这篇文章给大家介绍怎么在Spring Boot中利用netty实现客户端服务端交互,内容非常详细,感兴趣的小伙伴们可以参考借鉴,希望对大家能有所帮助。
首先,当然是在SpringBoot项目里添加netty的依赖了,注意不要用netty5的依赖,因为已经废弃了
<!--netty--> <dependency> <groupId>io.netty</groupId> <artifactId>netty-all</artifactId> <version>4.1.32.Final</version> </dependency>
将端口和IP写入application.yml文件里,我这里是我云服务器的内网IP,如果是本机测试,用127.0.0.1就ok
netty: port: 7000 url: 172.16.0.7
在这之后,开始写netty的服务器,这里服务端的逻辑就是将客户端发来的信息返回回去
因为采用依赖注入的方法实例化netty,所以加上@Component注释
package com.safelocate.app.nettyServer; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.*; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; @Component public class NettyServer { //logger private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(NettyServer.class); public void start(InetSocketAddress address){ EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap() .group(bossGroup,workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .localAddress(address) .childHandler(new ServerChannelInitializer()) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); // 绑定端口,开始接收进来的连接 ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(address).sync(); logger.info("Server start listen at " + address.getPort()); future.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }当然,这里的ServerChannelInitializer是我自己定义的类,这个类是继承ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>的,里面设置出站和入站的编码器和解码器
package com.safelocate.app.nettyServer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder; import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; public class ServerChannelInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel channel) throws Exception { channel.pipeline().addLast("decoder",new StringDecoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); channel.pipeline().addLast("encoder",new StringEncoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); channel.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler()); } }最好注意被别decoder和encoder写成了一样的,不然会出问题(我之前就是不小心都写成了StringDecoder...)
在这之后就是设置ServerHandler来处理一些简单的逻辑了
package com.safelocate.app.nettyServer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.Socket; public class ServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { System.out.println("channelActive----->"); } @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { System.out.println("server channelRead......"); System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress()+"----->Server :"+ msg.toString()); //将客户端的信息直接返回写入ctx ctx.write("server say :"+msg); //刷新缓存区 ctx.flush(); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }准备工作到这里,现在要做到就是去启动这个程序
将AppApplication实现CommandLineRunner这个接口,这个接口可以用来再启动SpringBoot时同时启动其他功能,比如配置,数据库连接等等
然后重写run方法,在run方法里启动netty服务器,Server类用@AutoWired直接实例化
package com.safelocate.app; import com.safelocate.app.nettyServer.NettyServer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; @SpringBootApplication public class AppApplication implements CommandLineRunner { @Value("${netty.port}") private int port; @Value("${netty.url}") private String url; @Autowired private NettyServer server; public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(AppApplication.class, args); } @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(url,port); System.out.println("run .... . ... "+url); server.start(address); } }ok,到这里服务端已经写完,本地我也已经测试完,现在需要打包部署服务器,当然这个程序只为练手...
控制台输入mvn clean package -D skipTests 然后将jar包上传服务器,在这之后,需要在腾讯云/阿里云那边配置好安全组,将之前yml文件里设定的端口的入站
规则设置好,不然访问会被拒绝
之后java -jar命令运行,如果需保持后台一直运行 就用nohup命令,可以看到程序已经跑起来了,等待客户端连接交互
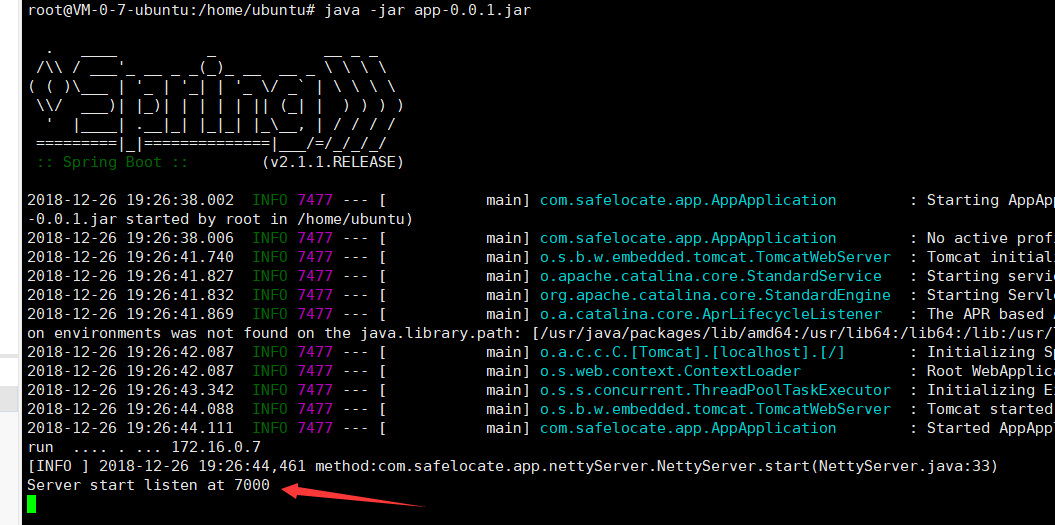
之后就是写客户端了,客户端其实是依葫芦画瓢,跟上面类似
Handler
package client; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter; public class ClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { System.out.println("ClientHandler Active"); } @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { System.out.println("--------"); System.out.println("ClientHandler read Message:"+msg); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }ChannelInitializer
package client; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder; import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; public class ClientChannelInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { protected void initChannel(SocketChannel channel) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline(); p.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); p.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); p.addLast(new ClientHandler()); } }主函数所在类,即客户端
package client; import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; import io.netty.channel.*; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder; public class Client { static final String HOST = System.getProperty("host", "服务器的IP地址"); static final int PORT = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("port", "7000")); static final int SIZE = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("size", "256")); public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { sendMessage("hhhh"); } public static void sendMessage(String content) throws InterruptedException{ // Configure the client. EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); b.group(group) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true) .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline(); p.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder()); p.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder()); p.addLast(new ClientHandler()); } }); ChannelFuture future = b.connect(HOST, PORT).sync(); future.channel().writeAndFlush(content); future.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { group.shutdownGracefully(); } } }启动客户端,这里就是简单发送一条"hhhh",可以看到客户端已经收到服务器发来的信息
 |
然后再看服务端,也有相应的信息打印
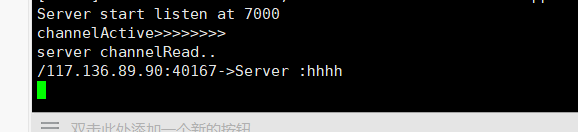
关于怎么在Spring Boot中利用netty实现客户端服务端交互就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。