Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn to use the SQL LIMIT clause to limit the number of rows returned from a query.
Introduction to SQL LIMIT clause #
To limit the number of rows returned by a SELECT statement, you use the LIMIT and OFFSET clauses.
Here’s the syntax of LIMIT & OFFSET clauses:
SELECT column_list FROM table1 ORDER BY column_list LIMIT row_count OFFSET row_to_skip;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
- The
LIMIT row_countdetermines the number of rows (row_count) returned by the query. - The
OFFSET row_to_skipclause skips therow_to_skip
The OFFSET clause is optional. If you omit it, the query will return the row_count rows from the first row returned by the SELECT clause.
When you use the LIMIT clause, it is important to use an ORDER BY clause to ensure the order of rows in the result set.
Not all database systems support the LIMIT clause. Therefore, the LIMIT clause is available only in some database systems such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Sybase SQL Anywhere, and HSQLDB.
If you use SQL Server, you can use the SELECT TOP instead.
SQL LIMIT clause examples #
We’ll use the employees table in the sample database to demonstrate the LIMITclause.

Limiting the number of rows to return #
The following query uses the LIMIT clause to return the first five employees sorted by first names:
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name FROM employees ORDER BY first_name LIMIT 5;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)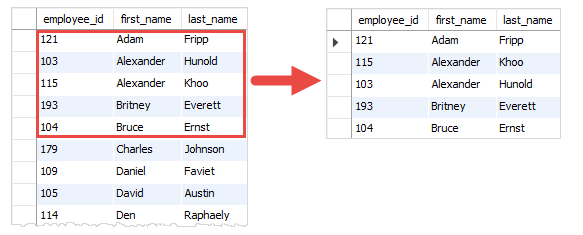
Using an offset #
The following query uses both LIMIT and OFFSET clauses to return five rows starting from the 4th row:
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name FROM employees ORDER BY first_name LIMIT 5 OFFSET 3;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)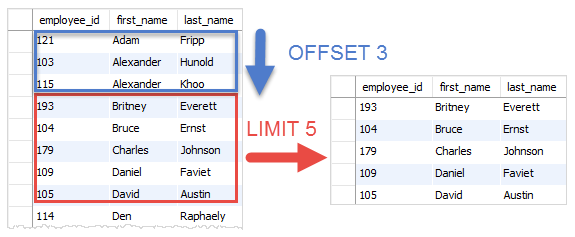
Retrieving the top N rows with the highest or lowest value #
You can use the LIMIT clause to get the top N rows with the highest or lowest value.
For example, the following query retrieves the top five employees with the highest salaries.
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary FROM employees ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 5;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)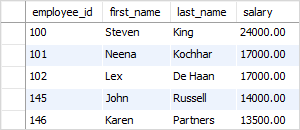
How the query works:
- First, the
ORDER BYclause sorts the employees by salary in descending order. - Second, the
LIMITclause returns five rows from the top of the result set.
To get the top five employees with the lowest salary, you sort the employees by salary in the ascending order instead:
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary FROM employees ORDER BY salary LIMIT 5;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
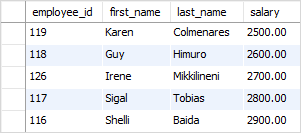
Getting the rows with the Nth highest value #
Suppose you have to get employees who have the 2nd highest salary in the company. To do so, you use the LIMIT OFFSET clauses as follows.
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary FROM employees ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
employee_id | first_name | last_name | salary -------------+------------+-----------+---------- 101 | Neena | Kochhar | 17000.00Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)How the query works:
- The
ORDER BYclause sorts the employees by salary in descending order. - The
LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1clause gets the second row from the result set.
This query works with the assumption that every employee has a different salary. It will fail if two employees have the same 2nd highest salary.
Additionally, if two or more employees have the same 2nd highest salary, the query returns only the first one.
To fix this issue, you can get the second highest salary first using the following statement:
SELECT DISTINCT salary FROM employees ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Result:
salary ---------- 17000.00Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And pass the result to another query:
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary FROM employees WHERE salary = 17000;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
employee_id | first_name | last_name | salary -------------+------------+-----------+---------- 101 | Neena | Kochhar | 17000.00 102 | Lex | De Haan | 17000.00Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you know subquery, you can combine both queries into a single query as follows:
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary FROM employees WHERE salary = ( SELECT DISTINCT salary FROM employees ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1 );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Summary #
- Use the
LIMITclause to limit the number of rows returned by a query. - Use the
OFFSETclause to skip some rows before returning the number of rows specified by theLIMITclause.