DataWorks allows you to create multiple types of database nodes for SQL task development, periodic scheduling, and integration with other jobs.
Prerequisites
The RAM user that you want to use is added to your workspace.
If you want to use a RAM user to develop tasks, you must add the RAM user to your workspace as a member and assign the Develop or Workspace Administrator role to the RAM user. The Workspace Administrator role has more permissions than necessary. Exercise caution when you assign the Workspace Administrator role. For more information about how to add a member and assign roles to the member, see Add workspace members and assign roles to them.
A data source is added to your workspace.
The data source is connected to the serverless resource group. For more information, see Network connectivity solutions.
The data source is added to the workspace in connection string mode. For more information, see Add and manage data sources.
The data source can be used to create a database node. For more information, see Supported data sources.
Nodes of the data source that corresponds to a database node are created before you use the database node to develop a task. For more information, see Create task nodes.
Step 1: Use a database node to develop a task
After you create a database node, you can develop a task based on the database node.
Select a data source.
Select the data source that you want to use to develop a task from the Select DataSource drop-down list.
 If you cannot find the data source that you want to use from the drop-down list, click Add Data Source to add a data source on the Data Sources page.
If you cannot find the data source that you want to use from the drop-down list, click Add Data Source to add a data source on the Data Sources page.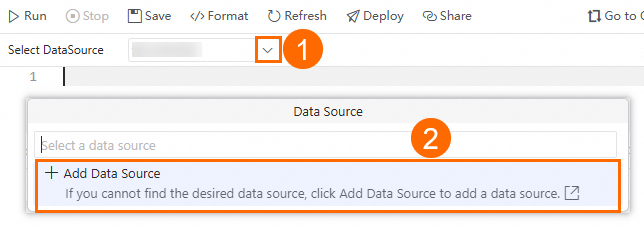 Note
NoteIn a workspace in standard mode, only data sources that are configured for both production and development environments are displayed in the Select DataSource drop-down list.
Database nodes can be used to develop tasks only for data sources that are added in connection string mode in the production environment.
Write SQL statements.
Write SQL statements in the SQL editor to create a task. In this example, a simple SQL query statement is used.
SELECT * FROM you_table_name; -- Query a table. SELECT '${var}'; -- Configure scheduling parameters.NoteYou can write SQL statements that you want to execute based on your business requirements and the syntax that is supported by the data source.
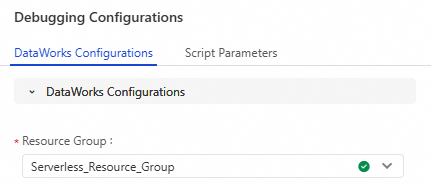
Select a resource group for debugging.
Click Debugging Configurations in the right-side navigation pane of the configuration tab of the node. On the Debugging Configurations tab, click DataWorks Configurations. Then, select an existing serverless resource group that passes the connectivity test from the Resource Group drop-down list.
 Note
NoteIf you want to access a data source over the Internet or a virtual private cloud (VPC), you must use the resource group for scheduling that is connected to the data source. For more information, see Network connectivity solutions.
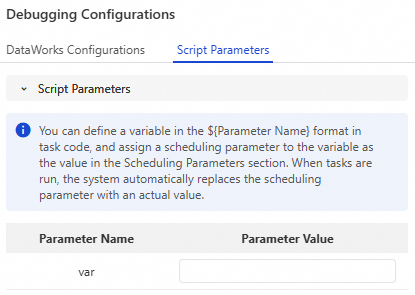
Configure debugging parameters.
Click Debugging Configurations in the right-side navigation pane of the configuration tab of the node. On the Debugging Configurations tab, click Script Parameters. Then, define variables in the node code and assign values to the variables.
After the debugging configurations are complete, click the
 icon to save the SQL node. Then, click the
icon to save the SQL node. Then, click the  icon to run the SQL script and check whether the SQL script meets expectations.
icon to run the SQL script and check whether the SQL script meets expectations.
After the debugging of the SQL script is complete, click Properties on the right side of the SQL Editor to configure task scheduling properties.
Step 2: Deploy the database node and perform O&M operations
After the node code and scheduling settings are configured, you can deploy the node to the production environment.
After the deployment is complete, go to the Auto Triggered Nodes page in Operation Center to view the auto triggered task that is deployed and perform O&M operations on the task. The node periodically runs as expected based on the scheduling settings that you configure. For more information, see Getting started with Operation Center.
Supported data sources
DataWorks allows you to create database nodes of various data source types. The following table describes the types of data sources that support database nodes.
The data source that is used to create a database node must be added to the workspace in connection string mode.
Specific databases support the stored procedure feature. However, the stored procedure feature cannot be used in DataWorks Data Studio.