Image is a file that defines the tools that will be installed when we create a container from that image. We can create an image from a container that has changes when it is created from another base image, or we can also create an Image using the Dockerfile. In this tutorial, I will guide you the first way!
Assuming that I now have an Image of Ubuntu 16.04, I want a new Image that when running the Container from this new Image, Git will be preset.
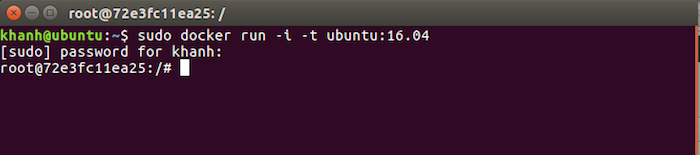
OK, now I will run a new container from Image Ubuntu 16.04 using -i, -t options to be able to access this container after creating it.
| 1 | sudo docker run -i -t ubuntu:16.04 |
To install Git for this new container, first you need to run the following command to update the repositories of Ubuntu 16.04:
| 1 | apt-get update |
Now, we will install Git by running the following command:
| 1 | apt-get install -Y git |
Result:
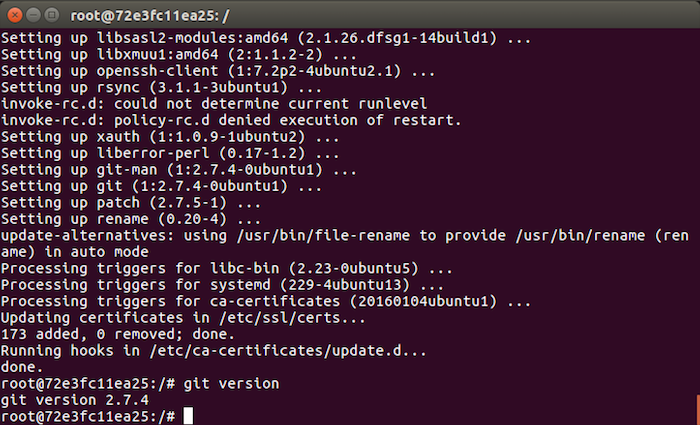
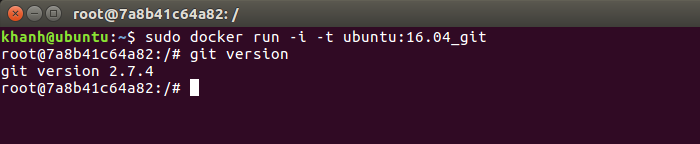
OK, so we have Git installed. Now exit this container with the exit command.
After we exit, we can check the list of containers that we have run using the command
| 1 | docker ps -a |
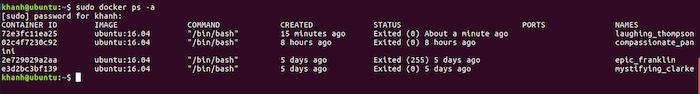
As you can see, the container I just ran was created 15 minutes ago called laughing_thompson. Now, I will use the commit command to create an image from this container.
The structure of the commit statement is as follows:
| 1 | docker commit container_id repository:version |
In this example, we will run the following statement:
| 1 | docker commit 72e3fc11ea25 ubuntu:16.06_git |
Result:

Check the images in our Repository, you will see the Image we just created.

Now if you create a new container from this new image, you will see that the Git tool is already installed.