жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
жң¬зҜҮеҶ…е®№дё»иҰҒи®Іи§ЈвҖңJavaйӣҶеҗҲе’Ңж•°жҚ®з»“жһ„жҺ’еәҸзҡ„е®һдҫӢд»Ӣз»ҚвҖқпјҢж„ҹе…ҙи¶Јзҡ„жңӢеҸӢдёҚеҰЁжқҘзңӢзңӢгҖӮжң¬ж–Үд»Ӣз»Қзҡ„ж–№жі•ж“ҚдҪңз®ҖеҚ•еҝ«жҚ·пјҢе®һз”ЁжҖ§ејәгҖӮдёӢйқўе°ұи®©е°Ҹзј–жқҘеёҰеӨ§е®¶еӯҰд№ вҖңJavaйӣҶеҗҲе’Ңж•°жҚ®з»“жһ„жҺ’еәҸзҡ„е®һдҫӢд»Ӣз»ҚвҖқеҗ§!
жҰӮеҝө
жҸ’е…ҘжҺ’еәҸ
зӣҙжҺҘжҸ’е…ҘжҺ’еәҸ
д»Јз Ғе®һзҺ°
жҖ§иғҪеҲҶжһҗ
еёҢе°”жҺ’еәҸ
д»Јз Ғе®һзҺ°
жҖ§иғҪеҲҶжһҗ
йҖүжӢ©жҺ’еәҸ
зӣҙжҺҘйҖүжӢ©жҺ’еәҸ
д»Јз Ғе®һзҺ°
жҖ§иғҪеҲҶжһҗ
е ҶжҺ’еәҸ
д»Јз Ғе®һзҺ°
жҖ§иғҪеҲҶжһҗ
дәӨжҚўжҺ’еәҸ
еҶ’жіЎжҺ’еәҸ
д»Јз Ғе®һзҺ°
жҖ§иғҪеҲҶжһҗ
еҝ«йҖҹжҺ’еәҸ
д»Јз Ғе®һзҺ°
жҖ§иғҪеҲҶжһҗ
йқһйҖ’еҪ’е®һзҺ°еҝ«йҖҹжҺ’еәҸ
д»Јз Ғе®һзҺ°
жҖ§иғҪеҲҶжһҗ
еҪ’并жҺ’еәҸ
еҪ’并жҺ’еәҸ
д»Јз Ғе®һзҺ°
жҖ§иғҪеҲҶжһҗ
йқһйҖ’еҪ’е®һзҺ°еҪ’并жҺ’еәҸ
д»Јз Ғе®һзҺ°
жҖ§иғҪеҲҶжһҗ
жө·йҮҸж•°жҚ®зҡ„жҺ’еәҸй—®йўҳ
жҺ’еәҸпјҢе°ұжҳҜдҪҝдёҖдёІи®°еҪ•пјҢжҢүз…§е…¶дёӯзҡ„жҹҗдёӘжҲ–жҹҗдәӣе…ій”®еӯ—зҡ„еӨ§е°ҸпјҢйҖ’еўһжҲ–йҖ’еҮҸзҡ„жҺ’еҲ—иө·жқҘзҡ„ж“ҚдҪңгҖӮ
е№іж—¶зҡ„дёҠдёӢж–ҮдёӯпјҢеҰӮжһңжҸҗеҲ°жҺ’еәҸпјҢйҖҡеёёжҢҮзҡ„жҳҜжҺ’еҚҮеәҸпјҲйқһйҷҚеәҸпјүгҖӮ
йҖҡеёёж„Ҹд№үдёҠзҡ„жҺ’еәҸпјҢйғҪжҳҜжҢҮзҡ„еҺҹең°жҺ’еәҸ(in place sort)гҖӮ
зЁіе®ҡжҖ§пјҡ дёӨдёӘзӣёзӯүзҡ„ж•°жҚ®пјҢеҰӮжһңз»ҸиҝҮжҺ’еәҸеҗҺпјҢжҺ’еәҸз®—жі•иғҪдҝқиҜҒе…¶зӣёеҜ№дҪҚзҪ®дёҚеҸ‘з”ҹеҸҳеҢ–пјҢеҲҷжҲ‘们称иҜҘз®—жі•жҳҜе…·еӨҮзЁіе®ҡжҖ§зҡ„жҺ’еәҸз®—жі•гҖӮ
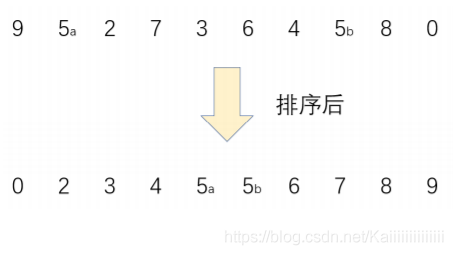

ж•ҙдёӘеҢәй—ҙиў«еҲҶдёә
жңүеәҸеҢәй—ҙ
ж— еәҸеҢәй—ҙ
жҜҸж¬ЎйҖүжӢ©ж— еәҸеҢәй—ҙзҡ„第дёҖдёӘе…ғзҙ пјҢеңЁжңүеәҸеҢәй—ҙеҶ…йҖүжӢ©еҗҲйҖӮзҡ„дҪҚзҪ®жҸ’е…Ҙ
йҖ»иҫ‘д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class InsertSort { public static void insertSort(int[] array) { for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) { int temp = array[i]; int j = i-1; for (; j >= 0; j--) { if (array[j] > temp) { array[j+1] = array[j]; }else { break; } } array[j+1] = temp; } } }и°ғиҜ•д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {10,3,2,7,19,78,65,127}; System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеүҚпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); InsertSort.insertSort(array); System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеҗҺпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); } }иҜҘд»Јз Ғзҡ„жү§иЎҢз»“жһңдёәпјҡ
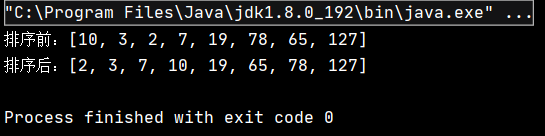
еҸҜи§ҒпјҢе®һзҺ°дәҶеҜ№еҺҹж•°з»„зҡ„еҚҮеәҸжҺ’еәҸгҖӮ
ж—¶й—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡ
жңҖеҘҪжғ…еҶөпјҡO(n)гҖҗж•°жҚ®жңүеәҸгҖ‘
е№іеқҮжғ…еҶөпјҡO(n2)
жңҖеқҸжғ…еҶөпјҡO(n2)гҖҗж•°жҚ®йҖҶеәҸгҖ‘
з©әй—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡO(1)
зЁіе®ҡжҖ§пјҡзЁіе®ҡ
еҜ№дәҺзӣҙжҺҘжҸ’е…ҘжҺ’еәҸпјҡи¶ҠжңүеәҸи¶Ҡеҝ«гҖӮеҸҰеӨ–пјҢзӣҙжҺҘжҸ’е…ҘжҺ’еәҸдјҡз”ЁеңЁдёҖдәӣжҺ’еәҸзҡ„дјҳеҢ–дёҠгҖӮ
еёҢе°”жҺ’еәҸжі•еҸҲз§°зј©е°ҸеўһйҮҸжі•гҖӮеёҢе°”жҺ’еәҸжі•зҡ„еҹәжң¬жҖқжғіжҳҜпјҡе…ҲйҖүе®ҡдёҖдёӘж•ҙж•°пјҢжҠҠеҫ…жҺ’еәҸж–Ү件дёӯжүҖжңүи®°еҪ•еҲҶжҲҗдёӘз»„пјҢжүҖжңүи·қзҰ»дёәзҡ„и®°еҪ•еҲҶеңЁеҗҢдёҖз»„еҶ…пјҢ并еҜ№жҜҸдёҖз»„еҶ…зҡ„и®°еҪ•иҝӣиЎҢжҺ’еәҸгҖӮ然еҗҺпјҢеҸ–пјҢйҮҚеӨҚдёҠиҝ°еҲҶз»„е’ҢжҺ’еәҸзҡ„е·ҘдҪңгҖӮеҪ“еҲ°иҫҫ=1ж—¶пјҢ жүҖжңүи®°еҪ•еңЁз»ҹдёҖз»„еҶ…жҺ’еҘҪеәҸгҖӮ
еёҢе°”жҺ’еәҸжҳҜеҜ№зӣҙжҺҘжҸ’е…ҘжҺ’еәҸзҡ„дјҳеҢ–гҖӮ
еҪ“gap > 1ж—¶йғҪжҳҜйў„жҺ’еәҸпјҢзӣ®зҡ„жҳҜи®©ж•°з»„жӣҙжҺҘиҝ‘дәҺжңүеәҸгҖӮеҪ“gap == 1ж—¶пјҢж•°з»„е·Із»ҸжҺҘиҝ‘жңүеәҸзҡ„дәҶпјҢиҝҷж ·е°ұдјҡеҫҲеҝ«гҖӮиҝҷж ·ж•ҙдҪ“иҖҢиЁҖпјҢеҸҜд»ҘиҫҫеҲ°дјҳеҢ–зҡ„ж•ҲжһңгҖӮжҲ‘们е®һзҺ°еҗҺеҸҜд»ҘиҝӣиЎҢжҖ§иғҪжөӢиҜ•зҡ„еҜ№жҜ”гҖӮ
йҖ»иҫ‘д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class ShellSort { public static void shell(int[] array,int gap) { for (int i = gap; i < array.length; i = i + gap) { int temp = array[i]; int j = i-gap; for (; j >= 0; j = j-gap) { if (array[j] > temp) { array[j+gap] = array[j]; }else { break; } } array[j+gap] = temp; } } public static void shellSort(int[] array) { int[] drr = {5,3,1};//еўһйҮҸж•°з»„-->жІЎжңүжҳҺзЎ®зҡ„规е®ҡпјҢдҪҶдҝқиҜҒдёәзҙ ж•°зҡ„еўһйҮҸеәҸеҲ— for (int i = 0; i < drr.length; i++) { shell(array,drr[i]); } } }жөӢиҜ•д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {10,3,2,7,19,78,65,127}; System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеүҚпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); ShellSort.shellSort(array); System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеҗҺпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); } }иҜҘд»Јз Ғзҡ„жү§иЎҢз»“жһңдёәпјҡ
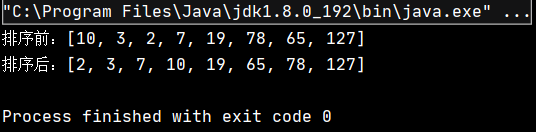
еҸҜи§ҒпјҢе®һзҺ°дәҶеҜ№еҺҹж•°з»„зҡ„еҚҮеәҸжҺ’еәҸгҖӮ
ж—¶й—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡ
жңҖеҘҪжғ…еҶөпјҡO(n)гҖҗж•°жҚ®жңүеәҸгҖ‘
е№іеқҮжғ…еҶөпјҡO(n1.3)
жңҖеқҸжғ…еҶөпјҡ O(n2) гҖҗжҜ”иҫғйҡҫжһ„йҖ гҖ‘
з©әй—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡO(1)
зЁіе®ҡжҖ§пјҡдёҚзЁіе®ҡ
жҜҸдёҖж¬Ўд»Һж— еәҸеҢәй—ҙйҖүеҮәжңҖеӨ§пјҲжҲ–жңҖе°Ҹпјүзҡ„дёҖдёӘе…ғзҙ пјҢеӯҳж”ҫеңЁж— еәҸеҢәй—ҙзҡ„жңҖеҗҺпјҲжҲ–жңҖеүҚпјүпјҢзӣҙеҲ°е…ЁйғЁеҫ…жҺ’еәҸзҡ„ж•°жҚ®е…ғзҙ жҺ’е®Ң гҖӮ
йҖ»иҫ‘д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class SelectSort { public static void selectSort(int[] array) { for (int i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++) { for (int j = i+1; j < array.length; j++) { if (array[i] > array[j]) { int temp = array[j]; array[j] = array[i]; array[i] = temp; } } } } }жөӢиҜ•д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {10,3,2,7,19,78,65,127}; System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеүҚпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); SelectSort.selectSort(array); System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеҗҺпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); } }иҜҘд»Јз Ғзҡ„жү§иЎҢз»“жһңдёәпјҡ
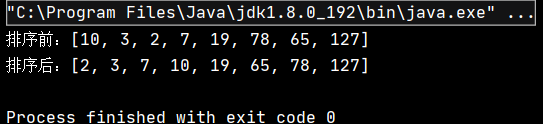
еҸҜи§ҒпјҢе®һзҺ°дәҶеҜ№еҺҹж•°з»„зҡ„еҚҮеәҸжҺ’еәҸгҖӮ
ж—¶й—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰ : дёҚз®ЎжҳҜжңҖеҘҪжғ…еҶөиҝҳжҳҜжңҖеқҸжғ…еҶөйғҪжҳҜO(n2) гҖҗж•°жҚ®дёҚж•Ҹж„ҹгҖ‘
з©әй—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰ: O(1)
зЁіе®ҡжҖ§пјҡдёҚзЁіе®ҡ
еҹәжң¬еҺҹзҗҶд№ҹжҳҜйҖүжӢ©жҺ’еәҸпјҢеҸӘжҳҜдёҚеңЁдҪҝз”ЁйҒҚеҺҶзҡ„ж–№ејҸжҹҘжүҫж— еәҸеҢәй—ҙзҡ„жңҖеӨ§зҡ„ж•°пјҢиҖҢжҳҜйҖҡиҝҮе ҶжқҘйҖүжӢ©ж— еәҸеҢәй—ҙзҡ„жңҖеӨ§зҡ„ж•°гҖӮ
жіЁж„ҸпјҡжҺ’еҚҮеәҸиҰҒе»әеӨ§е ҶпјӣжҺ’йҷҚеәҸиҰҒе»әе°Ҹе ҶгҖӮ
йҖ»иҫ‘д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class HeapSort { public static void heapSort(int[] array) { PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() { @Override public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) { return o1-o2; } }); for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { priorityQueue.add(array[i]); } for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { array[i] = priorityQueue.poll(); } } }жөӢиҜ•д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {10,3,2,7,19,78,65,127}; System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеүҚпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); HeapSort.heapSort(array); System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеҗҺпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); } }иҜҘд»Јз Ғзҡ„жү§иЎҢз»“жһңдёәпјҡ
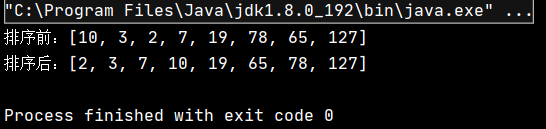
еҸҜи§ҒпјҢе®һзҺ°дәҶеҜ№еҺҹж•°з»„зҡ„еҚҮеәҸжҺ’еәҸгҖӮ
ж—¶й—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡдёҚз®ЎжҳҜжңҖеҘҪзҡ„жғ…еҶөиҝҳжҳҜжңҖеқҸзҡ„жғ…еҶөйғҪжҳҜO(n * log(n)) гҖӮ
з©әй—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡO(1)гҖӮ
зЁіе®ҡжҖ§пјҡдёҚзЁіе®ҡ
еңЁж— еәҸеҢәй—ҙпјҢйҖҡиҝҮзӣёйӮ»ж•°зҡ„жҜ”иҫғпјҢе°ҶжңҖеӨ§зҡ„ж•°еҶ’жіЎеҲ°ж— еәҸеҢәй—ҙзҡ„жңҖеҗҺпјҢжҢҒз»ӯиҝҷдёӘиҝҮзЁӢпјҢзӣҙеҲ°ж•°з»„ж•ҙдҪ“жңүеәҸгҖӮ
йҖ»иҫ‘д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class BubbleBort { public static void bubbleBort(int[] array) { for (int i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < array.length-i-1; j++) { if (array[j] > array[j+1]) { int temp = array[j]; array[j] = array[j+1]; array[j+1] = temp; } } } } }жөӢиҜ•д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {10,3,2,7,19,78,65,127}; System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеүҚпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); BubbleBort.bubbleBort(array); System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеҗҺпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); } }иҜҘд»Јз Ғзҡ„жү§иЎҢз»“жһңдёәпјҡ
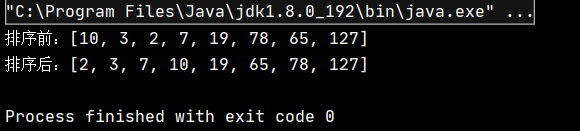
еҸҜи§ҒпјҢе®һзҺ°дәҶеҜ№еҺҹж•°з»„зҡ„еҚҮеәҸжҺ’еәҸгҖӮ
ж—¶й—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡ
жңҖеҘҪжғ…еҶөпјҡO(n)гҖҗж•°жҚ®жңүеәҸгҖ‘
е№іеқҮжғ…еҶөпјҡO(n2)
жңҖеқҸжғ…еҶөпјҡ O(n2) гҖҗж•°жҚ®йҖҶеәҸгҖ‘
з©әй—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡO(1)гҖӮ
зЁіе®ҡжҖ§пјҡзЁіе®ҡ
д»Һеҫ…жҺ’еәҸеҢәй—ҙйҖүжӢ©дёҖдёӘж•°пјҢдҪңдёәеҹәеҮҶеҖј(pivot)пјӣ
Partition: йҒҚеҺҶж•ҙдёӘеҫ…жҺ’еәҸеҢәй—ҙпјҢе°ҶжҜ”еҹәеҮҶеҖје°Ҹзҡ„пјҲеҸҜд»ҘеҢ…еҗ«зӣёзӯүзҡ„пјүж”ҫеҲ°еҹәеҮҶеҖјзҡ„е·Ұиҫ№пјҢе°ҶжҜ”еҹәеҮҶеҖјеӨ§зҡ„пјҲеҸҜд»ҘеҢ…еҗ«зӣёзӯүзҡ„пјүж”ҫеҲ°еҹәеҮҶеҖјзҡ„еҸіиҫ№пјӣ
йҮҮз”ЁеҲҶжІ»жҖқжғіпјҢеҜ№е·ҰеҸідёӨдёӘе°ҸеҢәй—ҙжҢүз…§еҗҢж ·зҡ„ж–№ејҸеӨ„зҗҶпјҢзӣҙеҲ°е°ҸеҢәй—ҙзҡ„й•ҝеәҰ = 1пјҢд»ЈиЎЁе·Із»ҸжңүеәҸпјҢжҲ–иҖ…е°ҸеҢәй—ҙзҡ„й•ҝеәҰ = 0пјҢд»ЈиЎЁжІЎжңүж•°жҚ®гҖӮ
йҖ»иҫ‘д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class QuickSort { public static void quick(int[] array,int low,int high) { if (low < high) { int piv = piovt(array,low,high);//жүҫеҹәеҮҶ quick(array,low,piv-1); quick(array,piv+1,high); } } private static int piovt(int[] array,int start,int end) { int temp = array[start]; while (start < end) { while (start < end && array[end] >= temp) { end--; } array[start] = array[end]; while (start < end && array[start] < temp) { start++; } array[end] = array[start]; } array[start] = temp; return start; } public static void quickSort(int[] array) { quick(array,0,array.length-1); } }жөӢиҜ•д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {10,3,2,7,19,78,65,127}; System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеүҚпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); QuickSort.quickSort(array); System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеҗҺпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); } }иҜҘд»Јз Ғзҡ„жү§иЎҢз»“жһңдёәпјҡ
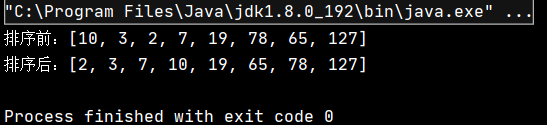
еҸҜи§ҒпјҢе®һзҺ°дәҶеҜ№еҺҹж•°з»„зҡ„еҚҮеәҸжҺ’еәҸгҖӮ
ж—¶й—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡ
жңҖеҘҪжғ…еҶөпјҡO(n * log(n))
е№іеқҮжғ…еҶөпјҡO(n * log(n))
жңҖеқҸжғ…еҶөпјҡ O(n2)
з©әй—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡ
жңҖеҘҪжғ…еҶөпјҡO(log(n))
е№іеқҮжғ…еҶөпјҡO(log(n))
жңҖеқҸжғ…еҶөпјҡO(n)
зЁіе®ҡжҖ§пјҡдёҚзЁіе®ҡ
йҖ»иҫ‘д»Јз Ғпјҡ
/** * йқһйҖ’еҪ’е®һзҺ°еҝ«йҖҹжҺ’еәҸ */ public class QuickSortNor { public static void quickSortNor(int[] array) { int low = 0; int high = array.length - 1; int piv = piovt(array, low, high); Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); if (piv > low + 1) { stack.push(low); stack.push(piv - 1); } if (piv < high - 1) { stack.push(piv + 1); stack.push(high); } while (!stack.isEmpty()) { high = stack.pop(); low = stack.pop(); piv = piovt(array, low, high); if (piv > low + 1) { stack.push(low); stack.push(piv - 1); } if (piv < high - 1) { stack.push(piv + 1); stack.push(high); } } } private static int piovt(int[] array, int start, int end) { int temp = array[start]; while (start < end) { while (start < end && array[end] >= temp) { end--; } array[start] = array[end]; while (start < end && array[start] < temp) { start++; } array[end] = array[start]; } array[start] = temp; return start; } }жөӢиҜ•д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {10,3,2,7,19,78,65,127}; System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеүҚпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); QuickSortNor.quickSortNor(array); System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеҗҺпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); } }иҜҘд»Јз Ғзҡ„жү§иЎҢз»“жһңдёәпјҡ
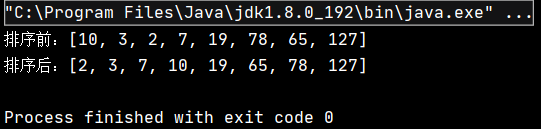
еҸҜи§ҒпјҢе®һзҺ°дәҶеҜ№еҺҹж•°з»„зҡ„еҚҮеәҸжҺ’еәҸгҖӮ
ж—¶й—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡ O(n * log(n))
з©әй—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡ
жңҖеҘҪжғ…еҶөпјҡO(log(n))
жңҖеқҸжғ…еҶөпјҡO(n)
зЁіе®ҡжҖ§пјҡдёҚзЁіе®ҡ
еҪ’并жҺ’еәҸпјҲMERGE-SORTпјүжҳҜе»әз«ӢеңЁеҪ’并ж“ҚдҪңдёҠзҡ„дёҖз§Қжңүж•Ҳзҡ„жҺ’еәҸз®—жі•,иҜҘз®—жі•жҳҜйҮҮз”ЁеҲҶжІ»жі•пјҲDivide and Conquerпјүзҡ„дёҖдёӘйқһеёёе…ёеһӢзҡ„еә”з”ЁгҖӮе°Ҷе·ІжңүеәҸзҡ„еӯҗеәҸеҲ—еҗҲ并пјҢеҫ—еҲ°е®Ңе…ЁжңүеәҸзҡ„еәҸеҲ—пјӣеҚіе…ҲдҪҝжҜҸдёӘеӯҗеәҸеҲ—жңүеәҸпјҢеҶҚдҪҝеӯҗеәҸеҲ—ж®өй—ҙжңүеәҸгҖӮиӢҘе°ҶдёӨдёӘжңүеәҸиЎЁеҗҲ并жҲҗдёҖдёӘжңүеәҸиЎЁпјҢз§°дёәдәҢи·ҜеҪ’并гҖӮ
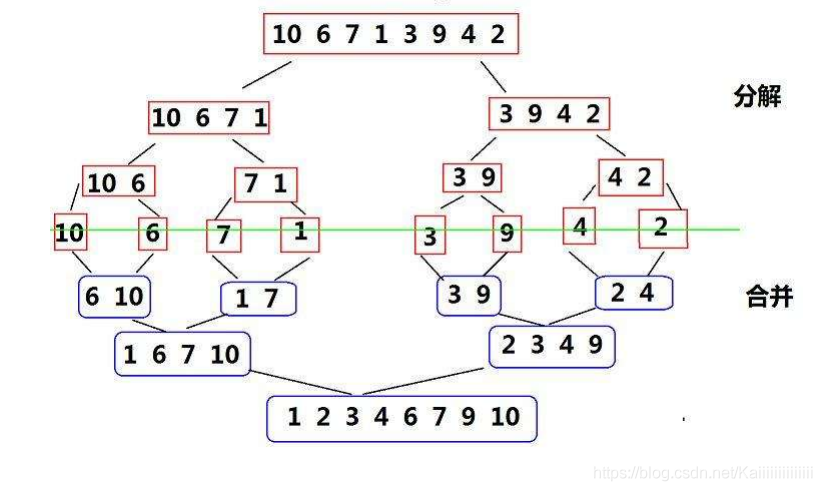
йҖ»иҫ‘д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class MergeSort { public static void merge(int[] array, int start, int mid, int end) { int s1 = start; int s2 = mid + 1; int[] temp = new int[end - start + 1]; int k = 0; while (s1 <= mid && s2 <= end) { if (array[s1] <= array[s2]) { temp[k++] = array[s1++]; } else { temp[k++] = array[s2++]; } } while (s1 <= mid) { temp[k++] = array[s1++]; } while (s2 <= end) { temp[k++] = array[s2++]; } for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) { array[i + start] = temp[i]; } } public static void mergeSortInternal(int[] array, int low, int high) { if (low >= high) return; //е…ҲеҲҶи§Ј int mid = (low + high) / 2; mergeSortInternal(array, low, mid); mergeSortInternal(array, mid + 1, high); //еҶҚеҗҲ并 merge(array, low, mid, high); } public static void mergeSort(int[] array) { mergeSortInternal(array, 0, array.length - 1); } }жөӢиҜ•д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {10,3,2,7,19,78,65,127}; System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеүҚпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); MergeSort.mergeSort(array); System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеҗҺпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); } }иҜҘд»Јз Ғзҡ„жү§иЎҢз»“жһңдёәпјҡ
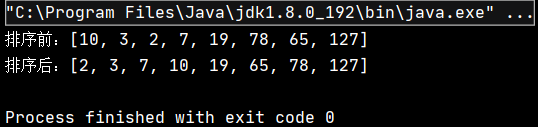
еҸҜи§ҒпјҢе®һзҺ°дәҶеҜ№еҺҹж•°з»„зҡ„еҚҮеәҸжҺ’еәҸгҖӮ
ж—¶й—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡ O(n * log(n))
з©әй—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡO(n)
зЁіе®ҡжҖ§пјҡзЁіе®ҡ
йҖ»иҫ‘д»Јз Ғпјҡ
/** * йқһйҖ’еҪ’е®һзҺ°еҪ’并жҺ’еәҸ */ public class MergeSortNor { public static void merge(int[] array, int gap) { int s1 = 0; int e1 = s1 + gap - 1; int s2 = e1 + 1; int e2 = s2 + gap - 1 < array.length ? s2 + gap - 1 : array.length - 1; int[] temp = new int[array.length]; int k = 0; while (s2 < array.length) { while (s1 <= e1 && s2 <= e2) { if (array[s1] <= array[s2]) { temp[k++] = array[s1++]; } else { temp[k++] = array[s2++]; } } while (s1 <= e1) { temp[k++] = array[s1++]; } while (s2 <= e2) { temp[k++] = array[s2++]; } s1 = e2+1; e1 = s1+gap-1; s2 = e1+1; e2 = s2 + gap - 1 < array.length ? s2 + gap - 1 : array.length - 1; } while (s1 < array.length) { temp[k++] = array[s1++]; } for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) { array[i] = temp[i]; } } public static void mergeSortNor(int[] array) { for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i *= 2) { merge(array, i); } } }жөӢиҜ•д»Јз Ғпјҡ
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {10,3,2,7,19,78,65,127}; System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеүҚпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); MergeSortNor.mergeSortNor(array); System.out.println("жҺ’еәҸеҗҺпјҡ" + Arrays.toString(array)); } }иҜҘд»Јз Ғзҡ„жү§иЎҢз»“жһңдёәпјҡ
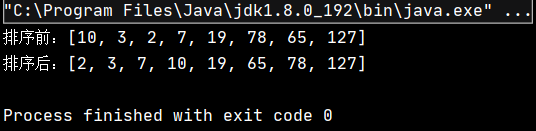
еҸҜи§ҒпјҢе®һзҺ°дәҶеҜ№еҺҹж•°з»„зҡ„еҚҮеәҸжҺ’еәҸгҖӮ
ж—¶й—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡ O(n * log(n))
з©әй—ҙеӨҚжқӮеәҰпјҡO(n)
зЁіе®ҡжҖ§пјҡзЁіе®ҡ
еӨ–йғЁжҺ’еәҸпјҡжҺ’еәҸиҝҮзЁӢйңҖиҰҒеңЁзЈҒзӣҳзӯүеӨ–йғЁеӯҳеӮЁиҝӣиЎҢзҡ„жҺ’еәҸ
еүҚжҸҗпјҡеҶ…еӯҳеҸӘжңү 1GпјҢйңҖиҰҒжҺ’еәҸзҡ„ж•°жҚ®жңү 100G
еӣ дёәеҶ…еӯҳдёӯеӣ дёәж— жі•жҠҠжүҖжңүж•°жҚ®е…ЁйғЁж”ҫдёӢпјҢжүҖд»ҘйңҖиҰҒеӨ–йғЁжҺ’еәҸпјҢиҖҢеҪ’并жҺ’еәҸжҳҜжңҖеёёз”Ёзҡ„еӨ–йғЁжҺ’еәҸгҖӮ
е…ҲжҠҠж–Ү件еҲҮеҲҶжҲҗ 200 д»ҪпјҢжҜҸдёӘ 512 M
еҲҶеҲ«еҜ№ 512 M жҺ’еәҸпјҢеӣ дёәеҶ…еӯҳе·Із»ҸеҸҜд»Ҙж”ҫзҡ„дёӢпјҢжүҖд»Ҙд»»ж„ҸжҺ’еәҸж–№ејҸйғҪеҸҜд»Ҙ
иҝӣиЎҢ 200 и·ҜеҪ’并пјҢеҗҢж—¶еҜ№ 200 д»ҪжңүеәҸж–Ү件еҒҡеҪ’并иҝҮзЁӢпјҢжңҖз»Ҳз»“жһңе°ұжңүеәҸдәҶ
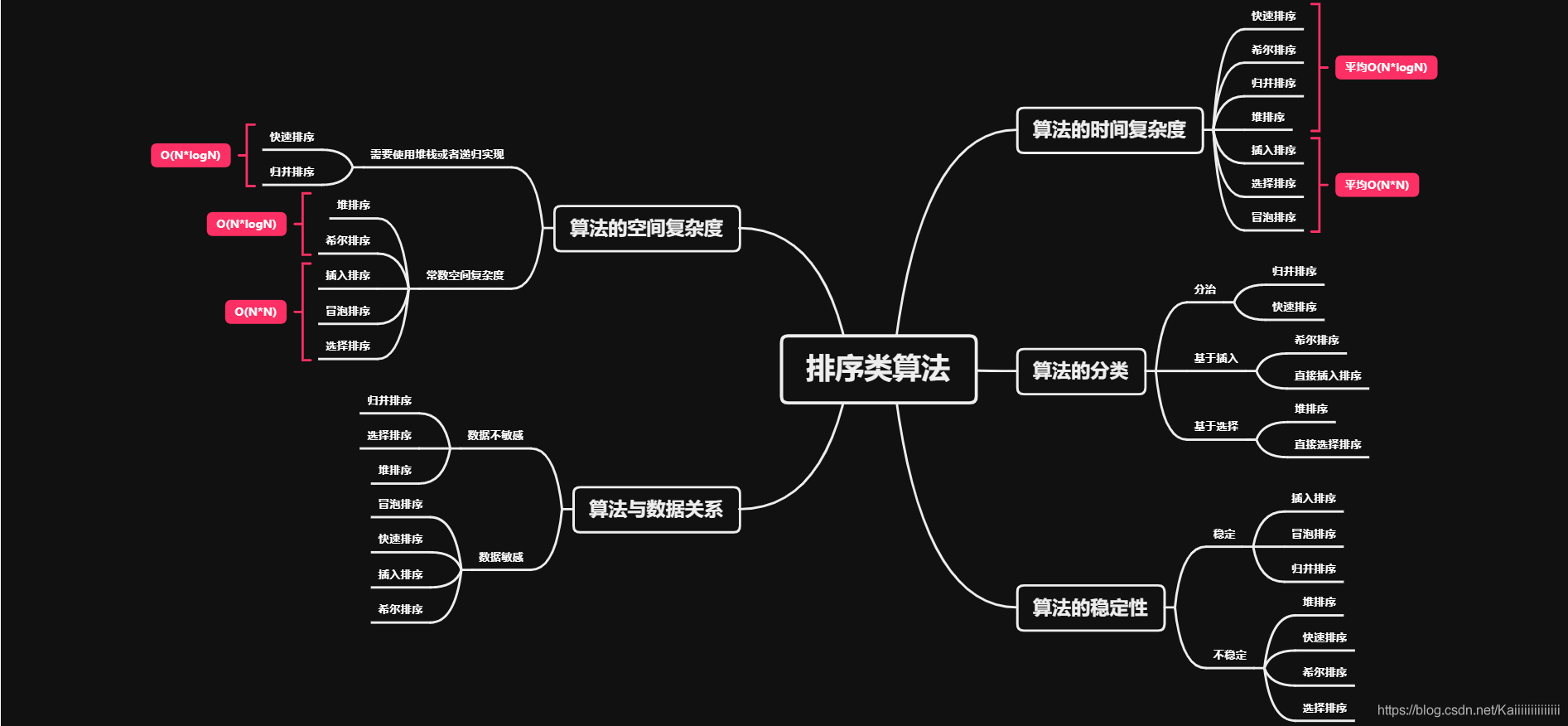
жҺ’еәҸжҖ»з»“
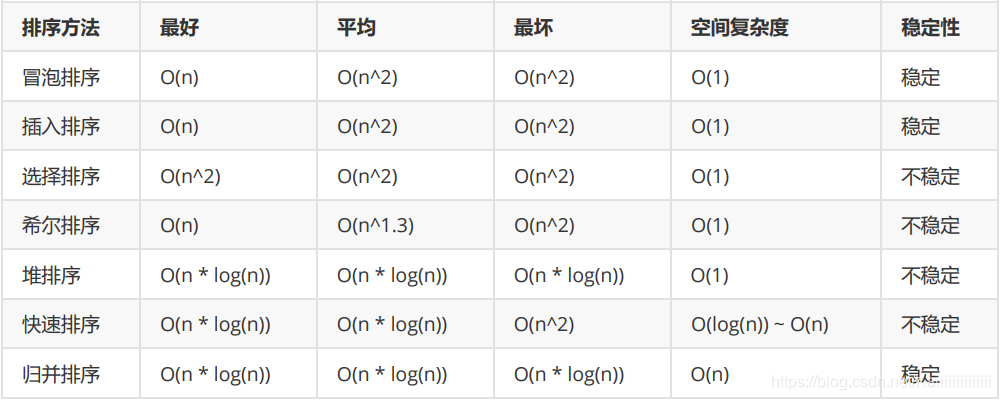
еҲ°жӯӨпјҢзӣёдҝЎеӨ§е®¶еҜ№вҖңJavaйӣҶеҗҲе’Ңж•°жҚ®з»“жһ„жҺ’еәҸзҡ„е®һдҫӢд»Ӣз»ҚвҖқжңүдәҶжӣҙж·ұзҡ„дәҶи§ЈпјҢдёҚеҰЁжқҘе®һйҷ…ж“ҚдҪңдёҖз•Әеҗ§пјҒиҝҷйҮҢжҳҜдәҝйҖҹдә‘зҪ‘з«ҷпјҢжӣҙеӨҡзӣёе…іеҶ…е®№еҸҜд»Ҙиҝӣе…Ҙзӣёе…ійў‘йҒ“иҝӣиЎҢжҹҘиҜўпјҢе…іжіЁжҲ‘们пјҢ继з»ӯеӯҰд№ пјҒ
е…ҚиҙЈеЈ°жҳҺпјҡжң¬з«ҷеҸ‘еёғзҡ„еҶ…е®№пјҲеӣҫзүҮгҖҒи§Ҷйў‘е’Ңж–Үеӯ—пјүд»ҘеҺҹеҲӣгҖҒиҪ¬иҪҪе’ҢеҲҶдә«дёәдё»пјҢж–Үз« и§ӮзӮ№дёҚд»ЈиЎЁжң¬зҪ‘з«ҷз«ӢеңәпјҢеҰӮжһңж¶үеҸҠдҫөжқғиҜ·иҒ”зі»з«ҷй•ҝйӮ®з®ұпјҡis@yisu.comиҝӣиЎҢдёҫжҠҘпјҢ并жҸҗдҫӣзӣёе…іиҜҒжҚ®пјҢдёҖз»ҸжҹҘе®һпјҢе°Ҷз«ӢеҲ»еҲ йҷӨж¶үе«ҢдҫөжқғеҶ…е®№гҖӮ