这篇文章主要讲解了“Java模拟退火算法优化Hash函数的方法”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“Java模拟退火算法优化Hash函数的方法”吧!
一、背景
二、放弃 hash 函数
三、优化 hash 函数
3.1、评价函数
3.2、训练策略
3.3、ForkJoin 框架
3.4、效果
现有个处理股票行情消息的系统,其架构如下:
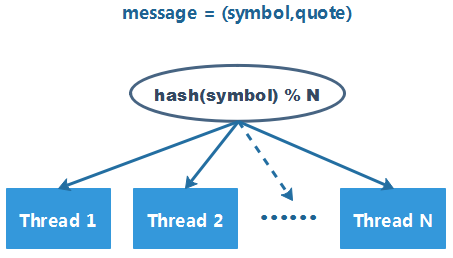
由于数据量巨大,系统中启动了 15 个线程来消费行情消息。消息分配的策略较为简单:对 symbol 的 hashCode 取模,将消息分配给其中一个线程进行处理。 经过验证,每个线程分配到的 symbol 数量较为均匀,于是系统愉快地上线了。
运行一段时间后,突然收到了系统的告警,但此时并非消息峰值时间段。经过排查后,发现问题出现在 hash 函数上:
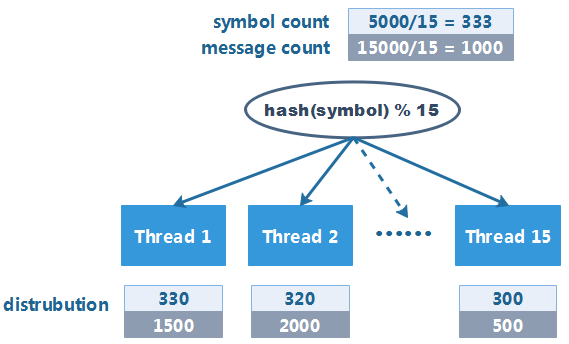
虽然每个线程被分配到的 symbol 数量较为均衡,但是部分热门 symbol 的报价消息量会更多,如果热门 symbol 集中到特定线程上,就会造成线程负载不均衡,使得系统整体的吞吐量大打折扣。
为提高系统的吞吐量,有必要消息分发逻辑进行一些改造,避免出现热点线程。为此,系统需要记录下某天内每个 symbol 的消息量,然后在第二天使用这些数据,对分发逻辑进行调整。具体的改造的方案可以分为两种:
放弃使用 hash 函数
对 hash 函数进行优化
问题可以抽象为:
将 5000 个非负整数分配至 15 个桶(bucket)中,并尽可能保证每个桶中的元素之和接近(每个桶中的元素个数无限制)。
每个整数元素可能的放置方法有 15 种,这个问题总共可能的解有 155000种,暴力求解的可能性微乎其微。作为工程问题,最优解不是必要的,可以退而求其次寻找一个可接受的次优解:
根据所有 symbol 的消息总数计算一个期望的分布均值(expectation)。将每个 symbol 的消息数按照 symbol 的顺序进行排列,最后将这组数组划分为 15 个区间,并且尽可能使得每个区间元素之和与 expection 接近。使用一个有序查找表记录每个区间的首个 symbol,后续就可以按照这个表对数据进行划分。
public class FindBestDistribution { static final int NUM_OF_SYMBOLS = 5000; static final int NUM_OF_BUCKETS = 15; public static void main(String[] args) { // 生成样本 IntStream ints = ThreadLocalRandom.current().ints(0, 1000); PrimitiveIterator.OfInt iterator = ints.iterator(); Map<String,Integer> symbolAndCount = new TreeMap<>(); for (int i=0; i<NUM_OF_SYMBOLS; i++) { symbolAndCount.put(Integer.toHexString(i).toUpperCase(), iterator.next()); } // 按照 symbol 划分每个桶的数量 TreeMap<String, Integer> distribution = findBestDistribution(symbolAndCount); // 测试效果 int[] buckets = new int[NUM_OF_BUCKETS]; for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : symbolAndCount.entrySet()) { Map.Entry<String, Integer> floor = distribution.floorEntry(entry.getKey()); int bucketIndex = floor == null ? 0 : floor.getValue(); buckets[bucketIndex] += entry.getValue(); } System.out.printf("buckets: %s\n", Arrays.toString(buckets)); } public static TreeMap<String, Integer> findBestDistribution(Map<String,Integer> symbolAndCount) { // 每个桶均匀分布的情况(最优情况) int avg = symbolAndCount.values().stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum() / NUM_OF_BUCKETS; // 尝试将 symbol 放入不同的桶 int bucketIdx = 0; int[] buckets = new int[NUM_OF_BUCKETS]; String[] bulkheads = new String[NUM_OF_BUCKETS-1]; for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : symbolAndCount.entrySet()) { // 如果首个 symbol 数据量过大,则分配给其一个独立的桶 int count = entry.getValue(); if (count / 2 > avg && bucketIdx == 0 && buckets[0] == 0) { buckets[bucketIdx] += count; continue; } // 评估将 symbol 放入桶后的效果 // 1. 如果桶中的数量更接近期望,则将其放入当前桶中 // 2. 如果桶中的数量更远离期望,则将其放入下个桶中 double before = Math.abs(buckets[bucketIdx] - avg); double after = Math.abs(buckets[bucketIdx] + count - avg); if (after > before && bucketIdx < buckets.length - 1) { bulkheads[bucketIdx++] = entry.getKey(); } buckets[bucketIdx] += count; } System.out.printf("expectation: %d\n", avg); System.out.printf("bulkheads: %s\n", Arrays.toString(bulkheads)); TreeMap<String,Integer> distribution = new TreeMap<>(); for (int i=0; i<bulkheads.length; i++) { distribution.put(bulkheads[i], i+1); } return distribution; } }该方法存在的问题:
分配策略并不是最优解,且无法对其分片效果进行直观的评估。
当区间数量较多时,查找表本身可能成为一个潜在的性能瓶颈。
可能的组合受到 key 的顺序限制,极大地限制了可能的解空间。
换个角度来看,造成分布不均匀的原因不是数据,而是 hash 函数本身。
项目中使用的 hash 函数是 JDK String 中的原生实现。经过查阅资料,发现该实现其实是 BKDRHash 的 seed = 31 的特殊情况。这样意味着:通过调整 seed 的值,可以改变 hash 函数的特性并使其适配特定的数据分布。
int BKDRHash(char[] value, int seed) { int hash = 0; for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) { hash = hash * seed + value[i]; } return hash & 0x7fffffff; }那么问题来了,应该如何评估某个 seed 的分布的优劣?
一种可行的方法是计算每个 seed 对应的 bucket 分布的标准差,标准差越小则分布越均匀,则该 seed 越优。
然而这一做法只考虑了每个 bucket 与均值之间的误差,无法量化不同 bucket 之间的误差。为了能够直观的量化 bucket 之间分布差异的情况,考虑使用下面的评估函数:
ouble calculateDivergence(long[] bucket, long expectation) { long divergence = 0; for (int i=0; i<bucket.length; i++) { final long a = bucket[i]; final long b = (a - expectation) * (a - expectation); for (int j=i+1; j<bucket.length; j++) { long c = (a - bucket[j]) * (a - bucket[j]); divergence += Math.max(b, c); } } return divergence; // the less the better }该数值越小,则证明 seed 对应的分布越均匀,其对应的 hash 函数越优。
seed 是一个 32bit 的无符号整数,其取值范围为 0 ~ 232-1。在 5000 个 symbol 的情况下,单线程尝试遍历所有 seed 的时间约为 25 小时。
通常情况下 symbol 的数量会超过 5000,因此实际的搜索时间会大于这个值。此外,受限于计算资源限制,无法进行大规模的并行搜索,因此穷举法的耗时是不可接受的。
幸好本例并不要求最优解,可以引入启发式搜索算法,加快训练速度。由于本人在这方面并不熟悉,为了降低编程难度,最终选择了模拟退火(simulated annealing)算法。它模拟固体退火过程的热平衡问题与随机搜索寻优问题的相似性来达到寻找全局最优或近似全局最优的目的。
相较于最简单的爬山法,模拟退火算法通以一定的概率接受较差的解,从而扩大搜索范围,保证解近似最优。
/** * Basic framework of simulated annealing algorithm * @param <X> the solution of given problem */ public abstract class SimulatedAnnealing<X> { protected final int numberOfIterations; // stopping condition for simulations protected final double coolingRate; // the percentage by which we reduce the temperature of the system protected final double initialTemperature; // the starting energy of the system protected final double minimumTemperature; // optional stopping condition protected final long simulationTime; // optional stopping condition protected final int detectionInterval; // optional stopping condition protected SimulatedAnnealing(int numberOfIterations, double coolingRate) { this(numberOfIterations, coolingRate, 10000000, 1, 0, 0); } protected SimulatedAnnealing(int numberOfIterations, double coolingRate, double initialTemperature, double minimumTemperature, long simulationTime, int detectionInterval) { this.numberOfIterations = numberOfIterations; this.coolingRate = coolingRate; this.initialTemperature = initialTemperature; this.minimumTemperature = minimumTemperature; this.simulationTime = simulationTime; this.detectionInterval = detectionInterval; } protected abstract double score(X currentSolution); protected abstract X neighbourSolution(X currentSolution); public X simulateAnnealing(X currentSolution) { final long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // Initialize searching X bestSolution = currentSolution; double bestScore = score(bestSolution); double currentScore = bestScore; double t = initialTemperature; for (int i = 0; i < numberOfIterations; i++) { if (currentScore < bestScore) { // If the new solution is better, accept it unconditionally bestScore = currentScore; bestSolution = currentSolution; } else { // If the new solution is worse, calculate an acceptance probability for the worse solution // At high temperatures, the system is more likely to accept the solutions that are worse boolean rejectWorse = Math.exp((bestScore - currentScore) / t) < Math.random(); if (rejectWorse || currentScore == bestScore) { currentSolution = neighbourSolution(currentSolution); currentScore = score(currentSolution); } } // Stop searching when the temperature is too low if ((t *= coolingRate) < minimumTemperature) { break; } // Stop searching when simulation time runs out if (simulationTime > 0 && (i+1) % detectionInterval == 0) { if (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime > simulationTime) break; } } return bestSolution; } } /** * Search best hash seed for given key distribution and number of buckets with simulated annealing algorithm */ @Data public class SimulatedAnnealingHashing extends SimulatedAnnealing<HashingSolution> { private static final int DISTRIBUTION_BATCH = 100; static final int SEARCH_BATCH = 200; private final int[] hashCodes = new int[SEARCH_BATCH]; private final long[][] buckets = new long[SEARCH_BATCH][]; @Data public class HashingSolution { private final int begin, range; // the begin and range for searching private int bestSeed; // the best seed found in this search private long bestScore; // the score corresponding to bestSeed private long calculateDivergence(long[] bucket) { long divergence = 0; for (int i=0; i<bucket.length; i++) { final long a = bucket[i]; final long b = (a - expectation) * (a - expectation); for (int j=i+1; j<bucket.length; j++) { long c = (a - bucket[j]) * (a - bucket[j]); divergence += Math.max(b, c); } } return divergence; // the less the better } private HashingSolution solve() { if (range != hashCodes.length) { throw new IllegalStateException(); } for (int i=0; i<range; i++) { Arrays.fill(buckets[i], hashCodes[i] = 0); } for (KeyDistribution[] bucket : distributions) { for (KeyDistribution distribution : bucket) { Hashing.BKDRHash(distribution.getKey(), begin, hashCodes); for (int k = 0; k< hashCodes.length; k++) { int n = hashCodes[k] % buckets[k].length; buckets[k][n] += distribution.getCount(); } } } int best = -1; long bestScore = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int i = 0; i< buckets.length; i++) { long score = calculateDivergence(buckets[i]); if (i == 0 || score < bestScore) { bestScore = score; best = i; } } if (best < 0) { throw new IllegalStateException(); } this.bestScore = bestScore; this.bestSeed = begin + best; return this; } @Override public String toString() { return String.format("(seed:%d, score:%d)", bestSeed, bestScore); } } private final KeyDistribution[][] distributions; // key and its count(2-dimensional array for better performance) private final long expectation; // the expectation count of each bucket private final int searchOutset; private int searchMin, searchMax; /** * SimulatedAnnealingHashing Prototype * @param keyAndCounts keys for hashing and count for each key * @param numOfBuckets number of buckets */ public SimulatedAnnealingHashing(Map<String, Integer> keyAndCounts, int numOfBuckets) { super(100000000, .9999); distributions = buildDistribution(keyAndCounts); long sum = 0; for (KeyDistribution[] batch : distributions) { for (KeyDistribution distribution : batch) { sum += distribution.getCount(); } } this.expectation = sum / numOfBuckets; this.searchOutset = 0; for (int i = 0; i< buckets.length; i++) { buckets[i] = new long[numOfBuckets]; } } /** * SimulatedAnnealingHashing Derivative * @param prototype prototype simulation * @param searchOutset the outset for searching * @param simulationTime the expect time consuming for simulation */ private SimulatedAnnealingHashing(SimulatedAnnealingHashing prototype, int searchOutset, long simulationTime) { super(prototype.numberOfIterations, prototype.coolingRate, prototype.initialTemperature, prototype.minimumTemperature, simulationTime, 10000); distributions = prototype.distributions; expectation = prototype.expectation; for (int i = 0; i< buckets.length; i++) { buckets[i] = new long[prototype.buckets[i].length]; } this.searchOutset = searchOutset; this.searchMax = searchMin = searchOutset; } @Override public String toString() { return String.format("expectation: %d, outset:%d, search(min:%d, max:%d)", expectation, searchOutset, searchMin, searchMax); } private KeyDistribution[][] buildDistribution(Map<String, Integer> symbolCounts) { int bucketNum = symbolCounts.size() / DISTRIBUTION_BATCH + Integer.signum(symbolCounts.size() % DISTRIBUTION_BATCH); KeyDistribution[][] distributions = new KeyDistribution[bucketNum][]; int bucketIndex = 0; List<KeyDistribution> batch = new ArrayList<>(DISTRIBUTION_BATCH); for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : symbolCounts.entrySet()) { batch.add(new KeyDistribution(entry.getKey().toCharArray(), entry.getValue())); if (batch.size() == DISTRIBUTION_BATCH) { distributions[bucketIndex++] = batch.toArray(new KeyDistribution[0]); batch.clear(); } } if (batch.size() > 0) { distributions[bucketIndex] = batch.toArray(new KeyDistribution[0]); batch.clear(); } return distributions; } @Override protected double score(HashingSolution currentSolution) { return currentSolution.solve().bestScore; } @Override protected HashingSolution neighbourSolution(HashingSolution currentSolution) { // The default range of neighbourhood is [-100, 100] int rand = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(-100, 101); int next = currentSolution.begin + rand; searchMin = Math.min(next, searchMin); searchMax = Math.max(next, searchMax); return new HashingSolution(next, currentSolution.range); } public HashingSolution solve() { searchMin = searchMax = searchOutset; HashingSolution initialSolution = new HashingSolution(searchOutset, SEARCH_BATCH); return simulateAnnealing(initialSolution); } public SimulatedAnnealingHashing derive(int searchOutset, long simulationTime) { return new SimulatedAnnealingHashing(this, searchOutset, simulationTime); } }为了达到更好的搜索效果,可以将整个搜索区域递归地划分为两两相邻的区域,然后在这些区域上执行并发的搜索,并递归地合并相邻区域的搜索结果。
使用 JDK 提供的 ForkJoinPool 与 RecursiveTask 能很好地完成以上任务。
@Data @Slf4j public class HashingSeedCalculator { /** * Recursive search task */ private class HashingSeedCalculatorSearchTask extends RecursiveTask<HashingSolution> { private SimulatedAnnealingHashing simulation; private final int level; private final int center, range; private HashingSeedCalculatorSearchTask() { this.center = 0; this.range = Integer.MAX_VALUE / SimulatedAnnealingHashing.SEARCH_BATCH; this.level = traversalDepth; this.simulation = hashingSimulation; } private HashingSeedCalculatorSearchTask(HashingSeedCalculatorSearchTask parent, int center, int range) { this.center = center; this.range = range; this.level = parent.level - 1; this.simulation = parent.simulation; } @Override protected HashingSolution compute() { if (level == 0) { long actualCenter = center * SimulatedAnnealingHashing.SEARCH_BATCH; log.info("Searching around center {}", actualCenter); HashingSolution solution = simulation.derive(center, perShardRunningMills).solve(); log.info("Searching around center {} found {}", actualCenter, solution); return solution; } else { int halfRange = range / 2; int leftCenter = center - halfRange, rightCenter = center + halfRange; ForkJoinTask<HashingSolution> leftTask = new HashingSeedCalculatorSearchTask(this, leftCenter, halfRange).fork(); ForkJoinTask<HashingSolution> rightTask = new HashingSeedCalculatorSearchTask(this, rightCenter, halfRange).fork(); HashingSolution left = leftTask.join(); HashingSolution right = rightTask.join(); return left.getBestScore() < right.getBestScore() ? left : right; } } } private final int poolParallelism; private final int traversalDepth; private final long perShardRunningMills; private final SimulatedAnnealingHashing hashingSimulation; /** * HashingSeedCalculator * @param numberOfShards the shard of the whole search range [Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE] * @param totalRunningHours the expect total time consuming for searching * @param symbolCounts the key and it`s distribution * @param numOfBuckets the number of buckets */ public HashingSeedCalculator(int numberOfShards, int totalRunningHours, Map<String, Integer> symbolCounts, int numOfBuckets) { int n = (int) (Math.log(numberOfShards) / Math.log(2)); if (Math.pow(2, n) != numberOfShards) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(); } this.traversalDepth = n; this.poolParallelism = Math.max(ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism() / 3 * 2, 1); // conservative estimation for parallelism this.perShardRunningMills = TimeUnit.HOURS.toMillis(totalRunningHours * poolParallelism) / numberOfShards; this.hashingSimulation = new SimulatedAnnealingHashing(symbolCounts, numOfBuckets); } @Override public String toString() { int numberOfShards = (int) Math.pow(2, traversalDepth); int totalRunningHours = (int) TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toHours(perShardRunningMills * numberOfShards) / poolParallelism; return "HashingSeedCalculator(" + "numberOfShards: " + numberOfShards + ", perShardRunningMinutes: " + TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toMinutes(perShardRunningMills) + ", totalRunningHours: " + totalRunningHours + ", poolParallelism: " + poolParallelism + ", traversalDepth: " + traversalDepth + ")"; } public synchronized HashingSolution searchBestSeed() { long now = System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info("SearchBestSeed start"); ForkJoinTask<HashingSolution> root = new HashingSeedCalculatorSearchTask().fork(); HashingSolution initSolution = hashingSimulation.derive(0, perShardRunningMills).solve(); HashingSolution bestSolution = root.join(); log.info("Found init solution {}", initSolution); log.info("Found best solution {}", bestSolution); if (initSolution.getBestScore() < bestSolution.getBestScore()) { bestSolution = initSolution; } long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - now; log.info("SearchBestSeed finish (cost:{}ms)", cost); return bestSolution; } }将改造后的代码部署到测试环境后,某日训练日志:
12:49:15.227 85172866 INFO hash.HashingSeedCalculator - Found init solution (seed:15231, score:930685828341164)
12:49:15.227 85172866 INFO hash.HashingSeedCalculator - Found best solution (seed:362333, score:793386389726926)
12:49:15.227 85172866 INFO hash.HashingSeedCalculator - SearchBestSeed finish (cost:10154898ms)
12:49:15.227 85172866 INFO hash.TrainingService -
Training result: (seed:362333, score:793386389726926)
Buckets: 15
Expectation: 44045697
Result of Hashing.HashCode(seed=362333): 21327108 [42512742, 40479608, 43915771, 47211553, 45354264, 43209190, 43196570, 44725786, 41999747, 46450288, 46079231, 45116615, 44004021, 43896194, 42533877]
Result of Hashing.HashCode(seed=31): 66929172 [39723630, 48721463, 43365391, 46301448, 43931616, 44678194, 39064877, 45922454, 43171141, 40715060, 33964547, 49709090, 58869949, 34964729, 47581868]
当晚使用 BKDRHash(seed=31) 对新的交易日数据的进行分片:
04:00:59.001 partition messages per minute [45171, 68641, 62001, 80016, 55977, 61916, 55102, 49322, 55982, 57081, 51100, 70437, 135992, 37823, 58552] , messages total [39654953, 48666261, 43310578, 46146841, 43834832, 44577454, 38990331, 45871075, 43106710, 40600708, 33781629, 49752592, 58584246, 34928991, 47545369]
当晚使用 BKDRHash(seed=362333) 对新的交易日数据的进行分片:
04:00:59.001 partition messages per minute [62424, 82048, 64184, 47000, 57206, 69439, 64430, 60096, 46986, 58182, 54557, 41523, 64310, 72402, 100326] , messages total [44985772, 48329212, 39995385, 43675702, 45216341, 45524616, 41335804, 44917938, 44605376, 44054821, 43371892, 42068637, 44000817, 42617562, 44652695]
对比日志发现 hash 经过优化后,分区的均匀程度有了显著的上升,并且热点分片也被消除了,基本达到当初设想的优化效果。
感谢各位的阅读,以上就是“Java模拟退火算法优化Hash函数的方法”的内容了,经过本文的学习后,相信大家对Java模拟退火算法优化Hash函数的方法这一问题有了更深刻的体会,具体使用情况还需要大家实践验证。这里是亿速云,小编将为大家推送更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。