Page
Validating your mirrored operators
.png)
After applying the cluster resources for Red Hat Operators, it is essential to validate the availability of the CatalogSource, IDMS, and ITMS components.
Prerequisites:
- Your operators to mirror from the previous lesson.
In this lesson, you will:
- Validate your mirrored operators and upgrades for Redis.
Validate your resources
Validating operator resources can be done by executing the following commands to ensure that the resources are correctly deployed and accessible within the cluster.
[root@registry cluster-resources]# oc get catalogsources -A NAMESPACE NAME DISPLAY TYPE PUBLISHER AGE openshift-marketplace cs-redhat-operator-index-v4-17 grpc 47s [root@registry cluster-resources]# [root@registry cluster-resources]# oc get imagedigestmirrorset NAME AGE idms-operator-0 6d1h [root@registry cluster-resources]# oc get imagetagmirrorset NAME AGE itms-generic-0 21h [root@registry cluster-resources]#Log in to the Red Hat OpenShift console and navigate to the OperatorHub tab to view the operators that have been successfully mirrored to the cluster. (Figure 1)
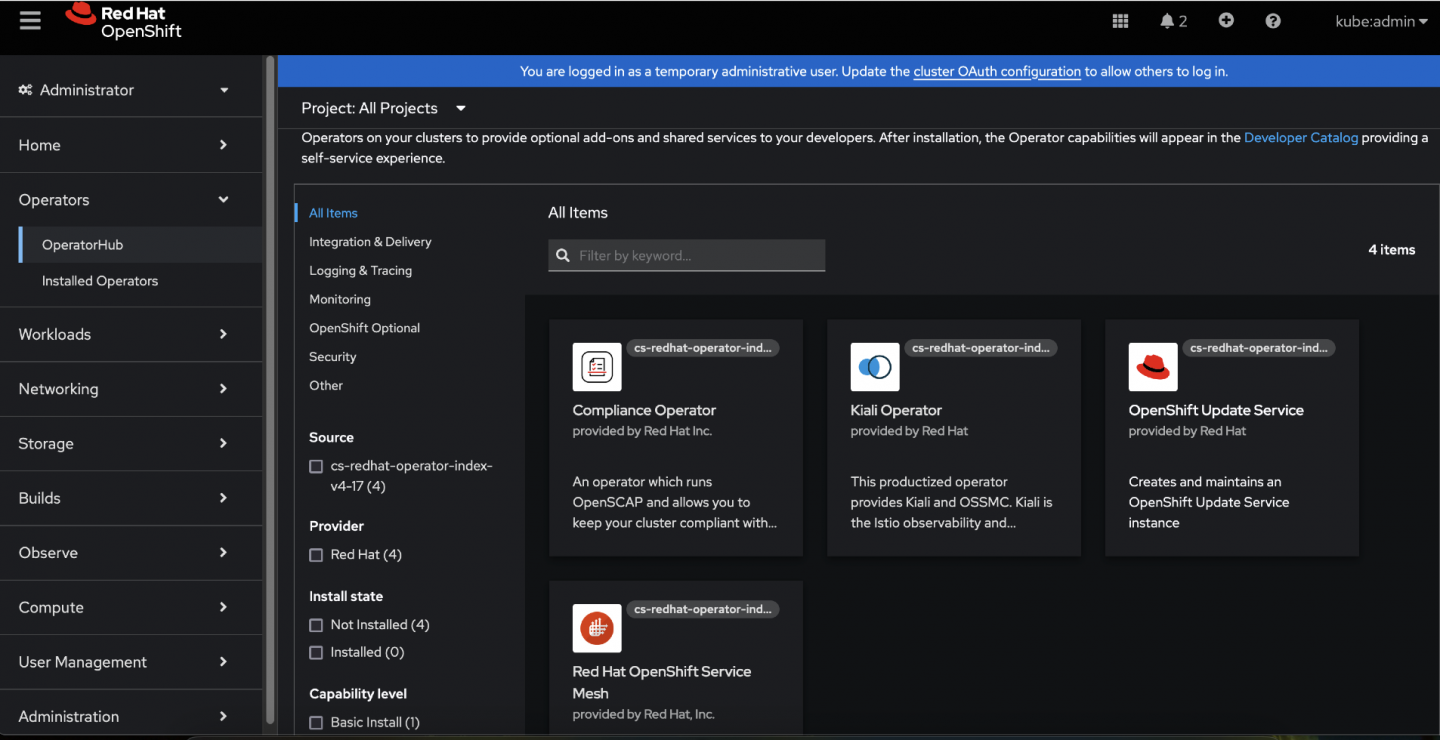
Figure 1: A screenshot of the OpenShift console showing all operators that were mirrored to the cluster. Next, navigate to the directory containing the Certified Operators cluster resources, as outlined below, and repeat the same validation steps performed for the Red Hat Operators to ensure proper mirroring and availability.
[root@registry cluster-resources]# ls cc-certified-operator-index-v4-17.yaml cs-certified-operator-index-v4-17.yaml idms-oc-mirror.yaml itms-oc-mirror.yaml [root@registry cluster-resources]# oc apply -f . catalogsource.operators.coreos.com/cs-certified-operator-index-v4-17 created imagedigestmirrorset.config.openshift.io/idms-operator-0 configured imagetagmirrorset.config.openshift.io/itms-generic-0 configured [root@registry cluster-resources]#[root@registry cluster-resources]# oc get catalogsources NAME DISPLAY TYPE PUBLISHER AGE cs-certified-operator-index-v4-17 grpc 48s cs-redhat-operator-index-v4-17 grpc 83m [root@registry cluster-resources]#Log in to the OpenShift console and navigate to the OperatorHub tab to view both the Certified Operators and Red Hat Operators that have been successfully mirrored to the cluster. (Figure 2)
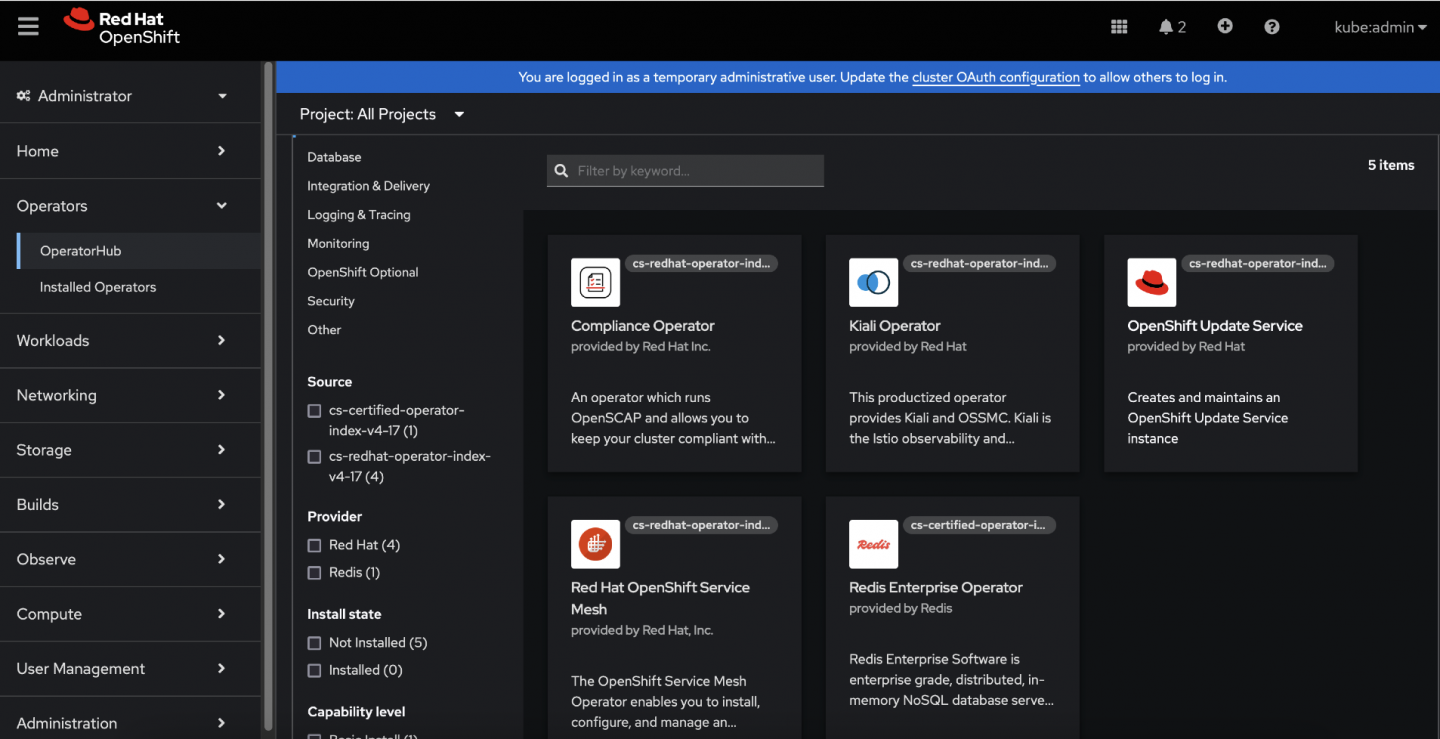
Figure 2: A screenshot of the OperatorHub tab showing Certified and Red Hat Operators that have been successfully mirrored to the disconnected cluster. . - List Available PackageManifests: Use the command
oc get packagemanifestto list all availablePackageManifestsin the cluster. - Describe Specific PackageManifest: For operators like Redis, describe the specific
PackageManifestusing the command:oc get packagemanifest redis-enterprise-operator-cert -oyaml Review the Status for Mirrored Versions: In the output YAML, locate the
entriessection under status. This section will list the versions of the operator that have been mirrored, based on the related configuration. With these steps, this will verify that all required versions of the operators have been successfully mirrored.[root@registry IB]# oc get packagemanifest NAME CATALOG AGE kiali-ossm 90m servicemeshoperator 90m redis-enterprise-operator-cert 7m39s cincinnati-operator 90m compliance-operator 90m [root@registry IB]# oc get packagemanifest redis-enterprise-operator-cert -oyaml apiVersion: packages.operators.coreos.com/v1 kind: PackageManifest metadata: creationTimestamp: "2025-05-06T09:11:42Z" labels: catalog: cs-certified-operator-index-v4-17 catalog-namespace: openshift-marketplace operatorframework.io/arch.amd64: supported operatorframework.io/os.linux: supported provider: Redis provider-url: "" name: redis-enterprise-operator-cert namespace: openshift-marketplace spec: {}status: [......] entries: - name: redis-enterprise-operator.v7.22.0-7.0 version: 7.22.0-7.0 - name: redis-enterprise-operator.v7.8.6-1.0 version: 7.8.6-1.0 - name: redis-enterprise-operator.v7.8.4-9.0 version: 7.8.4-9.0 name: production defaultChannel: production packageName: redis-enterprise-operator-cert provider: name: RedisTo demonstrate the operator upgrade process, the Redis Operator version 7.8.4.9 has been installed (Figure 3).
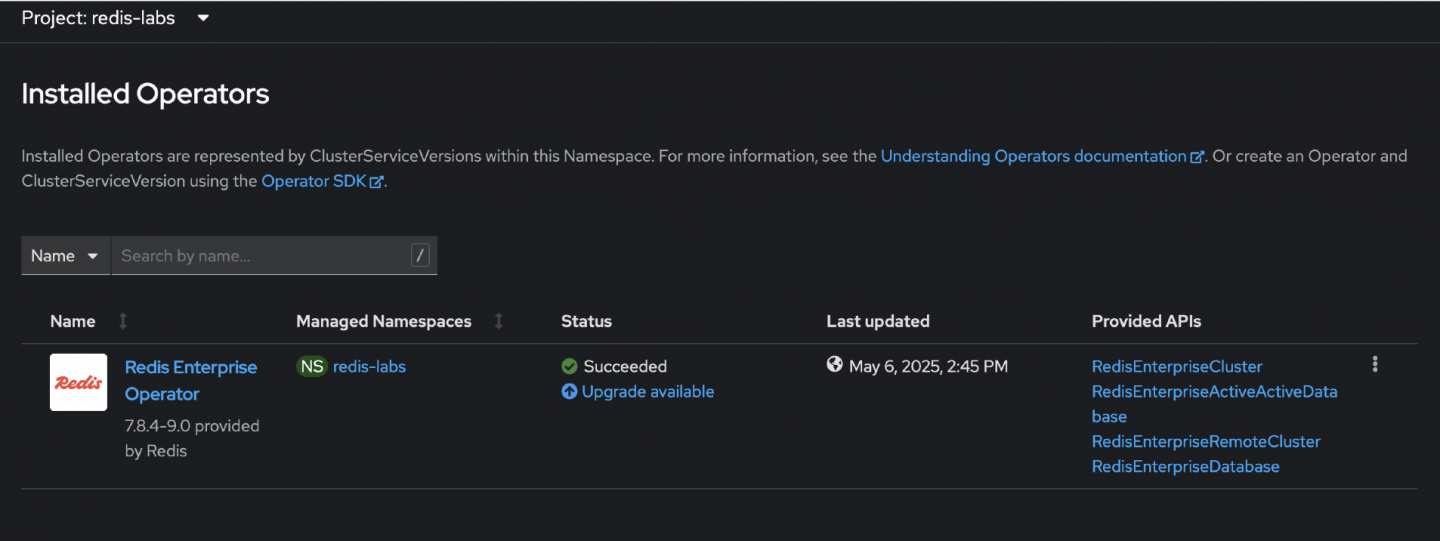
Figure 3: The OperatorHub tab showing Redis Enterprise Operator installed.
To view the available versions of the Redis Operator in the production channel, navigate to the OperatorHub tab in the OpenShift console. By default, selecting Upgrade Available will initiate an upgrade to the latest operator version in the channel, as the subscription is configured to track the latest release, and the Install Plan is automatically generated for that version.
Note
A RFE has already been submitted to address this limitation and provide greater control over operator version upgrades.
If you wish to upgrade to a specific version within a particular channel, please follow these instructions. This workaround focuses on the Redis Operator, with the objective of upgrading it to a specific version within a designated channel.
For illustration, this scenario uses version
7.8.6-1.1which is not the latest version. The latest available version in the production channel is7.22.0-7.0.[root@registry IB]# oc mirror list operators --catalog=registry.redhat.io/redhat/certified-operator-index:v4.17 --package=redis-enterprise-operator-cert --channel production VERSIONS 7.22.0-7.0 7.8.4-9.0 7.8.6-1.0 7.8.6-1.1 [root@registry IB]#Create the
ImageSetConfigurationfile to define the specific image set configurations for the cluster.[root@registry IB]# cat ce_op_ibimagest-config.yaml kind: ImageSetConfiguration apiVersion: mirror.openshift.io/v2alpha1 mirror: operators: - catalog: registry.redhat.io/redhat/certified-operator-index:v4.17 packages: - name: redis-enterprise-operator-cert channels: - name: production minVersion: '7.8.4-9.0' maxVersion: '7.8.6-1.1' additionalImages: - name: registry.redhat.io/ubi9/ubi:latest - name: registry.redhat.io/rhel9/support-tools:latest helm: {} [root@registry IB]#Mirror the operators according to the most recent
ImageSetConfigurationfile. This ensures that the correct versions of the operators, as specified in the configuration file, are mirrored into the target registry.[root@registry IB]# oc-mirror --v2 -c ce_op_ibimagest-config.yaml --workspace file:///registry/ocp417/certified-operators/ docker://registry.shemadhr.tamlab.rdu2.redhat.com/quayadmin/ocp417/certified-operators --dest-tls-verify=false 2025/05/06 14:55:19 [INFO] : 👋 Hello, welcome to oc-mirror 2025/05/06 14:55:19 [INFO] : ⚙️ setting up the environment for you... 2025/05/06 14:55:19 [INFO] : 🔀 workflow mode: mirrorToMirror 2025/05/06 14:55:19 [INFO] : 🕵 going to discover the necessary images... 2025/05/06 14:55:19 [INFO] : 🔍 collecting release images... ✓ (10s) redis-enterprise-operator-bundle@sha256:0801e696067de948c1ea5d01c01592f8123de2a5256000ccd1acc66efc2a13e9 ➡️ registry.shemadhr.t2025/05/06 14:55:19 [INFO] : 🔍 collecting operator images... ✓ (32s) Collecting catalog registry.redhat.io/redhat/certified-operator-index:v4.17 2025/05/06 14:55:51 [INFO] : 🔍 collecting additional images... 2025/05/06 14:55:51 [INFO] : 🔍 collecting helm images... 2025/05/06 14:55:51 [INFO] : 🔂 rebuilding catalogs ✓ (1s) Rebuilding catalog docker://registry.redhat.io/redhat/certified-operator-index:v4.17 2025/05/06 14:55:53 [INFO] : 🚀 Start copying the images... 2025/05/06 14:55:53 [INFO] : 📌 images to copy 19 ✓ (17s) call-home-client@sha256:4705d40e212b8921b5613f5e054bd51a1f988cab703789a4d18d15793602eb65 ➡️ registry.shemadhr.tamlab.rdu2.redhat.com/quayadmin/ocp417/certified-operators/redislabs/ ✓ (17s) redis-enterprise-operator@sha256:66ec124da16cc9d0abd66687e088be0b358e20cfd48f5774d34bf5874e6a4e65 ➡️ registry.shemadhr.tamlab.rdu2.redhat.com/quayadmin/ocp417/certified-operators/redislabs/ ✓ (15s) support-tools:latest ➡️ registry.shemadhr.tamlab.rdu2.redhat.com/quayadmin/ocp417/certified-operators/rhel9/ amlab.rdu2.redhat.com/quayadmin/ocp417/certified-operators/redislabs/ ✓ (31s) certified-operator-index:v4.17 ➡️ registry.shemadhr.tamlab.rdu2.redhat.com/quayadmin/ocp417/certified-operators/redhat/ 19 / 19 (1m1s) [=====================================================================================================================================================================================================================] 100 % ✓ (1m1s) redis-enterprise@sha256:21ac49d368ce4cd452f6a8439d0a63a948fb40a58f1e8a6a98584b6edb3f7301 ➡️ registry.shemadhr.tamlab.rdu2.redhat.com/quayadmin/ocp417/certified-operators/redislabs/ 2025/05/06 14:56:55 [INFO] : === Results === 2025/05/06 14:56:55 [INFO] : ✓ 17 / 17 operator images mirrored successfully 2025/05/06 14:56:55 [INFO] : ✓ 2 / 2 additional images mirrored successfully 2025/05/06 14:56:55 [INFO] : 📄 Generating IDMS file... 2025/05/06 14:56:55 [INFO] : /registry/ocp417/certified-operators/working-dir/cluster-resources/idms-oc-mirror.yaml file created 2025/05/06 14:56:55 [INFO] : 📄 Generating ITMS file... 2025/05/06 14:56:55 [INFO] : /registry/ocp417/certified-operators/working-dir/cluster-resources/itms-oc-mirror.yaml file created 2025/05/06 14:56:55 [INFO] : 📄 Generating CatalogSource file... 2025/05/06 14:56:55 [INFO] : /registry/ocp417/certified-operators/working-dir/cluster-resources/cs-certified-operator-index-v4-17.yaml file created 2025/05/06 14:56:55 [INFO] : 📄 Generating ClusterCatalog file... 2025/05/06 14:56:55 [INFO] : /registry/ocp417/certified-operators/working-dir/cluster-resources/cc-certified-operator-index-v4-17.yaml file created 2025/05/06 14:56:55 [INFO] : mirror time : 1m35.870240602s 2025/05/06 14:56:55 [INFO] : 👋 Goodbye, thank you for using oc-mirrorNavigate to the directory containing the Certified Operators cluster resources, as specified below, and apply the resources using the
oc applycommand.[root@registry cluster-resources]# ls cc-certified-operator-index-v4-17.yaml cs-certified-operator-index-v4-17.yaml idms-oc-mirror.yaml itms-oc-mirror.yaml [root@registry cluster-resources]# pwd /registry/ocp417/certified-operators/working-dir/cluster-resources [root@registry cluster-resources]# [root@registry cluster-resources]# oc apply -f . catalogsource.operators.coreos.com/cs-certified-operator-index-v4-17 unchanged imagedigestmirrorset.config.openshift.io/idms-operator-0 configured imagetagmirrorset.config.openshift.io/itms-generic-0 configured [root@registry cluster-resources]#To validate the available versions of an operator, describe the
PackageManifestassociated with the operator. Use the following command to describe thePackageManifest.[root@registry IB]# oc get packagemanifest NAME CATALOG AGE servicemeshoperator 101m redis-enterprise-operator-cert 19m cincinnati-operator 101m compliance-operator 101m kiali-ossm 101m [root@registry IB]# oc get packagemanifest redis-enterprise-operator-cert -oyaml apiVersion: packages.operators.coreos.com/v1 kind: PackageManifest metadata: creationTimestamp: "2025-05-06T09:11:42Z" labels: catalog: cs-certified-operator-index-v4-17 catalog-namespace: openshift-marketplace operatorframework.io/arch.amd64: supported operatorframework.io/os.linux: supported provider: Redis provider-url: "" name: redis-enterprise-operator-cert namespace: openshift-marketplace spec: {} status: [....] entries: - name: redis-enterprise-operator.v7.22.0-7.0 version: 7.22.0-7.0 - name: redis-enterprise-operator.v7.8.6-1.1 version: 7.8.6-1.1 - name: redis-enterprise-operator.v7.8.6-1.0 version: 7.8.6-1.0 - name: redis-enterprise-operator.v7.8.4-9.0 version: 7.8.4-9.0 name: production defaultChannel: production packageName: redis-enterprise-operator-cert provider: name: Redis
As noted earlier, the OpenShift Web Console does not provide a direct option to install or upgrade an operator to a specific version. However, this can be achieved through a CLI-based workaround. The process involves the following steps:
Back up existing resources
- Export the current
InstallPlan, Subscription, andClusterServiceVersion(CSV) associated with the operator usingoc get <resource> <resource-name> -o yaml > <resource>.yaml(Figure 4). -
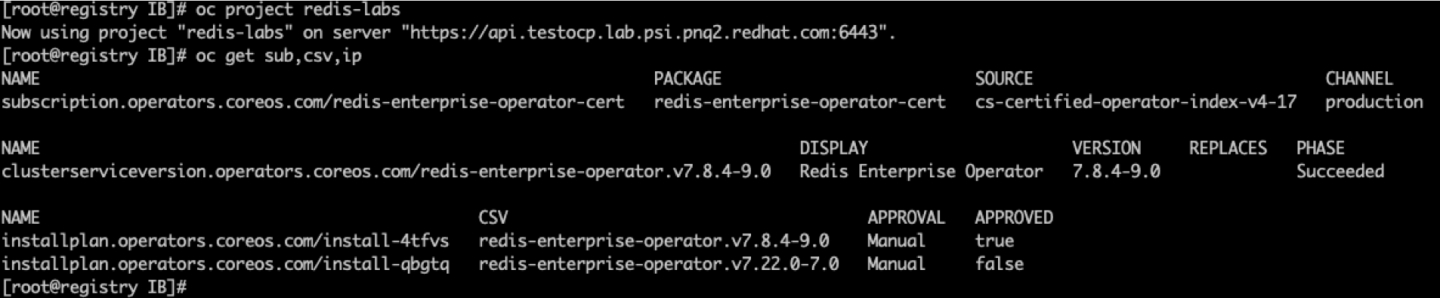
Figure 4: Screenshot of results from oc get command to backup existing resources.
[root@registry IB]# oc get subscription.operators.coreos.com/redis-enterprise-operator-cert -oyaml > redis-sub.yaml [root@registry IB]# oc get installplan.operators.coreos.com/install-4tfvs -oyaml > redis-ip.yaml [root@registry IB]# oc get clusterserviceversion.operators.coreos.com/redis-enterprise-operator.v7.8.4-9.0 -oyaml > redis-csv.yaml [root@registry IB]# cp redis-sub.yaml redis-sub_7.8.6.yaml- Export the current
Extract and edit the subscription
- Save a copy of the current Subscription resource and edit it to include the desired operator version by setting the starting CSV field. For example:
startingCSV: redis-enterprise-operator.v7.8.6-1.1.
[root@registry IB]# cat redis-sub_7.8.6.yaml apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 kind: Subscription metadata: labels: operators.coreos.com/redis-enterprise-operator-cert.redis-labs: "" name: redis-enterprise-operator-cert namespace: redis-labs spec: channel: production installPlanApproval: Manual name: redis-enterprise-operator-cert source: cs-certified-operator-index-v4-17 sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace startingCSV: redis-enterprise-operator.v7.8.6-1.1 [root@registry IB]#- Save a copy of the current Subscription resource and edit it to include the desired operator version by setting the starting CSV field. For example:
Delete the existing subscription and CSV
Remove the existing subscription and associated CSV to allow the updated configuration to take effect:
oc delete subscription <subscription-name> -n <namespace>oc delete csv <csv-name> -n <namespace>
[root@registry IB]# oc delete subscription.operators.coreos.com/redis-enterprise-operator-cert subscription.operators.coreos.com "redis-enterprise-operator-cert" deleted [root@registry IB]# oc delete clusterserviceversion.operators.coreos.com/redis-enterprise-operator.v7.8.4-9.0 clusterserviceversion.operators.coreos.com "redis-enterprise-operator.v7.8.4-9.0" deletedApply the updated subscription
- Apply the modified Subscription YAML to initiate the installation of the specific operator version using
oc apply -f <sub>.yaml.
[root@registry IB]# oc get sub,csv,ip NAME PACKAGE SOURCE CHANNEL subscription.operators.coreos.com/redis-enterprise-operator-cert redis-enterprise-operator-cert cs-certified-operator-index-v4-17 production NAME CSV APPROVAL APPROVED installplan.operators.coreos.com/install-5kwpd redis-enterprise-operator.v7.8.6-1.1 Manual false [root@registry IB]#- Apply the modified Subscription YAML to initiate the installation of the specific operator version using
Validate and approve the installPlan
Monitor the status of the new InstallPlan, and once it is generated, manually approve it to trigger the operator installation:
oc get installplan -n <namespace>oc patch installplan <installplan-name> --type merge -p '{"spec":{"approved":true}}'
[root@registry IB]# [root@registry IB]# oc patch installplan install-5kwpd --type merge -p '{"spec":{"approved":true}}' installplan.operators.coreos.com/install-5kwpd patched [root@registry IB]#Verify Installation
- Confirm the successful deployment of the operator through both the CLI and OpenShift Web Console (Figure 5).
[root@registry IB]# oc get sub,csv,ip NAME PACKAGE SOURCE CHANNEL subscription.operators.coreos.com/redis-enterprise-operator-cert redis-enterprise-operator-cert cs-certified-operator-index-v4-17 production NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE clusterserviceversion.operators.coreos.com/redis-enterprise-operator.v7.8.6-1.1 Redis Enterprise Operator 7.8.6-1.1 Succeeded NAME CSV APPROVAL APPROVED installplan.operators.coreos.com/install-5kwpd redis-enterprise-operator.v7.8.6-1.1 Manual true installplan.operators.coreos.com/install-jn2st redis-enterprise-operator.v7.22.0-7.0 Manual false [root@registry IB]#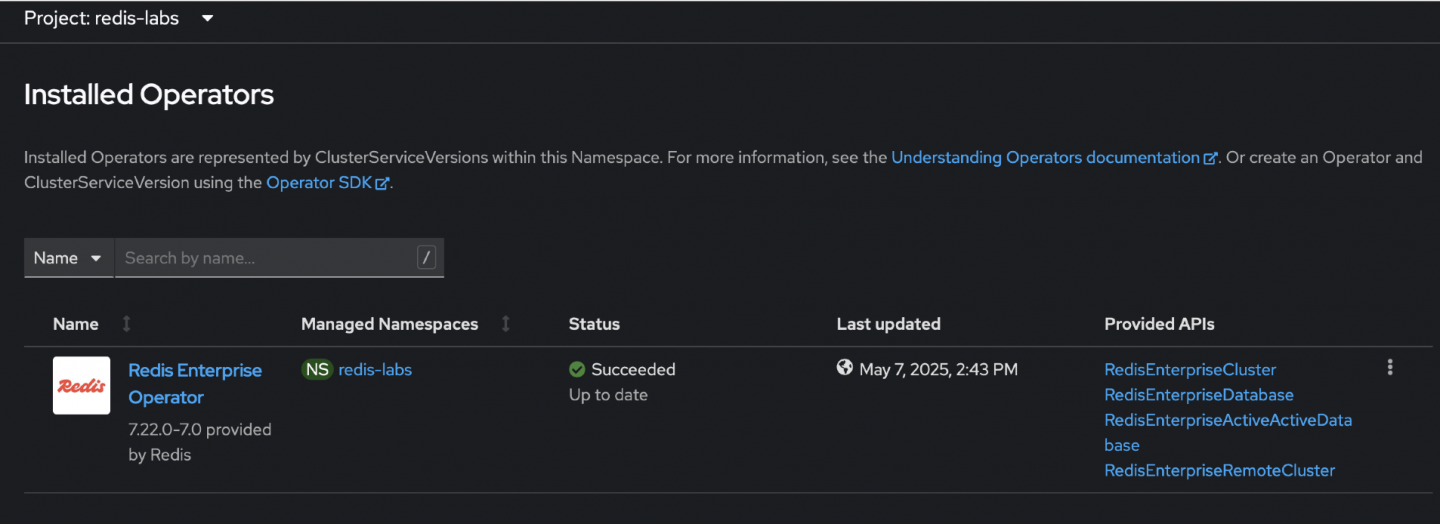
Figure 5: Screenshot of the Installed Operators tab within OpenShift, reflecting that the Redis Operator has a status of “Succeeded” from the latest upgrade. As demonstrated, the operator was successfully upgraded to the desired version within a specific channel (Figure 5). The next step involves installing the latest available version of the operator in the same channel.
To proceed, click on the Upgrade Available button in the OpenShift Web Console (Figure 6) then review the associated Install Plan to ensure the correct version and components are listed (Figure 7).
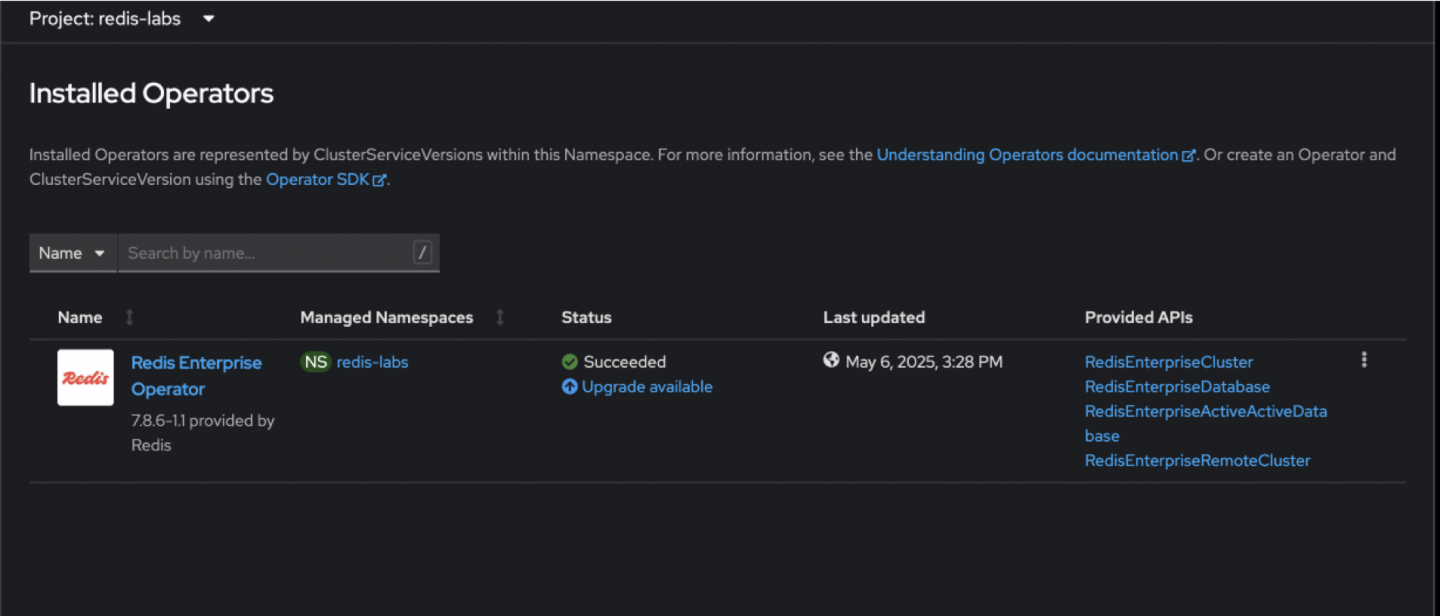
Figure 6: The Installed Operators page within the OpenShift console showing an upgrade available button under the Status column. 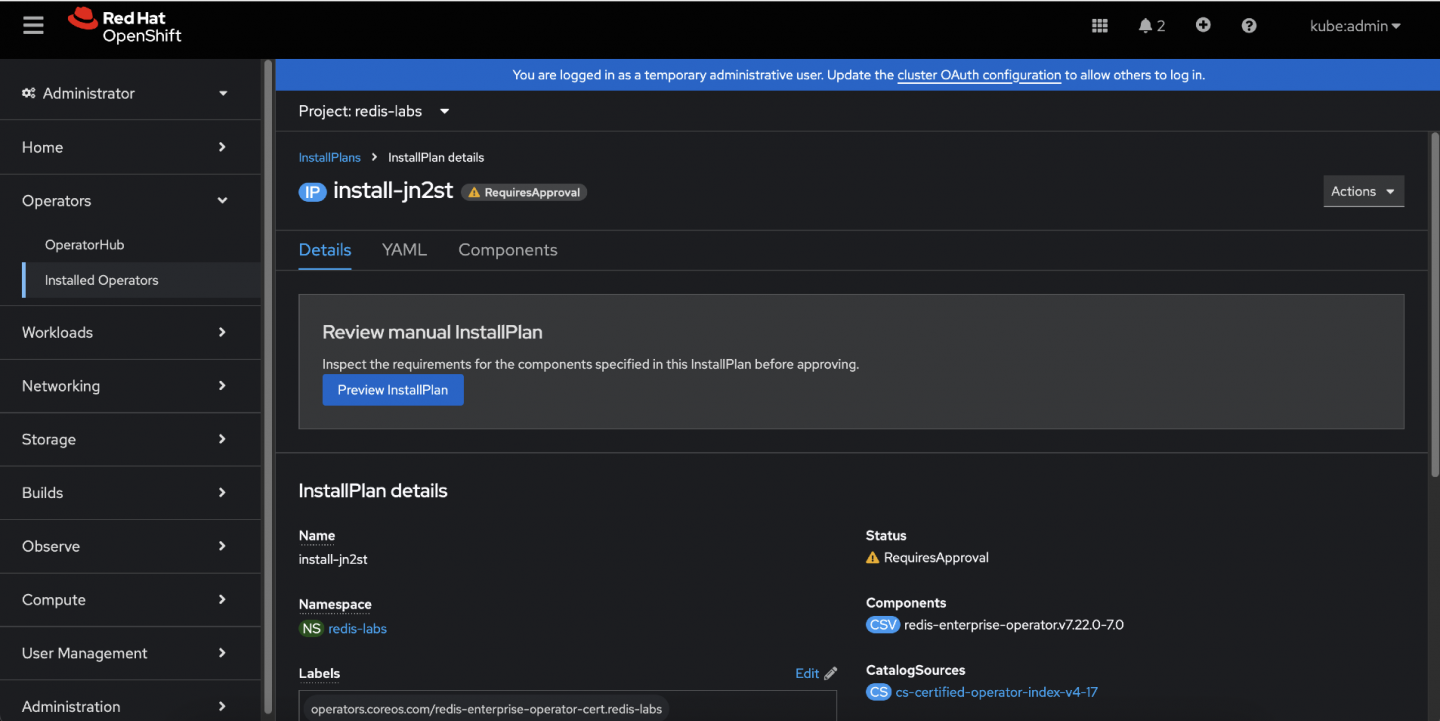
Figure 7: The InstallPlan page details within the OpenShift console, providing an option to review the details before the upgrade. Once verified, click Approve to allow the OLM to initiate the installation process. (Figure 8)
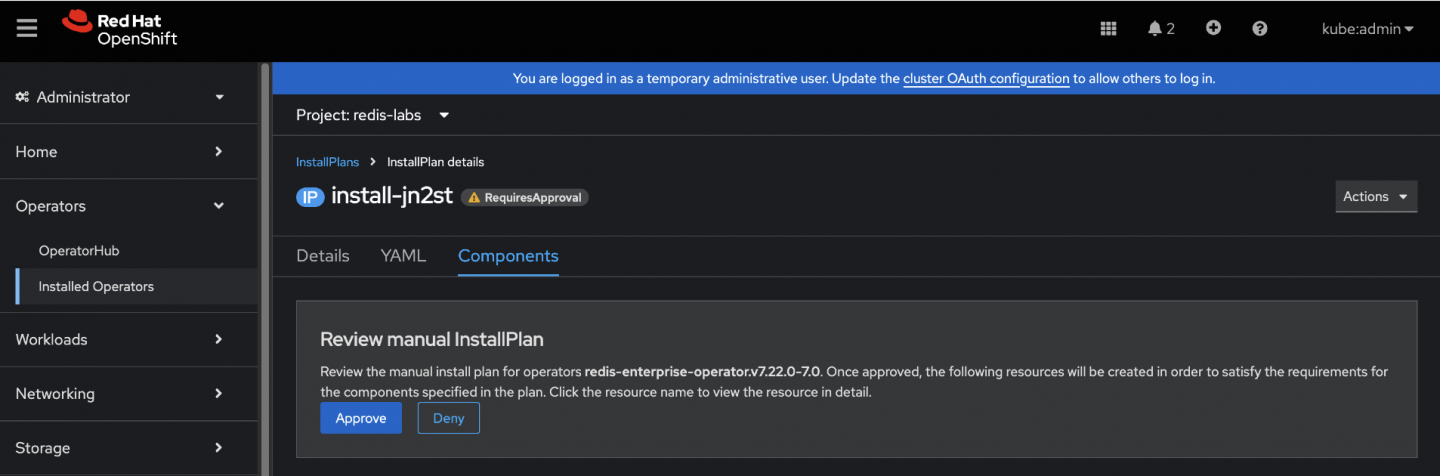
Figure 8: The InstallPlan page details within the OpenShift console, showing an Approve button to allow the installation to proceed. After the Install Plan completes, validate the operator installation status using both the OpenShift Web Console to ensure successful deployment (Figures 9-11).
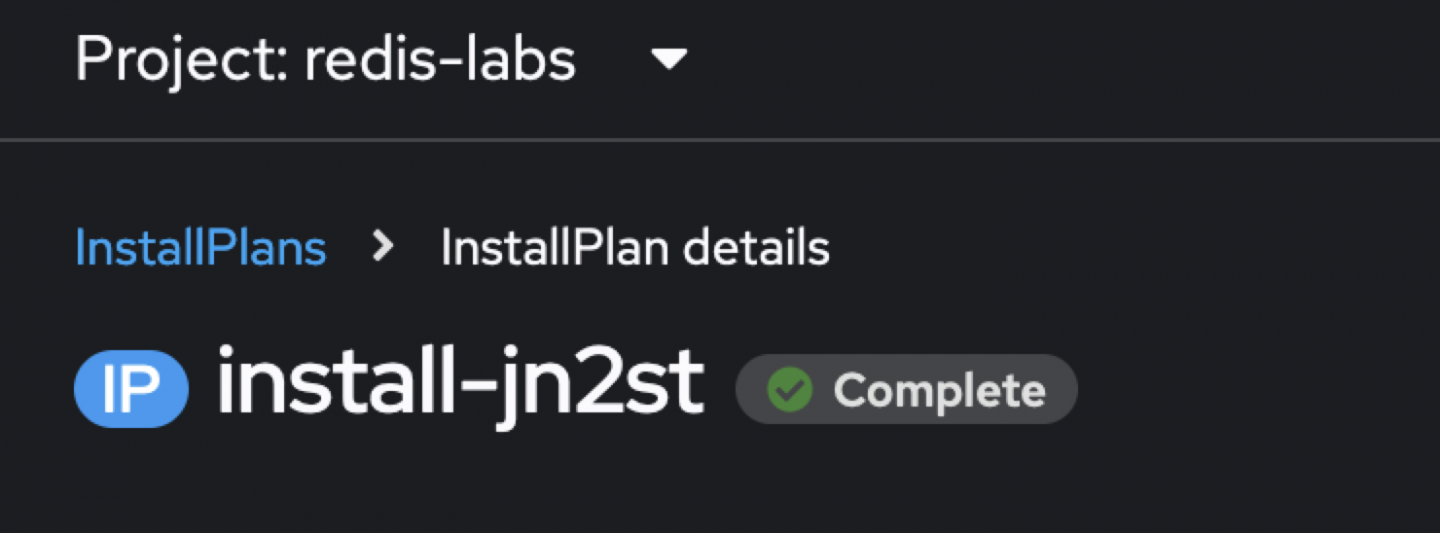
Figure 9: The correct InstallPlan has been installed. 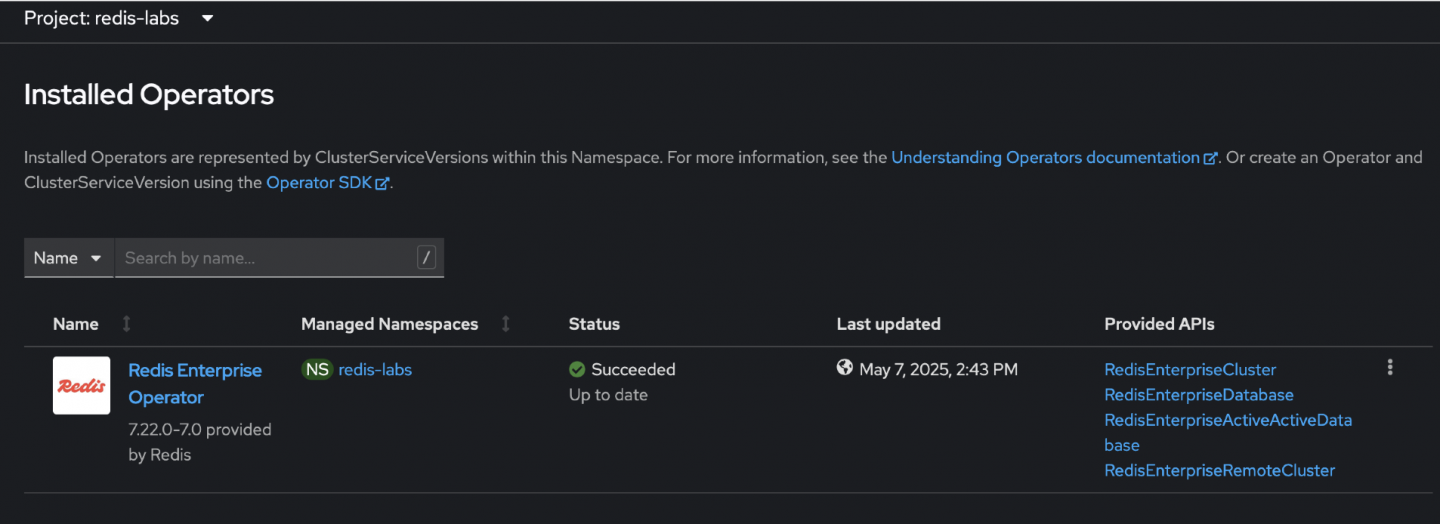
Figure 9: The Installed Operators page reflecting the successful update deployed under the Status and Last updated columns. 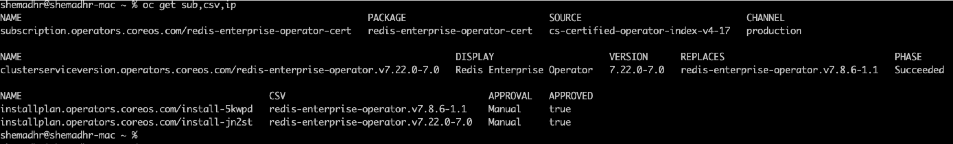
Figure 10: Console showing the results of the oc get command and displaying the successfully installed operators. Figure 11: Console showing the results of the oc get command and displaying the successfully installed operators.
Best practices
- Disable the auto update of operator versions to avoid unexpected updates.
- Clean up unused or old images to save storage space.
- Monitor the local registry’s performance and health.
Summary
Congratulations. You have successfully implemented an oc-mirror! Now your air-gapped environment can operate with minimal internet connectivity.
Ready to learn more about OpenShift? Check out these Red Hat OpenShift learning paths:
