This is an example Lambda handler that you can use as a before message send hook endpoint. The handler will receive a message payload and checks if the message text matches any regex. If there is a match the message will be rewritten as an error message.
This handler also checks that the message includes a correct signature, the signature can only be created using the API secret.
You can configure several things to match your use-case but it is very trivial to perform different logic by making minimal changes to the code (see cmd/lambda/main.go)
Make sure you have the latest version of Go installed, once you have that you only need to run make and you will get a ready to use lambda function (function.zip).
Note: make will fail if you config.yaml file does not exist.
You also need to have awscli installed on your laptop.
Before using the lambda you need to create your own config YML file. This configuration file contains the list of regexes your hook should match as well as the error message to use for the rewritten message.
cp example.config.yaml config.yamlThe configuration file is embedded in the final lambda function. Make sure to run make every time you change the configuration file.
Make sure you use the correct API Keys and to enable signature checking.
stream_api_key: api-key stream_api_secret: api-secret check_signature: trueThe list of patterns to match messages can be provided in two ways: via the configuration file or by storing it on S3.
When the S3 configuration is provided, the lambda function will read the S3 bucket and load all patterns in the file
s3_bucket: my-bucket-name s3_file: path/to/file s3_region: aws-region-nameIf you decide to use this approach, make sure that the Lambda function role can perform GetObject to your S3 bucket.
If S3 is not used, the lambda will load the list of patterns from the YAML file itself
patterns: - "[a-zA-Z0-9.!#$%&'*+/=?^_`{|}~-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9](?:[a-zA-Z0-9-]{0,61}[a-zA-Z0-9])?(?:\\.[a-zA-Z0-9](?:[a-zA-Z0-9-]{0,61}[a-zA-Z0-9])?)*" # emailsLet's asssume you want to call this function message-hook.
aws lambda create-function --function-name message-hook --runtime go1.x \ --zip-file fileb://function.zip --handler main \ --role arn:aws:iam::1234567:role/lambda-exec The lambda function itself does not work if invoked using the Lambda API and it is meant to be used as the handler for an API gateway route. Using something like aws lambda invoke will return an error since the payload is not the same as what API Gateway fordwards.
aws lambda update-function-code --function-name message-hook --zip-file fileb://function.zip Testing Lambdas can be annoying especially if you do not have a working setup for serverless. You can use the check command to do some basic checks.
echo '{"message": {"text": "name@example.com"}}' | go run cmd/check/main.go Once you have the lambda function up and running, make sure to create an API Gateway and to connect the lambda with a route.
- Go to API Gateway https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway
- Create a new API
- Select the HTTP API type
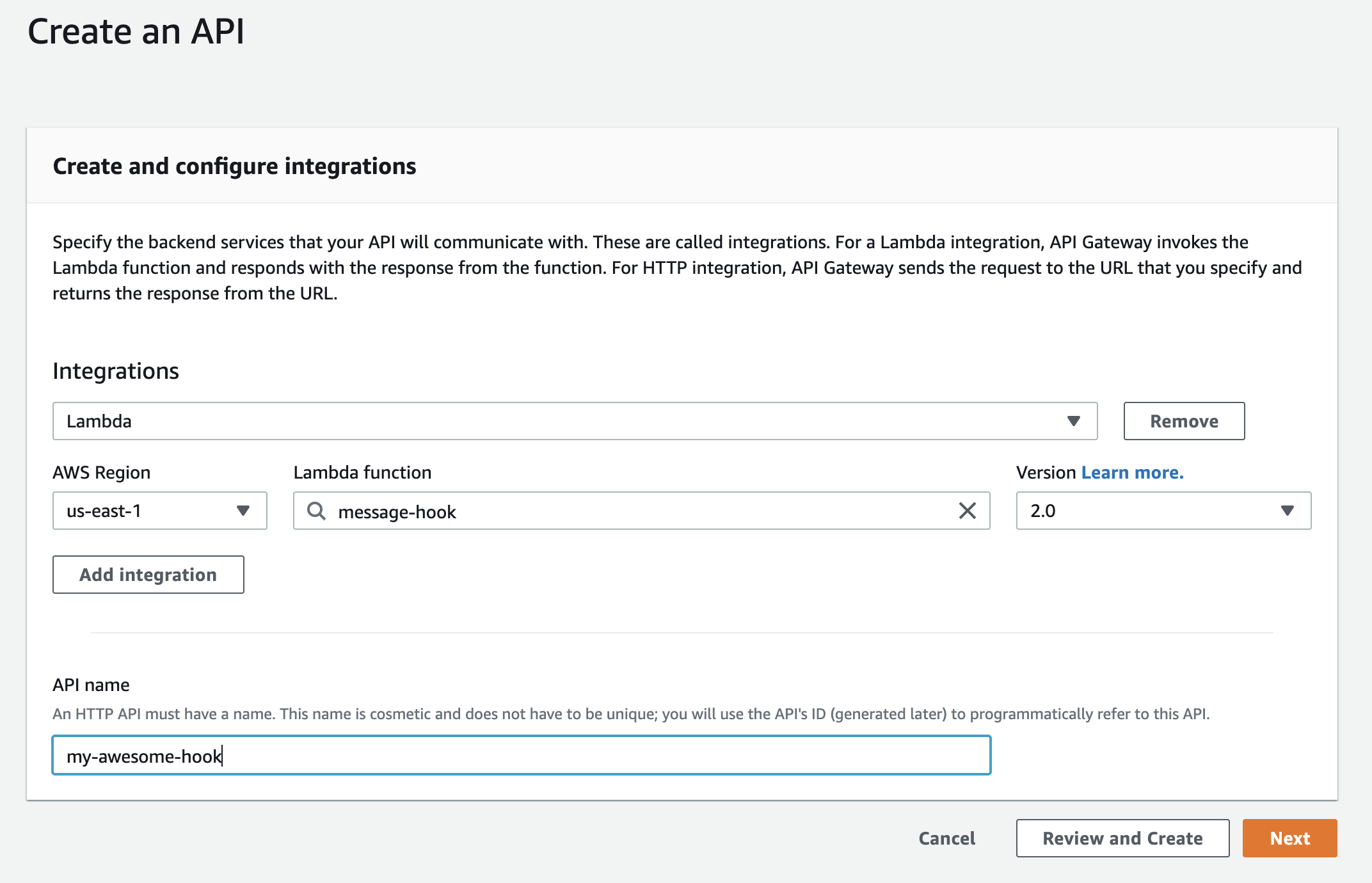
- Choose Lambda from the list of integrations and select the Lambda function created earlier
- Make sure to select version 2.0 or the Lambda will not work correctly
- Create a new route that sends POST requests to the Lambda function
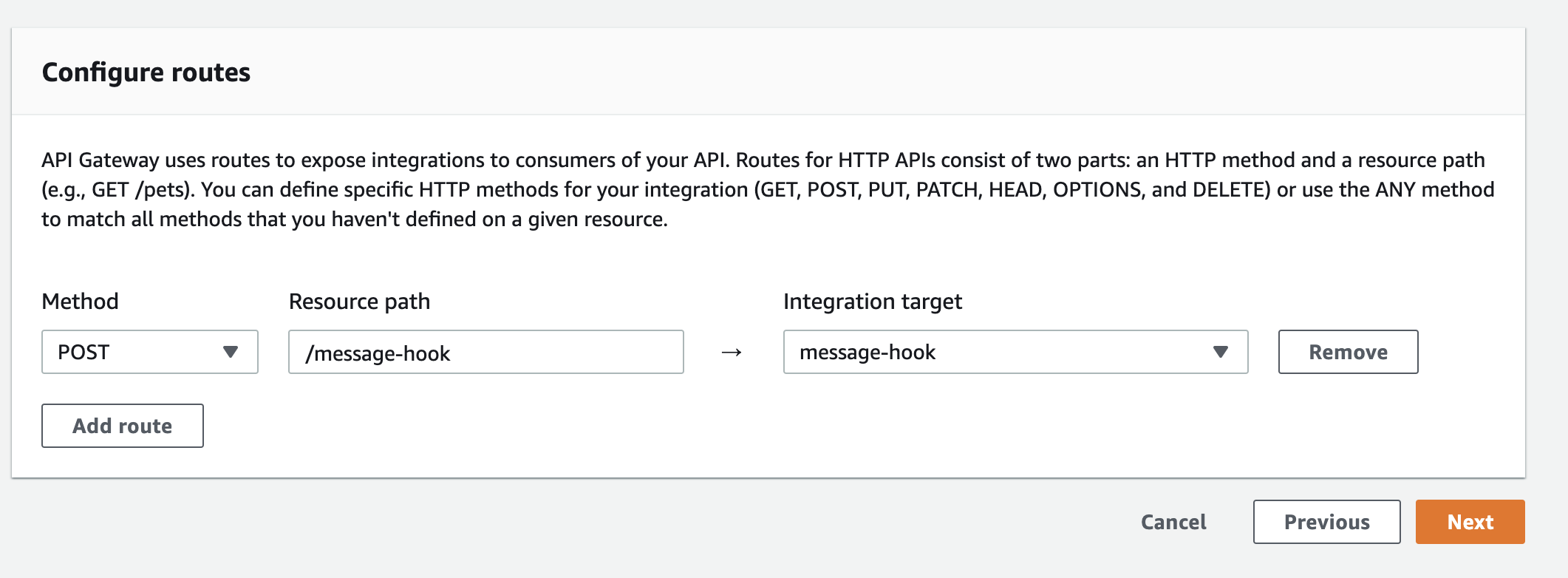
- Continue with the process until the API is created
- The URL of the API gateway will be visible at the end
- Make sure to build the full URL (Invoke URL + Route path) ie.
https://fuhlrrq4h0.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/message-hook
async function main() { const client = new StreamChat(apiKey, apiSecret); await client.updateAppSettings({ before_message_send_hook_url: 'http://127.0.0.1:4323', }); }