The batch synchronization feature in Data Integration provides Reader and Writer plugins. These plugins allow you to synchronize full or incremental data from a source database to a target database. You can perform this synchronization by defining the source and destination data sources and using DataWorks scheduling parameters. This topic describes the features of batch synchronization.
Core features
The following figure shows the features of batch synchronization.
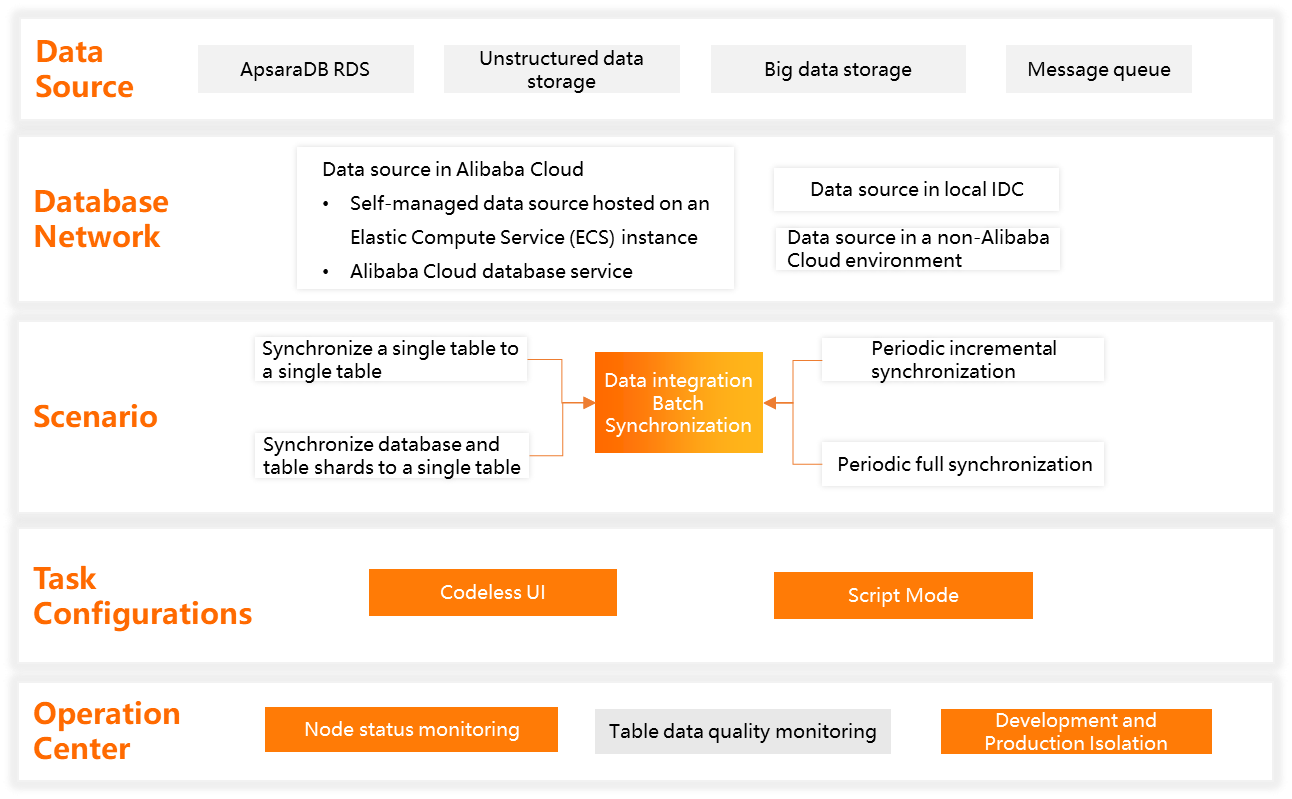
Capabilities | Description |
Data synchronization between disparate data sources | Data Integration supports data synchronization for over 50 types of data sources, including relational databases, unstructured storage, big data storage, and message queues. You can use the Reader and Writer plugins to transfer data between any structured or semi-structured data sources by defining the source and destination data sources. For more information, see Supported data sources and synchronization solutions. |
Data synchronization in complex network environments | Batch synchronization supports data synchronization in various environments. These environments include ApsaraDB databases, on-premises data centers, self-managed databases on ECS instances, or databases not hosted on Alibaba Cloud. You must ensure that there is network connectivity between the resource group and the source or destination. For more information about configuration, see Network connectivity solutions. |
Synchronization scenarios | 1. Supported synchronization modes
Note For more information about scheduling parameters, see Common scenarios for scheduling parameters in Data Integration and Supported formats of scheduling parameters. 2. Supported source structures
|
Configuration methods | You can configure Data Integration batch synchronization tasks in the following ways.
Note For more information about task configuration features, see Function Overview. |
Batch synchronization task O&M |
|
Function Overview
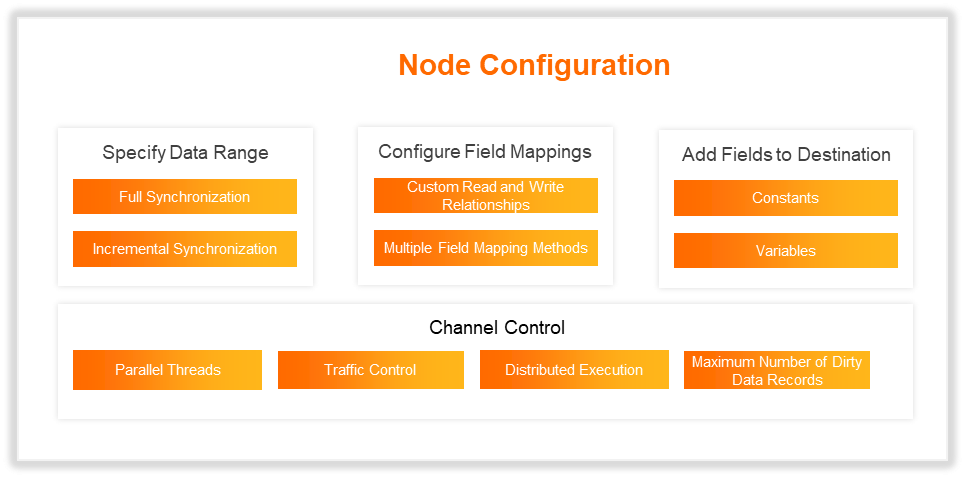
Feature | Description |
Full or incremental data synchronization | Batch synchronization tasks can perform full or incremental data synchronization. To do this, configure Data Filtering and use scheduling parameters. The configuration method for incremental synchronization varies by plugin. For more information about configuring incremental data synchronization, see Scenario: Configure a batch synchronization task for incremental data. |
Field mapping | Establish field mapping rules to write source data to the corresponding fields in the target based on the specified relationships. When you configure the mapping, ensure that the field types at both ends are compatible.
|
Job rate limiting |
|
Distributed task execution | For data sources that support distributed execution, task segmentation technology can be used to distribute a synchronization task for concurrent execution across multiple nodes. This allows synchronization speed to scale linearly with the cluster size, breaking through single-node performance bottlenecks. This mode is especially suitable for high-throughput, low-latency synchronization scenarios. It also efficiently schedules idle cluster resources, significantly improving hardware utilization. |
Dirty data policy | Dirty data refers to data records that fail to be written to the target due to errors, such as type mismatches or constraint violations. Batch synchronization lets you define a dirty data policy. You can specify the number of tolerable dirty data records and their effect on the task.
|
Time zone | To synchronize data across different time zones, you can set the source time zone to perform a time zone conversion. |
What to do next
For more information about how to create a task, see the following topics:
Configure a batch synchronization task using the codeless UI
Configure a batch synchronization task using the code editor