-
-
Couldn't load subscription status.
- Fork 33.3k
bpo-27145:small_ints[x] could be returned in long_add and long_sub #15716
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
bpo-27145:small_ints[x] could be returned in long_add and long_sub #15716
Conversation
| Can you please try to add a test to test_long? The test should be decorated with |
| @vstinner Thanks for your quick reply. I have added a test to test_long. |
Misc/NEWS.d/next/Core and Builtins/2019-09-06-16-40-12.bpo-27145.njuCXU.rst Outdated Show resolved Hide resolved
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
I think it should be handled in x_sub, because we can get small ints only with addition of single digit ints or with subtraction. But single digit ints are already handled here
Lines 3256 to 3258 in d8c93aa
| if (Py_ABS(Py_SIZE(a)) <= 1 && Py_ABS(Py_SIZE(b)) <= 1) { | |
| return PyLong_FromLong(MEDIUM_VALUE(a) + MEDIUM_VALUE(b)); | |
| } |
and here
Lines 3290 to 3292 in d8c93aa
| if (Py_ABS(Py_SIZE(a)) <= 1 && Py_ABS(Py_SIZE(b)) <= 1) { | |
| return PyLong_FromLong(MEDIUM_VALUE(a) - MEDIUM_VALUE(b)); | |
| } |
Also it should be clear how this change affects performance (i.e. benchmarks are needed).
This comment has been minimized.
This comment has been minimized.
@sir-sigurd It can't be handled in Lines 3261 to 3267 in d8c93aa
|
| Handling it in |
| @sir-sigurd You are right, only a positive number and a negative number will result a small int. Thank you for your commit. |
Please avoid the timeit module for microbenchmarks: it's not reliable at all.
Please use pyperf timeit: The best is to use pyperf timeit --compare-to, or store the result into 2 json files and then use pyperf compare_to. |
|
| "Not significant": good :-) |
| @hongweipeng did you compile it with PGO and LTO? |
| @sir-sigurd I use |
| @hongweipeng Here are my benchmark results: |
| IMO it worth to try this suggestions from BPO issue: It should be applied here: Lines 3219 to 3222 in b42130d
|
This comment has been minimized.
This comment has been minimized.
These results look sane, but it's better to test |
This comment has been minimized.
This comment has been minimized.
| Ping. I've reverted the code for some days. @vstinner Would you mind to review again? |
| I hacked longobject.c to check if other methods can return "de-normalized" results. I tested without your PR. The following functions should call maybe_small_long():
|
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
LGTM. But I would prefer to have a second review of another core dev.
@mdickinson, @serhiy-storchaka, @pablogsal, @methane, @nanjekyejoannah: Would you mind to review this PR?
| Here is my hack to ensure that the result of all long methods is normalized: And here are fixes to normalize results: I had to disable test_format() since it became too slow :-) Maybe my patch introduced a bug, I'm not sure. |
| Ah, one more method return a de-normalized long:
My fix: |
| A few more: When I run these tests alone, they pass. Maybe I messed up somewhere. |
| For reviewers: my previous comments are about my experient to check if other long methods should be modified or not. It's not directly related to this change which LGTM. |
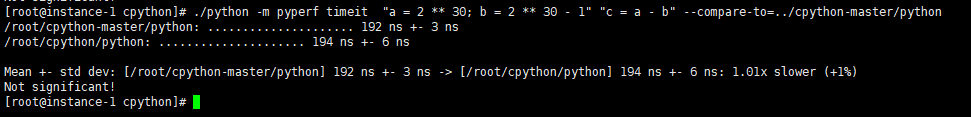
Master branch:
This PR:
https://bugs.python.org/issue27145