rabbitmq怎么在springboot中使用?相信很多没有经验的人对此束手无策,为此本文总结了问题出现的原因和解决方法,通过这篇文章希望你能解决这个问题。
概述
RabbitMQ是一个开源的消息代理和队列服务器,用来通过普通协议在完全不同的应用之间共享数据,或者简单地将作业队列以便让分布式服务器进行处理。
它现实了AMQP协议,并且遵循Mozilla Public License开源协议,它支持多种语言,可以方便的和spring集成。
消息队列使用消息将应用程序连接起来,这些消息通过像RabbitMQ这样的消息代理服务器在应用程序之间路由。
基本概念
Broker
用来处理数据的消息队列服务器实体
vhost
由RabbitMQ服务器创建的虚拟消息主机,拥有自己的权限机制,一个broker里可以开设多个vhost,用于不同用户的权限隔离,vhost之间是也完全隔离的。
productor
产生用于消息通信的数据
channel
消息通道,在AMQP中可以建立多个channel,每个channel代表一个会话任务。
exchange
direct
转发消息到routing-key指定的队列
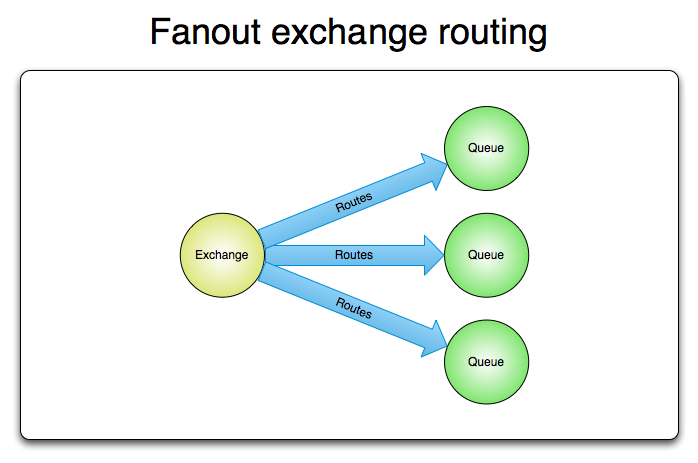
 fanout
fanout
fanout
转发消息到所有绑定的队列,类似于一种广播发送的方式。
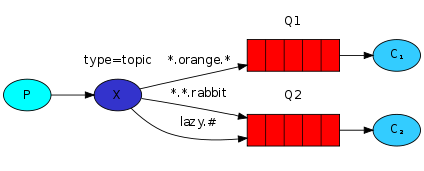
 topic
topic
topic
按照规则转发消息,这种规则多为模式匹配,也显得更加灵活
 queue
queue
queue
队列是RabbitMQ的内部对象,存储消息
以动态的增加消费者,队列将接受到的消息以轮询(round-robin)的方式均匀的分配给多个消费者。
binding
表示交换机和队列之间的关系,在进行绑定时,带有一个额外的参数binding-key,来和routing-key相匹配。
consumer
监听消息队列来进行消息数据的读取
springboot下三种Exchange模式(fanout,direct,topic)实现
pom.xml中引用spring-boot-starter-amqp
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId> </dependency>
增加rabbitmq配置
spring: rabbitmq: host: localhost port: 5672 username: guest password: guest
direct
direct模式一般情况下只需要定义queue 使用自带交换机(defaultExchange)无需绑定交换机
@Configuration public class RabbitP2PConfigure { public static final String QUEUE_NAME = "p2p-queue"; @Bean public Queue queue() { return new Queue(QUEUE_NAME, true); } }@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = BootCoreTestApplication.class) @Slf4j public class RabbitTest { @Autowired private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate; /** * 发送 */ @Test public void sendLazy() throws InterruptedException { City city = new City(234556666L, "direct_name", "direct_code"); amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitLazyConfigure.QUEUE_NAME, city); } /** * 领取 */ @Test public void receive() throws InterruptedException { Object obj = amqpTemplate.receiveAndConvert(RabbitLazyConfigure.QUEUE_NAME); Assert.notNull(obj, ""); log.debug(obj.toString()); } }适用场景:点对点
fanout
fanout则模式需要将多个queue绑定在同一个交换机上
@Configuration public class RabbitFanoutConfigure { public static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "fanout-exchange"; public static final String FANOUT_A = "fanout.A"; public static final String FANOUT_B = "fanout.B"; public static final String FANOUT_C = "fanout.C"; @Bean public Queue AMessage() { return new Queue(FANOUT_A); } @Bean public Queue BMessage() { return new Queue(FANOUT_B); } @Bean public Queue CMessage() { return new Queue(FANOUT_C); } @Bean public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() { return new FanoutExchange(EXCHANGE_NAME); } @Bean public Binding bindingExchangeA(Queue AMessage, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(AMessage).to(fanoutExchange); } @Bean public Binding bindingExchangeB(Queue BMessage, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(BMessage).to(fanoutExchange); } @Bean public Binding bindingExchangeC(Queue CMessage, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(CMessage).to(fanoutExchange); } }发送者
@Slf4j public class Sender { @Autowired private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate; public void sendFanout(Object message) { log.debug("begin send fanout message<" + message + ">"); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitFanoutConfigure.EXCHANGE_NAME, "", message); } }我们可以通过@RabbitListener监听多个queue来进行消费
@Slf4j @RabbitListener(queues = { RabbitFanoutConfigure.FANOUT_A, RabbitFanoutConfigure.FANOUT_B, RabbitFanoutConfigure.FANOUT_C }) public class Receiver { @RabbitHandler public void receiveMessage(String message) { log.debug("Received <" + message + ">"); } }适用场景
- 大规模多用户在线(MMO)游戏可以使用它来处理排行榜更新等全局事件
- 体育新闻网站可以用它来近乎实时地将比分更新分发给移动客户端
- 分发系统使用它来广播各种状态和配置更新
- 在群聊的时候,它被用来分发消息给参与群聊的用户
topic
这种模式较为复杂,简单来说,就是每个队列都有其关心的主题,所有的消息都带有一个“标题”,Exchange会将消息转发到所有关注主题能与RouteKey模糊匹配的队列。
在进行绑定时,要提供一个该队列关心的主题,如“topic.# (“#”表示0个或若干个关键字,“*”表示一个关键字。 )
@Configuration public class RabbitTopicConfigure { public static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "topic-exchange"; public static final String TOPIC = "topic"; public static final String TOPIC_A = "topic.A"; public static final String TOPIC_B = "topic.B"; @Bean public Queue queueTopic() { return new Queue(RabbitTopicConfigure.TOPIC); } @Bean public Queue queueTopicA() { return new Queue(RabbitTopicConfigure.TOPIC_A); } @Bean public Queue queueTopicB() { return new Queue(RabbitTopicConfigure.TOPIC_B); } @Bean public TopicExchange exchange() { TopicExchange topicExchange = new TopicExchange(EXCHANGE_NAME); topicExchange.setDelayed(true); return new TopicExchange(EXCHANGE_NAME); } @Bean public Binding bindingExchangeTopic(Queue queueTopic, TopicExchange exchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(queueTopic).to(exchange).with(RabbitTopicConfigure.TOPIC); } @Bean public Binding bindingExchangeTopics(Queue queueTopicA, TopicExchange exchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(queueTopicA).to(exchange).with("topic.#"); } }同时去监听三个queue
@Slf4j @RabbitListener(queues = { RabbitTopicConfigure.TOPIC, RabbitTopicConfigure.TOPIC_A, RabbitTopicConfigure.TOPIC_B }) public class Receiver { @RabbitHandler public void receiveMessage(String message) { log.debug("Received <" + message + ">"); } }通过测试我们可以发现
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = BootCoreTestApplication.class) public class RabbitTest { @Autowired private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate; @Test public void sendAll() { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitTopicConfigure.EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic.test", "send All"); } @Test public void sendTopic() { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitTopicConfigure.EXCHANGE_NAME, RabbitTopicConfigure.TOPIC, "send Topic"); } @Test public void sendTopicA() { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitTopicConfigure.EXCHANGE_NAME, RabbitTopicConfigure.TOPIC_A, "send TopicA"); } }适用场景
- 分发有关于特定地理位置的数据,例如销售点
- 由多个工作者(workers)完成的后台任务,每个工作者负责处理某些特定的任务
- 股票价格更新(以及其他类型的金融数据更新)
- 涉及到分类或者标签的新闻更新(例如,针对特定的运动项目或者队伍)
- 云端的不同种类服务的协调
- 分布式架构/基于系统的软件封装,其中每个构建者仅能处理一个特定的架构或者系统。
延迟队列
延迟消费:
如用户生成订单之后,需要过一段时间校验订单的支付状态,如果订单仍未支付则需要及时地关闭订单。
用户注册成功之后,需要过一段时间比如一周后校验用户的使用情况,如果发现用户活跃度较低,则发送邮件或者短信来提醒用户使用。
延迟重试:
如消费者从队列里消费消息时失败了,但是想要延迟一段时间后自动重试。
如果不使用延迟队列,那么我们只能通过一个轮询扫描程序去完成。这种方案既不优雅,也不方便做成统一的服务便于开发人员使用。但是使用延迟队列的话,我们就可以轻而易举地完成。
设置交换机延迟属性为true
@Configuration public class RabbitLazyConfigure { public static final String QUEUE_NAME = "lazy-queue-t"; public static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "lazy-exchange-t"; @Bean public Queue queue() { return new Queue(QUEUE_NAME, true); } @Bean public DirectExchange defaultExchange() { DirectExchange directExchange = new DirectExchange(EXCHANGE_NAME, true, false); directExchange.setDelayed(true); return directExchange; } @Bean public Binding binding() { return BindingBuilder.bind(queue()).to(defaultExchange()).with(QUEUE_NAME); } }发送时设置延迟时间即可
@Slf4j public class Sender { @Autowired private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate; public void sendLazy(Object msg) { log.debug("begin send lazy message<" + msg + ">"); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitLazyConfigure.EXCHANGE_NAME, RabbitLazyConfigure.QUEUE_NAME, msg, message -> { message.getMessageProperties().setHeader("x-delay", 10000); return message; } ); } }看完上述内容,你们掌握rabbitmq怎么在springboot中使用的方法了吗?如果还想学到更多技能或想了解更多相关内容,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道,感谢各位的阅读!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。