By Braulio Maldonado Casilla & Sergio Daniel Mogollon Caceres
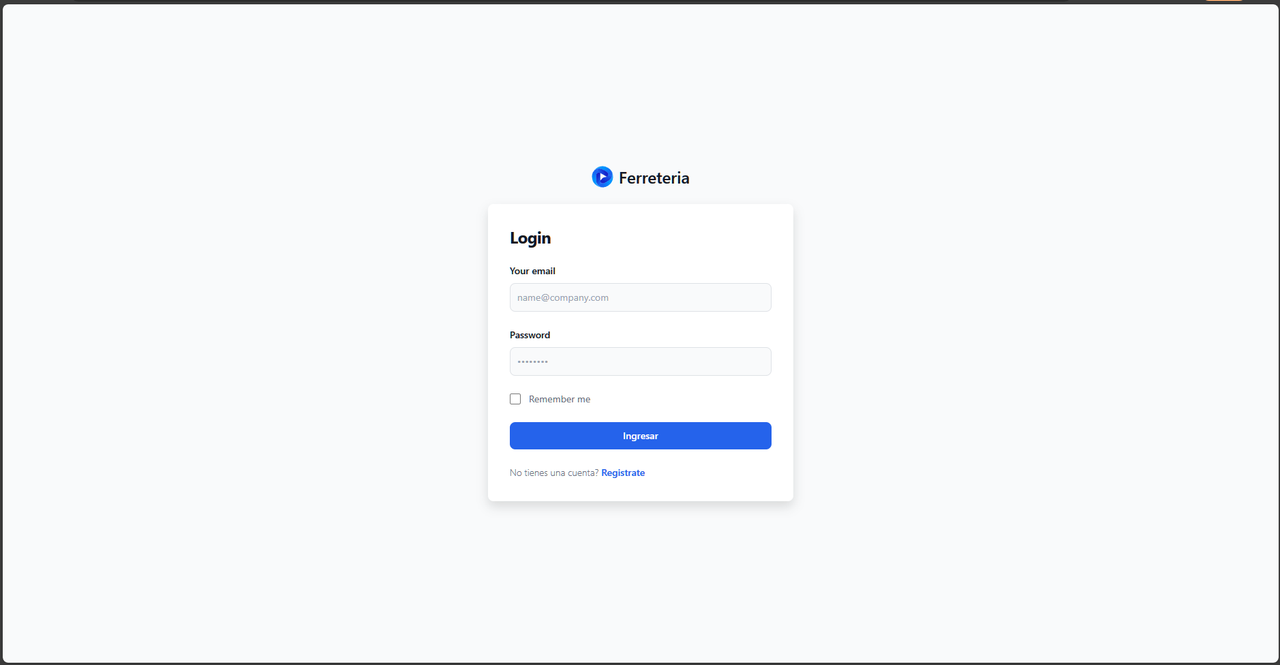
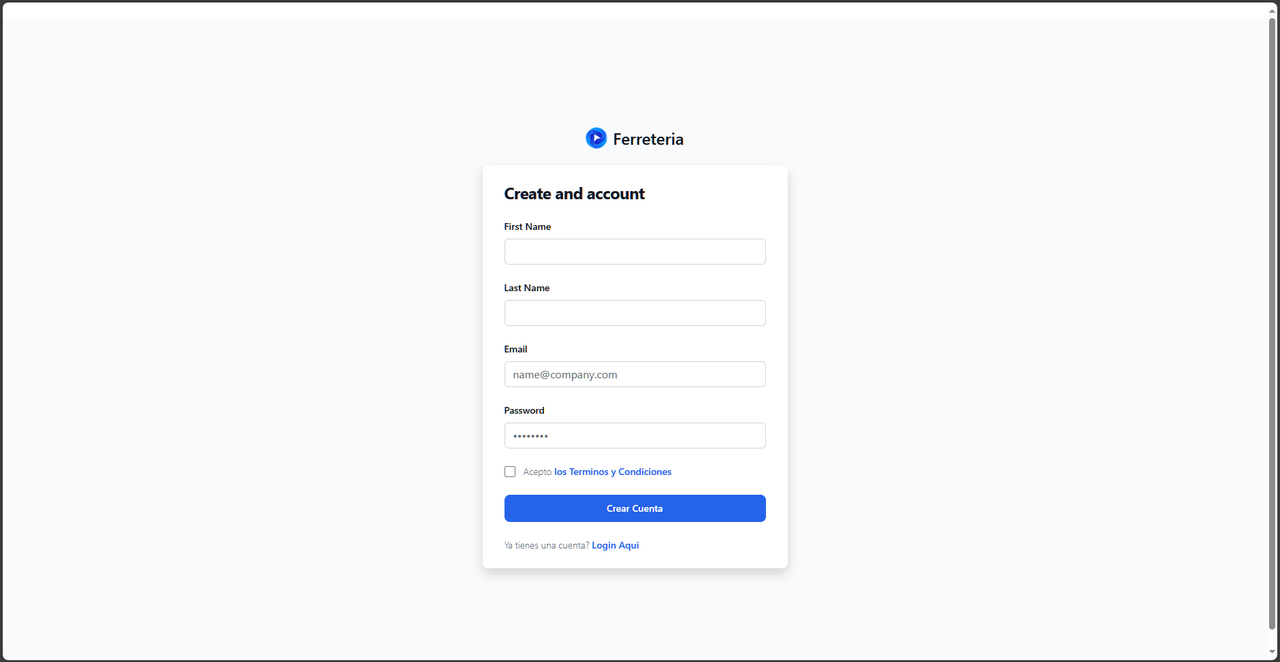
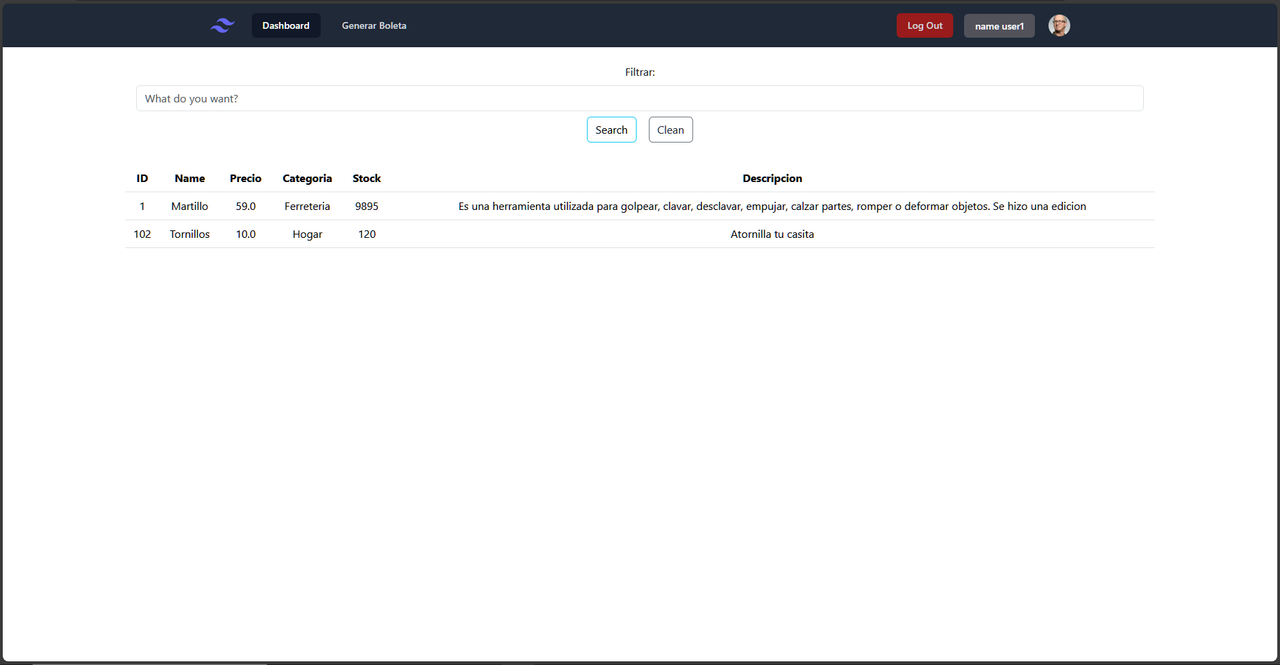
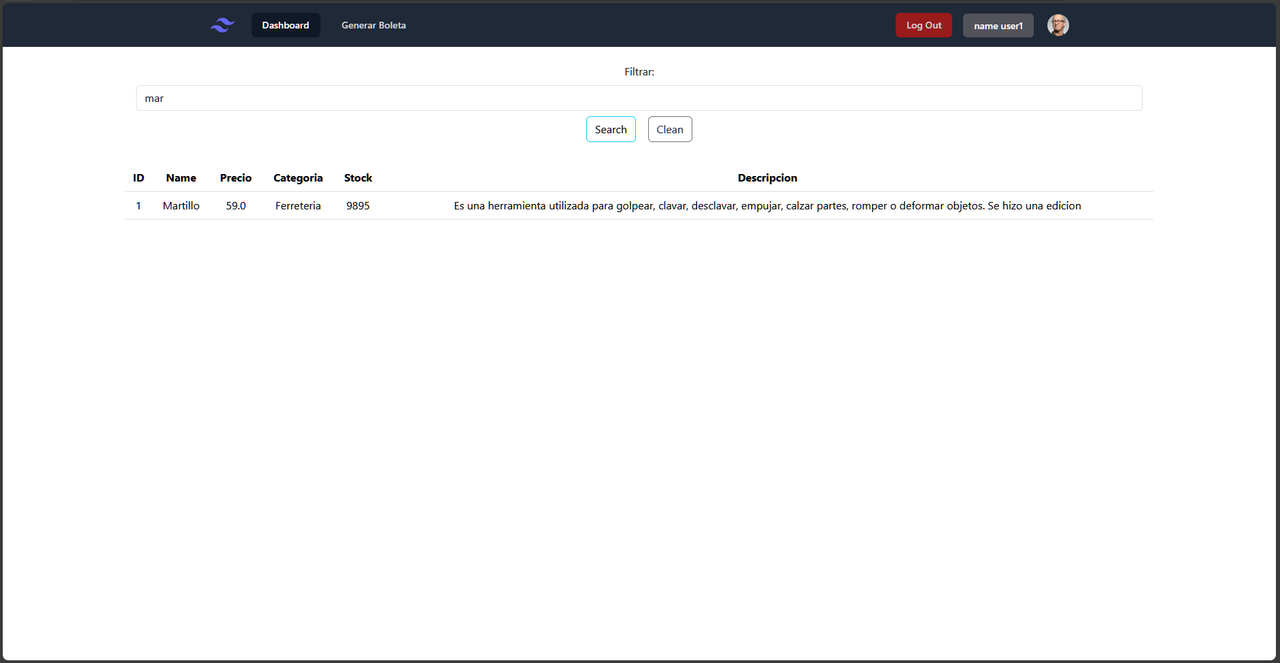
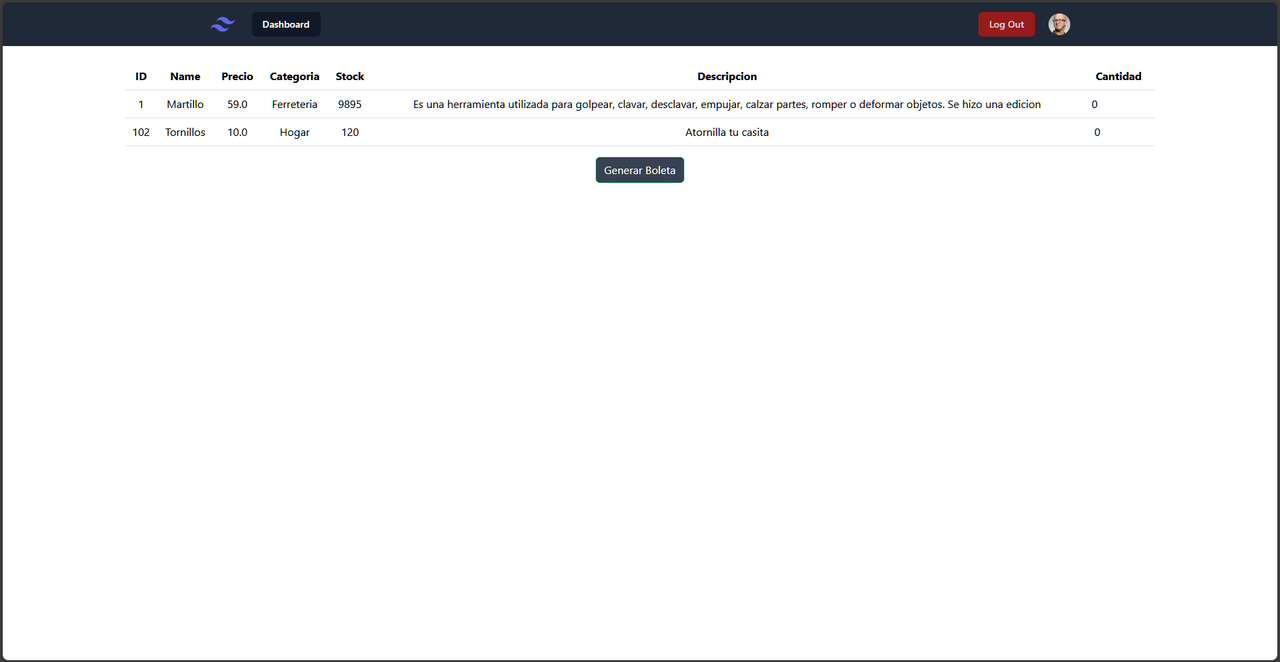
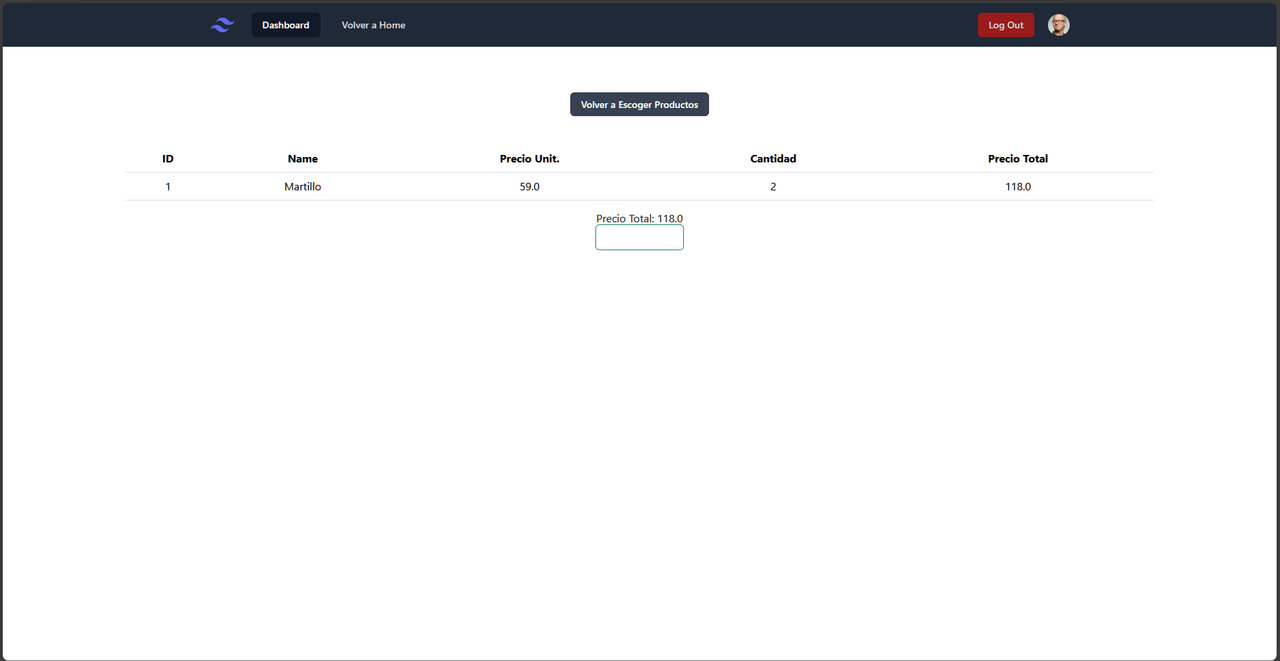
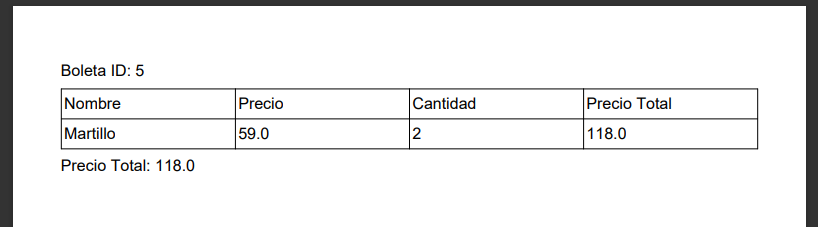
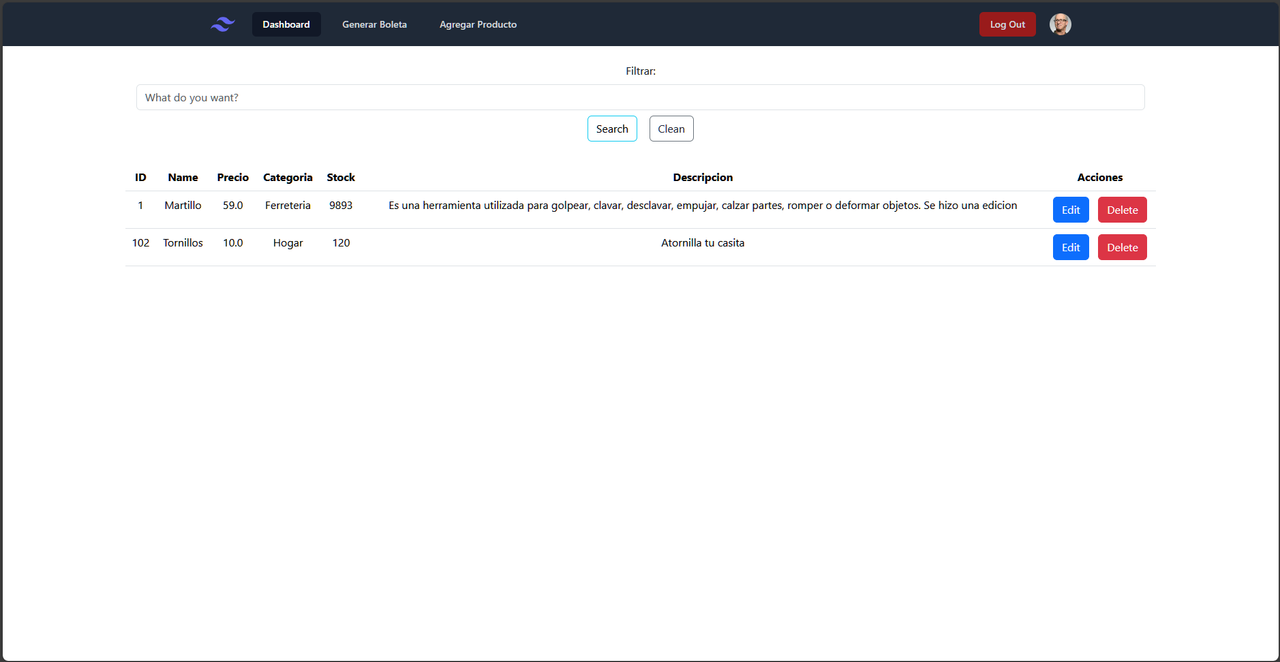
The project simulates the process of generating invoices for a hardware store. When users log in (or create an account), they are assigned different roles according to their position in the company. Standard employees can generate invoices by selecting products and their respective quantities, which culminates in the automatic creation of a PDF file ready for printing.
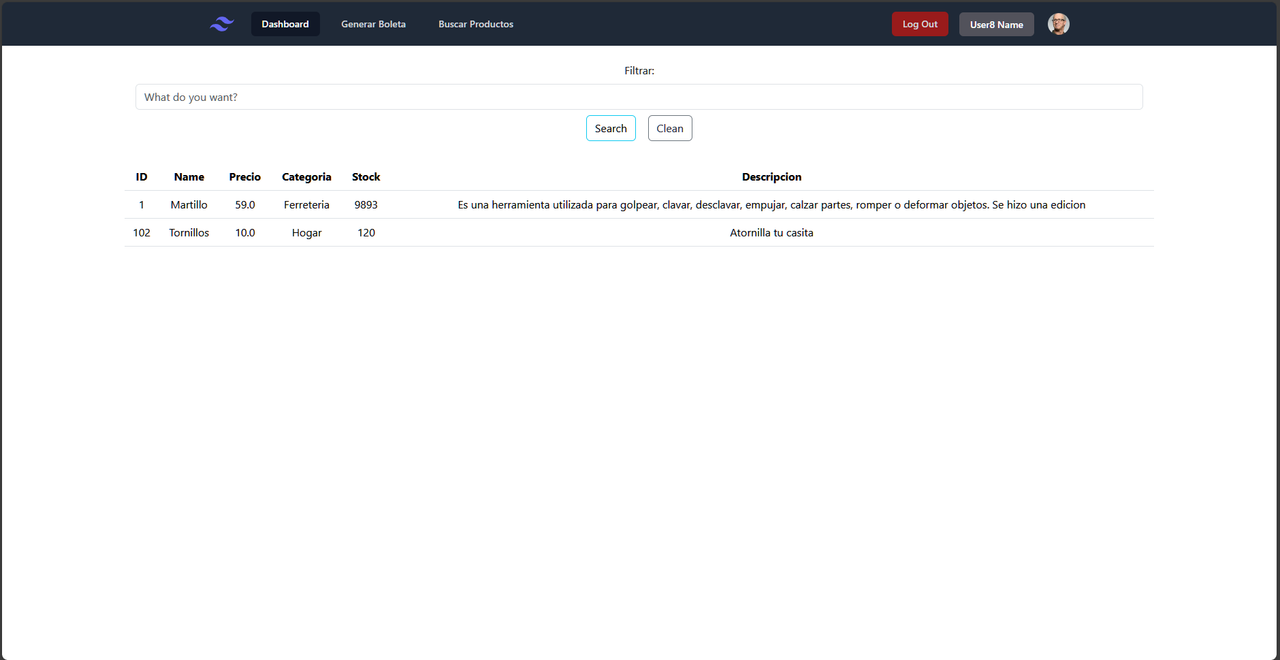
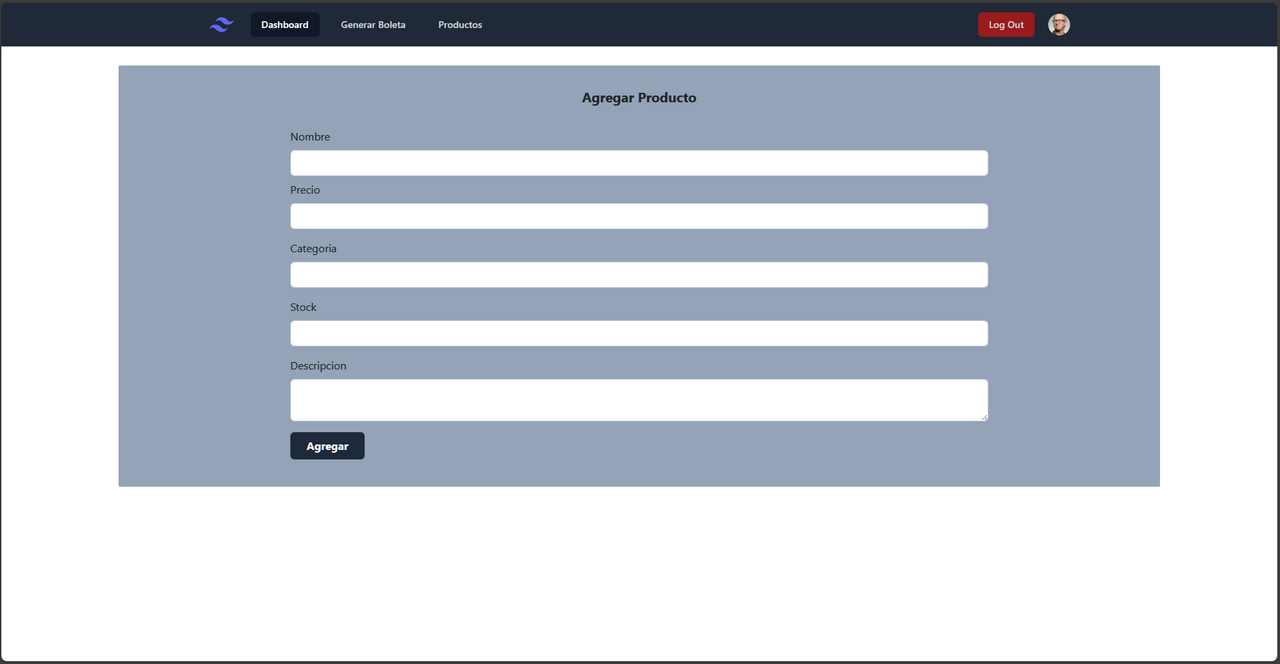
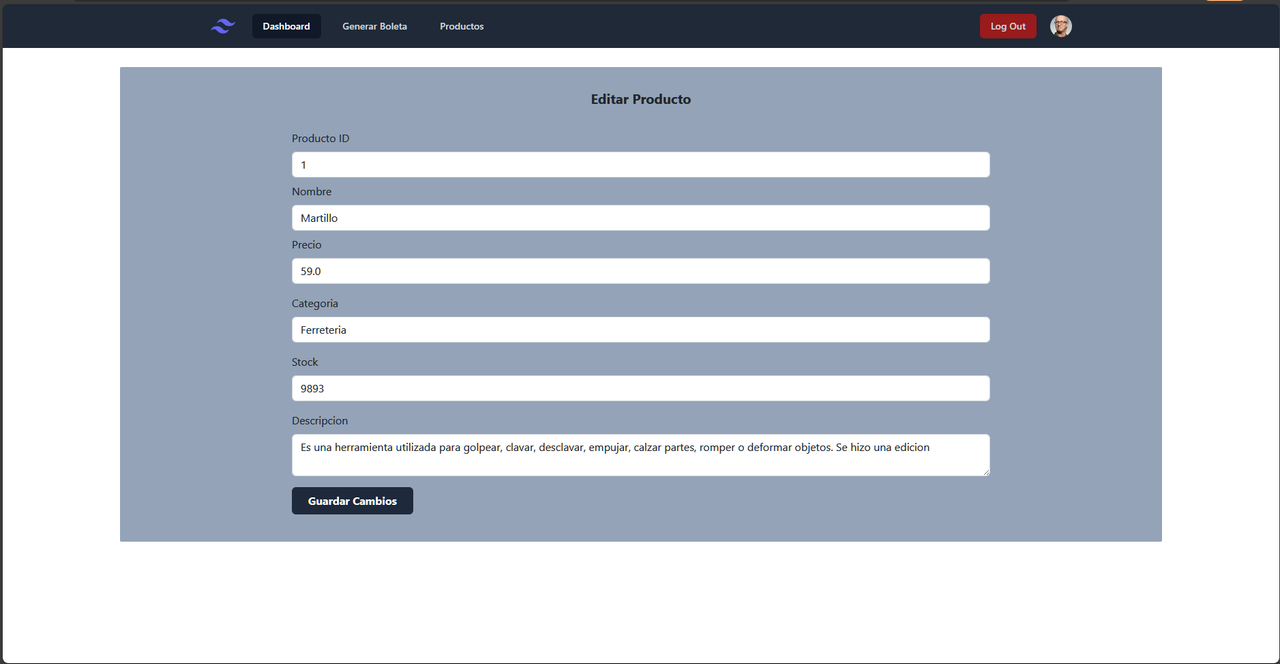
On the other hand, users with the ADMIN role have additional privileges. They have access to the complete management of product data, which includes Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) operations, allowing them to edit, add, and delete products from the hardware store's database.
This system offers a comprehensive solution that streamlines the generation of invoices for employees and facilitates the efficient management of products for administrators, thus optimizing the hardware store's daily operations.
For standard user access:
- Email: user@gmail.com
- Password: user
For administrative access:
- Email: example@gmail.com
- Password: admin
To run the project locally, you will need to have the following installed:
- Java Development Kit (JDK) - Version 17.
- Maven - Java project management tool.
The project makes use of the following tools and libraries:
- Spring Boot 3.2.0
- Thymeleaf
- Spring Boot Starter Data JPA
- Spring Boot Starter Security
- Spring Boot Starter Web
- iText 7 Core
- MySQL Connector/J
- Lombok
- Spring Boot Starter Validation (Hibernate)
In the application.yml file, you will find the database connection configuration. You can modify the following fields according to your credentials and specific database configuration:
spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://MYSQLHOST:MYSQLPORT/MYSQLDATABASE username: MYSQLUSER password: MYSQLPASSWORDDetailed description of the main functionalities of the project, including how to access them and their utility.
Thymeleaf is used in HTML files for data integration in views:
File: login.html
<!-- Link to the Thymeleaf library --> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="https://www.thymeleaf.org"> <!-- Using Thymeleaf to configure the form action --> <form class="space-y-4 md:space-y-6" th:action="@{/login}" method="post"> <!-- Using Thymeleaf to handle attributes and display data --> <label for="username" class="block mb-2 text-sm font-medium text-gray-900 dark:text-white" >Your email</label > <input type="email" name="username" id="username" th:placeholder="name@company.com" required /> <!-- ... --> <label for="password" class="block mb-2 text-sm font-medium text-gray-900 dark:text-white" >Password</label > <input type="password" name="password" id="password" th:placeholder="••••••••" required /> <!-- ... --> <button type="submit" class="w-full text-white bg-primary-600 hover:bg-primary-700 ..." > Log in </button> </form> </html>Hibernate Validator is used in entities to apply validation constraints:
File: Customer.java
import jakarta.validation.constraints.Email; import jakarta.validation.constraints.NotEmpty; import jakarta.validation.constraints.Size; @Entity @Table(name = "customer") public class Customer { // ... other attributes @Column(name = "email") @NotEmpty(message = "The email cannot be empty") @Email(message = "The email must be valid") private String email; // ... other attributes }Spring Security is used to configure authentication and authorization: The file is configured to define security rules. In this code snippet, authorization directives with HTTP are set up, allowing access to certain routes like /, register, /profile, among others. Additionally, the login form is specified at /login, the login request processing at the same URL, and the redirection to /profile after a successful login. Finally, the logout functionality is enabled at /logout, with redirection to the login page.
File: SpringSecurityConfig.java
@Configuration @EnableMethodSecurity public class SpringSecurityConfig { // ... other methods and configurations @Bean public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { // Authorization configuration with HTTP http.csrf(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable); http.authorizeHttpRequests(httpRequest -> // Configuration of specific routes and permissions httpRequest.requestMatchers("/", "register", "/profile**", "/agregateProduct**", "/newProduct**", "/editProduct**") .permitAll() .anyRequest().authenticated()) .formLogin(formLogin -> formLogin .loginPage("/login") .loginProcessingUrl("/login") .defaultSuccessUrl("/profile") .permitAll()) .logout(logout -> logout .logoutUrl("/logout") .logoutSuccessUrl("/login") .permitAll()); return http.build(); } // ... other attributes }Spring Data JPA is used to handle data persistence.
File: Boleta.java
@Entity @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class Boleta { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; @OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL) @JoinColumn(name = "boleta_id") private List<ProductoDetalle> detalles; private Double precioTotal; // ... other attributes }Spring Boot Starter Web is a dependency that provides features for building web applications. Here's an example of how it's used:
File: CustomerController.java
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; @Controller @RequestMapping("api/v1/customers") @RequiredArgsConstructor public class CustomerController { private final CustomerService customerService; @PostMapping("/register") public String createCustomer(@ModelAttribute("customer") Customer customer) { customerService.createCustomer(customer); return "redirect:/profile"; } }Lombok is a library that reduces code verbosity by automatically generating methods like getters, setters, constructors, etc. Here's an example of how it's used:
File: Customer.java
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import lombok.Setter; @Getter @Setter @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor @Entity @Table(name = "customer") public class Customer { @Id @GeneratedValue private Long customerId; @Column(name = "first_name") private String firstName; @Column(name = "last_name") private String lastName; @Column(name = "email") private String email; @Transient private String password; @OneToOne(mappedBy = "customer", cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.LAZY) private UserAccount userAccount; }In the project structure, each directory contains files related to specific system functionalities, such as authentication (auth), invoice management (boleta), configuration (config), customers (customer), products (product), security (security), and HTML resource files for views in templates. Additionally, the main project configuration file is located in application.yml within the resources directory.
src/main/java/com/tecsup/ferreteria/auth/Authority.javaRole.javaRoleRepository.javaRoleService.javaRoleServiceImpl.java
boleta/Boleta.javaBoletaController.javaBoletaRepository.javaBoletaService.javaBoletaServiceImpl.javaProductoDetalle.java
config/SpringSecurityConfig.java
customer/Customer.javaCustomerController.javaCustomerRepository.javaCustomerService.javaCustomerServiceImpl.java
product/Product.javaProductController.javaProductDTO.javaProductRepository.javaProductService.javaProductServiceImpl.java
security/AccountService.javaUserAccount.javaUserAccountController.javaUserAccountDetails.javaUserAccountPasswordEncoder.javaUserAccountRepository.javaUserAccountService.java
SpringSecurityApplication.java(main)
src/main/resources/templates/agregateProduct.htmlchooseProducts.htmldescargarBoleta.htmleditProduct.htmllogin.htmlproducts.htmlprofile.htmlregister.html
application.yml
This project is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International.