这篇文章给大家分享的是有关golang如何进行简单权限认证的内容。小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,一起跟随小编过来看看吧。
使用JWT进行认证
JSON Web Tokens (JWT) are a more modern approach to authentication.
As the web moves to a greater separation between the client and server, JWT provides a wonderful alternative to traditional cookie based authentication models.
JWTs provide a way for clients to authenticate every request without having to maintain a session or repeatedly pass login credentials to the server.
用户注册之后, 服务器生成一个 JWT token返回给浏览器, 浏览器向服务器请求数据时将 JWT token 发给服务器, 服务器用 signature 中定义的方式解码
JWT 获取用户信息.
一个 JWT token包含3部分:
1 header: 告诉我们使用的算法和 token 类型
2 Payload: 必须使用 sub key 来指定用户 ID, 还可以包括其他信息比如 email, username 等.
3 Signature: 用来保证 JWT 的真实性. 可以使用不同算法
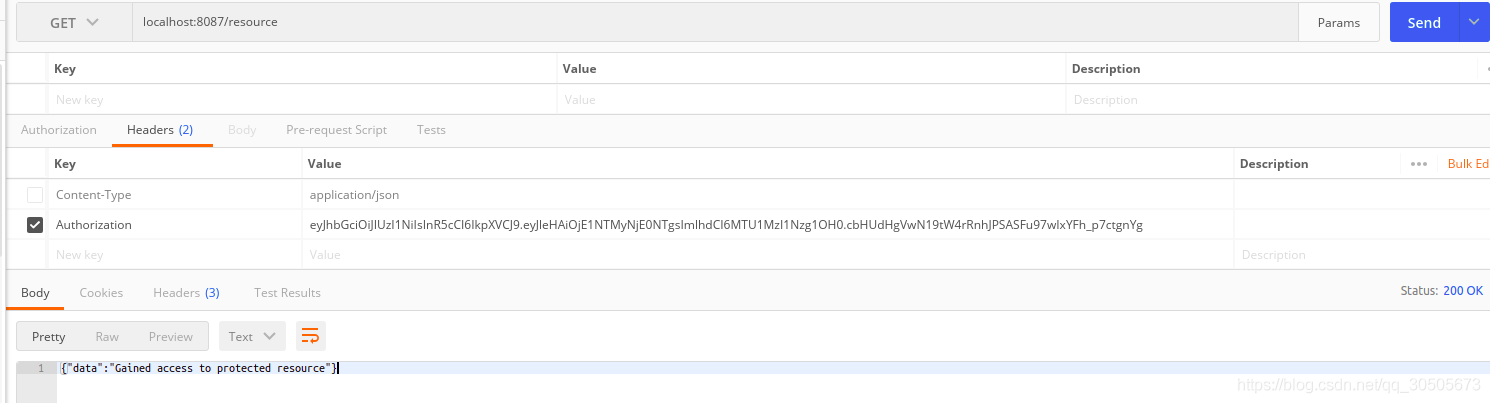
package main import ( "encoding/json" "fmt" "log" "net/http" "strings" "time" "github.com/codegangsta/negroni" "github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go" "github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go/request" ) const ( SecretKey = "welcome ---------" ) func fatal(err error) { if err != nil { log.Fatal(err) } } type UserCredentials struct { Username string `json:"username"` Password string `json:"password"` } type User struct { ID int `json:"id"` Name string `json:"name"` Username string `json:"username"` Password string `json:"password"` } type Response struct { Data string `json:"data"` } type Token struct { Token string `json:"token"` } func StartServer() { http.HandleFunc("/login", LoginHandler) http.Handle("/resource", negroni.New( negroni.HandlerFunc(ValidateTokenMiddleware), negroni.Wrap(http.HandlerFunc(ProtectedHandler)), )) log.Println("Now listening...") http.ListenAndServe(":8087", nil) } func main() { StartServer() } func ProtectedHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { response := Response{"Gained access to protected resource"} JsonResponse(response, w) } func LoginHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { var user UserCredentials err := json.NewDecoder(r.Body).Decode(&user) if err != nil { w.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden) fmt.Fprint(w, "Error in request") return } if strings.ToLower(user.Username) != "someone" { if user.Password != "p@ssword" { w.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden) fmt.Println("Error logging in") fmt.Fprint(w, "Invalid credentials") return } } token := jwt.New(jwt.SigningMethodHS256) claims := make(jwt.MapClaims) claims["exp"] = time.Now().Add(time.Hour * time.Duration(1)).Unix() claims["iat"] = time.Now().Unix() token.Claims = claims if err != nil { w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError) fmt.Fprintln(w, "Error extracting the key") fatal(err) } tokenString, err := token.SignedString([]byte(SecretKey)) if err != nil { w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError) fmt.Fprintln(w, "Error while signing the token") fatal(err) } response := Token{tokenString} JsonResponse(response, w) } func ValidateTokenMiddleware(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request, next http.HandlerFunc) { token, err := request.ParseFromRequest(r, request.AuthorizationHeaderExtractor, func(token *jwt.Token) (interface{}, error) { return []byte(SecretKey), nil }) if err == nil { if token.Valid { next(w, r) } else { w.WriteHeader(http.StatusUnauthorized) fmt.Fprint(w, "Token is not valid") } } else { w.WriteHeader(http.StatusUnauthorized) fmt.Fprint(w, "Unauthorized access to this resource") } } func JsonResponse(response interface{}, w http.ResponseWriter) { json, err := json.Marshal(response) if err != nil { http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError) return } w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK) w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json") w.Write(json) }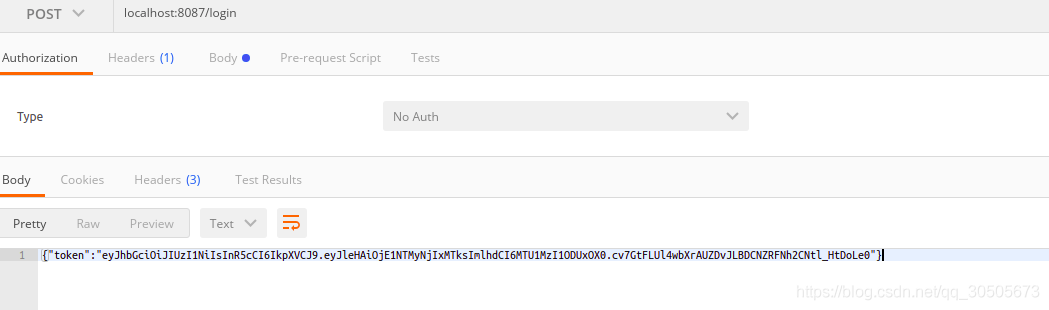
感谢各位的阅读!关于“golang如何进行简单权限认证”这篇文章就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,让大家可以学到更多知识,如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到吧!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。