Optional chaining can be really useful to help with potential errors when accessing a property of an object. It allows you to access a property deep within an object without risking an error if one of the properties is nullish (null or undefined).
Optional chaining is used to access a property that may or may not exist.
Optional Chaining (objects)
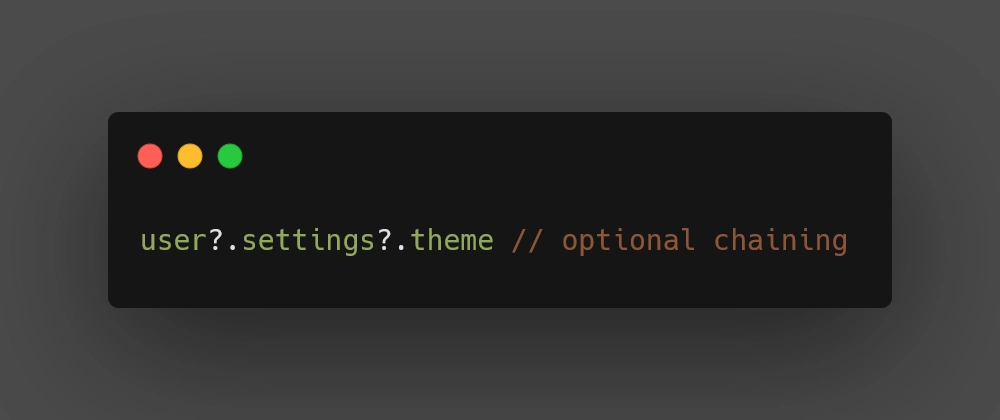
The syntax is to use dot notation but with a ? in front of the dot. Here's an example:
const user = { name: 'Joe', age: 27, settings: { theme: { mode: 'dark', text: '#d7e0ff', background: '#f87070', font: 'Kumbh Sans, sans-serif' }, }, friends: ['Brandon', 'Brian', 'Isaac'], } console.log(user?.settings?.theme) /* => { mode: 'dark', text: '#d7e0ff', background: '#f87070', font: 'Kumbh Sans, sans-serif' } */ Optional Chaining (arrays)
The benefit of optional chaining on an array is that if the results were null or undefined, your code won't break. It will short-circuit and return undefined.
const user = { name: 'Joe', age: 27, settings: { theme: { mode: 'dark', text: '#d7e0ff', background: '#f87070', font: 'Kumbh Sans, sans-serif' }, }, friends: ['Brandon', 'Brian', 'Isaac'], } /* // variable to hold the data let firstArrayValue = ''; // instead of using an if condition if (user.friends) { firstArrayValue = user?.friends?.[0]; } */ // use optional chaining const firstArrayValue = user?.friends?.[0] console.log(firstArrayValue) // => 'Brandon' Important notes
- You can only use optional chaining on an object that exists.
- Optional chaining is only used for reading. It cannot be used for assignment.
// profile is not defined console.log(profile?.settings?.theme) // Syntax error (Optional chaining cannot appear in left-hand side) user?.settings?.theme = 'light' 

Top comments (0)