This topic describes the backup and restoration feature of MaxCompute and provides related commands and examples.
Overview
MaxCompute provides the backup and restoration feature. This feature enables MaxCompute to automatically back up and retain original data for a specific period. Original data refers to data on which no operations, such as deletion or modification, are performed. You can restore data within the retention period to prevent data loss.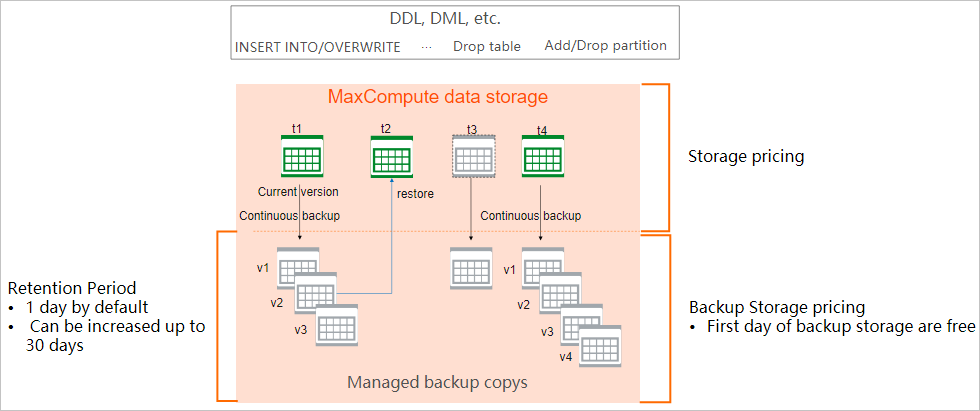
The backup and restoration feature provides the following benefits:
Automatic enabling
This feature is independent of external storage. By default, the retention period of data in all MaxCompute projects is 24 hours. Data backup and storage are free of charge.
Automatic and continuous backup
MaxCompute automatically backs up modified data. If you modify data multiple times, MaxCompute backs up data after each modification. This feature helps you prevent data loss more efficiently compared to a periodic data backup policy.
Quick and easy-to-use data restoration
MaxCompute provides advanced capabilities to manage multiple versions of data and metadata. Backup and restoration operations do not consume additional computing resources. You can run related commands to restore different volumes of data.
Precautions
When you use the backup and restoration feature, take note of the following points:
If you want to view the backup information of a table using the MaxCompute client, we recommend that you download the latest version of the client. Earlier versions may not allow you to view the backup and recovery parameters or the backup information of the table.
A backup table is generated each time you modify a table. No backup table is generated if you do not modify a table.
If the number of days for which a backup table is stored exceeds the backup data retention period configured for the project, MaxCompute deletes the backup table. The deleted backup table cannot be restored or queried.
After the purge command is run on a table, data in the table cannot be restored.
Dropped partitions or tables, including dropped Delta tables, cannot be directly restored to a specified log sequence number (LSN). You must first restore the partitions or tables and then restore them to a specified LSN.
Delta Table limitations:
You can completely restore a dropped partition or table. You cannot restore a dropped partition or table to a specific minor version. If you want to query data of a minor version, you can use the time travel feature.
After a dropped table or partition is restored, the behavior of Time Travel and Incremental queries is almost the same as it was before the drop. However, note the following details:
If you perform a query, such as a time travel query, on a dropped table before the table is restored, an error is reported. If you perform a query on a dropped partition before the partition is restored, no query result is returned, which is the same as a normal query.
If the query time specified for a time travel query or incremental query on a restored dropped table is earlier than the restoration time but later than or equal to the drop time, the system considers the queried data as deleted, and no query result is returned.
If the query time specified for a time travel query or incremental query on a restored dropped table is earlier than the drop time, the query result is the same as if no dropping operation was performed.
If the query time specified for a time travel query or incremental query on a restored dropped table is later than or equal to the restoration time, the query result is the same as if no dropping and restoration operations were performed. The restored data is not considered incremental data.
After you perform dropping and restoration operations, the system generates commit time and versions. If you restore a partitioned table, all partitions in the table are separately restored. The system generates a version for each partition.
Automatic backup and recovery of materialized views, object tables, and external tables are not supported.
Commands
The following table describes the commands involved when you use the backup and restoration feature.
Scenario | Command | Features | Permissions |
Configure a retention period for backup data |
| This command is used to configure a retention period for backup data. During the retention period, you can restore data of the version in use to the backup data of any version. The value of After the backup cycle is adjusted, the effective policy is as follows:
| Only Alibaba Cloud accounts or project administrators can perform this operation. |
| This command is run on the MaxCompute client to obtain information about project-level parameters. For more information about how to use the MaxCompute client, see MaxCompute client (odpscmd). You can view the value of odps.timemachine.retention.days parameter. If | ||
View backup data |
| View information about tables in the current project and tables in the backup state, including deleted tables. You can filter tables by table name. This command is different from the | You must have the List permission on the project. For more information, see MaxCompute permissions. |
| View the backup data of a specified table. You can use LIMIT to specify the record length, and OFFSET or version (LSN) to specify the starting position. For more information about parameters, see Parameter description. |
For more information, see MaxCompute permissions. | |
| This command is used to view the backup data of a dropped table and obtain information about the data versions within the retention period. You can run the | You must have the List permission on the project. For more information, see MaxCompute permissions. | |
| This command is used to view the backup data of a specified partition and obtain information about the data versions within the retention period. | None. | |
| This command is used to view the backup data of a dropped partition and obtain information about the data versions within the retention period. You can obtain the value of id from the ObjectId field in the command output of | ||
Restore data |
| Recover a deleted table. You can use the |
|
| Restore a table to a specified version. You can obtain the version information of a table using the | ||
| Recover a table to a specified version, rename it as a new table, or update data to a table with a different name. | ||
| This command is used to restore a dropped partition. You can restore multiple dropped partitions at a time. In normal cases, this command is used to restore the partitions for which the | ||
| This command is used to restore a specified partition to a specified version. You can restore multiple partitions at a time. In normal cases, this command is used to restore partitions that need to be recovered after the | ||
| Recover a specified partition to a specified version and rename it as a new table. |
Data file cleanup operations
Compared with standard tables, Delta tables retain historical data within the time travel period, which incurs additional storage costs. In other scenarios, the system automatically deletes unnecessary historical data files at an appropriate time (within one day at most). Users do not need to perform additional operations, which also saves corresponding storage costs. Historical data that can be deleted includes:
Historical data that is earlier than the time travel period. If a table is configured to not support time travel queries, all historical data can be automatically deleted.
Historical data that has exceeded the lifecycle or has been dropped, and has also exceeded the backup protection time.
Historical data must meet all the above conditions to be automatically deleted.
The historical data specifically refers to data files that have been moved to the recycle bin directory. Generally, in addition to exceeding the lifecycle or executing a drop operation, performing compaction or insert overwrite will also cause existing data files in the current data writing directory to be moved to the recycle bin directory, waiting for automatic deletion by the system.
File forced cleanup syntax
-- Manually force delete historical data files in the recycle bin. PURGE TABLE <table_name>;Usage notes and limitations
After executing this command, the system will immediately delete all historical data in the recycle bin, which may cause timetravel operations to be unable to query historical data.
This command is generally only executed in special scenarios for emergency purposes, such as when too many files cause disk read/write instability, or when too much historical data causes cost spikes. Under normal circumstances, historical data in the recycle bin can wait for automatic deletion by the system.
Example
CREATE TABLE mf_ttt (pk BIGINT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, val BIGINT NOT NULL) tblproperties ("transactional"="true"); INSERT INTO TABLE mf_ttt VALUES (1, 1), (2, 2); INSERT INTO TABLE mf_ttt VALUES (2, 20), (3, 3); SELECT * FROM mf_ttt version AS OF 2; -- The following result is returned: +------------+------------+ | pk | val | +------------+------------+ | 1 | 1 | | 2 | 2 | +------------+------------+ -- Perform a compaction, run a purge, and then execute a time travel query. ALTER TABLE mf_ttt compact major; SELECT * FROM mf_ttt version AS OF 2; -- The following result is returned: +------------+------------+ | pk | val | +------------+------------+ | 1 | 1 | | 2 | 2 | +------------+------------+ PURGE TABLE mf_ttt; SELECT * FROM mf_ttt version AS OF 2; --The following result is returned: +------------+------------+ | pk | val | +------------+------------+ | 1 | 1 | | 3 | 3 | | 2 | 20 | +------------+------------+
View backup data examples
This section describes how to view the backup data of tables in the test_restore project.
View the backup data of all tables.
Execute the
SHOW HISTORY FOR tables;command. Sample statement:-- Create the test_restore_x tables. CREATE TABLE test_restore_1(colname STRING); CREATE TABLE test_restore_2(colname INT); -- View the backup data of all tables. SHOW HISTORY FOR tables;The following result is returned:
ID = 20250718083243873gj6aesnzawr3 Name Id Type IsPartitioned CreateTime DropTime test_restore_1 a0b06367bd054d17a55505aa31601b89 MANAGED_TABLE FALSE 2025-07-18 16:32:13 test_restore_2 437b29466ba948b392b2090ec0a60fc2 MANAGED_TABLE FALSE 2025-07-18 16:32:14 OKView the backup data of a specified table.
Execute the
SHOW HISTORY FOR tables [LIKE <table_name>];command. Sample statement:-- View the backup data of the table test_restore1. SHOW HISTORY FOR tables LIKE test_restore_1;The following result is returned:
ID = 20250718083704294gcw24sgigrl Name Id Type IsPartitioned CreateTime DropTime test_restore_1 a0b06367bd054d17a55505aa31601b89 MANAGED_TABLE FALSE 2025-07-18 16:32:13 OKView the backup data of a dropped table.
Execute the
SHOW HISTORY FOR table <table_name>;command. Sample statement:-- Update the data of the test_restore_1 table. INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_1 values("0"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_1 values("1"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_1 values("2"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_1 values("3"); -- View the backup data of the test_restore_1 table. SHOW HISTORY FOR TABLE test_restore_1;The following result is returned:
ID = 2025071808522592gbougy83ad1 ObjectType ObjectId ObjectName VERSION(LSN) Time Operation TABLE a0b06367bd054d17a55505aa31601b89 test_restore_1 0000000000000001 2025-07-18 16:32:14 CREATE TABLE a0b06367bd054d17a55505aa31601b89 test_restore_1 0000000000000002 2025-07-18 16:52:08 OVERWRITE TABLE a0b06367bd054d17a55505aa31601b89 test_restore_1 0000000000000003 2025-07-18 16:52:12 OVERWRITE TABLE a0b06367bd054d17a55505aa31601b89 test_restore_1 0000000000000004 2025-07-18 16:52:14 OVERWRITE TABLE a0b06367bd054d17a55505aa31601b89 test_restore_1 0000000000000005 2025-07-18 16:52:17 OVERWRITE OKView the backup data of a partitioned table or partition.
Execute the
SHOW HISTORY FOR table <table_name> [LIMIT <limit_value>] (LSN <lsn_value> | OFFSET <offset_value>);command. Sample statement:SHOW HISTORY FOR TABLE test_restore_1 LIMIT 1 LSN '00000000000000000002';The result is as follows.
ID = 20250718090511323gzfl5f9glr2 ObjectType ObjectId ObjectName VERSION(LSN) Time Operation TABLE a0b06367bd054d17a55505aa31601b89 test_restore_1 0000000000000002 2025-07-18 16:52:08 OVERWRITE OKView the backup data of a dropped table.
Run the
SHOW HISTORY FOR TABLE table_name ('id'='xxxx');command. Example:-- Update the data of the test_restore_2 table. INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_2 values(0); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_2 values(1); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_2 values(2); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_2 values(3); -- Delete the test_restore_2 table. DROP TABLE test_restore_2; -- Confirm the deletion of the test_restore_2 table. Confirm to "drop table test_restore_2;" (yes/no)? yes -- View the backup data of the dropped table test_restore_2. SHOW HISTORY FOR TABLE test_restore_2('id'='437b29466ba948b392b2090ec0a60fc2');The following result is returned:
ID = 20250718091226165g1vtbsnyu4h ObjectType ObjectId ObjectName VERSION(LSN) Time Operation TABLE 437b29466ba948b392b2090ec0a60fc2 test_restore_2 0000000000000001 2025-07-18 16:32:14 CREATE TABLE 437b29466ba948b392b2090ec0a60fc2 test_restore_2 0000000000000002 2025-07-18 17:12:20 DROP OKView the backup data of a partitioned table.
Run the
SHOW HISTORY FOR TABLE table_name ('id'='xxxx');command to view the backup data of a partitioned table. Example:-- Create a table named test_restore_part_1. CREATE TABLE test_restore_part_1(colname string) PARTITIONED BY(ds string); -- Update the test_restore_part_1 table. INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_1 partition(ds="20250701") values ("1"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_1 partition(ds="20250702") values ("2"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_1 partition(ds="20250703") values ("3"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_1 partition(ds="20250704") values ("4"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_1 partition(ds="20250705") values ("5"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_1 partition(ds="20250706") values ("6"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_1 partition(ds="20250101") values ("20250101"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_1 partition(ds="20250102") values ("20250102"); -- View the backup data of the test_restore_part_1 table. SHOW HISTORY FOR TABLE test_restore_part_1('id'='fbee66b56cf544d2a9999d5d0ce5d352');The following result is returned:
ID = 20250718092558737ge7pyaa803e ObjectType ObjectId ObjectName VERSION(LSN) Time Operation TABLE fbee66b56cf544d2a9999d5d0ce5d352 test_restore_part_1 0000000000000001 2025-07-18 17:23:11 CREATE PARTITION 271aebf3e17a4a8e9f6b35733bf63db4 ds=20250701 0000000000000002 2025-07-18 17:25:23 CREATE PARTITION df9e7f502d464763a243fefe1da4f911 ds=20250702 0000000000000003 2025-07-18 17:25:27 CREATE PARTITION 24cf9953e8c5445bb2f1ead87ea09bae ds=20250703 0000000000000004 2025-07-18 17:25:28 CREATE PARTITION 1c4a9a608d3d4d22bc194ab402da4b8f ds=20250704 0000000000000005 2025-07-18 17:25:32 CREATE PARTITION be0d4c9ff5034c4f932d1a2245c2e65a ds=20250705 0000000000000006 2025-07-18 17:25:35 CREATE PARTITION 45957304be5f4d09a5a3ba66808604be ds=20250706 0000000000000007 2025-07-18 17:25:37 CREATE PARTITION c36933ddefb6415bacabd5f453ee3ce7 ds=20250101 0000000000000008 2025-07-18 17:25:42 CREATE PARTITION 0b01e0d234fc4bf6a3529752e3045037 ds=20250102 0000000000000009 2025-07-18 17:25:44 CREATE OKView the backup data of a partition.
Execute
SHOW HISTORY FOR TABLE table_name partition_spec;orSHOW HISTORY FOR TABLE table_name PARTITION('id'='xxxx');command to view the backup data of a partition. The following example shows the details.
-- View the backup data of the specified partitions in the test_restore_part_1 table. SHOW HISTORY FOR TABLE test_restore_part_1('id'='fbee66b56cf544d2a9999d5d0ce5d352') PARTITION(ds='20250701') PARTITION(ds='20250702');The following result is returned:
ID = 2025071809280096g7ou2qft0o2 ObjectType ObjectId ObjectName VERSION(LSN) Time Operation PARTITION 271aebf3e17a4a8e9f6b35733bf63db4 ds=20250701 0000000000000002 2025-07-18 17:25:23 CREATE PARTITION df9e7f502d464763a243fefe1da4f911 ds=20250702 0000000000000003 2025-07-18 17:25:27 CREATE OKRestore a non-partitioned table
This section describes how to restore a non-partitioned table in the test_restore project.
Restore a dropped table.
Run the
RESTORE TABLE table_name ('id'='xxxxx');command. Make sure that the name of the table you want to restore is unique. If another table has the same name, change its name first. Sample statement:-- Query the backup data of the dropped table test_restore_2. SHOW HISTORY FOR TABLE test_restore_2('id'='437b29466ba948b392b2090ec0a60fc2'); -- Create a table named test_restore_2. CREATE TABLE test_restore_2(colname string); -- Restore the dropped table test_restore_2. However, an error is returned because an existing table has the same name. RESTORE TABLE test_restore_2('id'='437b29466ba948b392b2090ec0a60fc2'); -- Rename the existing table test_restore_2. ALTER TABLE test_restore_2 rename TO test_restore_2_rename; -- Restore the dropped table test_restore_2. RESTORE TABLE test_restore_2('id'='437b29466ba948b392b2090ec0a60fc2');OK is returned.
Restore a table to a specified version. For a deleted table, you need to restore the table first before performing this operation.
Execute the
RESTORE TABLE table_name TO LSN 'xxxx';command. Sample statement:-- Restore the test_restore_1 table to a specified LSN. RESTORE TABLE test_restore_1 TO LSN '0000000000000004'; -- Query the data of the test_restore_1 table. SELECT * FROM test_restore_1;The following result is returned:
+------------+ | colname | +------------+ | 2 | +------------+Restore a table to a specified version and rename the table, or update data to a table with a different name.
Run the
RESTORE TABLE table_name TO LSN 'xxxx' AS new_table_name;command.This includes the following three scenarios:
Restore a table to a specified version and rename the table.
-- Restore the dropped table test_restore_2 to a specified LSN and rename the table as test_restore_new. RESTORE TABLE test_restore_2 TO LSN '0000000000000003' AS test_restore_new; -- Query the data of the test_restore_new table. SELECT * FROM test_restore_new;The following result is returned:
+------------+ | colname | +------------+ | 1 | +------------+Restore a table to a specified version and update data to an existing table with a different name.
-- Restore the test_restore_2 table to a specified version and save the data to the existing table test_restore_new. RESTORE TABLE test_restore_2 TO LSN '0000000000000005' AS test_restore_new; -- Query the backup data of the test_restore_new table. SHOW HISTORY FOR TABLE test_restore_new;The following result is returned:
ID = 20250722082102262gsizjcbzawr3 ObjectType ObjectId ObjectName VERSION(LSN) Time Operation TABLE 565b5e29eecf4fbd88965b24822ded6a test_restore_new 0000000000000001 2025-07-22 16:17:1CREATE TABLE 565b5e29eecf4fbd88965b24822ded6a test_restore_new 0000000000000002 2025-07-22 16:20:5OVERWRITE OKRestore a table to a specified version and update data to a table with a different name and schema. This operation fails because the two tables must have the same schema. Example:
-- Create a table with a different schema. CREATE TABLE test_restore_2cols(col1 string, col2 string); -- Restore the test_restore_1 table to a specified version and write the data to the test_restore_2cols table. RESTORE TABLE test_restore_1 TO LSN '0000000000000005' AS test_restore_2cols;The following result is returned:
FAILED: Catalog Service Failed, ErrorCode: 105, Error Message: ODPS-0110061: Failed to run ddltask - Restore table failed because: field schema not same, [{"comment":"","id":"","name":"colname","type":"string"}] vs [{"comment":"","id":"","name":"col1","type":"string"}, {"comment":"","id":"","name":"col2","type":"string"}]
Restore a partitioned table and partitions
This section describes how to restore a partitioned table or partitions in the test_restore project.
Restore a partitioned table.
Run the
RESTORE TABLE table_name ('id'='xxxxx');command. Sample statement:-- Create a table named test_restore_part_x. CREATE TABLE test_restore_part_x(a string) PARTITIONED BY(ds string); -- Update the test_restore_part_x table. INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_x partition(ds="20191201") values ("1"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_x partition(ds="20191202") values ("2"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_x partition(ds="20191203") values ("3"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_x partition(ds="20191204") values ("4"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_x partition(ds="20191205") values ("5"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_x partition(ds="20191205") values ("6"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_x partition(ds="20200101") values ("20200101"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_x partition(ds="20200102") values ("20200102"); -- View the partitions of the test_restore_part_x table. LIST PARTITIONS test_restore_part_x; -- View the data of the test_restore_part_x table. SELECT * FROM test_restore_part_x; -- Drop the test_restore_part_x table. DROP TABLE test_restore_part_x; -- Confirm the drop table operation. Confirm to "drop table test_restore_part_x;" (yes/no)? yes -- Restore the test_restore_part_x table. RESTORE TABLE test_restore_part_x('id'='94d436523fe14ba39f33d2dee738c018'); -- View the backup data of the test_restore_part_x table. SHOW HISTORY FOR TABLE test_restore_part_x('id'='94d436523fe14ba39f33d2dee738c018'); -- View the partitions of the test_restore_part_x table. LIST PARTITIONS test_restore_part_x;The following result is returned:
ds=20191201 ds=20191202 ds=20191203 ds=20191204 ds=20191205 ds=20200101 ds=20200102Restore partitions. For a deleted table, you need to restore the table first before performing this operation.
Execute the
RESTORE TABLE table_name PARTITION('id'='xxxx')[PARTITION('id'='xxxx')];command. Sample statement:-- Create a table named test_restore_part_y. CREATE TABLE test_restore_part_y(a string) PARTITIONED BY(ds string); -- Update the test_restore_part_y table. INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_y partition(ds="20250701") values ("1"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_y partition(ds="20250702") values ("2"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_y partition(ds="20250703") values ("3"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_y partition(ds="20250704") values ("4"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_y partition(ds="20250705") values ("5"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_y partition(ds="20250706") values ("6"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_y partition(ds="20250101") values ("20250101"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_y partition(ds="20250102") values ("20250102"); -- View the partitions of the test_restore_part_y table. LIST PARTITIONS test_restore_part_y; -- Drop partitions from the test_restore_part_y table. ALTER TABLE test_restore_part_y DROP PARTITION(ds='20250701'),PARTITION(ds='20250702'); -- Confirm the partition drop operation. Confirm to "alter table test_restore_part_y drop partition(ds='20250701'),partition(ds='20250702');" (yes/no)? yes -- View the partitions of the test_restore_part_y table. LIST PARTITIONS test_restore_part_y; -- View the partition IDs of the test_restore_part_y table. SHOW HISTORY FOR TABLE test_restore_part_y; -- Restore partitions of the test_restore_part_y table. RESTORE TABLE test_restore_part_y PARTITION('id'='a14d6cb4ab0c46378a6e284b257bbfaa') PARTITION('id'='8c85184ec0b44fba8198274401df2519'); -- View the partitions of the test_restore_part_y table. LIST PARTITIONS test_restore_part_y;The following result is returned:
ds=20250101 ds=20250102 ds=20250701 ds=20250702 ds=20250703 ds=20250704 ds=20250705 ds=20250706Restore partitions to a specified version. For a deleted table, you need to restore the table first before performing this operation.
Execute the
RESTORE TABLE table_name partition_spec1[partition_spec2] to LSN 'xxxx';command. Sample statement:-- Update the data of the test_restore_part_y table. INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_y PARTITION(ds="20250701") VALUES ("20250701_v1"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_y PARTITION(ds="20250702") VALUES ("20250702_v1"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_y PARTITION(ds="20250701") VALUES ("20250701_v2"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_restore_part_y PARTITION(ds="20250702") VALUES ("20250702_v2"); -- View the data of the specified partitions in the test_restore_part_y table. SELECT * FROM test_restore_part_y WHERE ds='20250701' or ds='20250702'; -- Restore the specified partitions in the test_restore_part_y table to a specified LSN. RESTORE TABLE test_restore_part_y PARTITION(ds='20250701') PARTITION(ds='20250702') to LSN '0000000000000010'; -- View the data of the specified partitions in the test_restore_part_y table. SELECT * FROM test_restore_part_y WHERE ds='20250701' or ds='20250702';The following result is returned:
-- The first query returns the following result. +------------+------------+ | a | ds | +------------+------------+ | 20250701_v2 | 20250701 | | 20250702_v2 | 20250702 | +------------+------------+ -- The second query returns the following result. +------------+------------+ | a | ds | +------------+------------+ | 2 | 20250702 | | 1 | 20250701 | +------------+------------+Restore partitions to a specified version and rename the table. For a deleted table, you need to restore the table first before performing this operation.
Execute the
RESTORE TABLE table_name partition_spec1[partition_spec2] to LSN 'xxxx' as new_table_name;command. Sample statement:-- Restore the partitions to a specified LSN and name the new table test_restore_part_y_v10. RESTORE TABLE test_restore_part_y PARTITION(ds='20250701') PARTITION(ds='20250702') TO LSN '0000000000000010' AS test_restore_part_y_v10; -- View the data of the test_restore_part_y_v10 table. SELECT * FROM test_restore_part_y_v10 WHERE ds='20250701' or ds='20250702';The following result is returned:
+------------+------------+ | a | ds | +------------+------------+ | 1 | 20250701 | | 2 | 20250702 | +------------+------------+
Delta Table examples
-- Create a table. CREATE TABLE mf_dt (pk BIGINT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, val BIGINT NOT NULL) PARTITIONED BY (dd STRING, hh STRING) TBLPROPERTIES ("transactional"="true"); INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE mf_dt PARTITION(dd='01', hh='01') VALUES (1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3); INSERT INTO TABLE mf_dt PARTITION(dd='01', hh='01') VALUES (3, 30), (4, 4), (5, 5); SELECT * FROM mf_dt WHERE dd='01' AND hh='01'; -- The following result is returned. +------------+------------+------------+------------+ | pk | val | dd | hh | +------------+------------+------------+------------+ | 1 | 1 | 01 | 01 | | 4 | 4 | 01 | 01 | | 5 | 5 | 01 | 01 | | 2 | 2 | 01 | 01 | | 3 | 30 | 01 | 01 | +------------+------------+------------+------------+ -- Restore the table. You can obtain the 'table_id' by running the DESC EXTENDED table command. DESC EXTENDED mf_dt; -- The following result is returned. +------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Owner: ALIYUN$*****cloud_com | | Project: mc_oss_external_tables | | TableComment: | +------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | CreateTime: 2025-07-21 15:31:42 | | LastDDLTime: 2025-07-21 15:31:42 | | LastModifiedTime: 2025-07-21 17:14:58 | +------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | InternalTable: YES | Size: 8976 | +------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Native Columns: | +------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Field | Type | Label | ExtendedLabel | Nullable | DefaultValue | Comment | +------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | pk | bigint | | | false | NULL | | | val | bigint | | | false | NULL | | +------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Partition Columns: | +------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | dd | string | | | hh | string | | +------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Extended Info: | +------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | TableID: cd607cd938dc4ca6886dd12212995604 | | IsArchived: false | | PhysicalSize: 26928 | | FileNum: 10 | | StoredAs: AliOrc | | CompressionStrategy: normal | | Transactional: true | | IsolationMin: NONSTRICT_SNAPSHOT_ISOLATION | | odps.timemachine.retention.days: 1 | | encryption_enable: false | | Primarykey: [pk] | | acid.data.retain.hours: 24 | | write.bucket.num: 16 | +------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ DROP TABLE mf_dt; Confirm to "DROP TABLE mf_dt" (yes/no)? yes RESTORE TABLE mf_dt ('id' = 'cd607cd938dc4ca6886dd12212995604'); SELECT * FROM mf_dt WHERE dd='01' AND hh='01'; -- The following result is returned. +------------+------------+------------+------------+ | pk | val | dd | hh | +------------+------------+------------+------------+ | 1 | 1 | 01 | 01 | | 4 | 4 | 01 | 01 | | 5 | 5 | 01 | 01 | | 2 | 2 | 01 | 01 | | 3 | 30 | 01 | 01 | +------------+------------+------------+------------+ -- Restore a partition. You can obtain the 'partition_id' by running the SHOW HISTORY FOR TABLE command. SHOW HISTORY FOR TABLE mf_dt; -- The following result is returned. ObjectType ObjectId ObjectName VERSION(LSN) Time Operation TABLE cd607cd938dc4ca6886dd12212995604 mf_dt 0000000000000001 2025-07-21 15:31:4CREATE PARTITION 51d38cc9ded344cf99188cd1a806e5d2 dd=01/hh=01 0000000000000002 2025-07-21 17:14:4CREATE PARTITION 51d38cc9ded344cf99188cd1a806e5d2 dd=01/hh=01 0000000000000003 2025-07-21 17:14:5APPEND TABLE cd607cd938dc4ca6886dd12212995604 mf_dt 0000000000000004 2025-07-21 17:18:4DROP TABLE cd607cd938dc4ca6886dd12212995604 mf_dt 0000000000000005 2025-07-21 17:18:5RESTORE PARTITION 51d38cc9ded344cf99188cd1a806e5d2 dd=01/hh=01 0000000000000006 2025-07-21 17:18:5RESTORE ALTER TABLE mf_dt DROP PARTITION (dd = '01', hh = '01'); Confirm to "ALTER TABLE mf_dt DROP PARTITION (dd = '01', hh = '01')" (yes/no)? yes RESTORE TABLE mf_dt PARTITION('id' = '51d38cc9ded344cf99188cd1a806e5d2'); SELECT * FROM mf_dt WHERE dd='01' AND hh='01'; -- The following result is returned. +------------+------------+------------+------------+ | pk | val | dd | hh | +------------+------------+------------+------------+ | 1 | 1 | 01 | 01 | | 4 | 4 | 01 | 01 | | 5 | 5 | 01 | 01 | | 2 | 2 | 01 | 01 | | 3 | 30 | 01 | 01 | +------------+------------+------------+------------+ -- Perform a time travel query on the restored table. SELECT * FROM mf_dt version AS OF 2 WHERE dd = '01' AND hh = '01'; -- The following result is returned. +------------+------------+------------+------------+ | pk | val | dd | hh | +------------+------------+------------+------------+ | 1 | 1 | 01 | 01 | | 3 | 3 | 01 | 01 | | 2 | 2 | 01 | 01 | +------------+------------+------------+------------+ SELECT * FROM mf_dt version AS OF get_latest_version('mf_dt') WHERE dd = '01' AND hh = '01'; -- The following result is returned. +------------+------------+------------+------------+ | pk | val | dd | hh | +------------+------------+------------+------------+ | 1 | 1 | 01 | 01 | | 4 | 4 | 01 | 01 | | 5 | 5 | 01 | 01 | | 2 | 2 | 01 | 01 | | 3 | 30 | 01 | 01 | +------------+------------+------------+------------+