QueryCollectionElectricCollectionTrailBaseCollectionRxDBCollectionLocalStorageCollectionLocalOnlyCollectionuseLiveQuery hookqueryBuilderWelcome to the TanStack DB documentation.
TanStack DB is a reactive client store for building super fast apps on sync. It extends TanStack Query with collections, live queries and optimistic mutations.
TanStack DB works by:
// Define collections to load data into const todoCollection = createCollection({ // ...your config onUpdate: updateMutationFn, }) const Todos = () => { // Bind data using live queries const { data: todos } = useLiveQuery((q) => q.from({ todo: todoCollection }).where(({ todo }) => todo.completed) ) const complete = (todo) => { // Instantly applies optimistic state todoCollection.update(todo.id, (draft) => { draft.completed = true }) } return ( <ul> {todos.map((todo) => ( <li key={todo.id} onClick={() => complete(todo)}> {todo.text} </li> ))} </ul> ) } // Define collections to load data into const todoCollection = createCollection({ // ...your config onUpdate: updateMutationFn, }) const Todos = () => { // Bind data using live queries const { data: todos } = useLiveQuery((q) => q.from({ todo: todoCollection }).where(({ todo }) => todo.completed) ) const complete = (todo) => { // Instantly applies optimistic state todoCollection.update(todo.id, (draft) => { draft.completed = true }) } return ( <ul> {todos.map((todo) => ( <li key={todo.id} onClick={() => complete(todo)}> {todo.text} </li> ))} </ul> ) } Collections are typed sets of objects that can be populated with data. They're designed to de-couple loading data into your app from binding data to your components.
Collections can be populated in many ways, including:
Once you have your data in collections, you can query across them using live queries in your components.
Live queries are used to query data out of collections. Live queries are reactive: when the underlying data changes in a way that would affect the query result, the result is incrementally updated and returned from the query, triggering a re-render.
TanStack DB live queries are implemented using d2ts, a Typescript implementation of differential dataflow. This allows the query results to update incrementally (rather than by re-running the whole query). This makes them blazing fast, usually sub-millisecond, even for highly complex queries.
Live queries support joins across collections. This allows you to:
Every query returns another collection which can also be queried.
For more details on live queries, see the Live Queries documentation.
Collections support insert, update and delete operations. When called, by default they trigger the corresponding onInsert, onUpdate, onDelete handlers which are responsible for writing the mutation to the backend.
// Define collection with persistence handlers const todoCollection = createCollection({ id: "todos", // ... other config onUpdate: async ({ transaction }) => { const { original, changes } = transaction.mutations[0] await api.todos.update(original.id, changes) }, }) // Immediately applies optimistic state todoCollection.update(todo.id, (draft) => { draft.completed = true }) // Define collection with persistence handlers const todoCollection = createCollection({ id: "todos", // ... other config onUpdate: async ({ transaction }) => { const { original, changes } = transaction.mutations[0] await api.todos.update(original.id, changes) }, }) // Immediately applies optimistic state todoCollection.update(todo.id, (draft) => { draft.completed = true }) The collection maintains optimistic state separately from synced data. When live queries read from the collection, they see a local view that overlays the optimistic mutations on top of the immutable synced data.
The optimistic state is held until the handler resolves, at which point the data is persisted to the server and synced back. If the handler throws an error, the optimistic state is rolled back.
For more complex mutations, you can create custom actions with createOptimisticAction or custom transactions with createTransaction. See the Mutations guide for details.
This combines to support a model of uni-directional data flow, extending the redux/flux style state management pattern beyond the client, to take in the server as well:
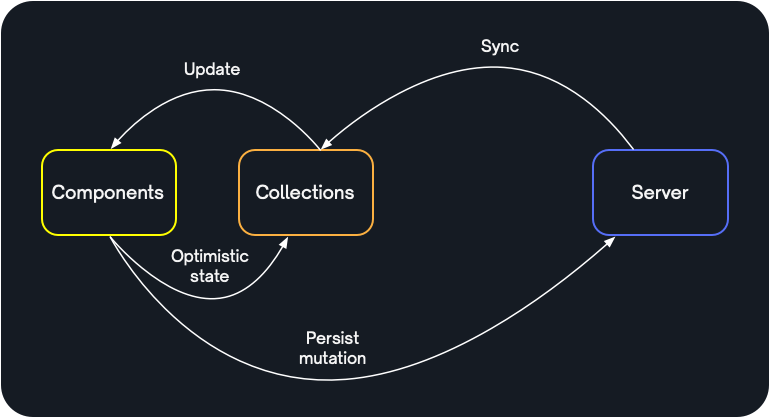
With an instant inner loop of optimistic state, superseded in time by the slower outer loop of persisting to the server and syncing the updated server state back into the collection.
There are a number of built-in collection types:
You can also use:
All collections optionally (though strongly recommended) support adding a schema.
If provided, this must be a Standard Schema compatible schema instance, such as a Zod or Effect schema.
The collection will use the schema to do client-side validation of optimistic mutations.
The collection will use the schema for its type so if you provide a schema, you can't also pass in an explicit type (e.g. createCollection<Todo>()).
TanStack Query fetches data using managed queries. Use queryCollectionOptions to fetch data into a collection using TanStack Query:
import { createCollection } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { queryCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/query-db-collection" const todoCollection = createCollection( queryCollectionOptions({ queryKey: ["todoItems"], queryFn: async () => { const response = await fetch("/api/todos") return response.json() }, getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: todoSchema, // any standard schema }) ) import { createCollection } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { queryCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/query-db-collection" const todoCollection = createCollection( queryCollectionOptions({ queryKey: ["todoItems"], queryFn: async () => { const response = await fetch("/api/todos") return response.json() }, getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: todoSchema, // any standard schema }) ) The collection will be populated with the query results.
Electric is a read-path sync engine for Postgres. It allows you to sync subsets of data out of a Postgres database, through your API, into a TanStack DB collection.
Electric's main primitive for sync is a Shape. Use electricCollectionOptions to sync a shape into a collection:
import { createCollection } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { electricCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/electric-db-collection" export const todoCollection = createCollection( electricCollectionOptions({ id: "todos", shapeOptions: { url: "https://example.com/v1/shape", params: { table: "todos", }, }, getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: todoSchema, }) ) import { createCollection } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { electricCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/electric-db-collection" export const todoCollection = createCollection( electricCollectionOptions({ id: "todos", shapeOptions: { url: "https://example.com/v1/shape", params: { table: "todos", }, }, getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: todoSchema, }) ) The Electric collection requires two Electric-specific options:
A new collections doesn't start syncing until you call collection.preload() or you query it.
Electric shapes allow you to filter data using where clauses:
export const myPendingTodos = createCollection( electricCollectionOptions({ id: "todos", shapeOptions: { url: "https://example.com/v1/shape", params: { table: "todos", where: ` status = 'pending' AND user_id = '${user.id}' `, }, }, getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: todoSchema, }) ) export const myPendingTodos = createCollection( electricCollectionOptions({ id: "todos", shapeOptions: { url: "https://example.com/v1/shape", params: { table: "todos", where: ` status = 'pending' AND user_id = '${user.id}' `, }, }, getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: todoSchema, }) ) Tip
Shape where clauses, used to filter the data you sync into ElectricCollections, are different from the live queries you use to query data in components.
Live queries are much more expressive than shapes, allowing you to query across collections, join, aggregate, etc. Shapes just contain filtered database tables and are used to populate the data in a collection.
If you need more control over what data syncs into the collection, Electric allows you to use your API as a proxy to both authorize and filter data.
See the Electric docs for more information.
TrailBase is an easy-to-self-host, single-executable application backend with built-in SQLite, a V8 JS runtime, auth, admin UIs and sync functionality.
TrailBase lets you expose tables via Record APIs and subscribe to changes when enable_subscriptions is set. Use trailBaseCollectionOptions to sync records into a collection:
import { createCollection } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { trailBaseCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/trailbase-db-collection" import { initClient } from "trailbase" const trailBaseClient = initClient(`https://trailbase.io`) export const todoCollection = createCollection<SelectTodo, Todo>( trailBaseCollectionOptions({ id: "todos", recordApi: trailBaseClient.records(`todos`), getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: todoSchema, parse: { created_at: (ts) => new Date(ts * 1000), }, serialize: { created_at: (date) => Math.floor(date.valueOf() / 1000), }, }) ) import { createCollection } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { trailBaseCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/trailbase-db-collection" import { initClient } from "trailbase" const trailBaseClient = initClient(`https://trailbase.io`) export const todoCollection = createCollection<SelectTodo, Todo>( trailBaseCollectionOptions({ id: "todos", recordApi: trailBaseClient.records(`todos`), getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: todoSchema, parse: { created_at: (ts) => new Date(ts * 1000), }, serialize: { created_at: (date) => Math.floor(date.valueOf() / 1000), }, }) ) This collection requires the following TrailBase-specific options:
A new collections doesn't start syncing until you call collection.preload() or you query it.
RxDB is a client-side database for JavaScript apps with replication, conflict resolution, and offline-first features.
Use rxdbCollectionOptions from @tanstack/rxdb-db-collection to integrate an RxDB collection with TanStack DB:
import { createCollection } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { rxdbCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/rxdb-db-collection" import { createRxDatabase } from "rxdb" const db = await createRxDatabase({ name: "mydb", storage: getRxStorageMemory(), }) await db.addCollections({ todos: { schema: { version: 0, primaryKey: "id", type: "object", properties: { id: { type: "string", maxLength: 100 }, text: { type: "string" }, completed: { type: "boolean" }, }, }, }, }) // Wrap the RxDB collection with TanStack DB export const todoCollection = createCollection( rxdbCollectionOptions({ rxCollection: db.todos, startSync: true, }) ) import { createCollection } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { rxdbCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/rxdb-db-collection" import { createRxDatabase } from "rxdb" const db = await createRxDatabase({ name: "mydb", storage: getRxStorageMemory(), }) await db.addCollections({ todos: { schema: { version: 0, primaryKey: "id", type: "object", properties: { id: { type: "string", maxLength: 100 }, text: { type: "string" }, completed: { type: "boolean" }, }, }, }, }) // Wrap the RxDB collection with TanStack DB export const todoCollection = createCollection( rxdbCollectionOptions({ rxCollection: db.todos, startSync: true, }) ) With this integration:
This makes RxDB a great choice for apps that need local-first storage, replication, or peer-to-peer sync combined with TanStack DB's live queries and transaction lifecycle.
localStorage collections store small amounts of local-only state that persists across browser sessions and syncs across browser tabs in real-time. All data is stored under a single localStorage key and automatically synchronized using storage events.
Use localStorageCollectionOptions to create a collection that stores data in localStorage:
import { createCollection } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { localStorageCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/react-db" export const userPreferencesCollection = createCollection( localStorageCollectionOptions({ id: "user-preferences", storageKey: "app-user-prefs", // localStorage key getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: userPrefsSchema, }) ) import { createCollection } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { localStorageCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/react-db" export const userPreferencesCollection = createCollection( localStorageCollectionOptions({ id: "user-preferences", storageKey: "app-user-prefs", // localStorage key getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: userPrefsSchema, }) ) The localStorage collection requires:
Mutation handlers (onInsert, onUpdate, onDelete) are completely optional. Data will persist to localStorage whether or not you provide handlers. You can provide alternative storage backends like sessionStorage or custom implementations that match the localStorage API.
export const sessionCollection = createCollection( localStorageCollectionOptions({ id: "session-data", storageKey: "session-key", storage: sessionStorage, // Use sessionStorage instead getKey: (item) => item.id, }) ) export const sessionCollection = createCollection( localStorageCollectionOptions({ id: "session-data", storageKey: "session-key", storage: sessionStorage, // Use sessionStorage instead getKey: (item) => item.id, }) ) Tip
localStorage collections are perfect for user preferences, UI state, and other data that should persist locally but doesn't need server synchronization. For server-synchronized data, use QueryCollection or ElectricCollection instead.
LocalOnly collections are designed for in-memory client data or UI state that doesn't need to persist across browser sessions or sync across tabs. They provide a simple way to manage temporary, session-only data with full optimistic mutation support.
Use localOnlyCollectionOptions to create a collection that stores data only in memory:
import { createCollection } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { localOnlyCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/react-db" export const uiStateCollection = createCollection( localOnlyCollectionOptions({ id: "ui-state", getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: uiStateSchema, // Optional initial data to populate the collection initialData: [ { id: "sidebar", isOpen: false }, { id: "theme", mode: "light" }, ], }) ) import { createCollection } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { localOnlyCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/react-db" export const uiStateCollection = createCollection( localOnlyCollectionOptions({ id: "ui-state", getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: uiStateSchema, // Optional initial data to populate the collection initialData: [ { id: "sidebar", isOpen: false }, { id: "theme", mode: "light" }, ], }) ) The LocalOnly collection requires:
Optional configuration:
Mutation handlers are completely optional. When provided, they are called before the optimistic state is confirmed. The collection automatically manages the transition from optimistic to confirmed state internally.
export const tempDataCollection = createCollection( localOnlyCollectionOptions({ id: "temp-data", getKey: (item) => item.id, onInsert: async ({ transaction }) => { // Custom logic before confirming the insert console.log("Inserting:", transaction.mutations[0].modified) }, onUpdate: async ({ transaction }) => { // Custom logic before confirming the update const { original, modified } = transaction.mutations[0] console.log("Updating from", original, "to", modified) }, }) ) export const tempDataCollection = createCollection( localOnlyCollectionOptions({ id: "temp-data", getKey: (item) => item.id, onInsert: async ({ transaction }) => { // Custom logic before confirming the insert console.log("Inserting:", transaction.mutations[0].modified) }, onUpdate: async ({ transaction }) => { // Custom logic before confirming the update const { original, modified } = transaction.mutations[0] console.log("Updating from", original, "to", modified) }, }) ) Tip
LocalOnly collections are perfect for temporary UI state, form data, or any client-side data that doesn't need persistence. For data that should persist across sessions, use LocalStorageCollection instead.
Live queries return collections. This allows you to derive collections from other collections.
For example:
import { createLiveQueryCollection, eq } from "@tanstack/db" // Imagine you have a collection of todos. const todoCollection = createCollection({ // config }) // You can derive a new collection that's a subset of it. const completedTodoCollection = createLiveQueryCollection({ startSync: true, query: (q) => q.from({ todo: todoCollection }).where(({ todo }) => todo.completed), }) import { createLiveQueryCollection, eq } from "@tanstack/db" // Imagine you have a collection of todos. const todoCollection = createCollection({ // config }) // You can derive a new collection that's a subset of it. const completedTodoCollection = createLiveQueryCollection({ startSync: true, query: (q) => q.from({ todo: todoCollection }).where(({ todo }) => todo.completed), }) This also works with joins to derive collections from multiple source collections. And it works recursively -- you can derive collections from other derived collections. Changes propagate efficiently using differential dataflow and it's collections all the way down.
There is a Collection interface in ../packages/db/src/collection.ts. You can use this to implement your own collection types.
See the existing implementations in ../packages/db, ../packages/query-db-collection, ../packages/electric-db-collection and ../packages/trailbase-db-collection for reference.
Use the useLiveQuery hook to assign live query results to a state variable in your React components:
import { useLiveQuery } from '@tanstack/react-db' import { eq } from '@tanstack/db' const Todos = () => { const { data: todos } = useLiveQuery((q) => q .from({ todo: todoCollection }) .where(({ todo }) => eq(todo.completed, false)) .orderBy(({ todo }) => todo.created_at, 'asc') .select(({ todo }) => ({ id: todo.id, text: todo.text })) ) return <List items={ todos } /> } import { useLiveQuery } from '@tanstack/react-db' import { eq } from '@tanstack/db' const Todos = () => { const { data: todos } = useLiveQuery((q) => q .from({ todo: todoCollection }) .where(({ todo }) => eq(todo.completed, false)) .orderBy(({ todo }) => todo.created_at, 'asc') .select(({ todo }) => ({ id: todo.id, text: todo.text })) ) return <List items={ todos } /> } You can also query across collections with joins:
import { useLiveQuery } from '@tanstack/react-db' import { eq } from '@tanstack/db' const Todos = () => { const { data: todos } = useLiveQuery((q) => q .from({ todos: todoCollection }) .join( { lists: listCollection }, ({ todos, lists }) => eq(lists.id, todos.listId), 'inner' ) .where(({ lists }) => eq(lists.active, true)) .select(({ todos, lists }) => ({ id: todos.id, title: todos.title, listName: lists.name })) ) return <List items={ todos } /> } import { useLiveQuery } from '@tanstack/react-db' import { eq } from '@tanstack/db' const Todos = () => { const { data: todos } = useLiveQuery((q) => q .from({ todos: todoCollection }) .join( { lists: listCollection }, ({ todos, lists }) => eq(lists.id, todos.listId), 'inner' ) .where(({ lists }) => eq(lists.active, true)) .select(({ todos, lists }) => ({ id: todos.id, title: todos.title, listName: lists.name })) ) return <List items={ todos } /> } You can also build queries directly (outside of the component lifecycle) using the underlying queryBuilder API:
import { createLiveQueryCollection, eq } from "@tanstack/db" const completedTodos = createLiveQueryCollection({ startSync: true, query: (q) => q .from({ todo: todoCollection }) .where(({ todo }) => eq(todo.completed, true)), }) const results = completedTodos.toArray import { createLiveQueryCollection, eq } from "@tanstack/db" const completedTodos = createLiveQueryCollection({ startSync: true, query: (q) => q .from({ todo: todoCollection }) .where(({ todo }) => eq(todo.completed, true)), }) const results = completedTodos.toArray Note also that:
See the Live Queries documentation for more details.
For more complex mutations beyond simple CRUD operations, TanStack DB provides createOptimisticAction and createTransaction for creating custom mutations with full control over the mutation lifecycle.
See the Mutations guide for comprehensive documentation on:
Here we illustrate two common ways of using TanStack DB:
Tip
You can combine these patterns. One of the benefits of TanStack DB is that you can integrate different ways of loading data and handling mutations into the same app. Your components don't need to know where the data came from or goes.
You can use TanStack DB with your existing REST API via TanStack Query.
The steps are to:
import { useLiveQuery, createCollection } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { queryCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/query-db-collection" // Load data into collections using TanStack Query. // It's common to define these in a `collections` module. const todoCollection = createCollection( queryCollectionOptions({ queryKey: ["todos"], queryFn: async () => fetch("/api/todos"), getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: todoSchema, // any standard schema onInsert: async ({ transaction }) => { const { changes: newTodo } = transaction.mutations[0] // Handle the local write by sending it to your API. await api.todos.create(newTodo) }, // also add onUpdate, onDelete as needed. }) ) const listCollection = createCollection( queryCollectionOptions({ queryKey: ["todo-lists"], queryFn: async () => fetch("/api/todo-lists"), getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: todoListSchema, onInsert: async ({ transaction }) => { const { changes: newTodo } = transaction.mutations[0] // Handle the local write by sending it to your API. await api.todoLists.create(newTodo) }, // also add onUpdate, onDelete as needed. }) ) const Todos = () => { // Read the data using live queries. Here we show a live // query that joins across two collections. const { data: todos } = useLiveQuery((q) => q .from({ todo: todoCollection }) .join( { list: listCollection }, ({ todo, list }) => eq(list.id, todo.list_id), "inner" ) .where(({ list }) => eq(list.active, true)) .select(({ todo, list }) => ({ id: todo.id, text: todo.text, status: todo.status, listName: list.name, })) ) // ... } import { useLiveQuery, createCollection } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { queryCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/query-db-collection" // Load data into collections using TanStack Query. // It's common to define these in a `collections` module. const todoCollection = createCollection( queryCollectionOptions({ queryKey: ["todos"], queryFn: async () => fetch("/api/todos"), getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: todoSchema, // any standard schema onInsert: async ({ transaction }) => { const { changes: newTodo } = transaction.mutations[0] // Handle the local write by sending it to your API. await api.todos.create(newTodo) }, // also add onUpdate, onDelete as needed. }) ) const listCollection = createCollection( queryCollectionOptions({ queryKey: ["todo-lists"], queryFn: async () => fetch("/api/todo-lists"), getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: todoListSchema, onInsert: async ({ transaction }) => { const { changes: newTodo } = transaction.mutations[0] // Handle the local write by sending it to your API. await api.todoLists.create(newTodo) }, // also add onUpdate, onDelete as needed. }) ) const Todos = () => { // Read the data using live queries. Here we show a live // query that joins across two collections. const { data: todos } = useLiveQuery((q) => q .from({ todo: todoCollection }) .join( { list: listCollection }, ({ todo, list }) => eq(list.id, todo.list_id), "inner" ) .where(({ list }) => eq(list.active, true)) .select(({ todo, list }) => ({ id: todo.id, text: todo.text, status: todo.status, listName: list.name, })) ) // ... } This pattern allows you to extend an existing TanStack Query application, or any application built on a REST API, with blazing fast, cross-collection live queries and local optimistic mutations with automatically managed optimistic state.
One of the most powerful ways of using TanStack DB is with a sync engine, for a fully local-first experience with real-time sync. This allows you to incrementally adopt sync into an existing app, whilst still handling writes with your existing API.
Here, we illustrate this pattern using ElectricSQL as the sync engine.
import type { Collection } from "@tanstack/db" import type { MutationFn, PendingMutation, createCollection, } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { electricCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/electric-db-collection" export const todoCollection = createCollection( electricCollectionOptions({ id: "todos", schema: todoSchema, // Electric syncs data using "shapes". These are filtered views // on database tables that Electric keeps in sync for you. shapeOptions: { url: "https://api.electric-sql.cloud/v1/shape", params: { table: "todos", }, }, getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: todoSchema, onInsert: async ({ transaction }) => { const response = await api.todos.create(transaction.mutations[0].modified) return { txid: response.txid } }, // You can also implement onUpdate, onDelete as needed. }) ) const AddTodo = () => { return ( <Button onClick={() => todoCollection.insert({ text: "🔥 Make app faster" })} /> ) } import type { Collection } from "@tanstack/db" import type { MutationFn, PendingMutation, createCollection, } from "@tanstack/react-db" import { electricCollectionOptions } from "@tanstack/electric-db-collection" export const todoCollection = createCollection( electricCollectionOptions({ id: "todos", schema: todoSchema, // Electric syncs data using "shapes". These are filtered views // on database tables that Electric keeps in sync for you. shapeOptions: { url: "https://api.electric-sql.cloud/v1/shape", params: { table: "todos", }, }, getKey: (item) => item.id, schema: todoSchema, onInsert: async ({ transaction }) => { const response = await api.todos.create(transaction.mutations[0].modified) return { txid: response.txid } }, // You can also implement onUpdate, onDelete as needed. }) ) const AddTodo = () => { return ( <Button onClick={() => todoCollection.insert({ text: "🔥 Make app faster" })} /> ) } When using TanStack DB with React Native, you need to install and configure a UUID generation library since React Native doesn't include crypto.randomUUID() by default.
Install the react-native-random-uuid package:
npm install react-native-random-uuid npm install react-native-random-uuid Then import it at the entry point of your React Native app (e.g., in your App.js or index.js):
import "react-native-random-uuid" import "react-native-random-uuid" This polyfill provides the crypto.randomUUID() function that TanStack DB uses internally for generating unique identifiers.
If you have questions / need help using TanStack DB, let us know on the Discord or start a GitHub discussion:
Your weekly dose of JavaScript news. Delivered every Monday to over 100,000 devs, for free.
Your weekly dose of JavaScript news. Delivered every Monday to over 100,000 devs, for free.


