryption algorithm. For more information about the fees, see KMS billing.
Can I disable data replication after it is enabled?
Yes, you can. Click Disable Replication to the right of the rule.
After replication is disabled, the replicated data is retained in the destination Bucket. Incremental data in the source Bucket is no longer replicated to the destination Bucket.