这篇文章主要为大家展示了“Python如何实现对照片中的人脸进行颜值预测”,内容简而易懂,条理清晰,希望能够帮助大家解决疑惑,下面让小编带领大家一起研究并学习一下“Python如何实现对照片中的人脸进行颜值预测”这篇文章吧。
**Python版本:**3.5.4(64bit)
opencv_python模块
sklearn模块
numpy模块
dlib模块
一些Python自带的模块。
(1)安装相应版本的Python并添加到环境变量中;
(2)pip安装相关模块中提到的模块。
例如:
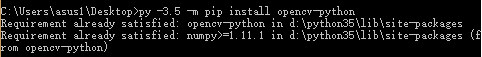
若pip安装报错,请自行到:
http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/
下载pip安装报错模块的whl文件,并使用:
pip install whl文件路径+whl文件名安装。
例如:
(已在相关文件中提供了编译好的用于dlib库安装的whl文件——>因为这个库最不好装)

参考文献链接
【1】xxxPh.D.的博客
http://www.learnopencv.com/computer-vision-for-predicting-facial-attractiveness/
【2】华南理工大学某实验室
http://www.hcii-lab.net/data/SCUT-FBP/EN/introduce.html
(1)模型训练
用了PCA算法对特征进行了压缩降维;
然后用随机森林训练模型。
数据源于网络,据说数据“发源地”就是华南理工大学某实验室,因此我在参考文献上才加上了这个实验室的链接。
(2)提取人脸关键点
主要使用了dlib库。
使用官方提供的模型构建特征提取器。
(3)特征生成
完全参考了xxxPh.D.的博客。
(4)颜值预测
利用之前的数据和模型进行颜值预测。
使用方式
有特殊疾病者请慎重尝试预测自己的颜值,本人不对颜值预测的结果和带来的所有负面影响负责!!!
言归正传。
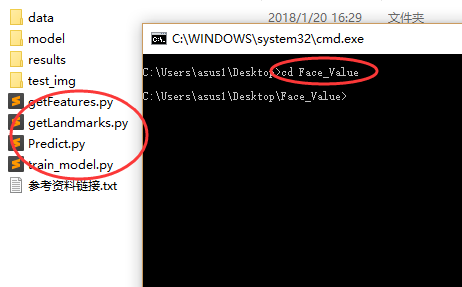
环境搭建完成后,解压相关文件中的Face_Value.rar文件,cmd窗口切换到解压后的*.py文件所在目录。
例如:
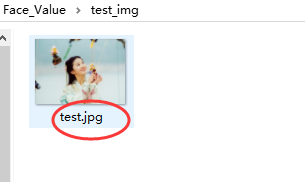
打开test_img文件夹,将需要预测颜值的照片放入并重命名为test.jpg。
例如:
若嫌麻烦或者有其他需求,请自行修改:
getLandmarks.py文件中第13行。
最后依次运行:
train_model.py(想直接用我模型的请忽略此步)
# 模型训练脚本 import numpy as np from sklearn import decomposition from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor from sklearn.externals import joblib # 特征和对应的分数路径 features_path = './data/features_ALL.txt' ratings_path = './data/ratings.txt' # 载入数据 # 共500组数据 # 其中前480组数据作为训练集,后20组数据作为测试集 features = np.loadtxt(features_path, delimiter=',') features_train = features[0: -20] features_test = features[-20: ] ratings = np.loadtxt(ratings_path, delimiter=',') ratings_train = ratings[0: -20] ratings_test = ratings[-20: ] # 训练模型 # 这里用PCA算法对特征进行了压缩和降维。 # 降维之后特征变成了20维,也就是说特征一共有500行,每行是一个人的特征向量,每个特征向量有20个元素。 # 用随机森林训练模型 pca = decomposition.PCA(n_components=20) pca.fit(features_train) features_train = pca.transform(features_train) features_test = pca.transform(features_test) regr = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=50, max_depth=None, min_samples_split=10, random_state=0) regr = regr.fit(features_train, ratings_train) joblib.dump(regr, './model/face_rating.pkl', compress=1) # 训练完之后提示训练结束 print('Generate Model Successfully!')getLandmarks.py
# 人脸关键点提取脚本 import cv2 import dlib import numpy # 模型路径 PREDICTOR_PATH = './model/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat' # 使用dlib自带的frontal_face_detector作为人脸提取器 detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector() # 使用官方提供的模型构建特征提取器 predictor = dlib.shape_predictor(PREDICTOR_PATH) face_img = cv2.imread("test_img/test.jpg") # 使用detector进行人脸检测,rects为返回的结果 rects = detector(face_img, 1) # 如果检测到人脸 if len(rects) >= 1: print("{} faces detected".format(len(rects))) else: print('No faces detected') exit() with open('./results/landmarks.txt', 'w') as f: f.truncate() for faces in range(len(rects)): # 使用predictor进行人脸关键点识别 landmarks = numpy.matrix([[p.x, p.y] for p in predictor(face_img, rects[faces]).parts()]) face_img = face_img.copy() # 使用enumerate函数遍历序列中的元素以及它们的下标 for idx, point in enumerate(landmarks): pos = (point[0, 0], point[0, 1]) f.write(str(point[0, 0])) f.write(',') f.write(str(point[0, 1])) f.write(',') f.write('\n') f.close() # 成功后提示 print('Get landmarks successfully')getFeatures.py
# 特征生成脚本 # 具体原理请参见参考论文 import math import numpy import itertools def facialRatio(points): x1 = points[0] y1 = points[1] x2 = points[2] y2 = points[3] x3 = points[4] y3 = points[5] x4 = points[6] y4 = points[7] dist1 = math.sqrt((x1-x2)**2 + (y1-y2)**2) dist2 = math.sqrt((x3-x4)**2 + (y3-y4)**2) ratio = dist1/dist2 return ratio def generateFeatures(pointIndices1, pointIndices2, pointIndices3, pointIndices4, allLandmarkCoordinates): size = allLandmarkCoordinates.shape if len(size) > 1: allFeatures = numpy.zeros((size[0], len(pointIndices1))) for x in range(0, size[0]): landmarkCoordinates = allLandmarkCoordinates[x, :] ratios = [] for i in range(0, len(pointIndices1)): x1 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices1[i]-1)] y1 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices1[i] - 1] x2 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices2[i]-1)] y2 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices2[i] - 1] x3 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices3[i]-1)] y3 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices3[i] - 1] x4 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices4[i]-1)] y4 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices4[i] - 1] points = [x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4] ratios.append(facialRatio(points)) allFeatures[x, :] = numpy.asarray(ratios) else: allFeatures = numpy.zeros((1, len(pointIndices1))) landmarkCoordinates = allLandmarkCoordinates ratios = [] for i in range(0, len(pointIndices1)): x1 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices1[i]-1)] y1 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices1[i] - 1] x2 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices2[i]-1)] y2 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices2[i] - 1] x3 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices3[i]-1)] y3 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices3[i] - 1] x4 = landmarkCoordinates[2*(pointIndices4[i]-1)] y4 = landmarkCoordinates[2*pointIndices4[i] - 1] points = [x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4] ratios.append(facialRatio(points)) allFeatures[0, :] = numpy.asarray(ratios) return allFeatures def generateAllFeatures(allLandmarkCoordinates): a = [18, 22, 23, 27, 37, 40, 43, 46, 28, 32, 34, 36, 5, 9, 13, 49, 55, 52, 58] combinations = itertools.combinations(a, 4) i = 0 pointIndices1 = [] pointIndices2 = [] pointIndices3 = [] pointIndices4 = [] for combination in combinations: pointIndices1.append(combination[0]) pointIndices2.append(combination[1]) pointIndices3.append(combination[2]) pointIndices4.append(combination[3]) i = i+1 pointIndices1.append(combination[0]) pointIndices2.append(combination[2]) pointIndices3.append(combination[1]) pointIndices4.append(combination[3]) i = i+1 pointIndices1.append(combination[0]) pointIndices2.append(combination[3]) pointIndices3.append(combination[1]) pointIndices4.append(combination[2]) i = i+1 return generateFeatures(pointIndices1, pointIndices2, pointIndices3, pointIndices4, allLandmarkCoordinates) landmarks = numpy.loadtxt("./results/landmarks.txt", delimiter=',', usecols=range(136)) featuresALL = generateAllFeatures(landmarks) numpy.savetxt("./results/my_features.txt", featuresALL, delimiter=',', fmt = '%.04f') print("Generate Feature Successfully!")Predict.py
# 颜值预测脚本 from sklearn.externals import joblib import numpy as np from sklearn import decomposition pre_model = joblib.load('./model/face_rating.pkl') features = np.loadtxt('./data/features_ALL.txt', delimiter=',') my_features = np.loadtxt('./results/my_features.txt', delimiter=',') pca = decomposition.PCA(n_components=20) pca.fit(features) predictions = [] if len(my_features.shape) > 1: for i in range(len(my_features)): feature = my_features[i, :] feature_transfer = pca.transform(feature.reshape(1, -1)) predictions.append(pre_model.predict(feature_transfer)) print('照片中的人颜值得分依次为(满分为5分):') k = 1 for pre in predictions: print('第%d个人:' % k, end='') print(str(pre)+'分') k += 1 else: feature = my_features feature_transfer = pca.transform(feature.reshape(1, -1)) predictions.append(pre_model.predict(feature_transfer)) print('照片中的人颜值得分为(满分为5分):') k = 1 for pre in predictions: print(str(pre)+'分') k += 1以上是“Python如何实现对照片中的人脸进行颜值预测”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的内容对大家有所帮助,如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。