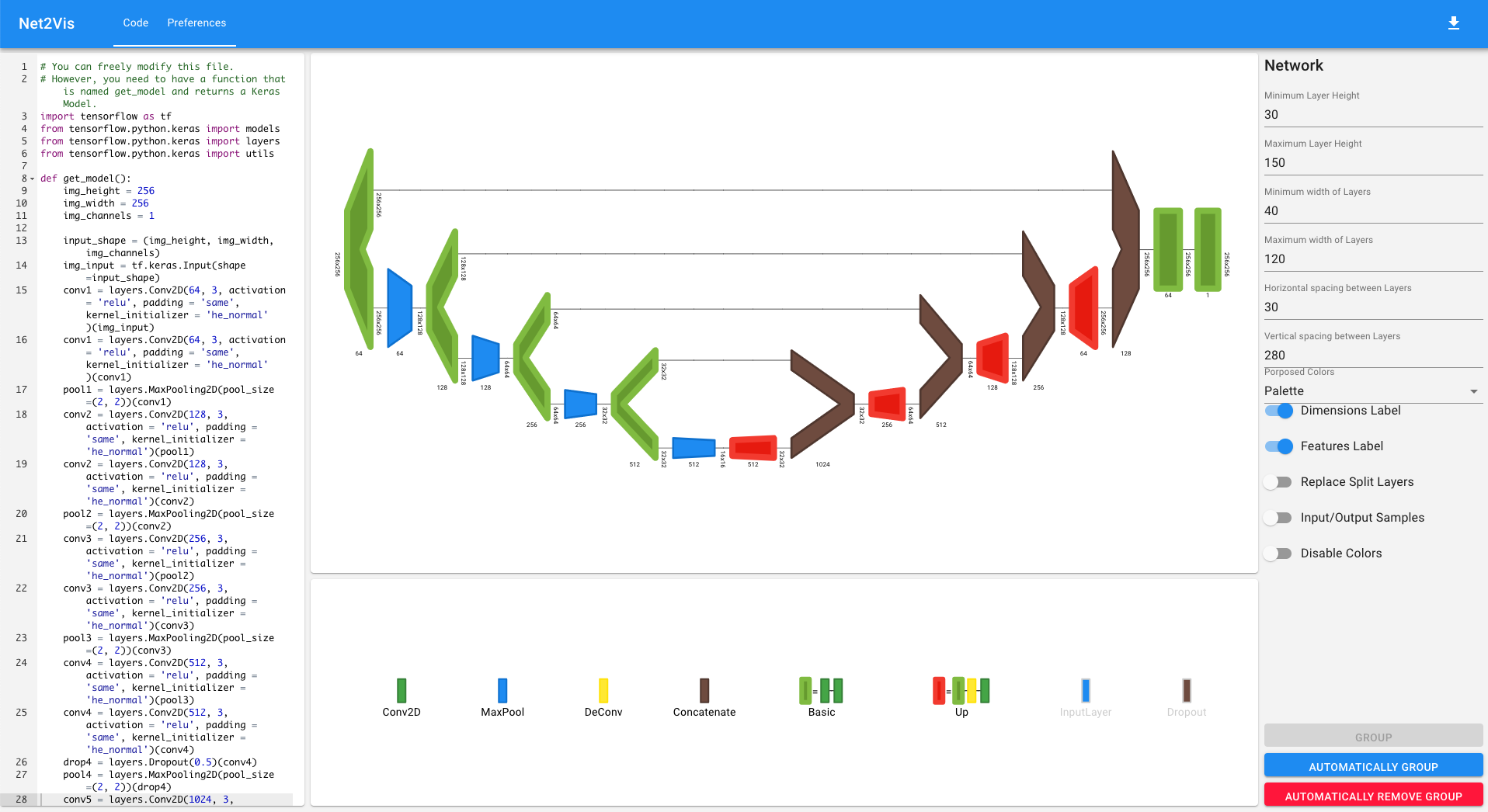
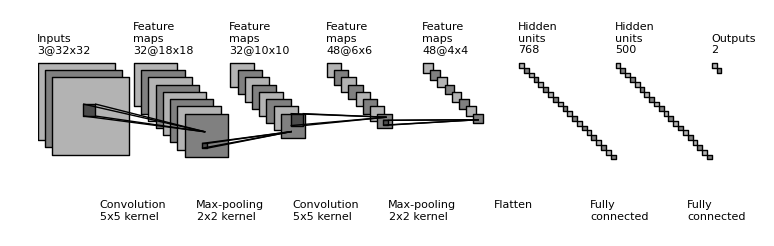
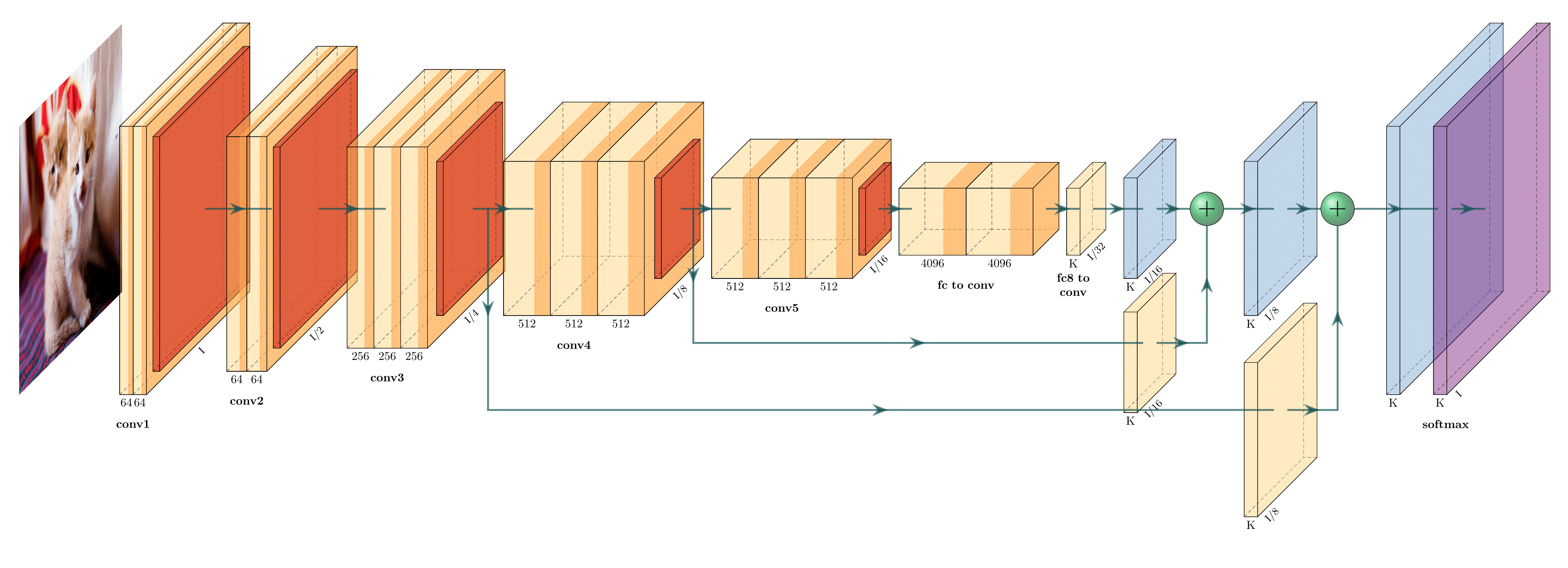
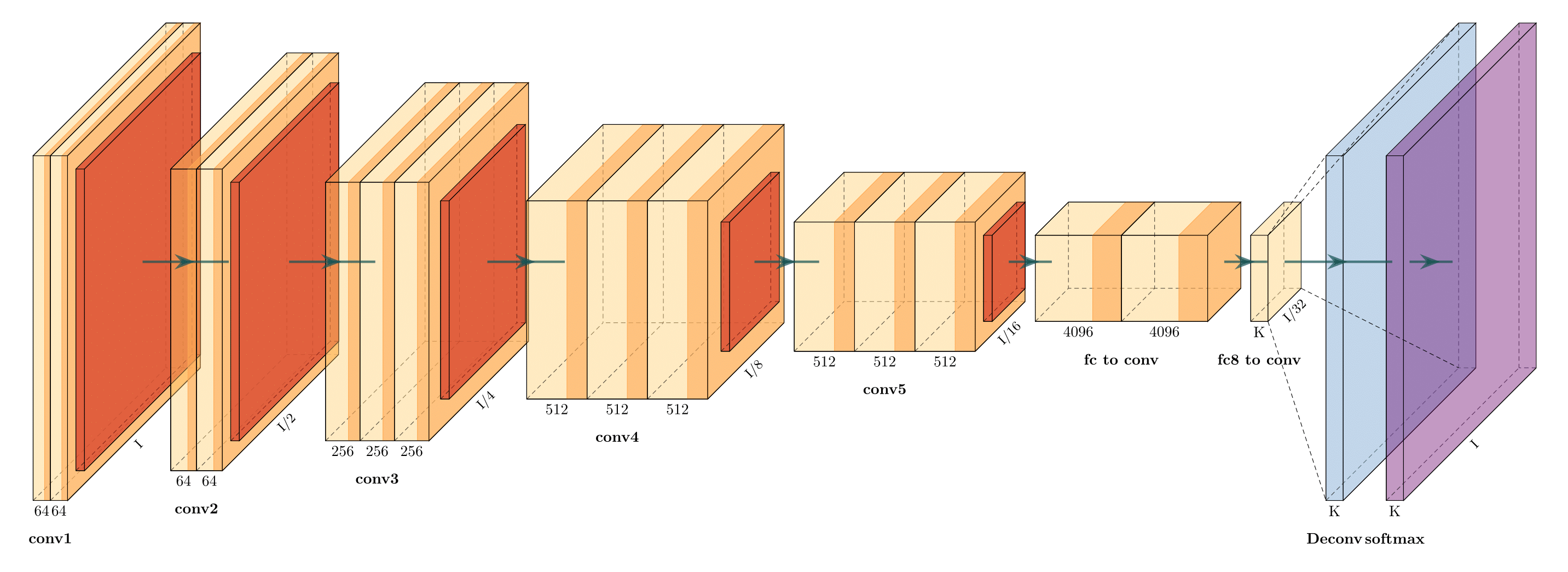
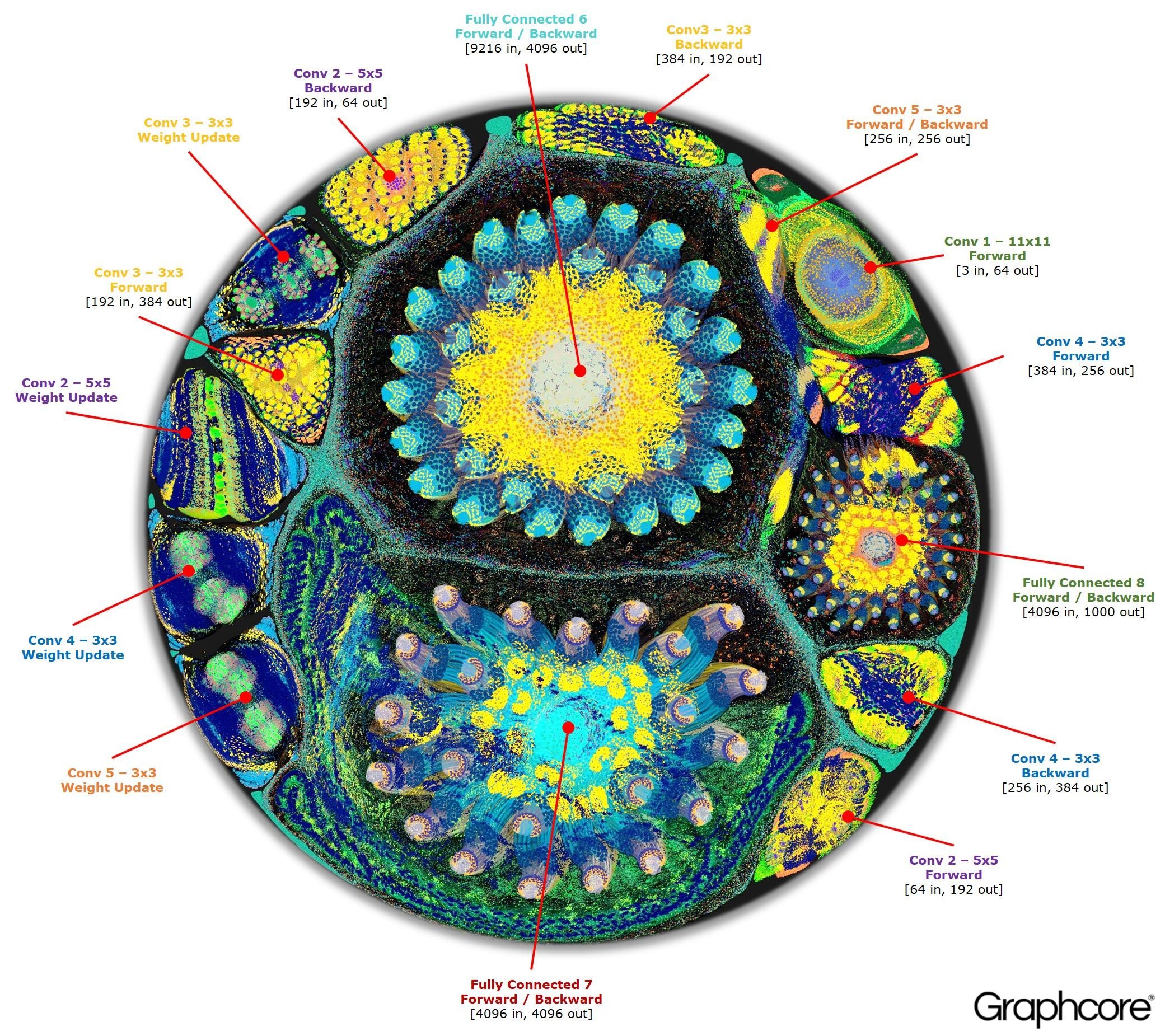
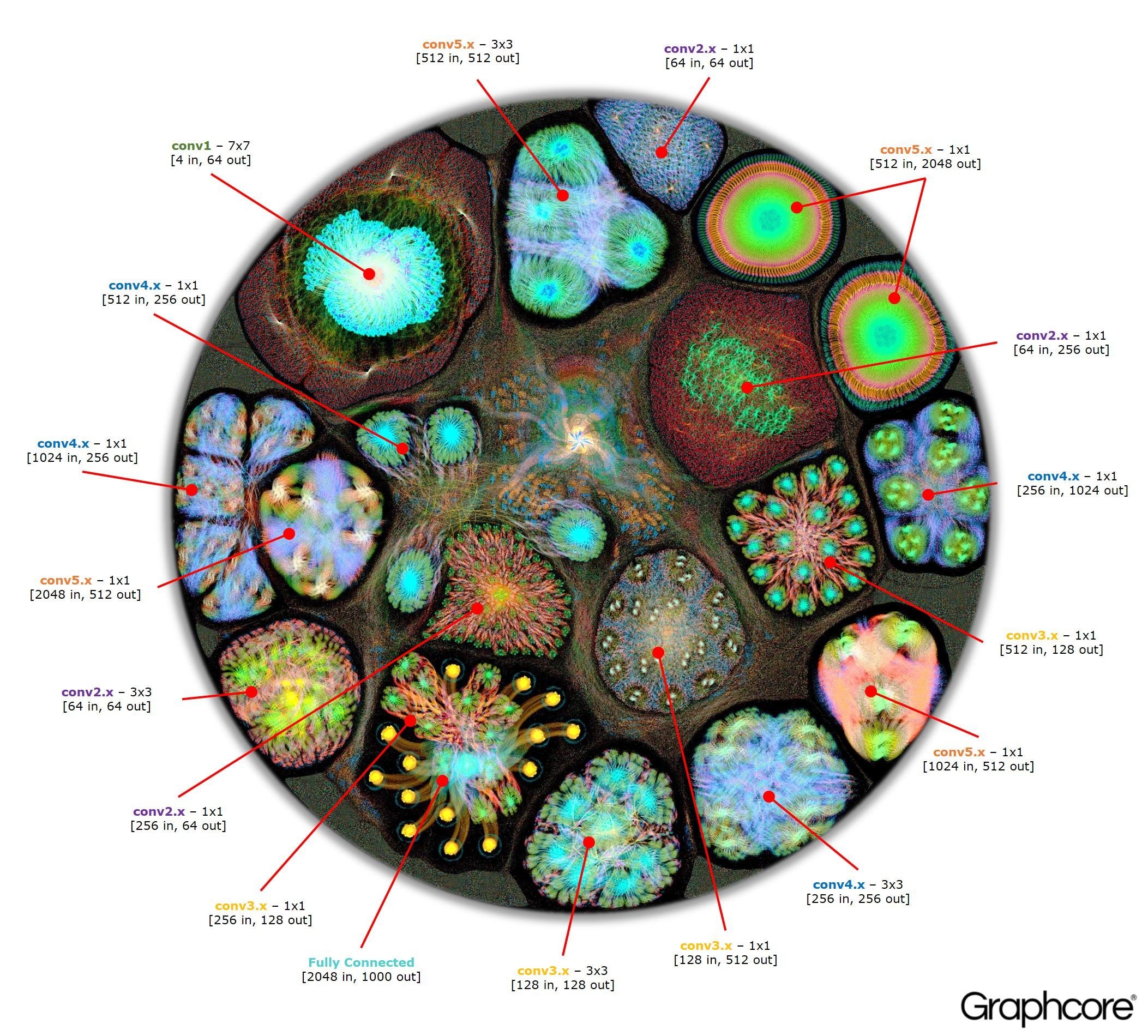
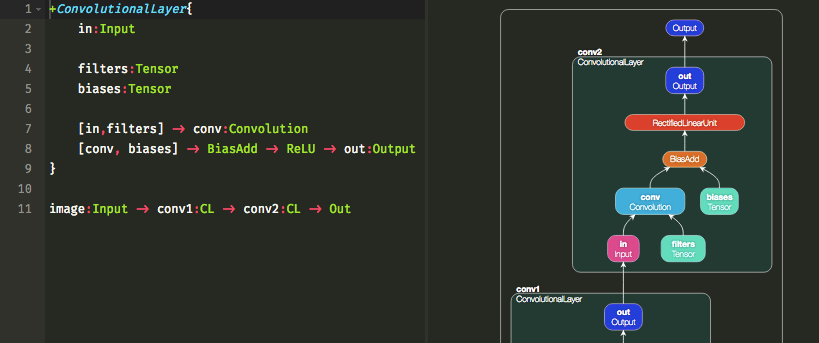
Net2Vis automatically generates abstract visualizations for convolutional neural networks from Keras code.
Visualkeras is a Python package to help visualize Keras (either standalone or included in tensorflow) neural network architectures. It allows easy styling to fit most needs. As of now it supports layered style architecture generation which is great for CNNs (Convolutional Neural Networks) and a grap style architecture.
import visualkeras model = ... visualkeras.layered_view(model).show() # display using your system viewer visualkeras.layered_view(model, to_file='output.png') # write to disk visualkeras.layered_view(model, to_file='output.png').show() # write and show visualkeras.layered_view(model)Python script for illustrating Convolutional Neural Network (ConvNet)
Latex code for drawing neural networks for reports and presentation. Have a look into examples to see how they are made. Additionally, lets consolidate any improvements that you make and fix any bugs to help more people with this code.
TensorBoard’s Graphs dashboard is a powerful tool for examining your TensorFlow model.
In Caffe you can use caffe/draw.py to draw the NetParameter protobuffer:
A library for Keras for investigating architectures and parameters of sequential models.
OPERATION DATA DIMENSIONS WEIGHTS(N) WEIGHTS(%) Input ##### 3 224 224 InputLayer | ------------------- 0 0.0% ##### 3 224 224 Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 1792 0.0% relu ##### 64 224 224 Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 36928 0.0% relu ##### 64 224 224 MaxPooling2D Y max ------------------- 0 0.0% ##### 64 112 112 Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 73856 0.1% relu ##### 128 112 112 Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 147584 0.1% relu ##### 128 112 112 MaxPooling2D Y max ------------------- 0 0.0% ##### 128 56 56 Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 295168 0.2% relu ##### 256 56 56 Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 590080 0.4% relu ##### 256 56 56 Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 590080 0.4% relu ##### 256 56 56 MaxPooling2D Y max ------------------- 0 0.0% ##### 256 28 28 Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 1180160 0.9% relu ##### 512 28 28 Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 2359808 1.7% relu ##### 512 28 28 Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 2359808 1.7% relu ##### 512 28 28 MaxPooling2D Y max ------------------- 0 0.0% ##### 512 14 14 Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 2359808 1.7% relu ##### 512 14 14 Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 2359808 1.7% relu ##### 512 14 14 Convolution2D \|/ ------------------- 2359808 1.7% relu ##### 512 14 14 MaxPooling2D Y max ------------------- 0 0.0% ##### 512 7 7 Flatten ||||| ------------------- 0 0.0% ##### 25088 Dense XXXXX ------------------- 102764544 74.3% relu ##### 4096 Dense XXXXX ------------------- 16781312 12.1% relu ##### 4096 Dense XXXXX ------------------- 4097000 3.0% softmax ##### 1000 The keras.utils.vis_utils module provides utility functions to plot a Keras model (using graphviz)
The Python package conx can visualize networks with activations with the function net.picture() to produce SVG, PNG, or PIL Images like this:
Working on a drag-and-drop neural network visualizer (and more). Here's an example of a visualization for a LeNet-like architecture.
data(infert, package="datasets") plot(neuralnet(case~parity+induced+spontaneous, infert))These approaches are more oriented towards visualizing neural network operation, however, NN architecture is also somewhat visible on the resulting diagrams.
Neataptic offers flexible neural networks; neurons and synapses can be removed with a single line of code. No fixed architecture is required for neural networks to function at all. This flexibility allows networks to be shaped for your dataset through neuro-evolution, which is done using multiple threads.
TensorSpace is a neural network 3D visualization framework built by TensorFlow.js, Three.js and Tween.js. TensorSpace provides Layer APIs to build deep learning layers, load pre-trained models, and generate a 3D visualization in the browser. By applying TensorSpace API, it is more intuitive to visualize and understand any pre-trained models built by TensorFlow, Keras, TensorFlow.js, etc.
Interactive Notation for Computational Graphs https://mlajtos.github.io/moniel/
\documentclass{article} \usepackage{tikz} \begin{document} \pagestyle{empty} \def\layersep{2.5cm} \begin{tikzpicture}[shorten >=1pt,->,draw=black!50, node distance=\layersep] \tikzstyle{every pin edge}=[<-,shorten <=1pt] \tikzstyle{neuron}=[circle,fill=black!25,minimum size=17pt,inner sep=0pt] \tikzstyle{input neuron}=[neuron, fill=green!50]; \tikzstyle{output neuron}=[neuron, fill=red!50]; \tikzstyle{hidden neuron}=[neuron, fill=blue!50]; \tikzstyle{annot} = [text width=4em, text centered] % Draw the input layer nodes \foreach \name / \y in {1,...,4} % This is the same as writing \foreach \name / \y in {1/1,2/2,3/3,4/4} \node[input neuron, pin=left:Input \#\y] (I-\name) at (0,-\y) {}; % Draw the hidden layer nodes \foreach \name / \y in {1,...,5} \path[yshift=0.5cm] node[hidden neuron] (H-\name) at (\layersep,-\y cm) {}; % Draw the output layer node \node[output neuron,pin={[pin edge={->}]right:Output}, right of=H-3] (O) {}; % Connect every node in the input layer with every node in the % hidden layer. \foreach \source in {1,...,4} \foreach \dest in {1,...,5} \path (I-\source) edge (H-\dest); % Connect every node in the hidden layer with the output layer \foreach \source in {1,...,5} \path (H-\source) edge (O); % Annotate the layers \node[annot,above of=H-1, node distance=1cm] (hl) {Hidden layer}; \node[annot,left of=hl] {Input layer}; \node[annot,right of=hl] {Output layer}; \end{tikzpicture} % End of code \end{document}References: