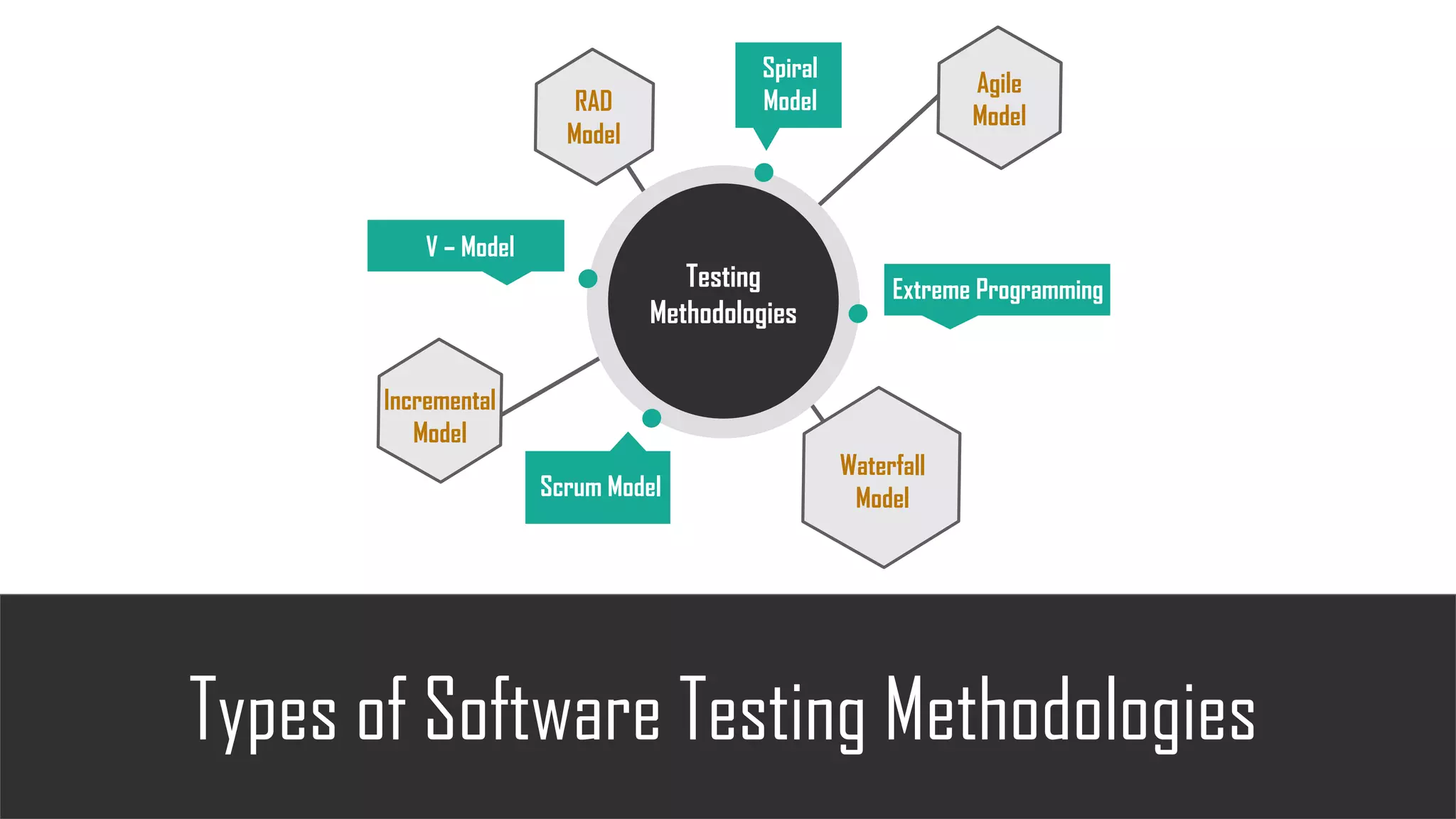
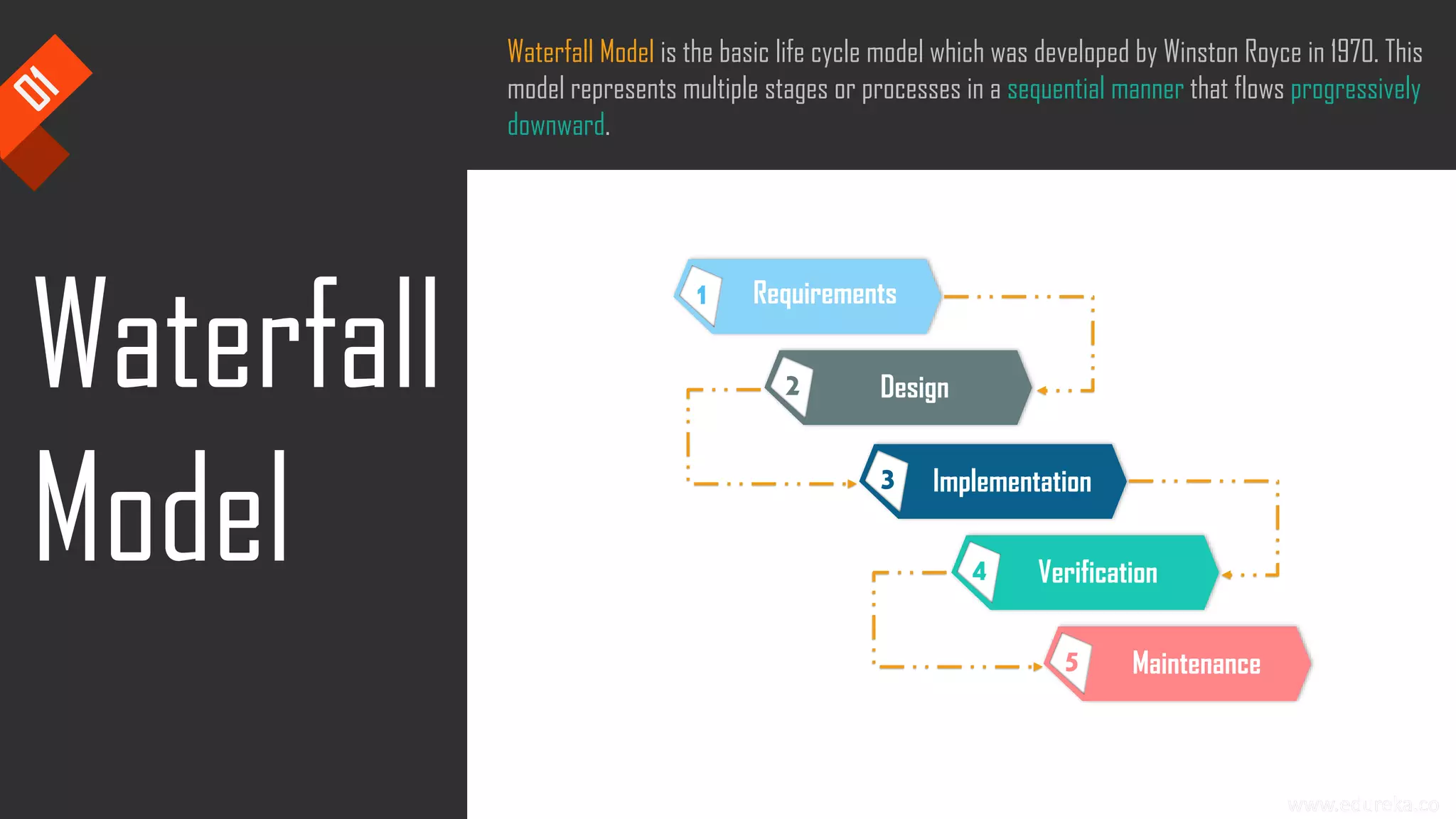
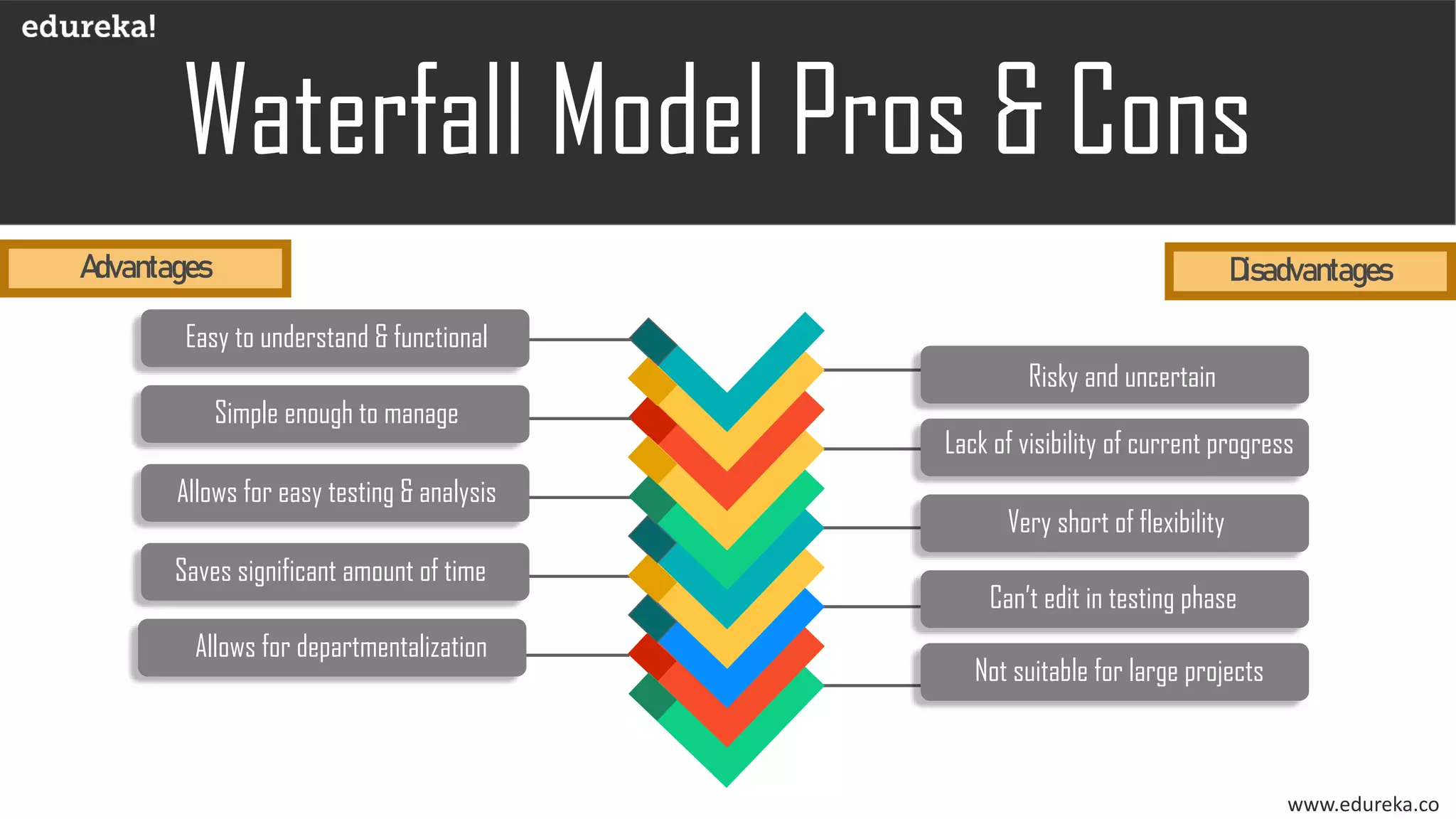
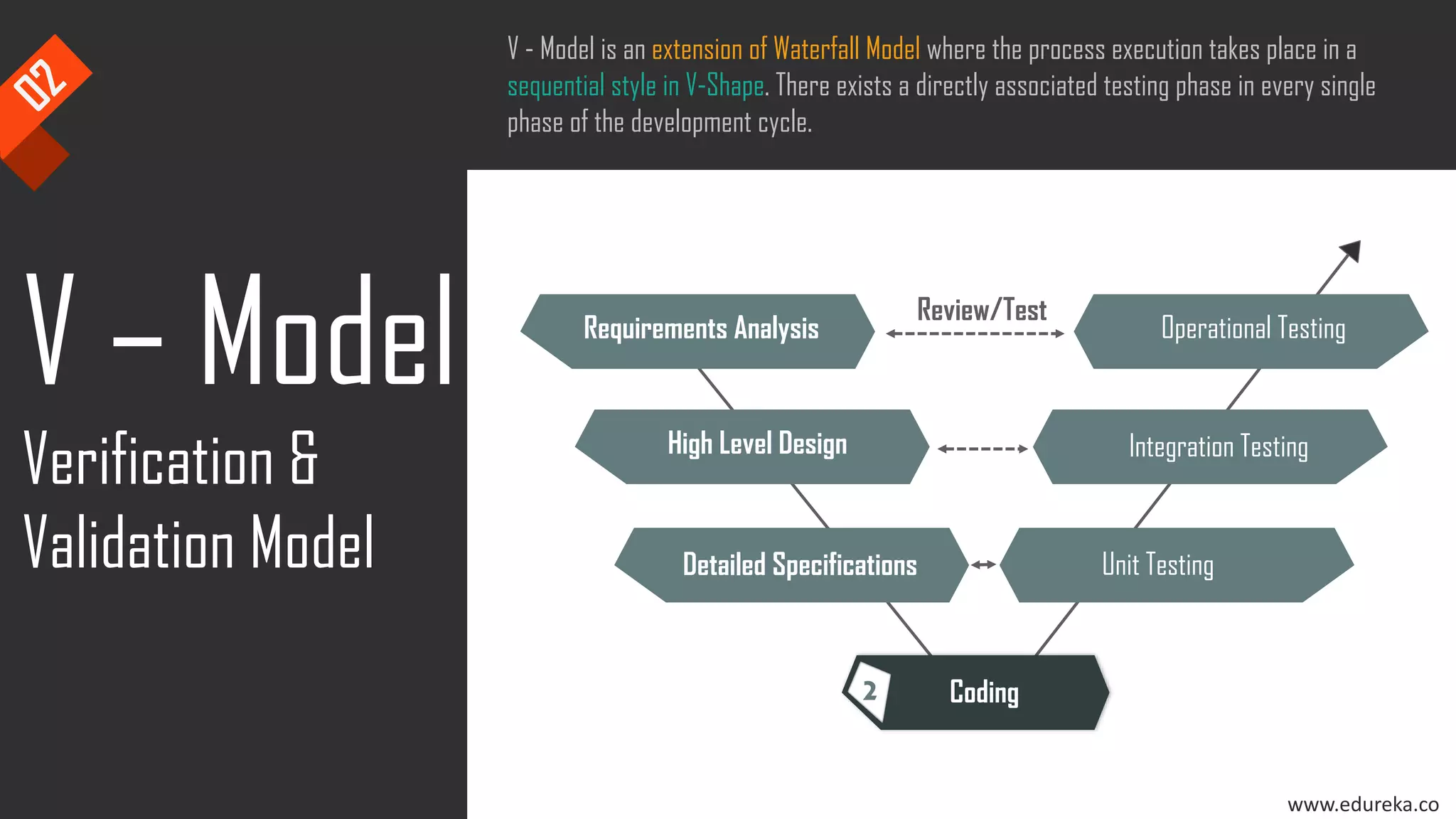
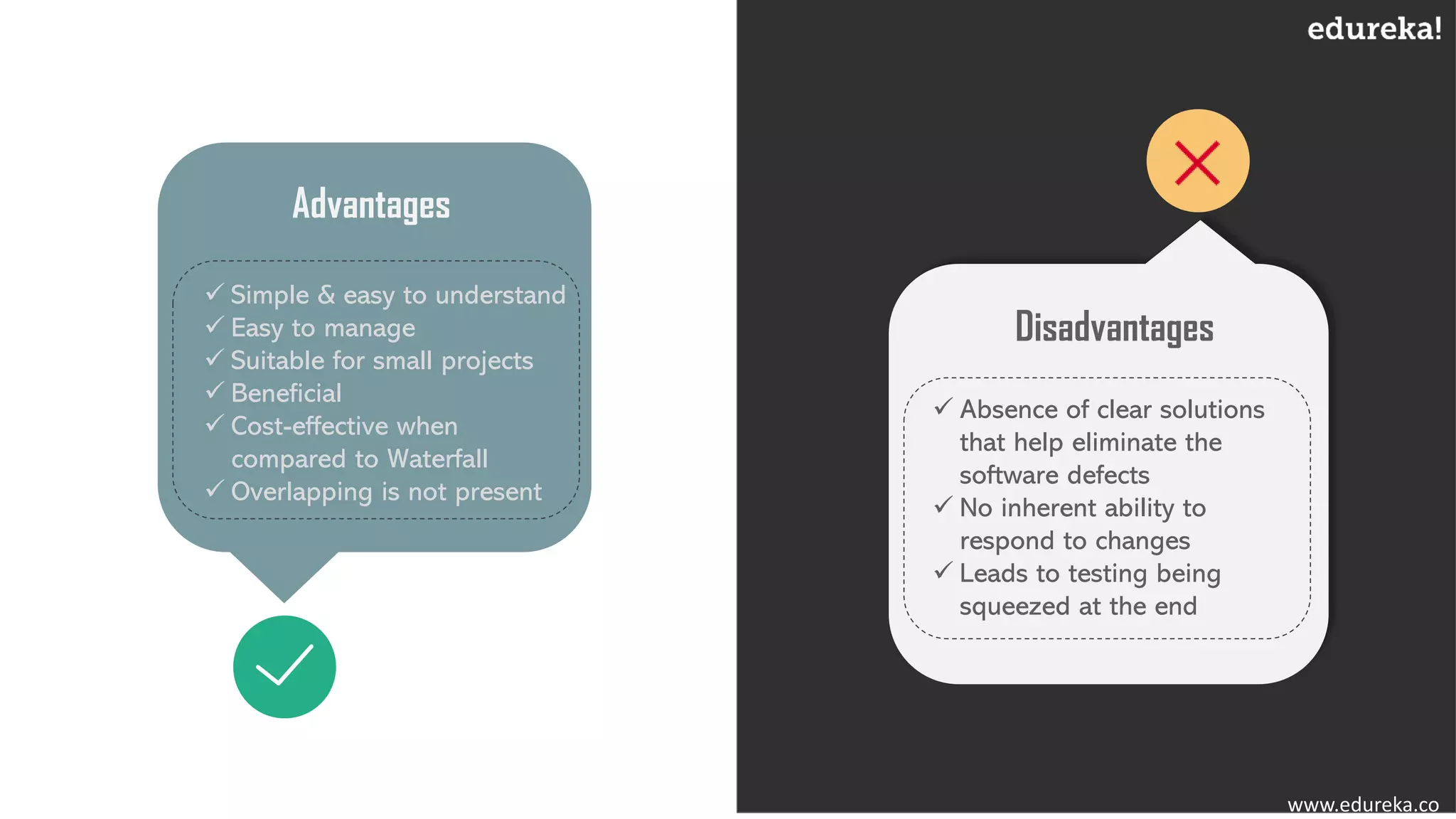
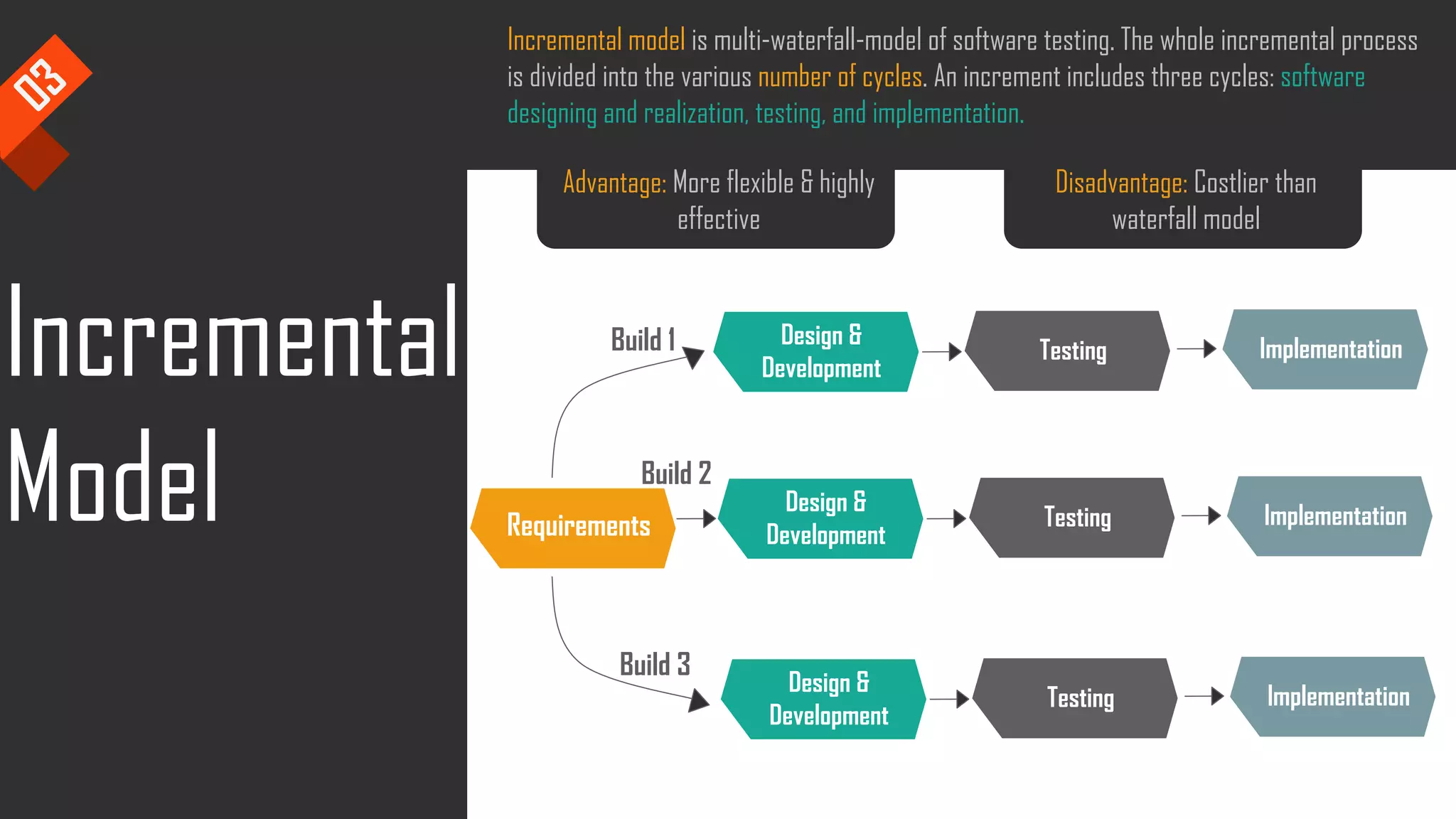
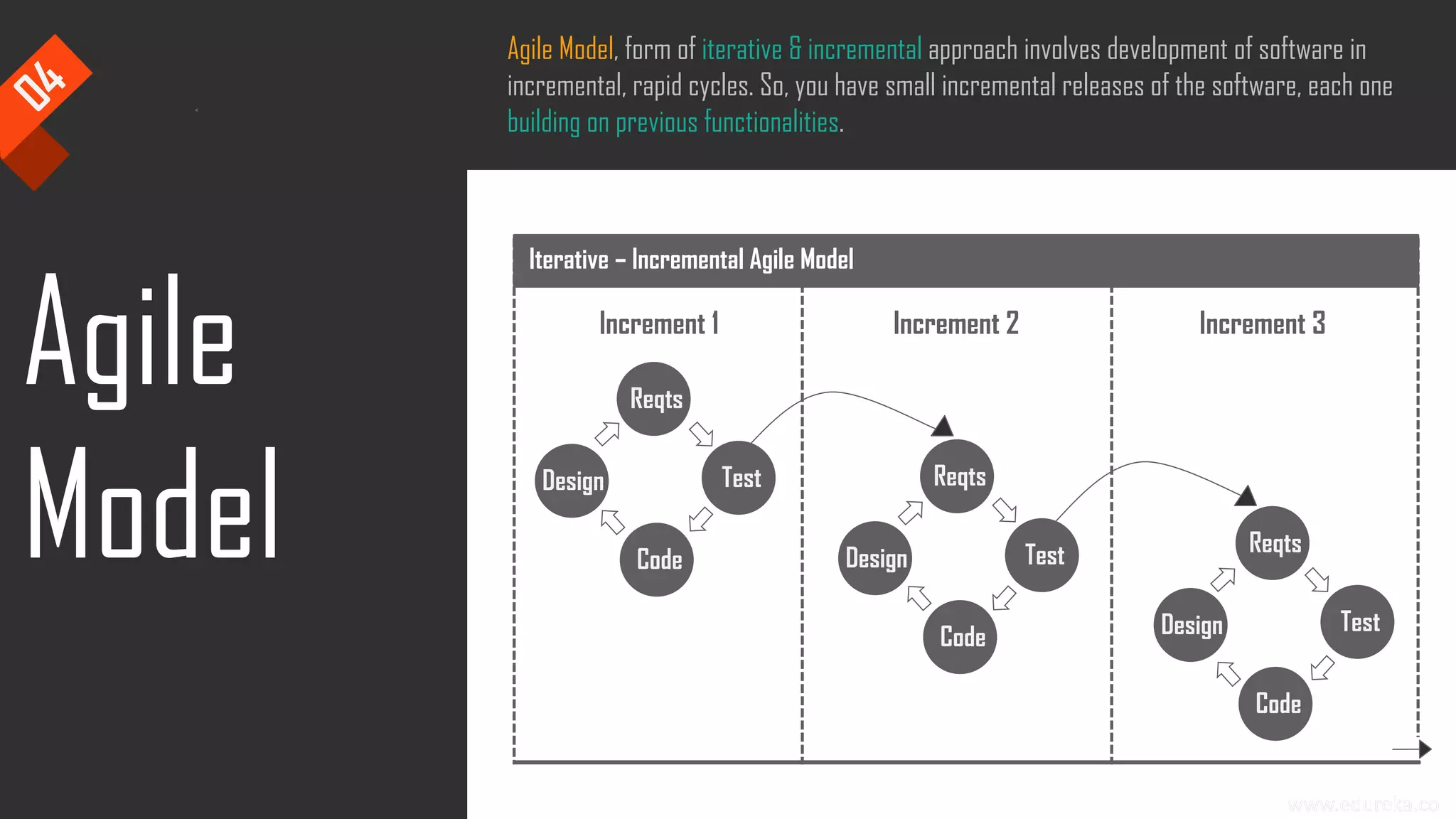
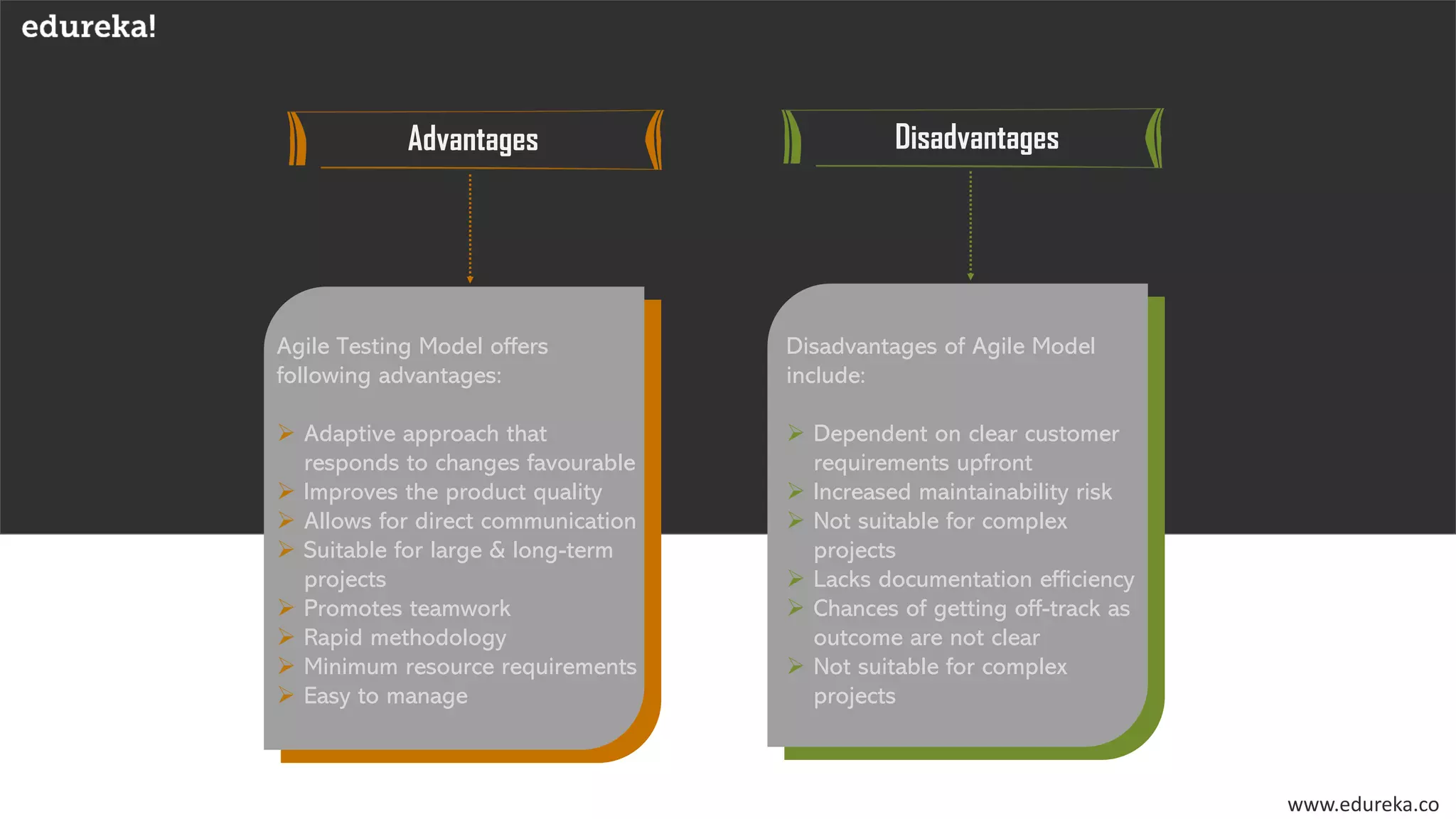
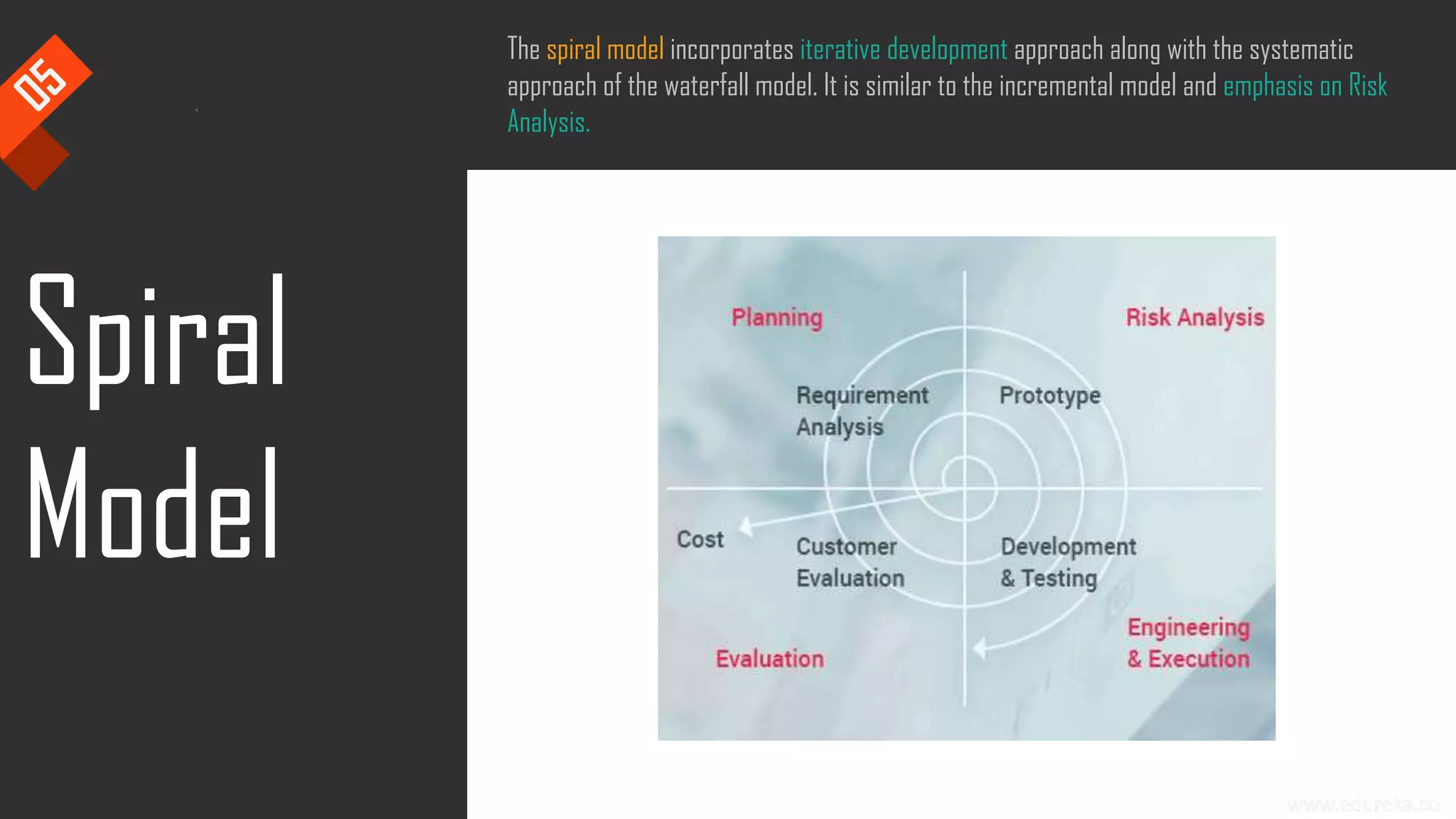
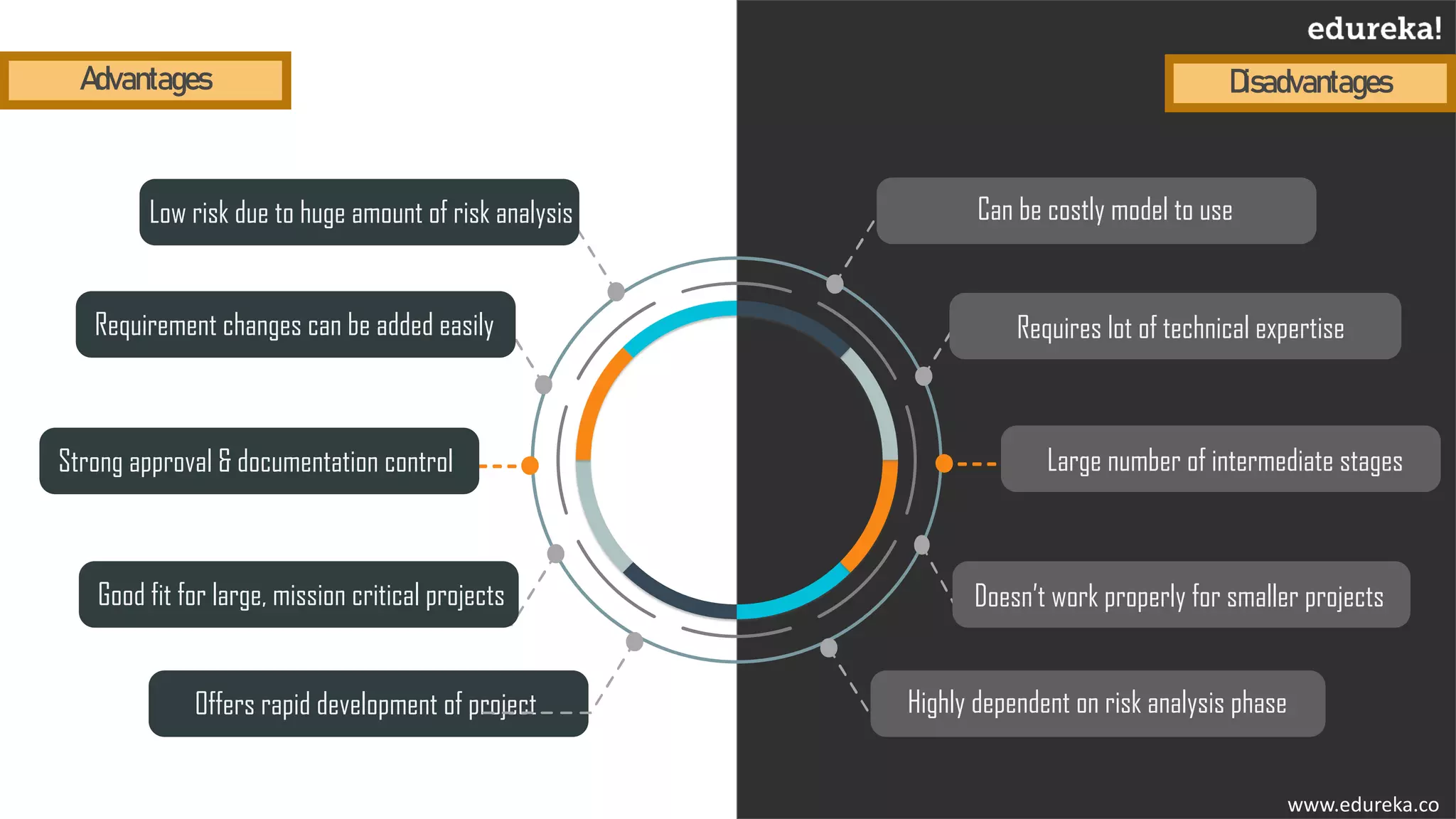
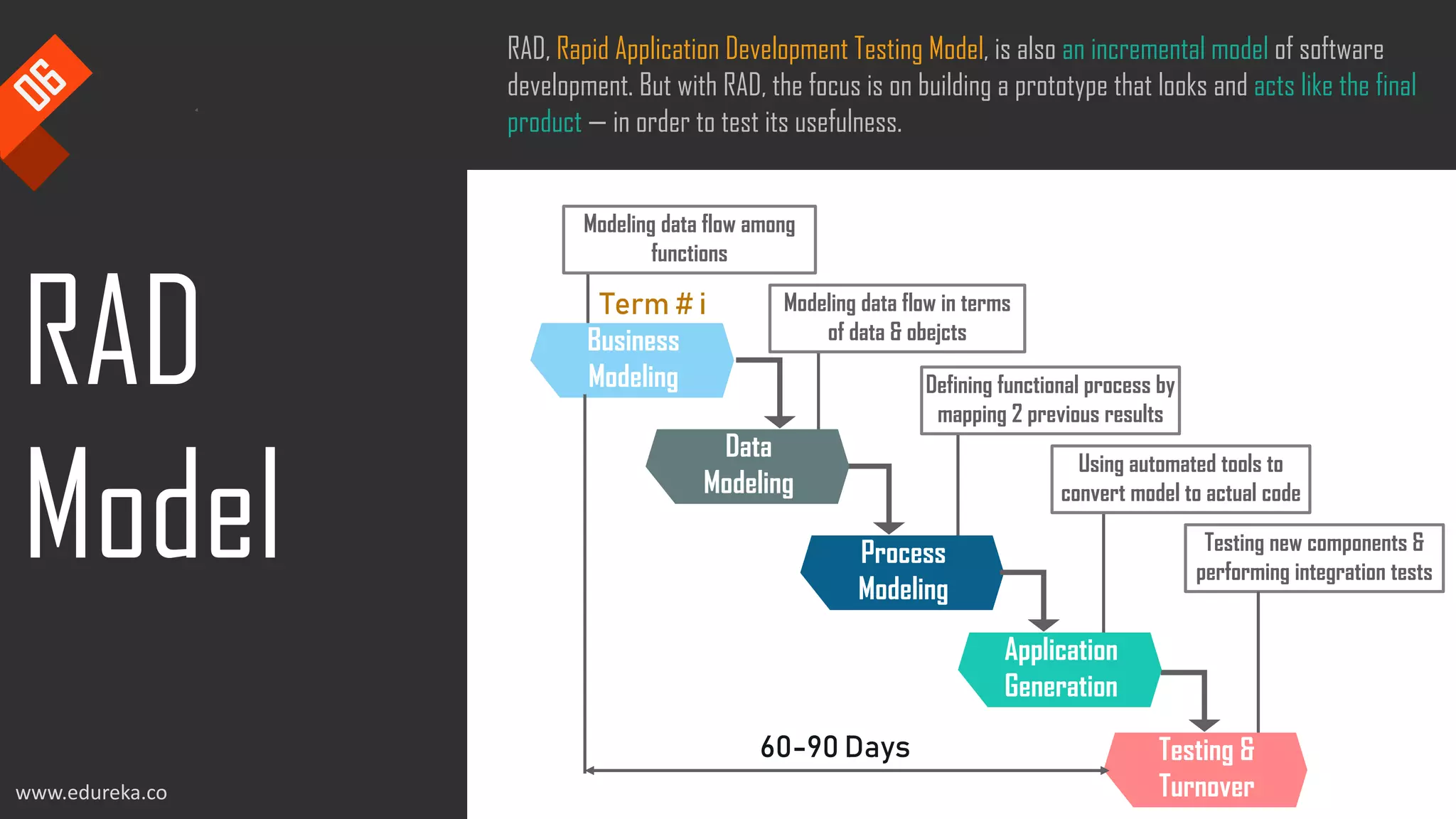
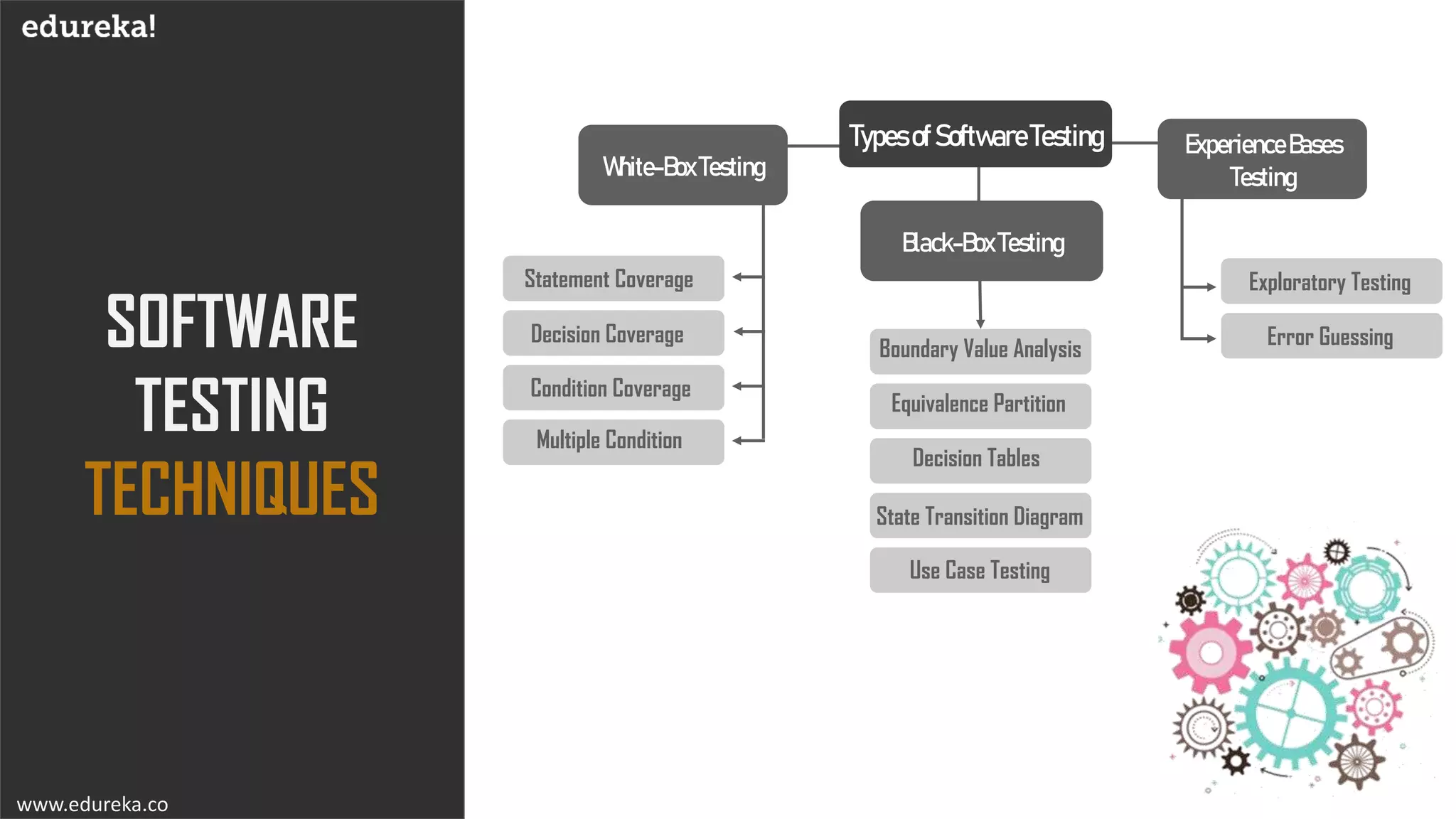
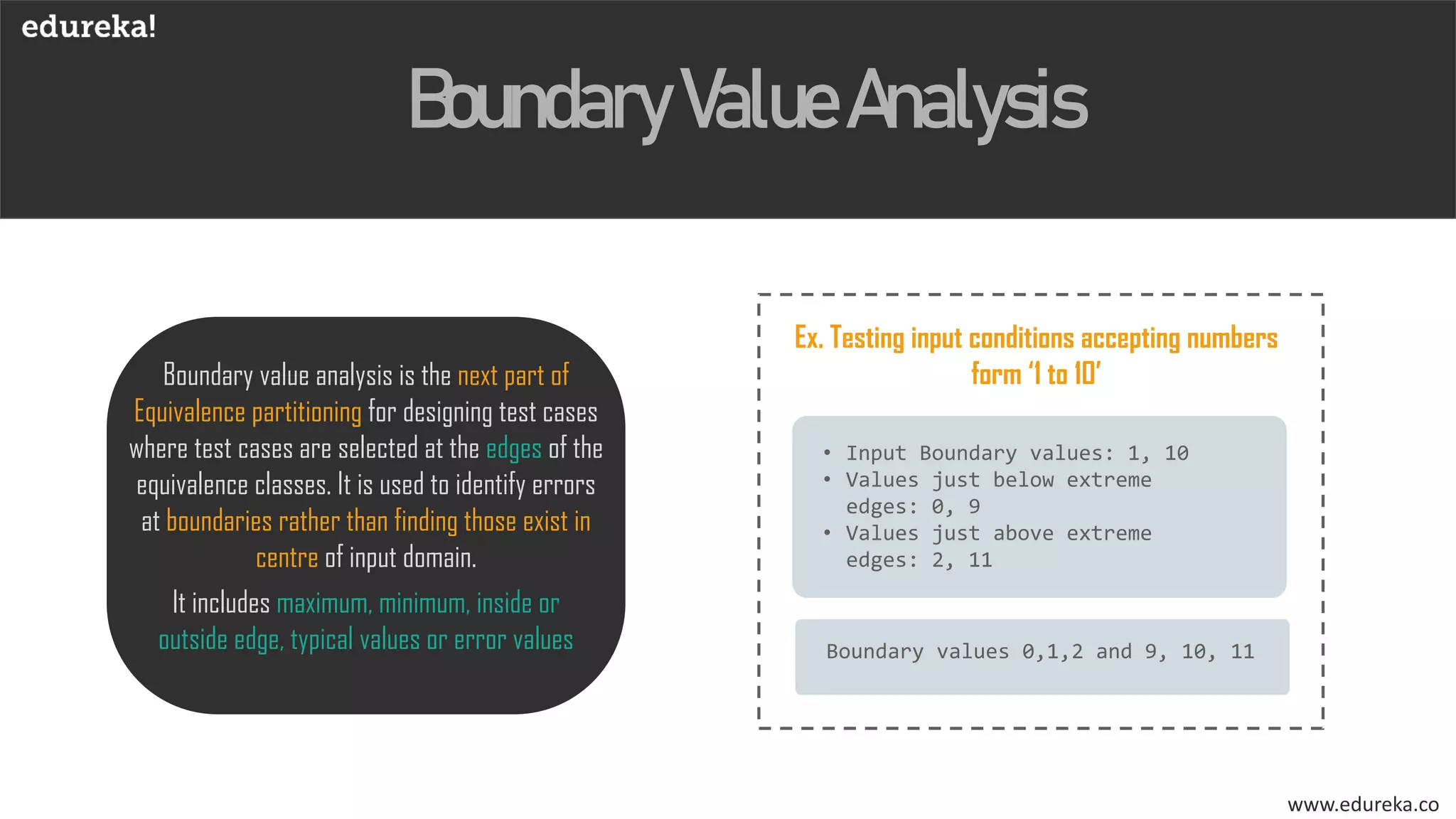
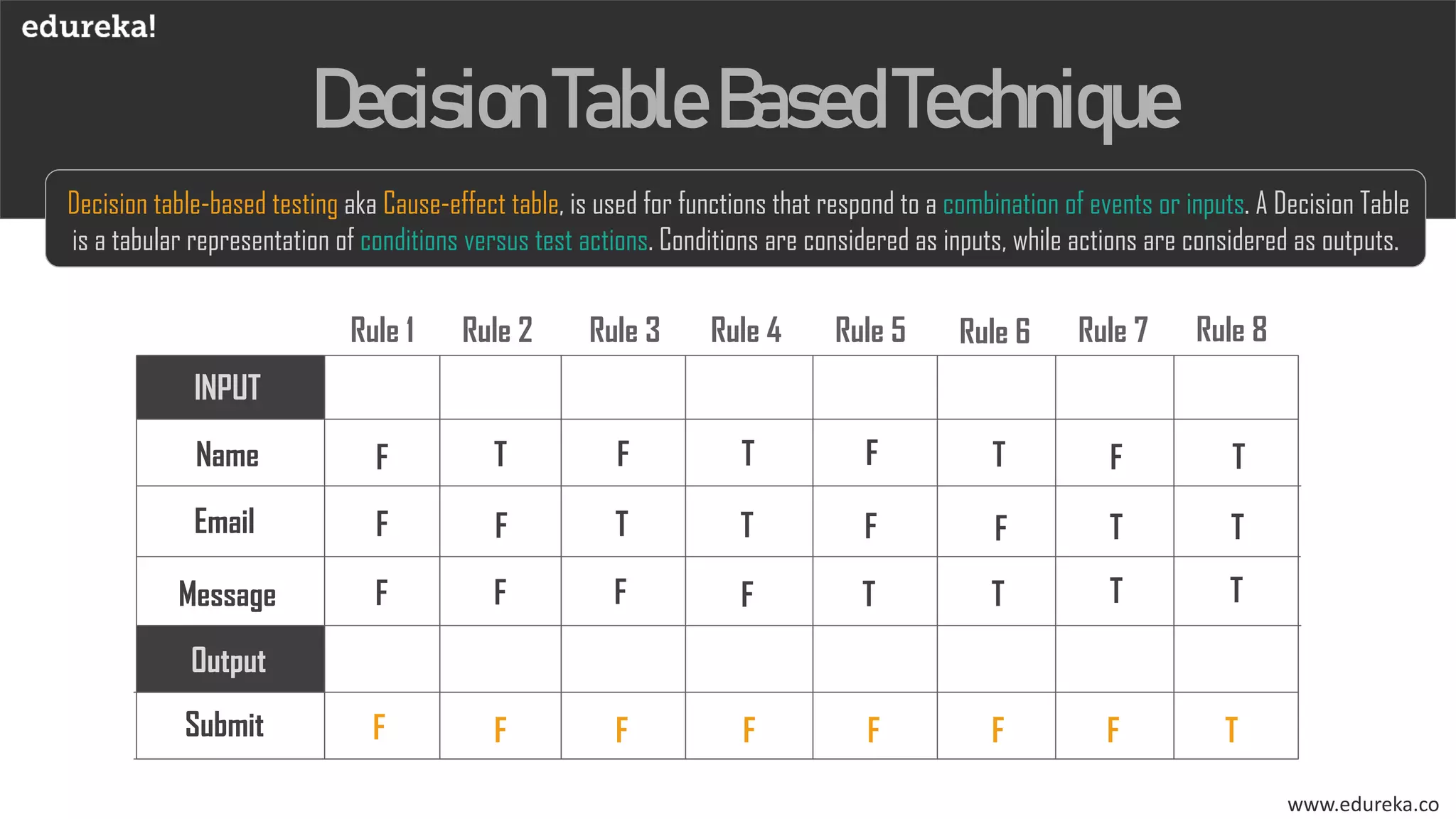
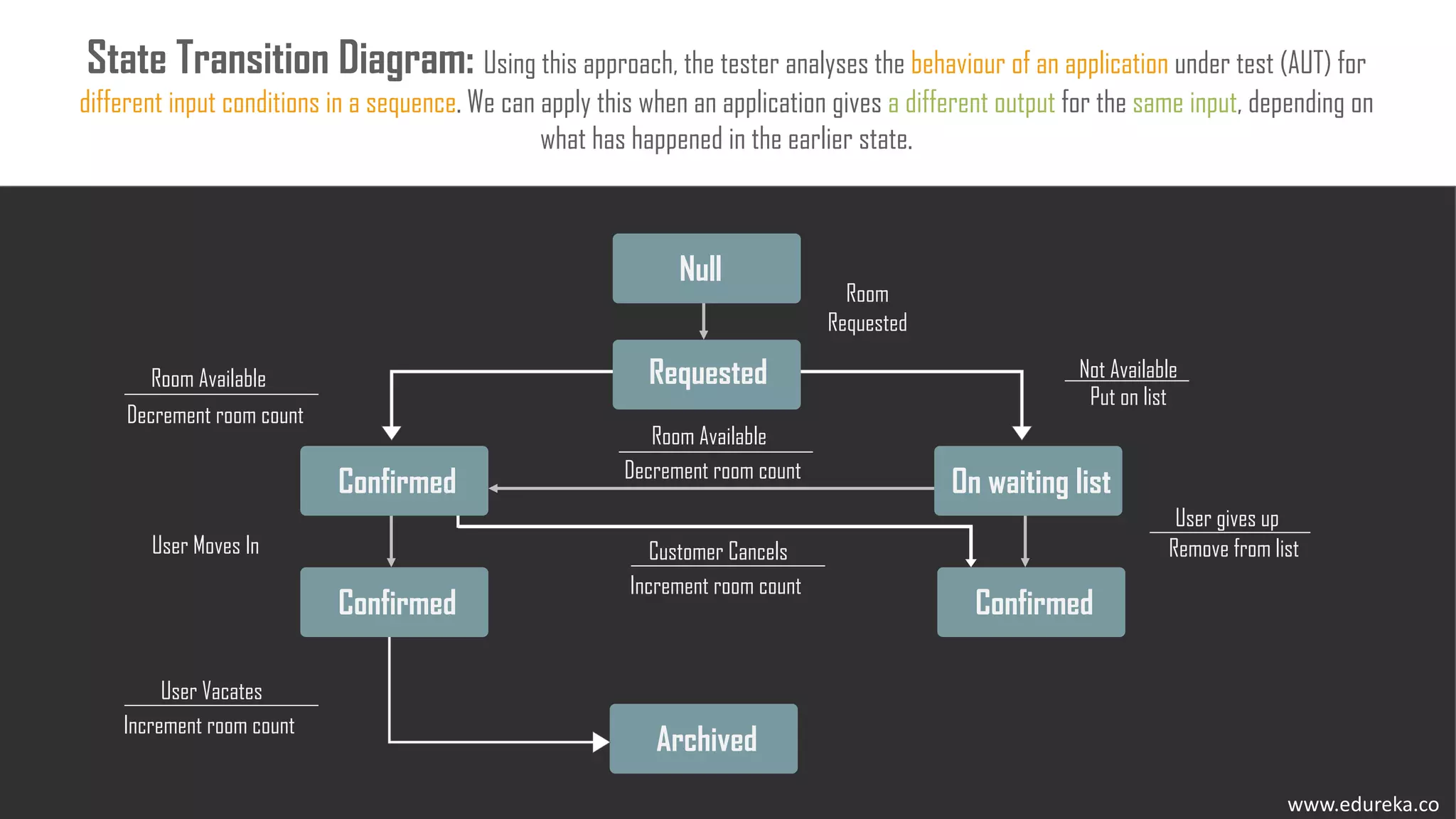
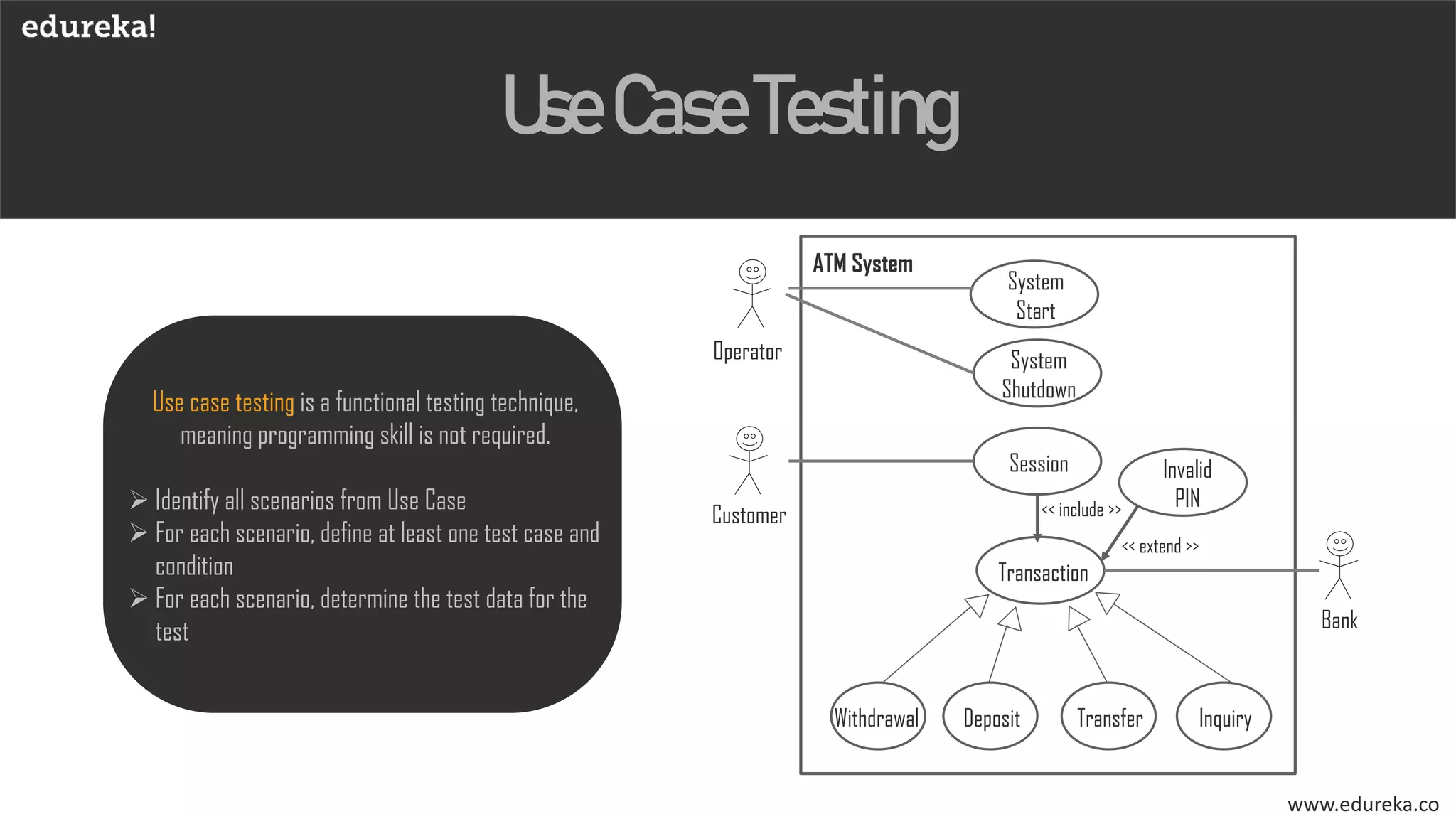
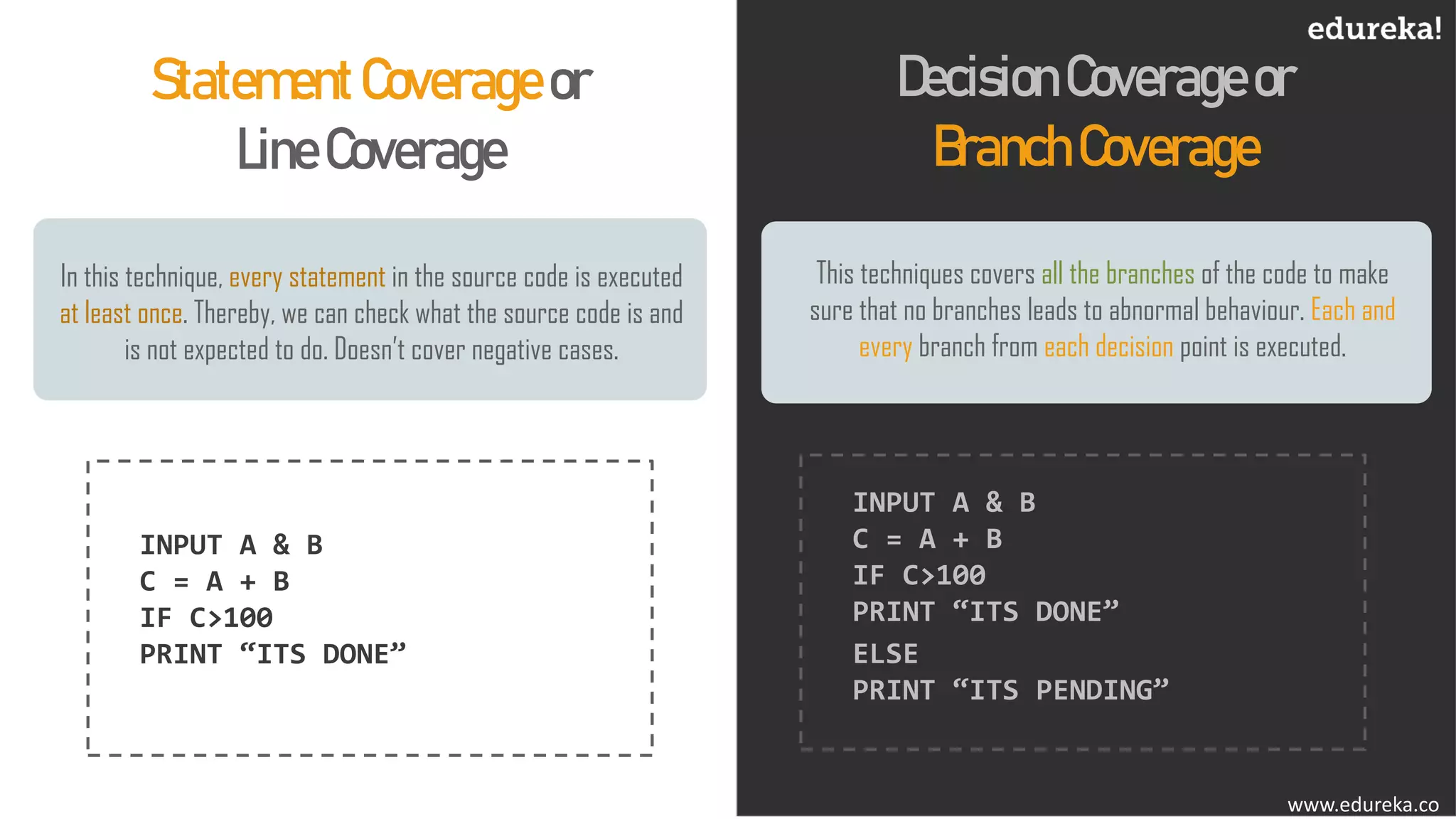
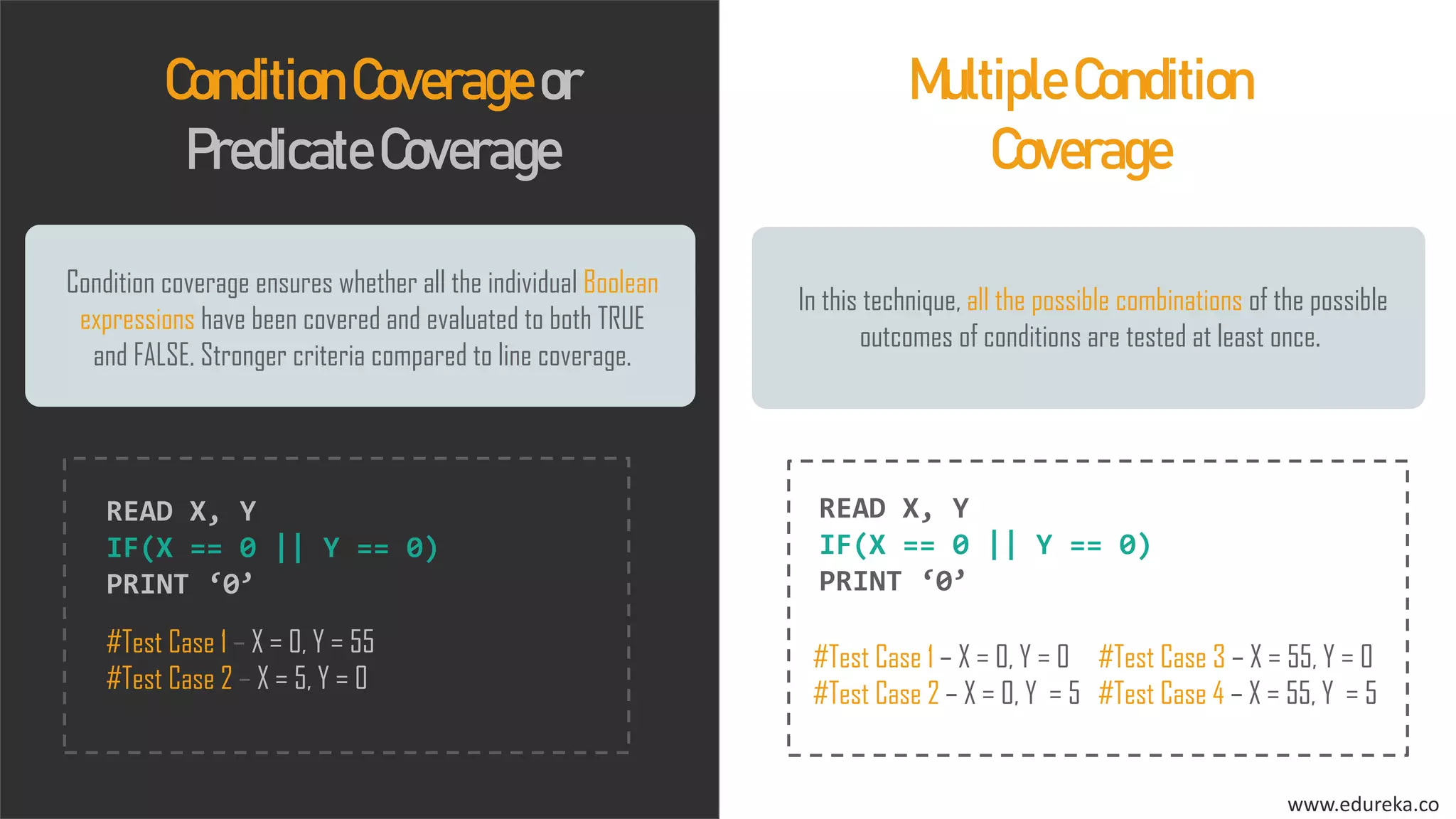
The document discusses the importance of software testing, its methodologies, and techniques to ensure high-quality software applications. It covers various methodologies such as the waterfall model, agile model, spiral model, and rapid application development, detailing their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it describes various testing techniques, including black-box and white-box testing, highlighting their specific approaches to identifying software flaws.