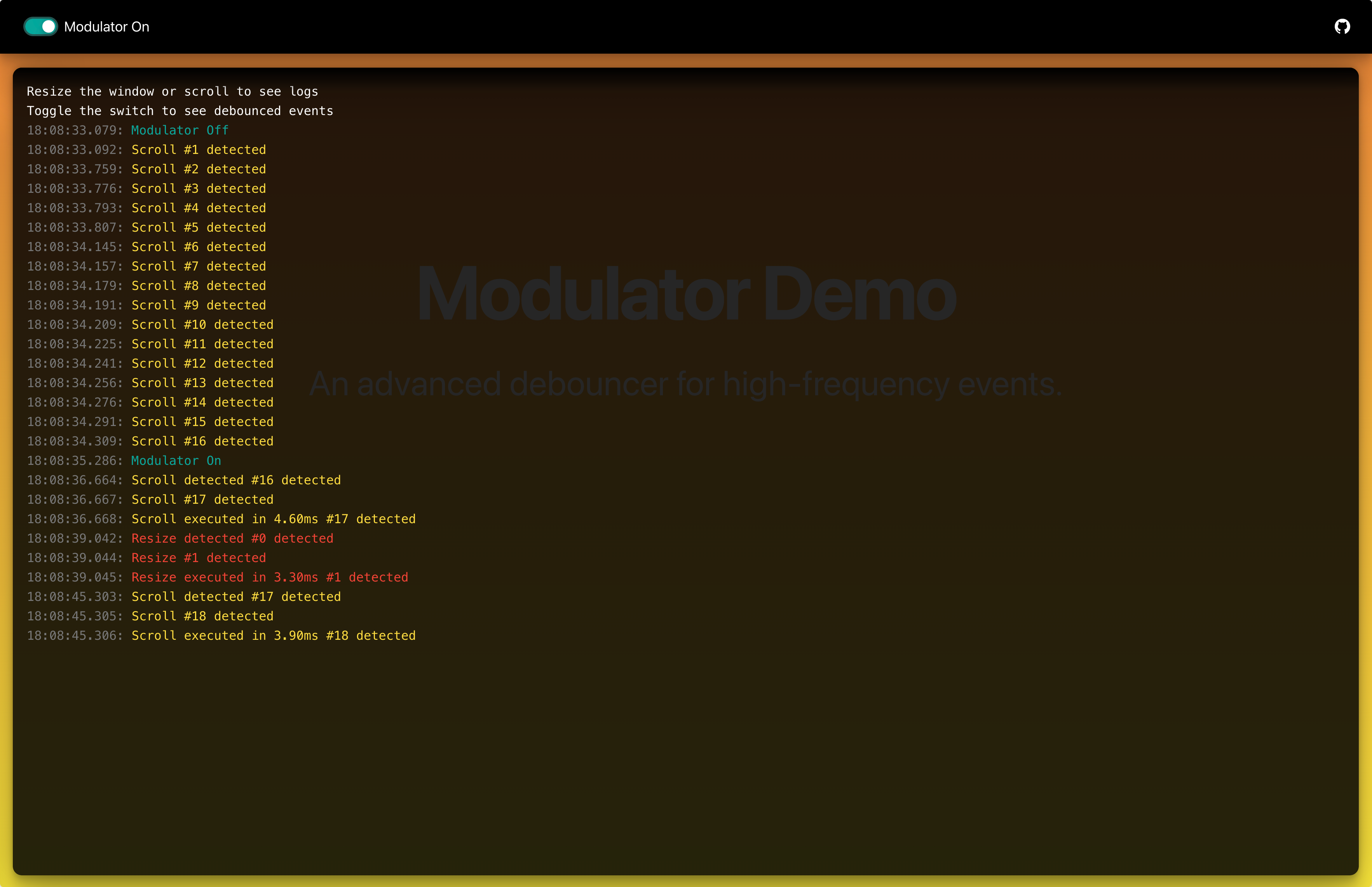
Modulator is an advanced debouncing utility, now written in TypeScript, designed to optimize high-frequency events in web applications (e.g., scroll, resize, input). This standalone solution offers enhanced performance and flexibility compared to basic debouncing functions.
Key features include:
- Promise-based Return: Always returns a Promise that resolves with the result of your function or rejects on error/cancellation.
- Configurable Caching: Optional result caching based on arguments with controllable
maxCacheSize. - Immediate Execution: Option (
immediate: true) to trigger the function on the leading edge. - Maximum Wait Time: Optional
maxWaitparameter to guarantee execution after a certain period, even with continuous calls. - Cancellation: A
.cancel()method to abort pending debounced calls and reject their associated Promise. - TypeScript Support: Ships with built-in type definitions for a better developer experience.
npm install @danielhaim/modulator # or yarn add @danielhaim/modulatorimport { modulate } from '@danielhaim/modulator'; // or import default Modulator from '@danielhaim/modulator'; // If using the object wrapper (less common now) async function myAsyncFunction(query) { console.log('Executing with:', query); // Simulate work await new Promise(res => setTimeout(res, 50)); if (query === 'fail') throw new Error('Failed!'); return `Result for ${query}`; } const debouncedFunc = modulate(myAsyncFunction, 300); debouncedFunc('query1') .then(result => console.log('Success:', result)) // Logs 'Success: Result for query1' after 300ms .catch(error => console.error('Caught:', error)); debouncedFunc('fail') .then(result => console.log('Success:', result)) .catch(error => console.error('Caught:', error)); // Logs 'Caught: Error: Failed!' after 300ms // Using async/await async function run() { try { const result = await debouncedFunc('query2'); console.log('Async Success:', result); } catch (error) { console.error('Async Error:', error); } } run();const { modulate } = require('@danielhaim/modulator'); const debouncedFunc = modulate(/* ... */); // ... usage is the sameInclude the UMD build:
<!-- Download dist/modulator.umd.js or use a CDN like jsDelivr/unpkg --> <script src="path/to/modulator.umd.js"></script> <script> // Modulator is available globally const debouncedFunc = Modulator.modulate(myFunction, 200); myButton.addEventListener('click', async () => { try { const result = await debouncedFunc('data'); console.log('Got:', result); } catch (e) { console.error('Error:', e); } }); </script>requirejs(['path/to/modulator.amd'], function(Modulator) { const debouncedFunc = Modulator.modulate(myFunction, 200); // ... });Creates a debounced function that delays invoking func until after wait milliseconds have elapsed since the last time the debounced function was invoked.
Returns: DebouncedFunction - A new function that returns a Promise. This promise resolves with the return value of the original func or rejects if func throws an error, returns a rejected promise, or if the debounced call is cancelled via .cancel().
| Name | Type | Attributes | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
func | Function | The function to debounce. Can be synchronous or asynchronous (return a Promise). | ||
wait | number | The debouncing wait time in milliseconds. Must be non-negative. | ||
immediate? | boolean | <optional> | false | If true, triggers func on the leading edge instead of the trailing edge. Subsequent calls within the wait period are ignored until the cooldown finishes. |
context? | object | <optional> | null | The context (this) to apply when invoking func. Defaults to the context the debounced function is called with. |
maxCacheSize? | number | <optional> | 100 | The maximum number of results to cache based on arguments. Uses JSON.stringify for keys. Set to 0 to disable caching. Must be non-negative. |
maxWait? | number | null | <optional> | null | The maximum time (in ms) func is allowed to be delayed before it's invoked, even if calls keep occurring. Must be >= wait if set. |
The returned debounced function has an additional method:
debouncedFunc.cancel(): Cancels any pending invocation of the debounced function. If a call was pending, thePromisereturned by that call will be rejected with an error indicating cancellation. This does not clear the result cache.
- When
maxCacheSize > 0, Modulator caches the results (resolved values) of successfulfuncinvocations. - The cache key is generated using
JSON.stringify(arguments). This works well for primitive arguments but may have limitations with complex objects, functions, or circular references. - If a subsequent call is made with the same arguments (generating the same cache key) while the result is in the cache, the cached result is returned immediately via a resolved Promise, and
funcis not invoked. - The cache uses a simple Least Recently Used (LRU) eviction strategy: when the cache exceeds
maxCacheSize, the oldest entry is removed. Accessing a cached item marks it as recently used.
function handleInput(value) { console.log('Processing input:', value); // e.g., make API call } // Debounce to run only 500ms after the user stops typing const debouncedHandleInput = modulate(handleInput, 500); searchInput.addEventListener('input', (event) => { debouncedHandleInput(event.target.value) .catch(err => console.error("Input Error:", err)); // Optional: Catch potential errors });function handleClick() { console.log('Button clicked!'); // Perform action immediately, but prevent rapid re-clicks } // Trigger immediately, then ignore calls for 1000ms const debouncedClick = modulate(handleClick, 1000, true); myButton.addEventListener('click', () => { debouncedClick().catch(err => { // Only log if it's not a cancellation error, as we don't cancel here if (err.message !== 'Debounced function call was cancelled.') { console.error("Click Error:", err); } }); });async function searchAPI(query) { if (!query) return []; // Handle empty query console.log(`Searching API for: ${query}`); const response = await fetch(`/api/search?q=${query}`); if (!response.ok) throw new Error(`API Error: ${response.statusText}`); return response.json(); } const debouncedSearch = modulate(searchAPI, 400); const statusElement = document.getElementById('search-status'); // Assume element exists const searchInput = document.getElementById('search-input'); // Assume element exists searchInput.addEventListener('input', async (event) => { const query = event.target.value; statusElement.textContent = 'Searching...'; try { // debouncedSearch returns a promise here const results = await debouncedSearch(query); // Check if query is still relevant before updating UI if (query === searchInput.value) { statusElement.textContent = `Found ${results.length} results.`; // Update UI with results } else { console.log("Query changed, ignoring results for:", query); } } catch (error) { // Handle errors from searchAPI OR cancellation errors if (error.message === 'Debounced function call was cancelled.') { console.log('Search cancelled.'); // Status might already be 'Searching...' which is fine } else { console.error('Search failed:', error); statusElement.textContent = `Error: ${error.message}`; } } }); // Example of cancellation (Alternative approach combining input/cancel) let currentQuery = ''; searchInput.addEventListener('input', async (event) => { const query = event.target.value; currentQuery = query; statusElement.textContent = 'Typing...'; // Cancel any previous pending search before starting a new one debouncedSearch.cancel(); // Cancel previous timer/promise if (!query) { // Handle empty input immediately statusElement.textContent = 'Enter search term.'; // Clear results UI return; } // Only proceed if query is not empty after debounce period try { statusElement.textContent = 'Waiting...'; // Indicate waiting for debounce // Start new search (will wait 400ms unless cancelled again) const results = await debouncedSearch(query); // New promise for this call // Re-check if the query changed *after* the await completed if (query === currentQuery) { statusElement.textContent = `Found ${results.length} results.`; // Update UI } else { console.log('Results ignored, query changed.'); // Status might remain 'Typing...' from next input event } } catch (error) { // Handle errors from the awaited promise if (error.message !== 'Debounced function call was cancelled.') { console.error('Search failed:', error); statusElement.textContent = `Error: ${error.message}`; } else { // Ignore cancellation errors here as we trigger cancel often console.log('Search promise cancelled.'); } } });function saveData() { console.log('Saving data to server...'); // API call to save return Promise.resolve({ status: 'Saved' }); // Example return } // Debounce saving by 1 second, but ensure it saves // at least once every 5 seconds even if user keeps typing. const debouncedSave = modulate(saveData, 1000, false, null, 0, 5000); // No cache, maxWait 5s const saveStatus = document.getElementById('save-status'); // Assume element exists const textArea = document.getElementById('my-textarea'); // Assume element exists textArea.addEventListener('input', () => { saveStatus.textContent = 'Changes detected, waiting to save...'; debouncedSave() .then(result => { // Check if still relevant (optional) saveStatus.textContent = `Saved successfully at ${new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}`; console.log('Save result:', result); }) .catch(err => { if (err.message !== 'Debounced function call was cancelled.') { console.error("Save Error:", err); saveStatus.textContent = `Save failed: ${err.message}`; } else { console.log("Save cancelled."); // Status remains 'waiting...' or might be updated by next input } }); });- The Debouncing and Throttling Explained article on the CSS-Tricks website
- The Underscore.js documentation on the debounce function
- The Lodash documentation on the debounce function
If you encounter any bugs while using Modulator, please report them to the GitHub issue tracker. When submitting a bug report, please include as much information as possible, such as:
- Version of Modulator used.
- Browser/Node.js environment and version.
- Steps to reproduce the bug.
- Expected behavior vs. actual behavior.
- Any relevant code snippets.