Hologres is deeply integrated with the Alibaba Cloud account system, which includes Alibaba Cloud accounts and RAM users. Hologres users are authenticated by Alibaba Cloud accounts. This topic describes the Alibaba Cloud account system used in Hologres.
Accounts
The following table describes Hologres account types. To grant permissions on a Hologres instance to Alibaba Cloud accounts and RAM users, use their login accounts or account IDs. For more information, see Login accounts and Account IDs.
Account type | Description |
Alibaba Cloud account | Creates and manages Hologres instances. Example:
|
RAM user | With relevant permissions, a RAM user can create and manage Hologres instances. Resources are still owned by Alibaba Cloud accounts, not RAM users. |
Custom account | With relevant permissions, a custom account can perform operations on databases, including the following:
Note The password of a custom account is encrypted with |
Login accounts
When granting permissions to an Alibaba Cloud account or a RAM user, use the login account of the Alibaba Cloud account. You can obtain it on the Security Settings page of the Account Center. 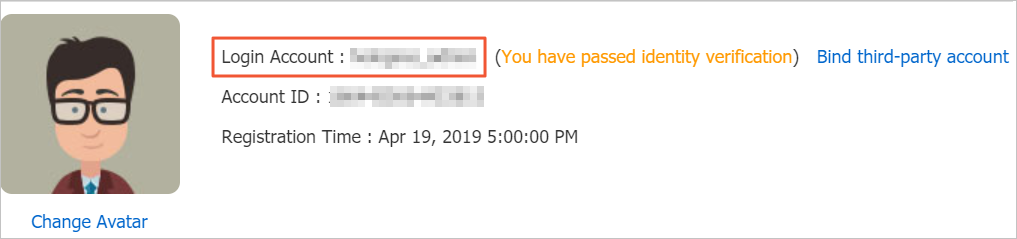
When you grant permissions to an Alibaba Cloud account, the full expression of the Alibaba Cloud account must contain the login account. The following table describes the account formats.
Account format
Description
Example
ALIYUN$<Login Account>@aliyun.com
Replace <Login Account> with your actual value.
ALIYUN$company***@aliyun.com
<Login Account>@aliyun.com
company***@aliyun.com
When you grant permissions to a RAM user, the full expression of the RAM user must contain the login account of the Alibaba Cloud account it belongs. The following table describes the account formats.
Account format
Description
Example
<subUserName>@<Login Account>.onaliyun.com
The account formats contain the following parameters:
<subUserName>: the name of the RAM user.
<Login Account>: the login account of the Alibaba Cloud account.
<AccountID>: the account ID of the Alibaba Cloud account.
holouser***@company.onaliyun.com
<subUserName>@<Login Account>
holouser@company
<subUserName>@<Account ID>.onaliyun.com
holouser@123456789xxxx
RAM$<subUserName>
RAM$holo_test
RAM$<Login Account>:<subUserName>
RAM$company:holouser
RAM$<Account ID>:<subUserName>
RAM$123456789xxxx:holouser
<subUserName>@<Account ID>
holouser@123456789xxxx
Account IDs
An account ID is a string of digits. Example: 189813715xxxx. Obtain the account ID on the Security Settings page of the Account Center. 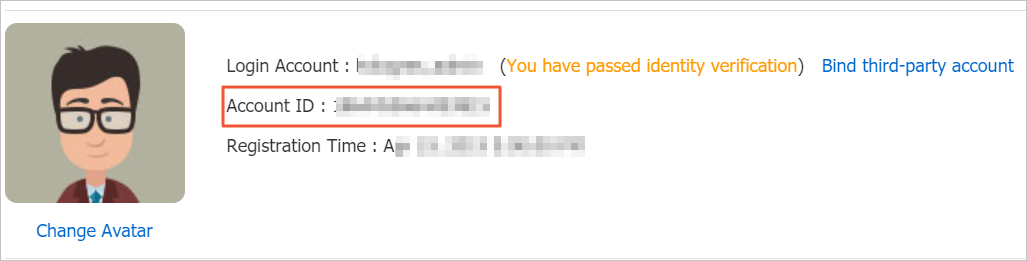
To obtain the account ID of a RAM user, also called its UID, go to the RAM users page. Then click the target user name.
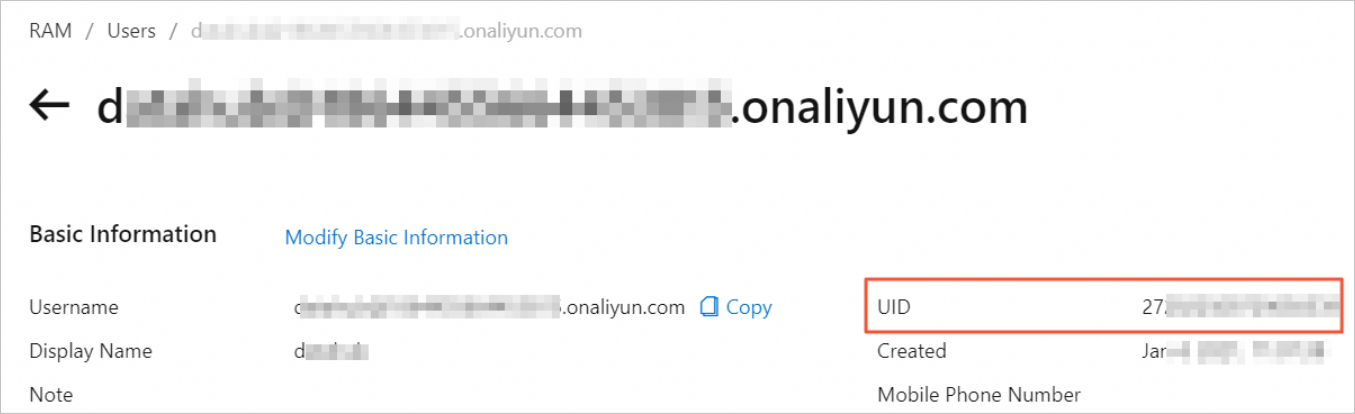
When you grant permissions to a RAM user using its UID, follow this format: p4_UID. Example: p4_12333388xxx.
Grant permissions to Hologres users using account IDs:
CREATE USER "189813715xxxx"; --Authorize the user whose Alibaba Cloud account ID is 189813715xxxx to connect to Hologres. CREATE USER "p4_12333388xxx" superuser; --Assign the superuser role to the RAM user whose UID is 12333388xxx. View your account ID:
SELECT current_user;AccessKey ID and secret
The AccessKey ID and secret are access credentials issued by Alibaba Cloud for you to connect to Hologres instances. The AccessKey ID is similar to a logon account, and the AccessKey secret is similar to a logon password. You can view the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret on the Security Management page of the User Management console.
The AccessKey ID and secret have a validity period. If they expire, create another AccessKey pair. For more information, see Create an Alibaba Cloud account.
When you connect to Hologres from a PostgreSQL client or a JDBC client, enter your AccessKey ID and secret as the username and password.
Custom accounts
With relevant permissions, custom accounts can perform operations on databases. Custom accounts can be used only in Hologres instances. For more information, see Create a custom account.
By default, custom accounts cannot access MaxCompute tables. To access MaxCompute tables, map a custom account to a RAM user with the required permissions. For more information, see Common errors and troubleshooting.