The Kafka data source provides a bidirectional channel to read data from and write data to Kafka. This topic describes the data synchronization capabilities that DataWorks provides for Kafka.
Supported versions
DataWorks supports Alibaba Cloud Kafka and self-managed Kafka versions from 0.10.2 to 3.6.x.
Data synchronization is not supported for Kafka versions earlier than 0.10.2. This is because these versions do not support retrieving partition offsets and their data structures may not support timestamps.
Real-time read
If you use a subscription Serverless resource group, you must estimate the required specifications in advance to prevent task failures due to insufficient resources.
Estimate 1 CU per topic. You must also estimate resources based on traffic:
For uncompressed Kafka data, estimate 1 CU for every 10 MB/s of traffic.
For compressed Kafka data, estimate 2 CU for every 10 MB/s of traffic.
For compressed Kafka data that requires JSON parsing, estimate 3 CU for every 10 MB/s of traffic.
When you use a subscription Serverless resource group or an old version of an exclusive resource group for Data Integration:
If your workload has a high tolerance for failover, the cluster slot usage should not exceed 80%.
If your workload has a low tolerance for failover, the cluster slot usage should not exceed 70%.
The actual resource usage depends on factors such as the data content and format. You must adjust the resources based on the actual runtime conditions after your initial estimation.
Limits
The Kafka data source supports Serverless resource groups (recommended) and old versions of exclusive resource groups for Data Integration.
Offline read from a single table
If both parameter.groupId and parameter.kafkaConfig.group.id are configured, parameter.groupId takes precedence over group.id in the kafkaConfig parameter.
Real-time write to a single table
Data deduplication is not supported for write operations. If a task is restarted after an offset reset or a failover, duplicate data may be written.
Real-time write for an entire database
Real-time data synchronization tasks support Serverless resource groups (recommended) and old versions of exclusive resource groups for Data Integration.
If the source table has a primary key, the primary key value is used as the key for the Kafka record. This ensures that changes to the same primary key are written to the same Kafka partition in order.
If the source table does not have a primary key, you have two options. If you select the option to synchronize tables without primary keys, the key for the Kafka record is empty. To ensure that table changes are written to Kafka in order, the destination Kafka topic must have only a single partition. If you select a custom primary key, a combination of one or more non-primary key fields is used as the key for the Kafka record.
If the Kafka cluster returns an exception and you need to ensure that changes to the same primary key are written to the same Kafka partition in order, add the following configuration to the extended parameters of the Kafka data source.
{"max.in.flight.requests.per.connection":1,"buffer.memory": 100554432}ImportantThis configuration significantly degrades replication performance. You must balance performance with the need for strict ordering and reliability.
For more information about the overall format of messages written to Kafka in real-time synchronization, the format of heartbeat messages, and the format of messages corresponding to source data changes, see Appendix: Message format.
Supported field types
Kafka provides unstructured data storage. A Kafka record typically includes a key, value, offset, timestamp, headers, and partition. When DataWorks reads data from or writes data to Kafka, DataWorks processes the data based on the following policies.
Offline data read
When DataWorks reads data from Kafka, it can parse the data in JSON format. The following table describes how each data module is processed.
Kafka record data module | Processed data type |
key | Depends on the keyType configuration item in the data synchronization task. For more information about the keyType parameter, see the full parameter description in the appendix. |
value | Depends on the valueType configuration item in the data synchronization task. For more information about the valueType parameter, see the full parameter description in the appendix. |
offset | Long |
timestamp | Long |
headers | String |
partition | Long |
Offline data write
When DataWorks writes data to Kafka, it supports writing data in JSON or text format. The data processing policy varies based on the data synchronization solution. The following tables describe the details.
When data is written in text format, field names are not included. Field values are separated by a separator.
When data is written to Kafka in a real-time synchronization task, the built-in JSON format is used. The written data includes all information, such as database change messages, business time, and DDL information. For more information about the data format, see Appendix: Message format.
Synchronization task type | Format of the value written to Kafka | Source field type | Processing method for write operations |
Offline synchronization Offline synchronization node in DataStudio | json | String | UTF-8 encoded string |
Boolean | Converted to the UTF-8 encoded string "true" or "false" | ||
Time/Date | UTF-8 encoded string in yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss format | ||
Numeric | UTF-8 encoded numeric string | ||
Byte stream | The byte stream is treated as a UTF-8 encoded string and converted to a string. | ||
text | String | UTF-8 encoded string | |
Boolean | Converted to the UTF-8 encoded string "true" or "false" | ||
Time/Date | UTF-8 encoded string in yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss format | ||
Numeric | UTF-8 encoded numeric string | ||
Byte stream | The byte stream is treated as a UTF-8 encoded string and converted to a string. | ||
Real-time synchronization: Real-time ETL to Kafka Real-time synchronization node in DataStudio | json | String | UTF-8 encoded string |
Boolean | JSON Boolean type | ||
Time/Date |
| ||
Numeric | JSON numeric type | ||
Byte stream | The byte stream is Base64-encoded and then converted to a UTF-8 encoded string. | ||
text | String | UTF-8 encoded string | |
Boolean | Converted to the UTF-8 encoded string "true" or "false" | ||
Time/Date | UTF-8 encoded string in yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss format | ||
Numeric | UTF-8 encoded numeric string | ||
Byte stream | The byte stream is Base64-encoded and then converted to a UTF-8 encoded string. | ||
Real-time synchronization: Real-time synchronization of an entire database to Kafka Real-time synchronization of only incremental data | Built-in JSON format | String | UTF-8 encoded string |
Boolean | JSON Boolean type | ||
Time/Date | 13-digit millisecond timestamp | ||
Numeric | JSON numeric value | ||
Byte stream | The byte stream is Base64-encoded and then converted to a UTF-8 encoded string. | ||
Synchronization solution: One-click real-time synchronization to Kafka Full offline synchronization + incremental real-time synchronization | Built-in JSON format | String | UTF-8 encoded string |
Boolean | JSON Boolean type | ||
Time/Date | 13-digit millisecond timestamp | ||
Numeric | JSON numeric value | ||
Byte stream | The byte stream is Base64-encoded and then converted to a UTF-8 encoded string. |
Add a data source
Before you develop a synchronization task in DataWorks, you must add the required data source to DataWorks by following the instructions in Add and manage data sources. You can view the infotips of parameters in the DataWorks console to understand the meanings of the parameters when you add a data source.
Develop a data synchronization task
For information about the entry point for and the procedure of configuring a synchronization task, see the following configuration guides.
Configure an offline synchronization task for a single table
For more information about the procedure, see Configure an offline synchronization task in the codeless UI and Configure an offline synchronization task in the code editor.
For the full list of parameters and a script demo for the code editor, see Appendix: Script demos and parameter descriptions.
Configure a real-time synchronization task for a single table or an entire database
For more information about the procedure, see Configure a real-time synchronization task in DataStudio.
Configure a full and incremental real-time synchronization task for a single table or an entire database
For more information about the procedure, see Configure a synchronization task in Data Integration.
Authentication configuration
SSL
If you set the Special Authentication Method for a Kafka data source to SSL or SASL_SSL, SSL authentication is enabled for the Kafka cluster. You must upload the client truststore certificate file and enter the truststore passphrase.
If the Kafka cluster is an Alibaba Cloud Kafka instance, see SSL certificate algorithm upgrade instructions to download the correct truststore certificate file. The truststore passphrase is KafkaOnsClient.
If the Kafka cluster is an EMR instance, see Use SSL encryption for Kafka connections to download the correct truststore certificate file and obtain the truststore passphrase.
For a self-managed cluster, you must upload the correct truststore certificate and enter the correct truststore passphrase.
The keystore certificate file, keystore passphrase, and SSL passphrase are required only when bidirectional SSL authentication is enabled for the Kafka cluster. The Kafka cluster server uses this to authenticate the client's identity. Bidirectional SSL authentication is enabled when ssl.client.auth=required is set in the server.properties file of the Kafka cluster. For more information, see Use SSL encryption for Kafka connections.
GSSAPI
If you set Sasl Mechanism to GSSAPI when configuring a Kafka data source, you must upload three authentication files: a JAAS configuration file, a Kerberos configuration file, and a Keytab file. You must also configure the DNS/HOST settings for the exclusive resource group. The following sections describe these files and the required DNS and HOST settings.
For a Serverless resource group, you must configure the host address information using internal DNS resolution. For more information, see Internal DNS resolution (PrivateZone).
JAAS configuration file
The JAAS file must start with KafkaClient, followed by all configuration items enclosed in a pair of braces {}:
The first line inside the braces defines the logon component class to use. For different SASL authentication mechanisms, the logon component class is fixed. Each subsequent configuration item is written in the key=value format.
All configuration items except the last one must not end with a semicolon.
The last configuration item must end with a semicolon. A semicolon must also be added after the closing brace "}".
If the format requirements are not met, the JAAS configuration file cannot be parsed. The following code shows a typical JAAS configuration file format. Replace the xxx placeholders with your actual information.
KafkaClient { com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required useKeyTab=true keyTab="xxx" storeKey=true serviceName="kafka-server" principal="kafka-client@EXAMPLE.COM"; };Configuration item
Description
Logon module
Must be set to com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule.
useKeyTab
Must be set to true.
keyTab
You can specify any path. When the synchronization task runs, the keytab file uploaded during the data source configuration is automatically downloaded to a local path. This local file path is then used to fill in the keyTab configuration item.
storeKey
Specifies whether the client saves the key. You can set this to true or false. It does not affect data synchronization.
serviceName
Corresponds to the sasl.kerberos.service.name configuration item in the server.properties configuration file of the Kafka server. Configure this item as needed.
principal
The Kerberos principal used by the Kafka client. Configure this item as needed and make sure that the uploaded keytab file contains the key for this principal.
Kerberos configuration file
The Kerberos configuration file must contain two modules: [libdefaults] and [realms].
The [libdefaults] module specifies Kerberos authentication parameters. Each configuration item in the module is written in the key=value format.
The [realms] module specifies the KDC address. It can contain multiple realm submodules. Each realm submodule starts with realm name=.
This is followed by a set of configuration items enclosed in braces. Each configuration item is also written in the key=value format. The following code shows a typical Kerberos configuration file format. Replace the xxx placeholders with your actual information.
[libdefaults] default_realm = xxx [realms] xxx = { kdc = xxx }Configuration item
Description
[libdefaults].default_realm
The default realm used when accessing Kafka cluster nodes. This is usually the same as the realm of the client principal specified in the JAAS configuration file.
Other [libdefaults] parameters
The [libdefaults] module can specify other Kerberos authentication parameters, such as ticket_lifetime. Configure them as needed.
[realms].realm name
Must be the same as the realm of the client principal specified in the JAAS configuration file and the [libdefaults].default_realm. If the realm of the client principal in the JAAS configuration file is different from [libdefaults].default_realm, you need to include two realms submodules. These submodules must correspond to the realm of the client principal in the JAAS configuration file and the [libdefaults].default_realm, respectively.
[realms].realm name.kdc
Specifies the KDC address and port in the ip:port format. For example, kdc=10.0.0.1:88. If the port is omitted, the default port 88 is used. For example, kdc=10.0.0.1.
Keytab file
The Keytab file must contain the key for the principal specified in the JAAS configuration file and must be verifiable by the KDC. For example, if there is a file named client.keytab in the current working directory, you can run the following command to verify whether the Keytab file contains the key for the specified principal.
klist -ket ./client.keytab Keytab name: FILE:client.keytab KVNO Timestamp Principal ---- ------------------- ------------------------------------------------------ 7 2018-07-30T10:19:16 te**@**.com (des-cbc-md5)DNS and HOST configuration for an exclusive resource group
In a Kafka cluster with Kerberos authentication enabled, the hostname of a node in the cluster is used as part of the principal registered for that node in the KDC (Key Distribution Center). When a client accesses a node in the Kafka cluster, it infers the node's principal based on the local DNS and HOST settings to obtain an access credential for the node from the KDC. When you use an exclusive resource group to access a Kafka cluster with Kerberos authentication enabled, you must correctly configure the DNS and HOST settings to ensure that the access credential for the cluster nodes can be obtained from the KDC:
DNS settings
If a PrivateZone instance is used for domain name resolution of the Kafka cluster nodes in the VPC where the exclusive resource group is attached, you can add a custom route for the IP addresses 100.100.2.136 and 100.100.2.138 to the VPC attachment of the exclusive resource group in the DataWorks console. This ensures that the PrivateZone domain name resolution settings for the Kafka cluster nodes apply to the exclusive resource group.
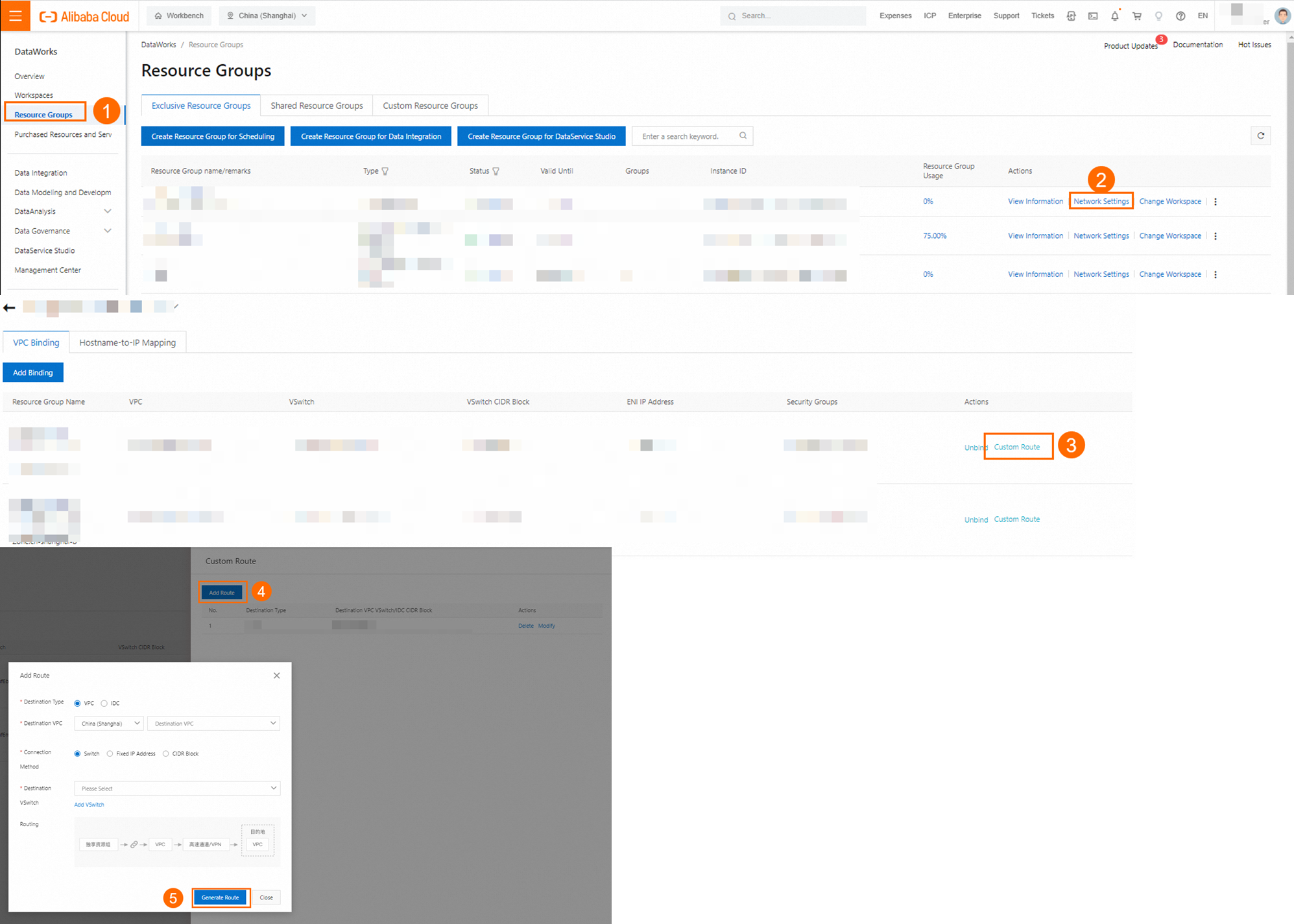
HOST settings
If a PrivateZone instance is not used for domain name resolution of the Kafka cluster nodes in the VPC where the exclusive resource group is attached, you must add the IP address-to-domain name mappings for each Kafka cluster node to the Host configuration in the network settings for the exclusive resource group in the DataWorks console.
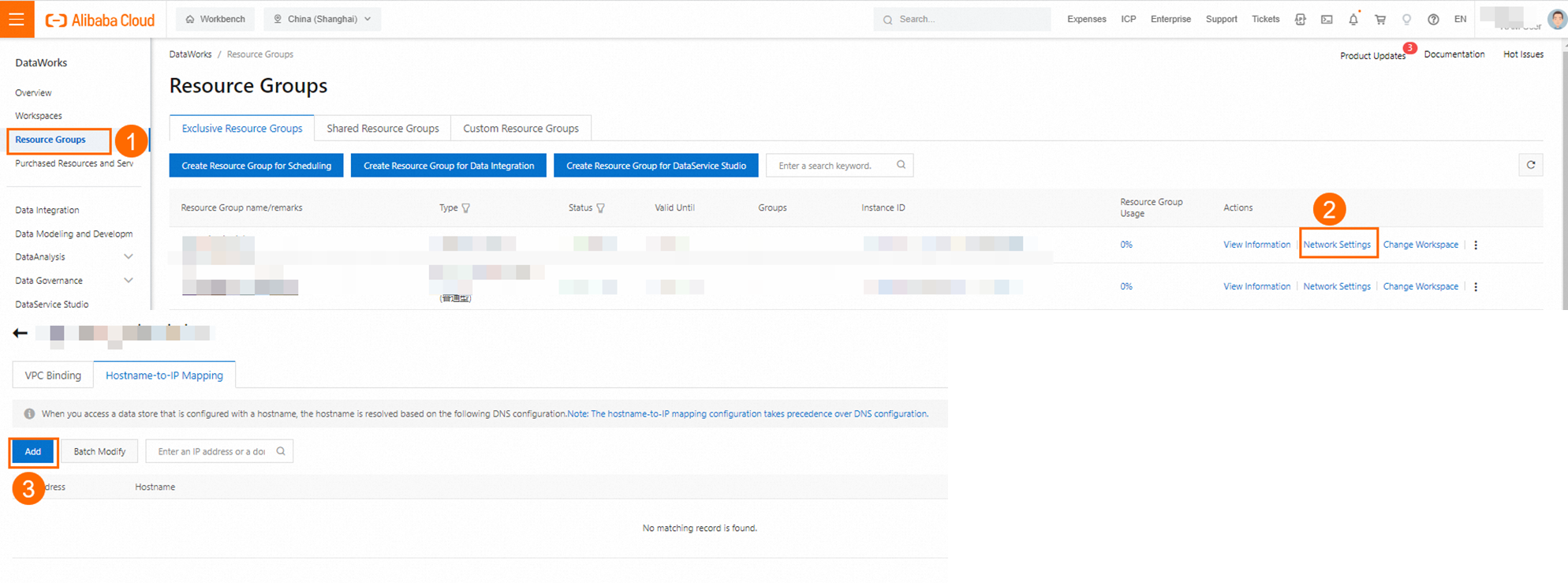
PLAIN
When you configure a Kafka data source, if you set Sasl Mechanism to PLAIN, the JAAS file must start with KafkaClient, followed by all configuration items enclosed in a pair of braces {}.
The first line inside the braces defines the logon component class to use. For different SASL authentication mechanisms, the logon component class is fixed. Each subsequent configuration item is written in the key=value format.
All configuration items except the last one must not end with a semicolon.
The last configuration item must end with a semicolon. A semicolon must also be added after the closing brace "}".
If the format requirements are not met, the JAAS configuration file cannot be parsed. The following code shows a typical JAAS configuration file format. Replace the xxx placeholders with your actual information.
KafkaClient { org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username="xxx" password="xxx"; };Configuration item | Description |
Logon module | Must be set to org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModul |
username | The username. Configure this item as needed. |
password | The password. Configure this item as needed. |
FAQ
Appendix: Script demos and parameter descriptions
Configure a batch synchronization task by using the code editor
If you want to configure a batch synchronization task by using the code editor, you must configure the related parameters in the script based on the unified script format requirements. For more information, see Configure a batch synchronization task by using the code editor. The following information describes the parameters that you must configure for data sources when you configure a batch synchronization task by using the code editor.
Reader script demo
The following code shows the JSON configuration for reading data from Kafka.
{ "type": "job", "steps": [ { "stepType": "kafka", "parameter": { "server": "host:9093", "column": [ "__key__", "__value__", "__partition__", "__offset__", "__timestamp__", "'123'", "event_id", "tag.desc" ], "kafkaConfig": { "group.id": "demo_test" }, "topic": "topicName", "keyType": "ByteArray", "valueType": "ByteArray", "beginDateTime": "20190416000000", "endDateTime": "20190416000006", "skipExceedRecord": "true" }, "name": "Reader", "category": "reader" }, { "stepType": "stream", "parameter": { "print": false, "fieldDelimiter": "," }, "name": "Writer", "category": "writer" } ], "version": "2.0", "order": { "hops": [ { "from": "Reader", "to": "Writer" } ] }, "setting": { "errorLimit": { "record": "0" }, "speed": { "throttle": true,//When throttle is false, the mbps parameter does not take effect, which means that the rate is not limited. When throttle is true, the rate is limited. "concurrent": 1,//The number of concurrent threads. "mbps":"12"//The maximum transmission rate. 1 mbps is equal to 1 MB/s. } } }Reader script parameters
Parameter | Description | Required |
datasource | The name of the data source. The code editor supports adding data sources. The value of this parameter must be the same as the name of the added data source. | Yes |
server | The address of the Kafka broker server in ip:port format. You can configure only one server, but you must make sure that DataWorks can connect to the IP addresses of all brokers in the Kafka cluster. | Yes |
topic | The Kafka topic. A topic is an aggregation of message feeds that Kafka processes. | Yes |
column | The Kafka data to read. Constant columns, data columns, and attribute columns are supported.
| Yes |
keyType | The type of the Kafka key. Valid values: BYTEARRAY, DOUBLE, FLOAT, INTEGER, LONG, and SHORT. | Yes |
valueType | The type of the Kafka value. Valid values: BYTEARRAY, DOUBLE, FLOAT, INTEGER, LONG, and SHORT. | Yes |
beginDateTime | The start offset for data consumption. This is the left boundary of the time range (inclusive). It is a time string in the yyyymmddhhmmss format. You can use it with Scheduling Parameters. For more information, see Supported formats of scheduling parameters. Note This feature is supported in Kafka 0.10.2 and later. | You must specify either this parameter or beginOffset. Note beginDateTime and endDateTime are used together. |
endDateTime | The end offset for data consumption. This is the right boundary of the time range (exclusive). It is a time string in the yyyymmddhhmmss format. You can use it with Scheduling Parameters. For more information, see Supported formats of scheduling parameters. Note This feature is supported in Kafka 0.10.2 and later. | You must specify either this parameter or endOffset. Note endDateTime and beginDateTime are used together. |
beginOffset | The start offset for data consumption. You can configure it in the following forms:
| You must specify either this parameter or beginDateTime. |
endOffset | The end offset for data consumption. This is used to control when the data consumption task exits. | You must specify either this parameter or endDateTime. |
skipExceedRecord | Kafka uses
| No. The default value is false. |
partition | A Kafka topic has multiple partitions (partition). By default, a data synchronization task reads data from an offset range that covers all partitions in the topic. You can also specify a partition to read data only from the offset range of a single partition. | No. No default value. |
kafkaConfig | When creating a KafkaConsumer client for data consumption, you can specify extended parameters such as bootstrap.servers, auto.commit.interval.ms, and session.timeout.ms. You can use kafkaConfig to control the consumption behavior of KafkaConsumer. | No |
encoding | When keyType or valueType is set to STRING, the encoding specified by this parameter is used to parse the string. | No. The default value is UTF-8. |
waitTIme | The maximum time, in seconds, that the consumer object waits to pull data from Kafka in a single attempt. | No. The default value is 60. |
stopWhenPollEmpty | The valid values are true and false. If this parameter is set to true and the consumer pulls empty data from Kafka (usually because all data in the topic has been read, or due to network or Kafka cluster availability issues), the task stops immediately. Otherwise, it retries until data is read again. | No. The default value is true. |
stopWhenReachEndOffset | This parameter takes effect only when stopWhenPollEmpty is true. The valid values are true and false.
| No. The default value is false. Note This is for compatibility with historical logic. Kafka versions earlier than V0.10.2 cannot check if the latest data from all partitions of a Kafka topic has been read. However, some code editor tasks may be reading data from Kafka versions earlier than V0.10.2. |
The following table describes the kafkaConfig parameters.
Parameter | Description |
fetch.min.bytes | Specifies the minimum number of bytes of messages that the consumer can get from the broker. The data is returned to the consumer only when there is enough data. |
fetch.max.wait.ms | The maximum time to wait for the broker to return data. The default value is 500 milliseconds. Data is returned based on whichever condition is met first: fetch.min.bytes or fetch.max.wait.ms. |
max.partition.fetch.bytes | Specifies the maximum number of bytes that the broker can return to the consumer from each partition. The default value is 1 MB. |
session.timeout.ms | Specifies the time that the consumer can be disconnected from the server before it stops receiving services. The default value is 30 seconds. |
auto.offset.reset | The action that the consumer takes when reading with no offset or an invalid offset (because the consumer has been inactive for a long time and the record with the offset has expired and been deleted). The default value is none, which means the offset is not automatically reset. You can change it to earliest, which means the consumer reads the partition records from the earliest offset. |
max.poll.records | The number of messages that can be returned by a single call to the poll method. |
key.deserializer | The deserialization method for the message key, such as org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer. |
value.deserializer | The deserialization method for the data value, such as org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer. |
ssl.truststore.location | The path of the SSL root certificate. |
ssl.truststore.password | The password for the root certificate store. If you are using Alibaba Cloud Kafka, set this to KafkaOnsClient. |
security.protocol | The access protocol. Currently, only the SASL_SSL protocol is supported. |
sasl.mechanism | The SASL authentication method. If you are using Alibaba Cloud Kafka, use PLAIN. |
java.security.auth.login.config | The path of the SASL authentication file. |
Writer script demo
The following code shows the JSON configuration for writing data to Kafka.
{ "type":"job", "version":"2.0",//The version number. "steps":[ { "stepType":"stream", "parameter":{}, "name":"Reader", "category":"reader" }, { "stepType":"Kafka",//The plug-in name. "parameter":{ "server": "ip:9092", //The server address of Kafka. "keyIndex": 0, //The column to be used as the key. Must follow camel case naming conventions, with k in lowercase. "valueIndex": 1, //The column to be used as the value. Currently, you can only select one column from the source data or leave this parameter empty. If empty, all source data is used. //For example, to use the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th columns of an ODPS table as the kafkaValue, create a new ODPS table, clean and integrate the data from the original ODPS table into the new table, and then use the new table for synchronization. "keyType": "Integer", //The type of the Kafka key. "valueType": "Short", //The type of the Kafka value. "topic": "t08", //The Kafka topic. "batchSize": 1024 //The amount of data written to Kafka at a time, in bytes. }, "name":"Writer", "category":"writer" } ], "setting":{ "errorLimit":{ "record":"0"//The number of error records. }, "speed":{ "throttle":true,//When throttle is false, the mbps parameter does not take effect, which means that the rate is not limited. When throttle is true, the rate is limited. "concurrent":1, //The number of concurrent jobs. "mbps":"12"//The maximum transmission rate. 1 mbps is equal to 1 MB/s. } }, "order":{ "hops":[ { "from":"Reader", "to":"Writer" } ] } }Writer script parameters
Parameter | Description | Required |
datasource | The name of the data source. The code editor supports adding data sources. The value of this parameter must be the same as the name of the added data source. | Yes |
server | The address of the Kafka server in ip:port format. | Yes |
topic | The Kafka topic. It is a category for different message feeds that Kafka processes. Each message published to a Kafka cluster has a category, which is called a topic. A topic is a collection of a group of messages. | Yes |
valueIndex | The column in the Kafka writer that is used as the value. If this is not specified, all columns are concatenated to form the value by default. The separator is specified by fieldDelimiter. | No |
writeMode | When valueIndex is not configured, this parameter determines the format for concatenating all columns of the source record to form the value of the Kafka record. Valid values are text and JSON. The default value is text.
For example, if a source record has three columns with values a, b, and c, and writeMode is set to text and fieldDelimiter is set to #, the value of the Kafka record written is the string a#b#c. If writeMode is set to JSON and column is set to [{"name":"col1"},{"name":"col2"},{"name":"col3"}], the value of the Kafka record written is the string {"col1":"a","col2":"b","col3":"c"}. If valueIndex is configured, this parameter is invalid. | No |
column | The fields in the destination table to which data is to be written, separated by commas. For example: When valueIndex is not configured and writeMode is set to JSON, this parameter defines the field names in the JSON structure for the column values of the source record. For example,
If valueIndex is configured, or if writeMode is set to text, this parameter is invalid. | Required when valueIndex is not configured and writeMode is set to JSON. |
partition | Specifies the number of the partition in the Kafka topic to which data is written. This must be an integer greater than or equal to 0. | No |
keyIndex | The column in the Kafka writer that is used as the key. The value of the keyIndex parameter must be an integer greater than or equal to 0. Otherwise, the task will fail. | No |
keyIndexes | An array of the ordinal numbers of the columns in the source record that are used as the key for the Kafka record. The column ordinal number starts from 0. For example, [0,1,2] will concatenate the values of all configured column numbers with commas to form the key of the Kafka record. If this is not specified, the key of the Kafka record is null, and the data is written to the partitions of the topic in a round-robin fashion. You can only specify either this parameter or keyIndex. | No |
fieldDelimiter | When writeMode is set to text and valueIndex is not configured, all columns of the source record are concatenated using the column separator specified by this parameter to form the value of the Kafka record. You can configure a single character or multiple characters as the separator. You can configure Unicode characters in the format \u0001. Escape characters such as \t and \n are supported. The default value is \t. If writeMode is not set to text or if valueIndex is configured, this parameter is invalid. | No |
keyType | The type of the Kafka key. Valid values: BYTEARRAY, DOUBLE, FLOAT, INTEGER, LONG, and SHORT. | Yes |
valueType | The type of the Kafka value. Valid values: BYTEARRAY, DOUBLE, FLOAT, INTEGER, LONG, and SHORT. | Yes |
nullKeyFormat | If the value of the source column specified by keyIndex or keyIndexes is null, it is replaced with the string specified by this parameter. If this is not configured, no replacement is made. | No |
nullValueFormat | If the value of a source column is null, it is replaced with the string specified by this parameter when assembling the value of the Kafka record. If this is not configured, no replacement is made. | No |
acks | The acks configuration when initializing the Kafka producer. This determines the acknowledgment method for successful writes. By default, the acks parameter is set to all. The valid values for acks are:
| No |
Appendix: Definition of message format for writing to Kafka
After you configure and run a real-time synchronization task, the data read from the source database is written to a Kafka topic in JSON format. First, all existing data in the specified source table is written to the corresponding Kafka topic. Then, the task starts real-time synchronization to continuously write incremental data to the topic. Incremental DDL change information from the source table is also written to the Kafka topic in JSON format. You can obtain the status and change information of messages written to Kafka. For more information, see Appendix: Message format.
In the JSON structure of data written to Kafka by an offline synchronization task, the payload.sequenceId, payload.timestamp.eventTime and payload.timestamp.checkpointTime fields are set to -1.
Appendix: JSON field types
When writeMode is set to JSON, you can use the type field in the column parameter to specify the JSON data type. During a write operation, the system attempts to convert the value of the column in the source record to the specified type. If this conversion fails, dirty data is generated.
Valid value | Description |
JSON_STRING | Converts the source record column value to a string and writes it to the JSON field. For example, if the source record column value is the integer |
JSON_NUMBER | Converts the source record column value to a number and writes it to the JSON field. For example, if the source record column value is the string |
JSON_BOOL | Converts the source record column value to a Boolean value and writes it to the JSON field. For example, if the source record column value is the string |
JSON_ARRAY | Converts the source record column value to a JSON array and writes it to the JSON field. For example, if the source record column value is the string |
JSON_MAP | Converts the source record column value to a JSON object and writes it to the JSON field. For example, if the source record column value is the string |
JSON_BASE64 | Converts the binary byte content of the source record column value to a BASE64-encoded string and writes it to the JSON field. For example, if the source record column value is a byte array of length 2, represented in hexadecimal as |
JSON_HEX | Converts the binary byte content of the source record column value to a hexadecimal numeric string and writes it to the JSON field. For example, if the source record column value is a byte array of length 2, represented in hexadecimal as |