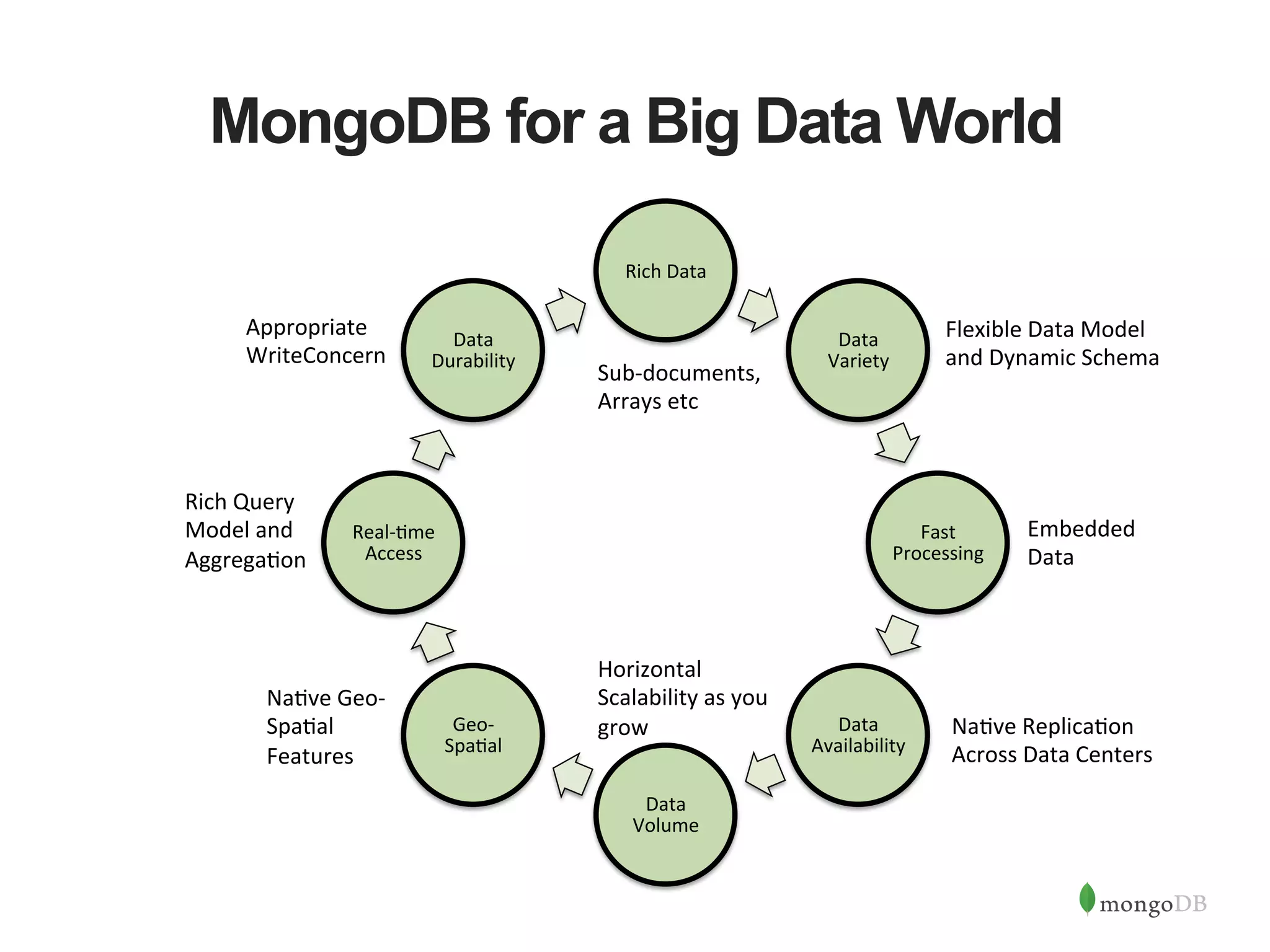
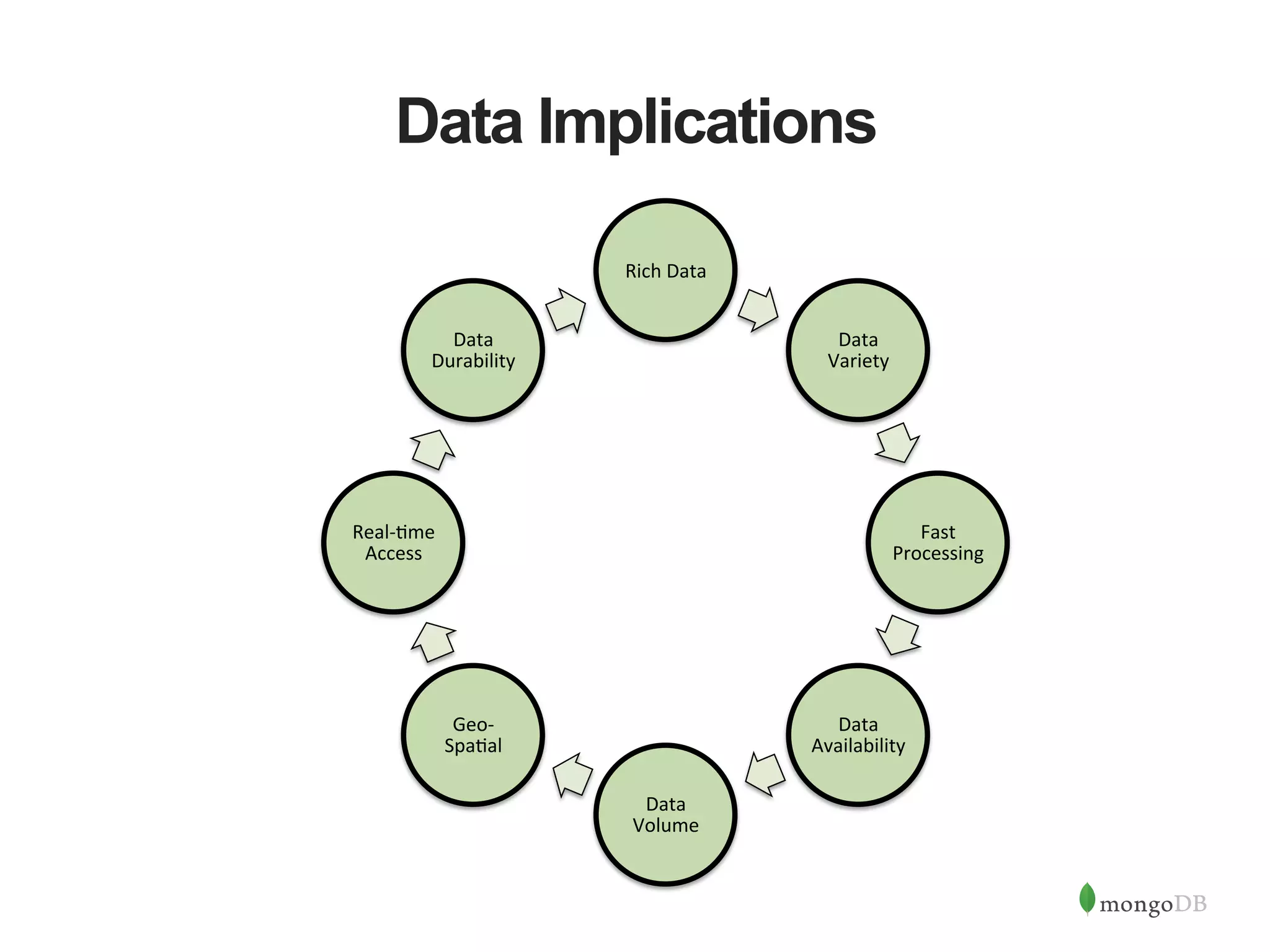
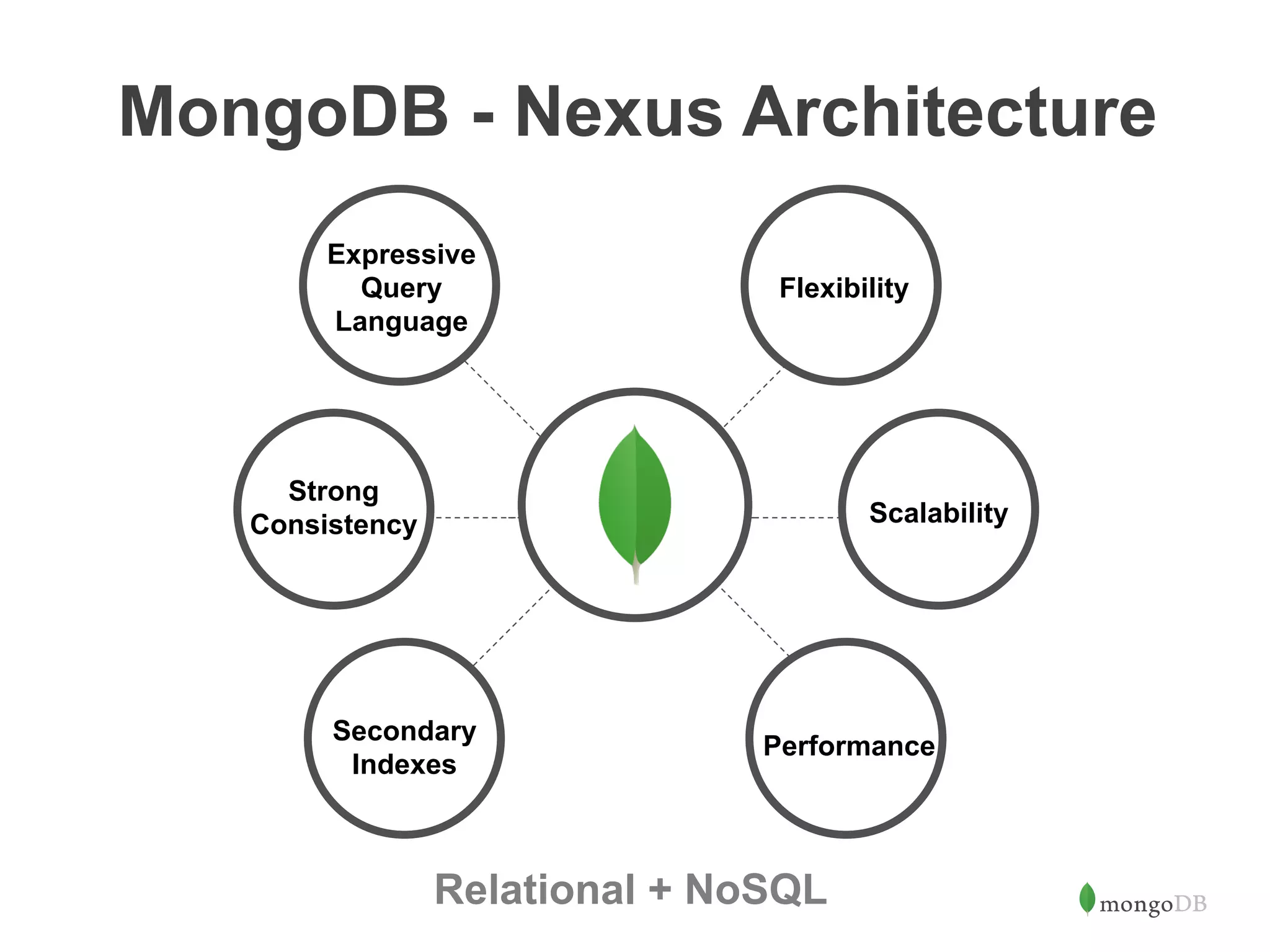
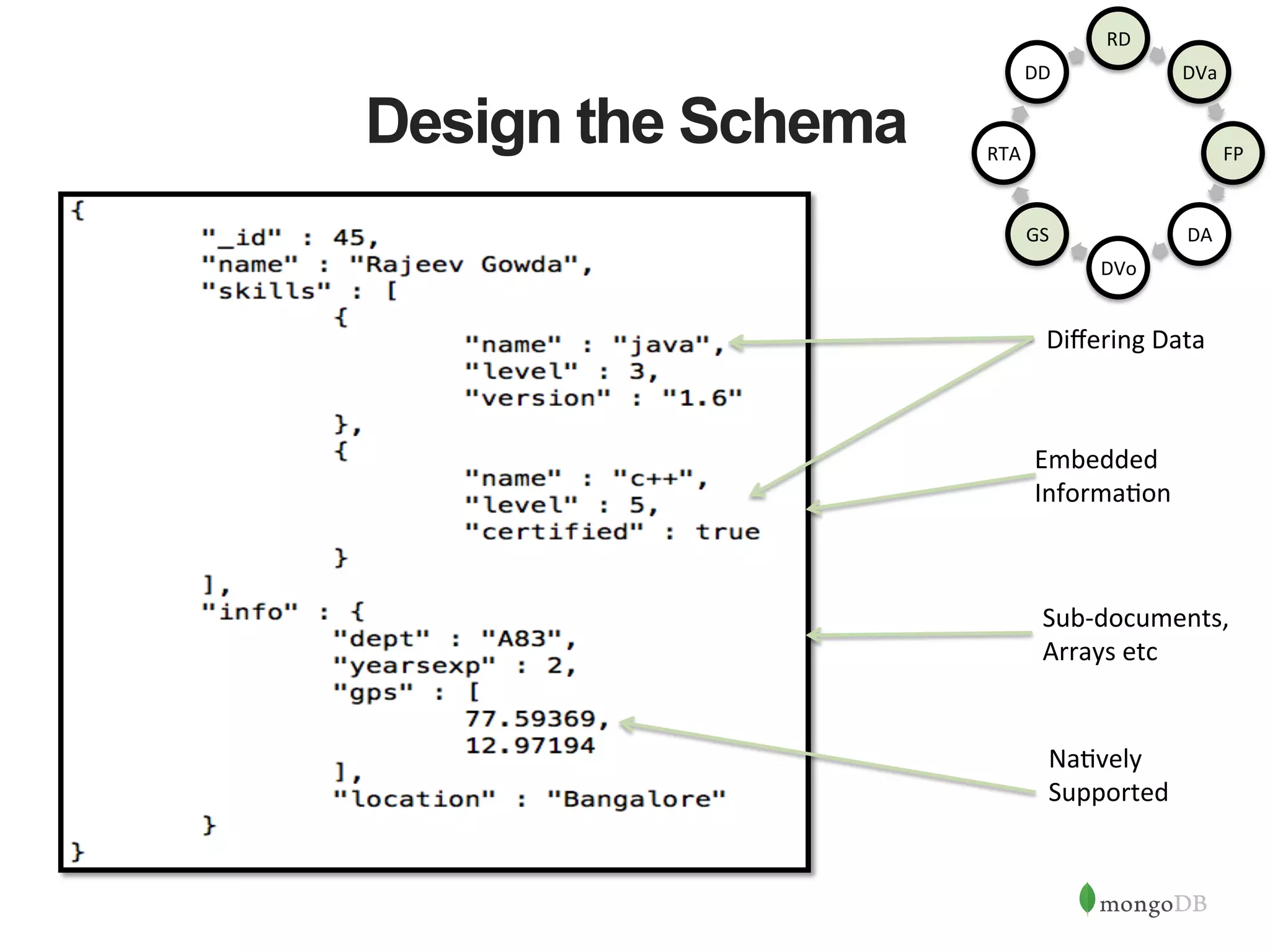
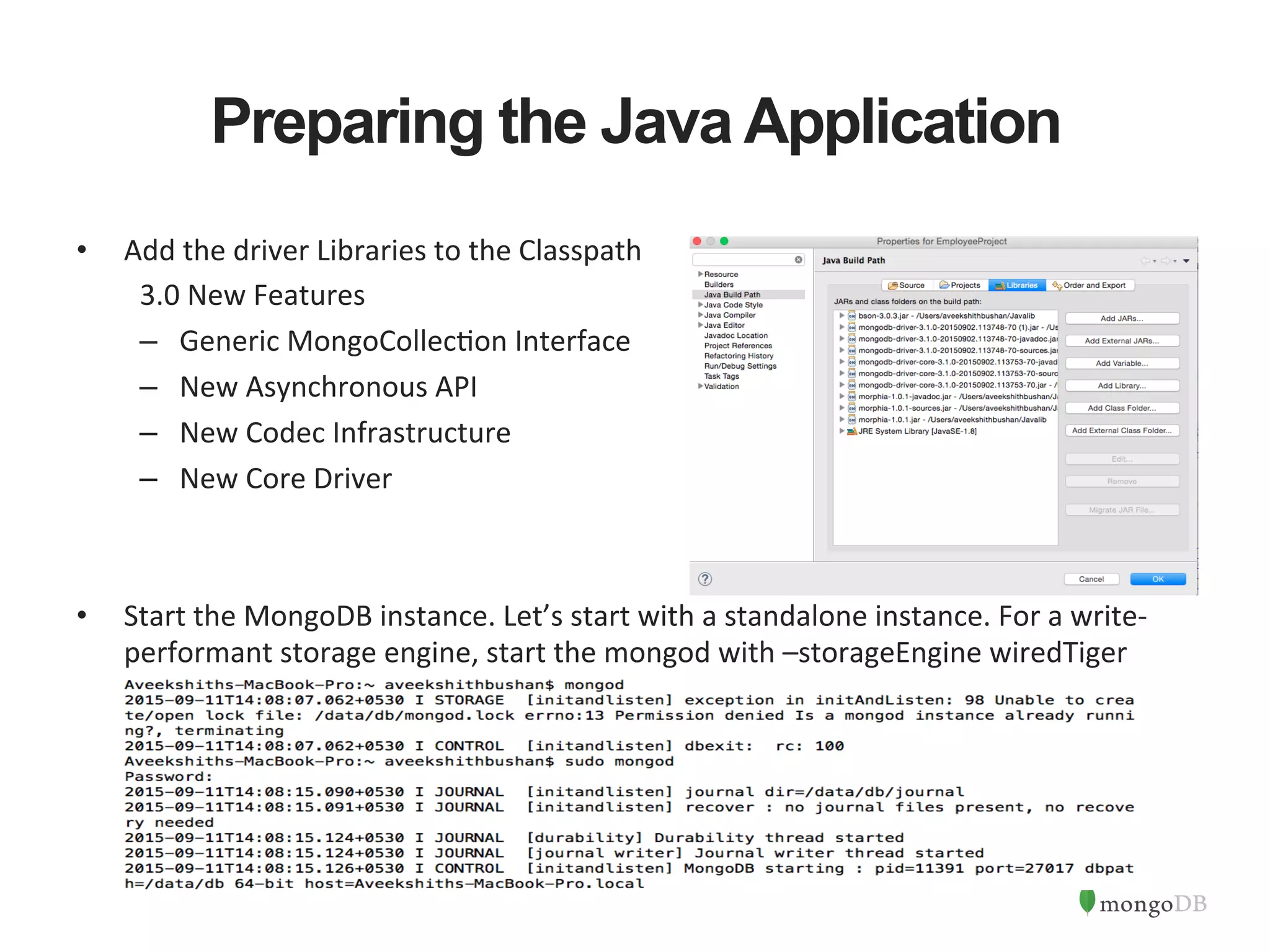
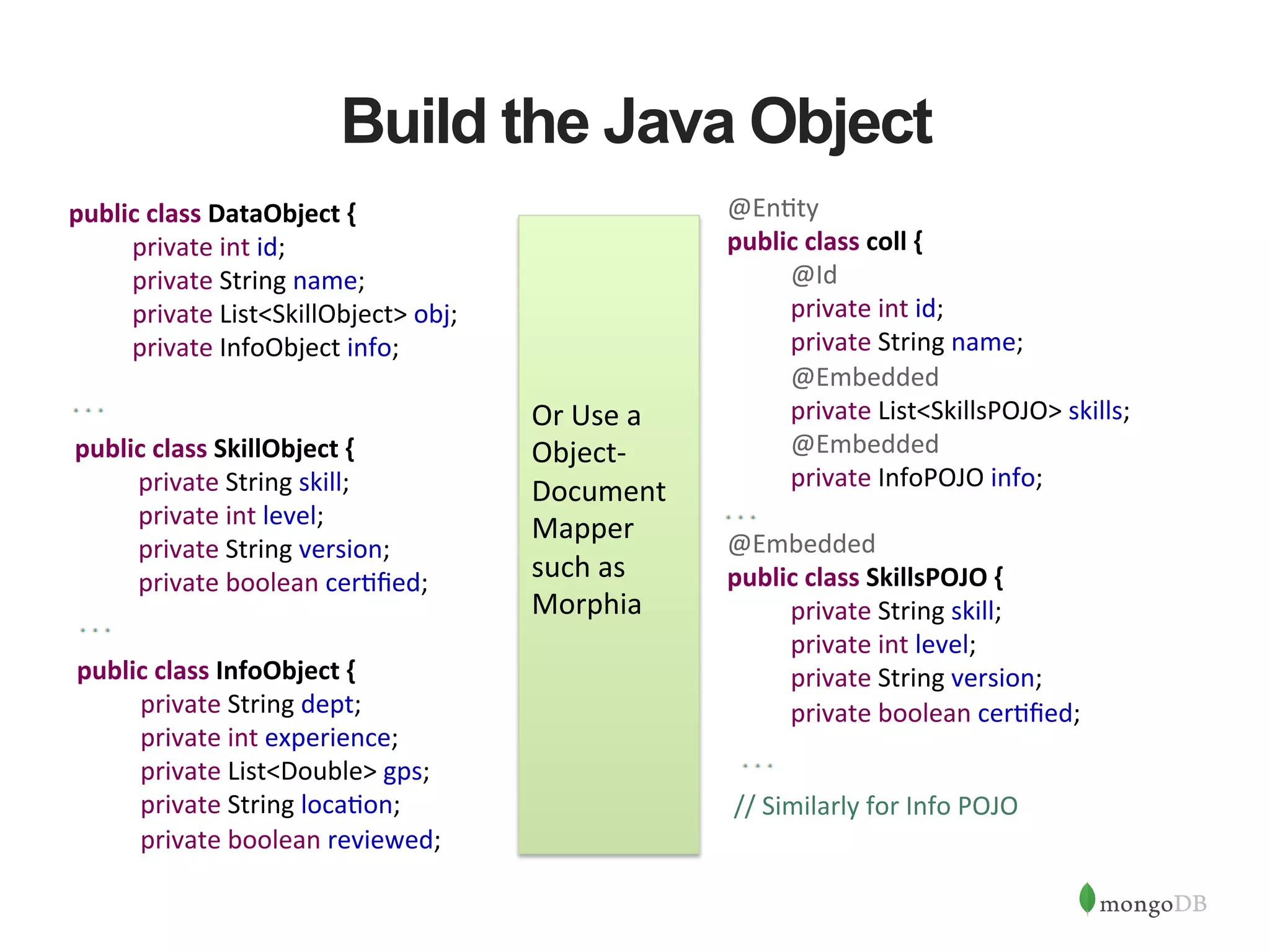
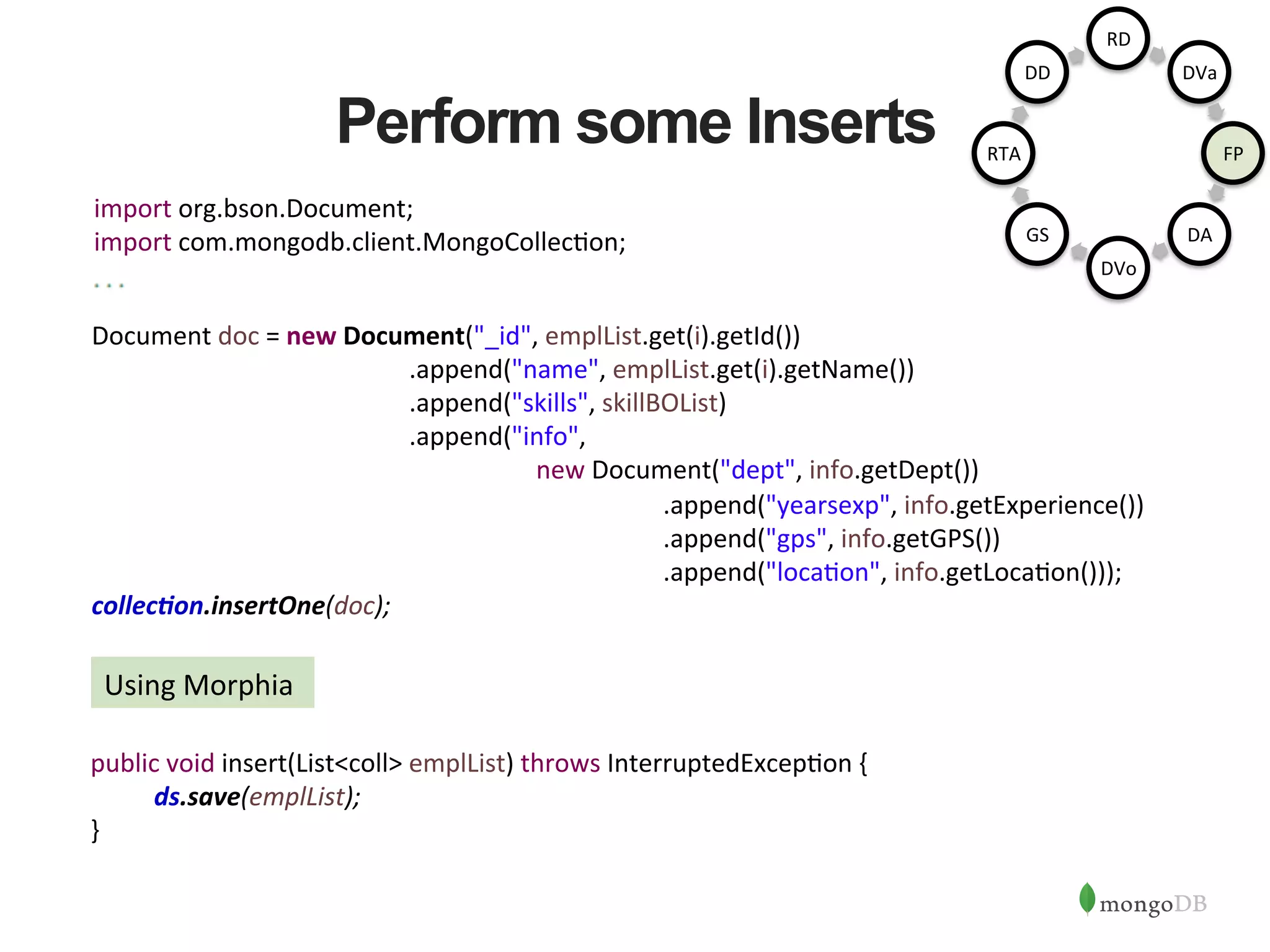
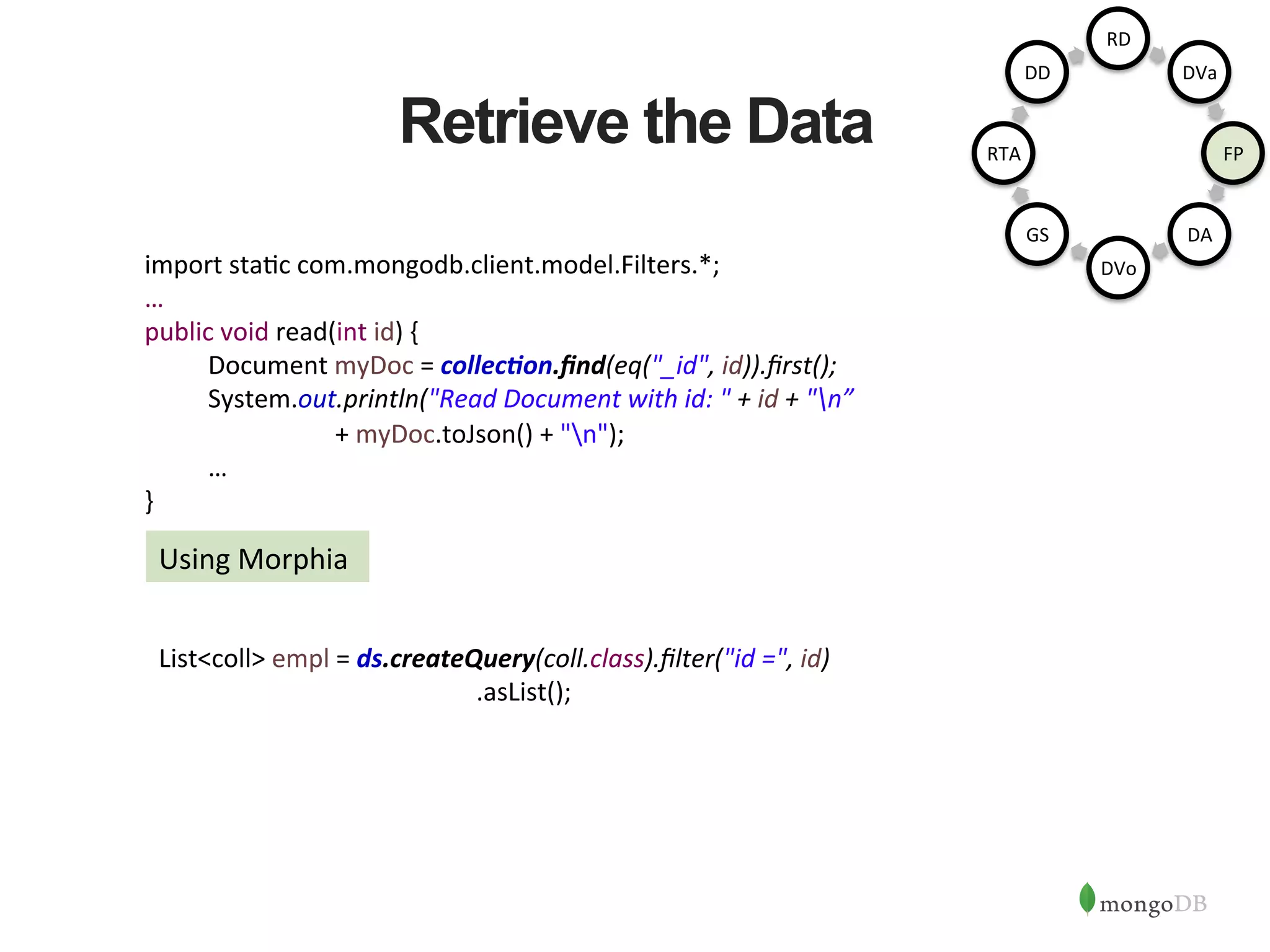
The document discusses building Java applications that use MongoDB as the database. It covers connecting to MongoDB from Java using the driver, designing schemas for embedded documents and arrays, building Java objects to represent and insert data, and performing basic operations like inserts. The document also mentions using an object-document mapper like Morphia to simplify interactions between Java objects and MongoDB documents.



![DB Tier Connect to MongoDB mongod Java Client Driver public void MongoConnect(String[] hosts) { List<ServerAddress> seeds = new ArrayList<ServerAddress>(); for (String h : hosts) { // MongoDB Server address and Port seeds.add(new ServerAddress(h)); } // MongoDB client with internal connec1on pooling. client = new MongoClient(seeds); // The database to connect to database = client.getDatabase("mydb"); // The collec1on to connect to collec6on = database.getCollec/on("coll"); } import com.mongodb.MongoClient; import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollec1on; import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingjavaapplicationsonmongodb-150923184742-lva1-app6892/75/Webinar-Building-Your-First-App-with-MongoDB-and-Java-12-2048.jpg)
![Or Use an ODM import com.mongodb.MongoClient; import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollec1on; import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase; import org.mongodb.morphia.Datastore; import org.mongodb.morphia.Morphia; public void MorphiaConnect(String[] hosts) { List<ServerAddress> seeds = new ArrayList<ServerAddress>(); for (String h : hosts) { seeds.add(new ServerAddress(h)); } client = new MongoClient(seeds); morphia = new Morphia(); // Map the Morphia Object morphia.map(coll.class).map(SkillsPOJO.class). map(InfoPOJO.class); // Create a datastore to interact with MongoDB // using POJOs ds = morphia.createDatastore(client, "mydb"); } DB Tier mongod Java Client Driver](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingjavaapplicationsonmongodb-150923184742-lva1-app6892/75/Webinar-Building-Your-First-App-with-MongoDB-and-Java-13-2048.jpg)
![Authentication String dbName = ”testdb"; String userName = "user1"; char[] password = {‘p',’w',’d'}; MongoCreden1al creden1al = MongoCredenAal.createMongoCRCreden/al( dbName, userName, password); // With the appropriate Creden1al client = new MongoClient(seeds, Arrays.asList(creden1al));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingjavaapplicationsonmongodb-150923184742-lva1-app6892/75/Webinar-Building-Your-First-App-with-MongoDB-and-Java-14-2048.jpg)

![Retrieving a Datapoint { "_id" : 5, "name" : "John Snow", "skills" : [ { "name" : "java", "level" : 3, "cerAfied" : true }, { "name" : "mongo", "level" : 5 } ], "info" : { "dept" : "A91", "yearsexp" : 3, "gps" : [-‐74.00597, 40.71427], "locaAon" : "New York" } } RD DVa FP DA DVo GS RTA DD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingjavaapplicationsonmongodb-150923184742-lva1-app6892/75/Webinar-Building-Your-First-App-with-MongoDB-and-Java-18-2048.jpg)
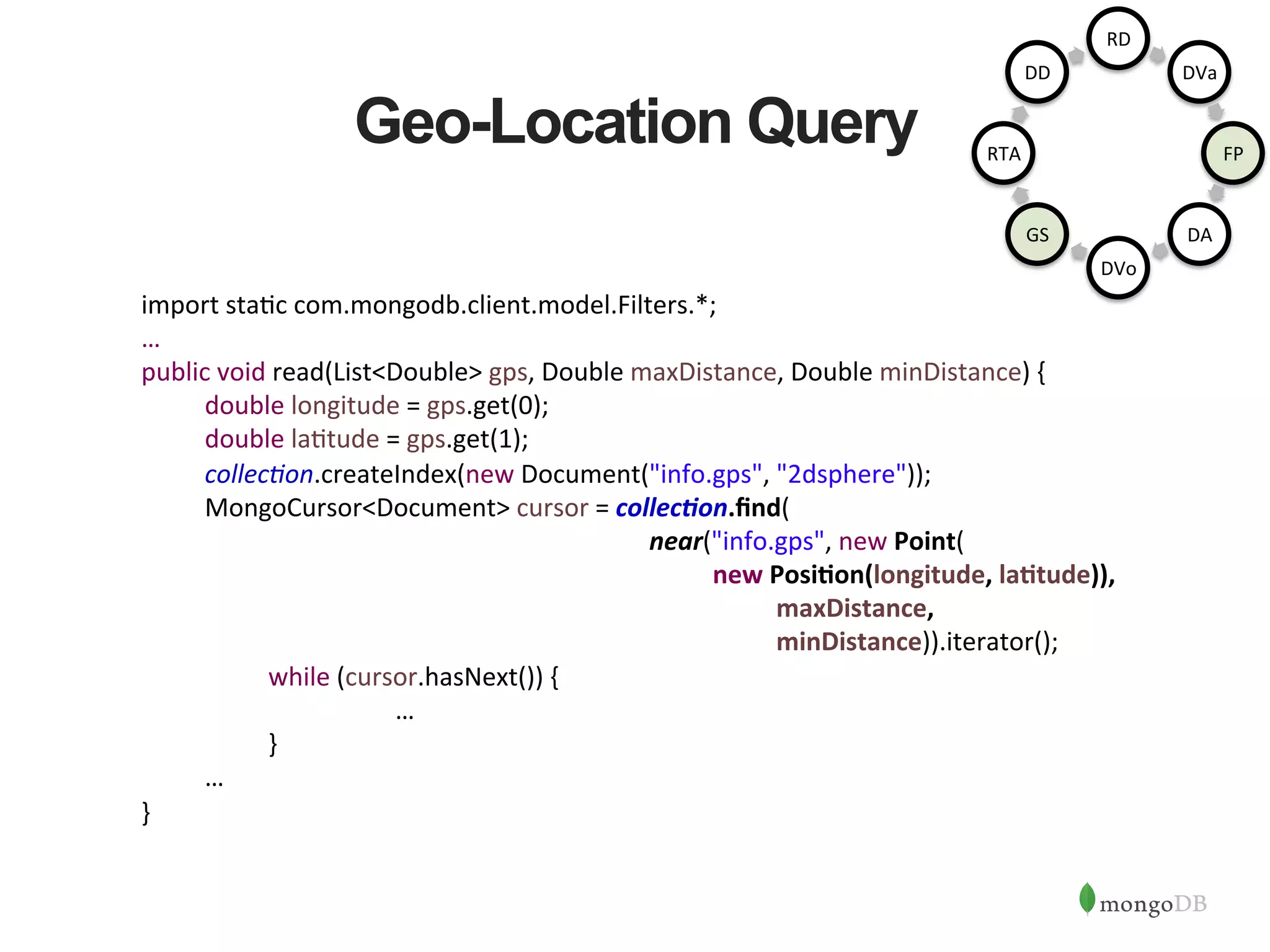
![Geo-Location - Output • Query to get all employees in and around Boston(GPS coordinates Lat 42.35843, Long -71.05977), within maxDistance of 400,000 Ms { "_id" : 5, "name" : "John Snow", "skills" : [ { "name" : "java", "level" : 3, "cerAfied" : true }, { "name" : "mongo", "level" : 5 } ], "info" : { "dept" : "A91", "yearsexp" : 3, "gps" : [-‐74.00597, 40.71427], "locaAon" : "New York" } } { "_id" :45, "name" : ”Jack Kingsley", "skills" : [ { "name" : ”c++", "level" : 4 }, { "name" : "mongo", "level" : 2, “version”: “3.0” } ], "info" : { "dept" : ”A83", "yearsexp" : 18, "gps" : [-‐71.05977, 42.35843], "locaAon" : ”Boston" } RD DVa FP DA DVo GS RTA DD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingjavaapplicationsonmongodb-150923184742-lva1-app6892/75/Webinar-Building-Your-First-App-with-MongoDB-and-Java-20-2048.jpg)
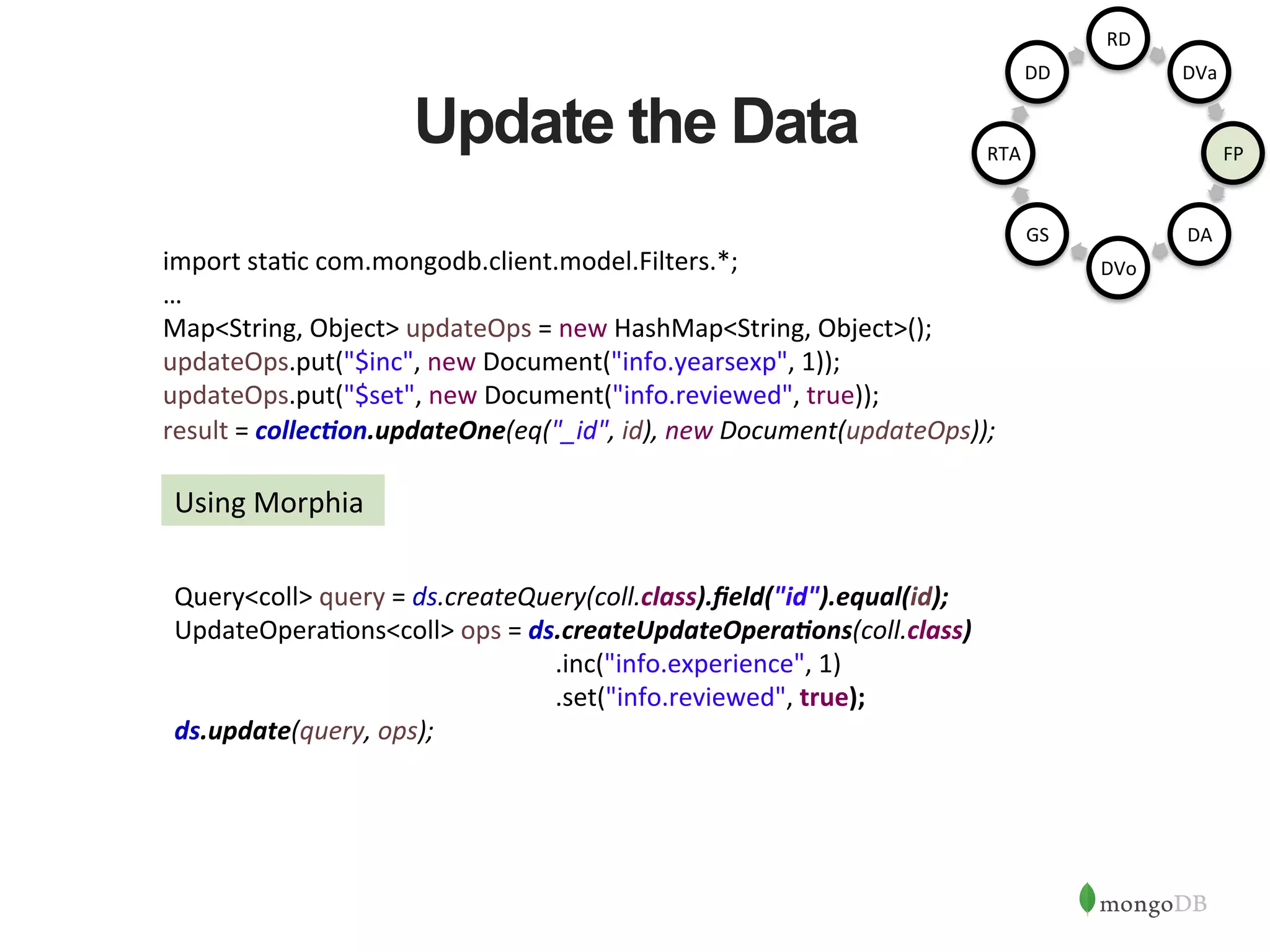
![Update - Output • Data point has been reviewed after 1 more year of employment { "_id" : 5, "name" : "John Snow", "skills" : [ { "name" : "java", "level" : 3, "cer1fied" : true }, { "name" : "mongo", "level" : 5 } ], "info" : { "dept" : "A91", "yearsexp" : 3, "gps" : [-‐74.00597, 40.71427], "loca1on" : "New York" } } { "_id" : 5, "name" : "John Snow", "skills" : [ { "name" : "java", "level" : 3, "cer1fied" : true }, { "name" : "mongo", "level" : 5 } ], "info" : { "dept" : "A91", "yearsexp" : 4, "gps" : [-‐74.00597, 40.71427], "loca1on" : "New York”, “reviewied” : true } } RD DVa FP DA DVo GS RTA DD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingjavaapplicationsonmongodb-150923184742-lva1-app6892/75/Webinar-Building-Your-First-App-with-MongoDB-and-Java-22-2048.jpg)
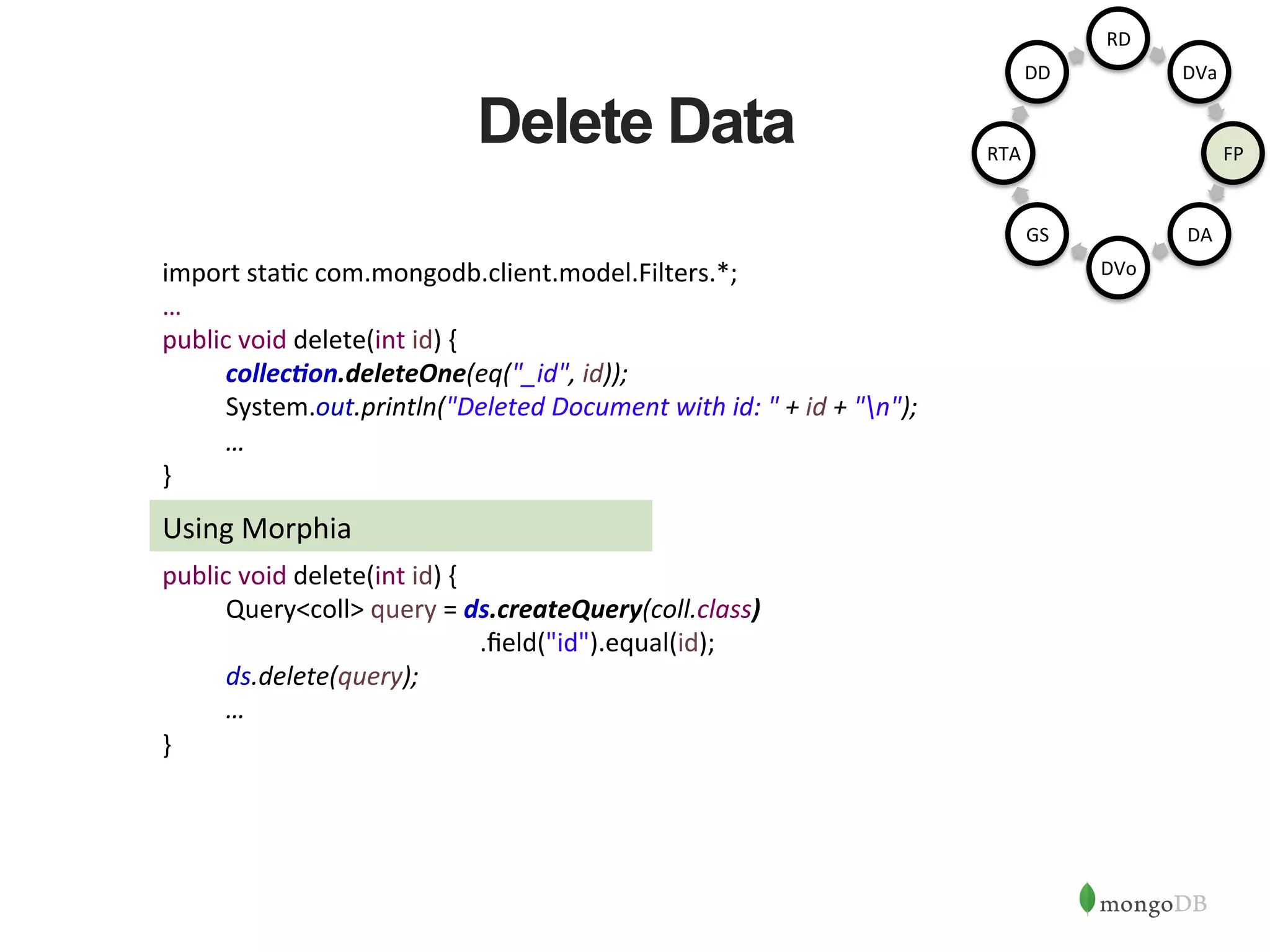
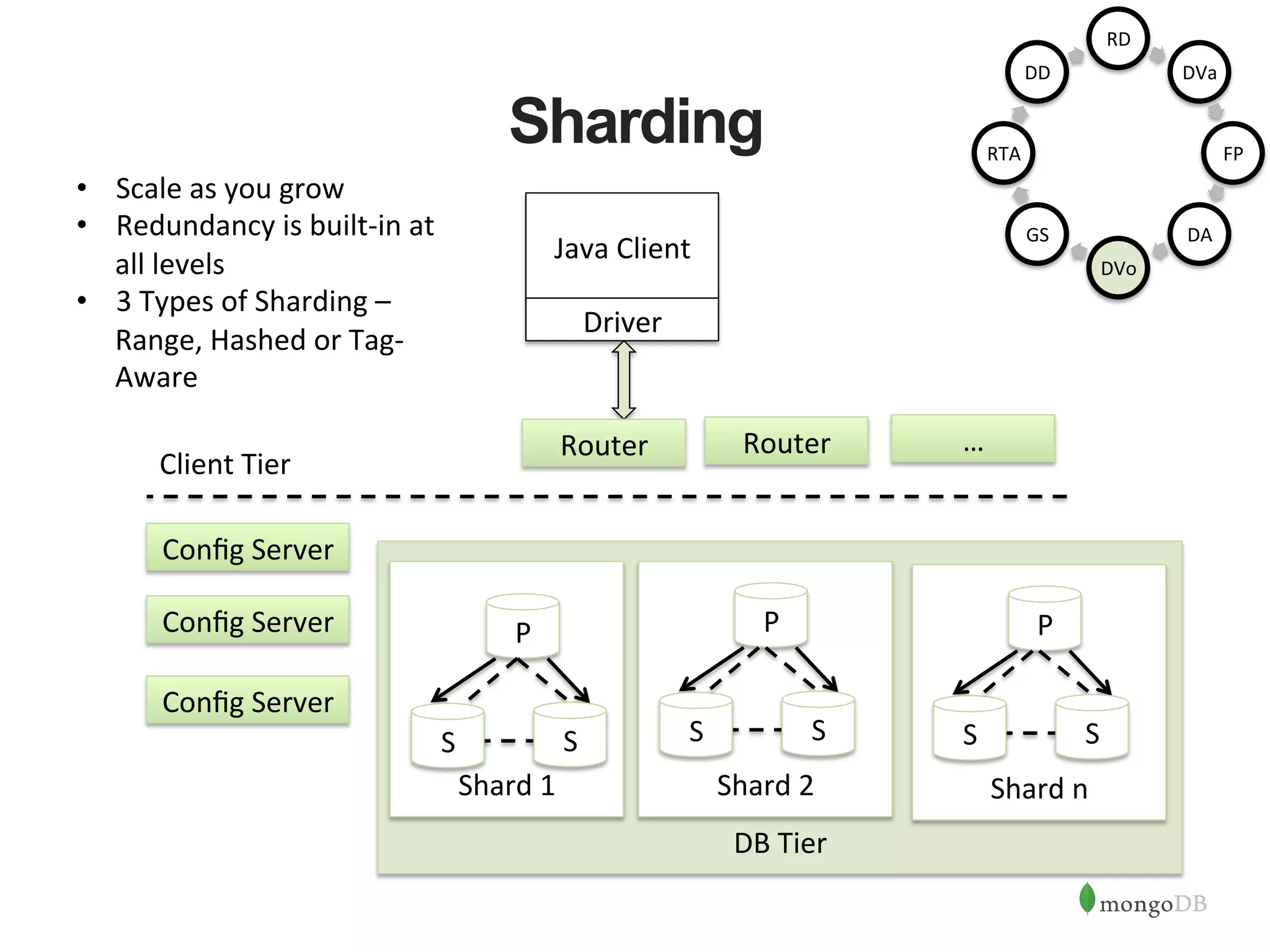
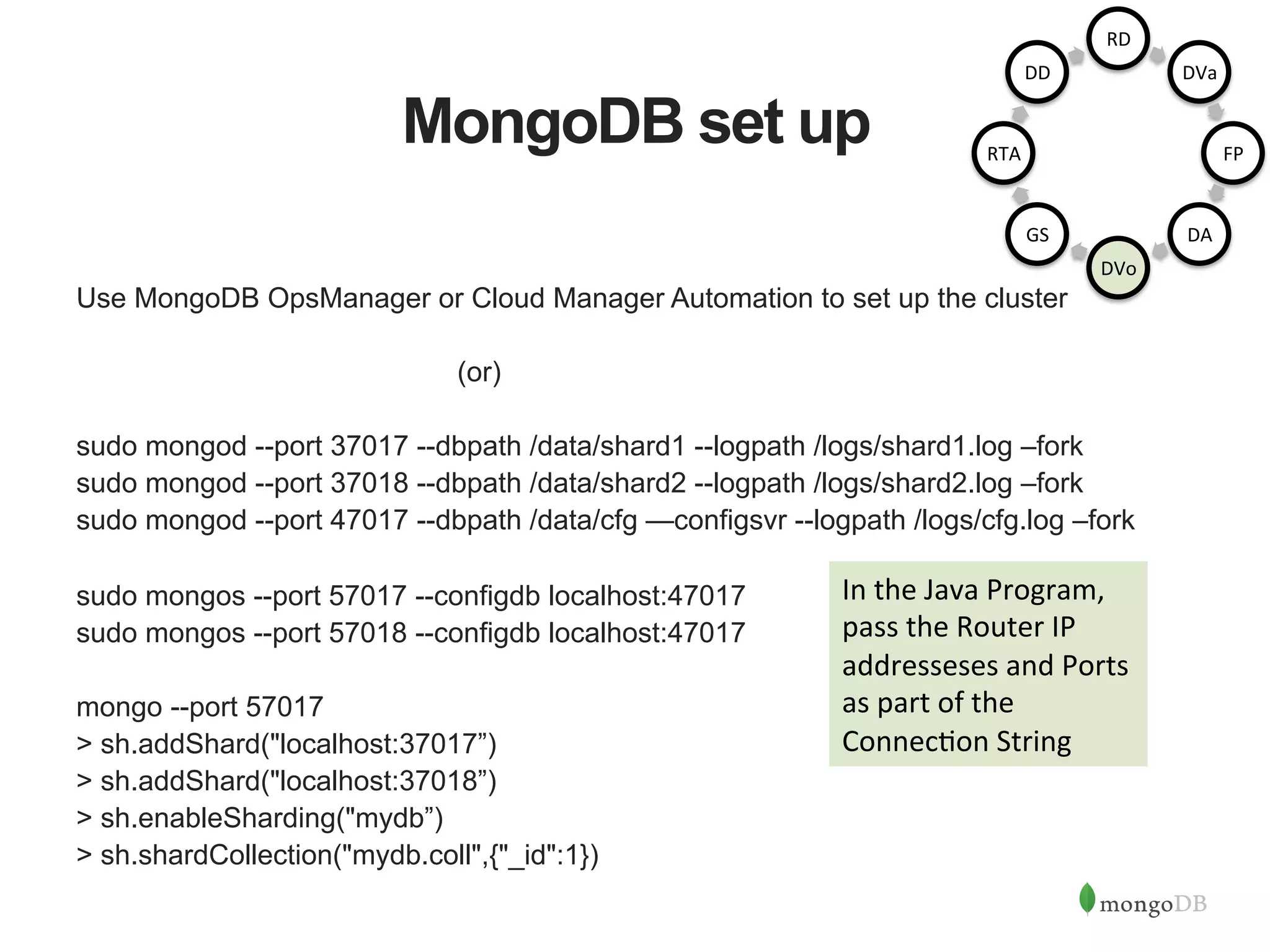
![MongoDB set up Use MongoDB OpsManager or Cloud Manager Automation to set up the cluster (or) sudo mongod --port 27017 --dbpath /data/rs1 --replSet rs --logpath /logs/rs1.log --fork sudo mongod --port 27018 --dbpath /data/rs2 --replSet rs --logpath /logs/rs2.log --fork sudo mongod --port 27019 --dbpath /data/rs3 --replSet rs --logpath /logs/rs3.log --fork mongo --port 27017 > config = { "_id" : "rs", "members" : [ ... {"host":"localhost:27017", "_id":0}, ... {"host":"localhost:27018", "_id":1}, ... {"host":"localhost:27019", "_id":2} ... ] ... } rs.initiate(config) In the Java Program, pass the addresseses and Ports of the replica set members as part of the Connec1on String RD DVa FP DA DVo GS RTA DD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingjavaapplicationsonmongodb-150923184742-lva1-app6892/75/Webinar-Building-Your-First-App-with-MongoDB-and-Java-25-2048.jpg)
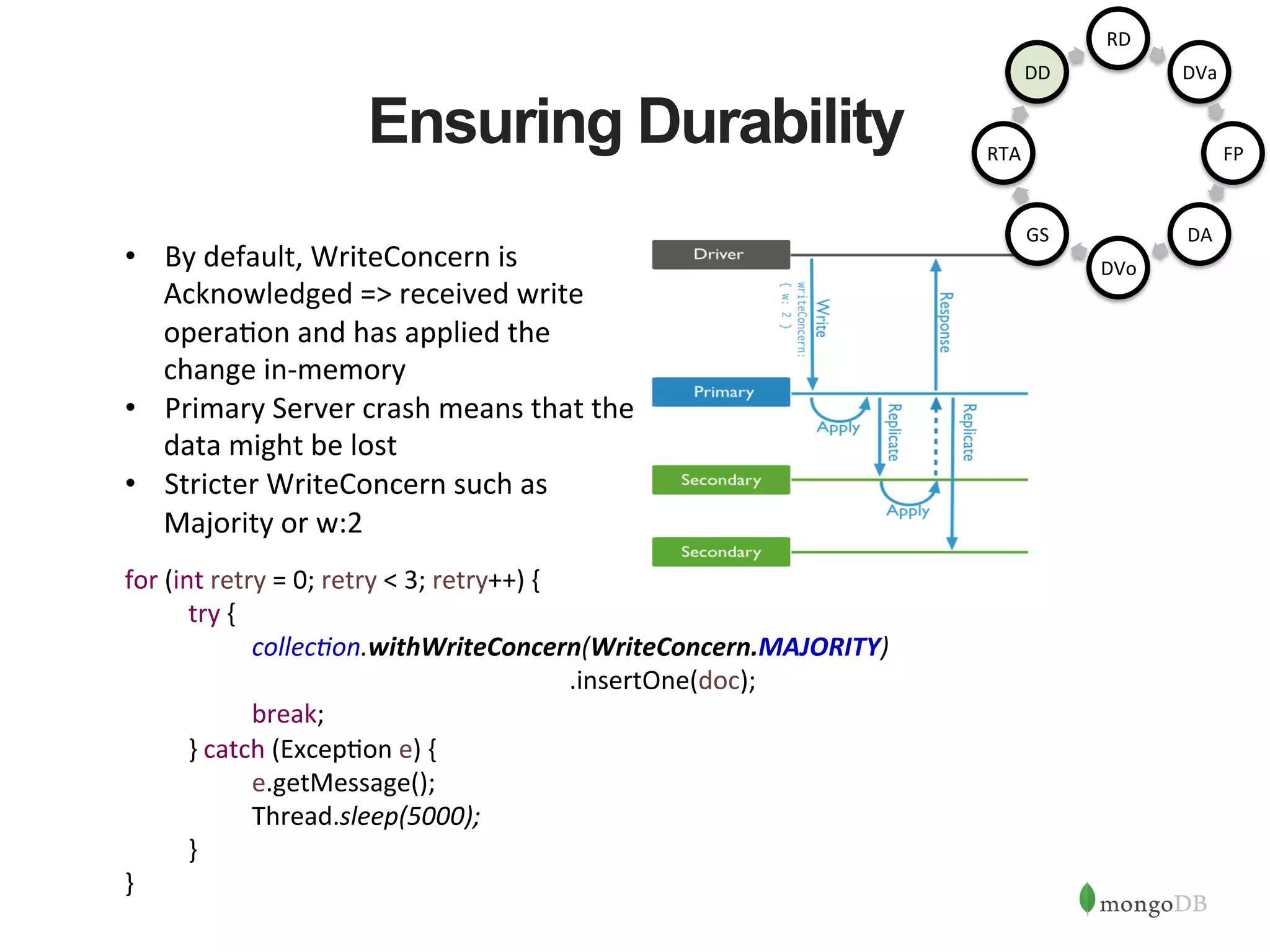
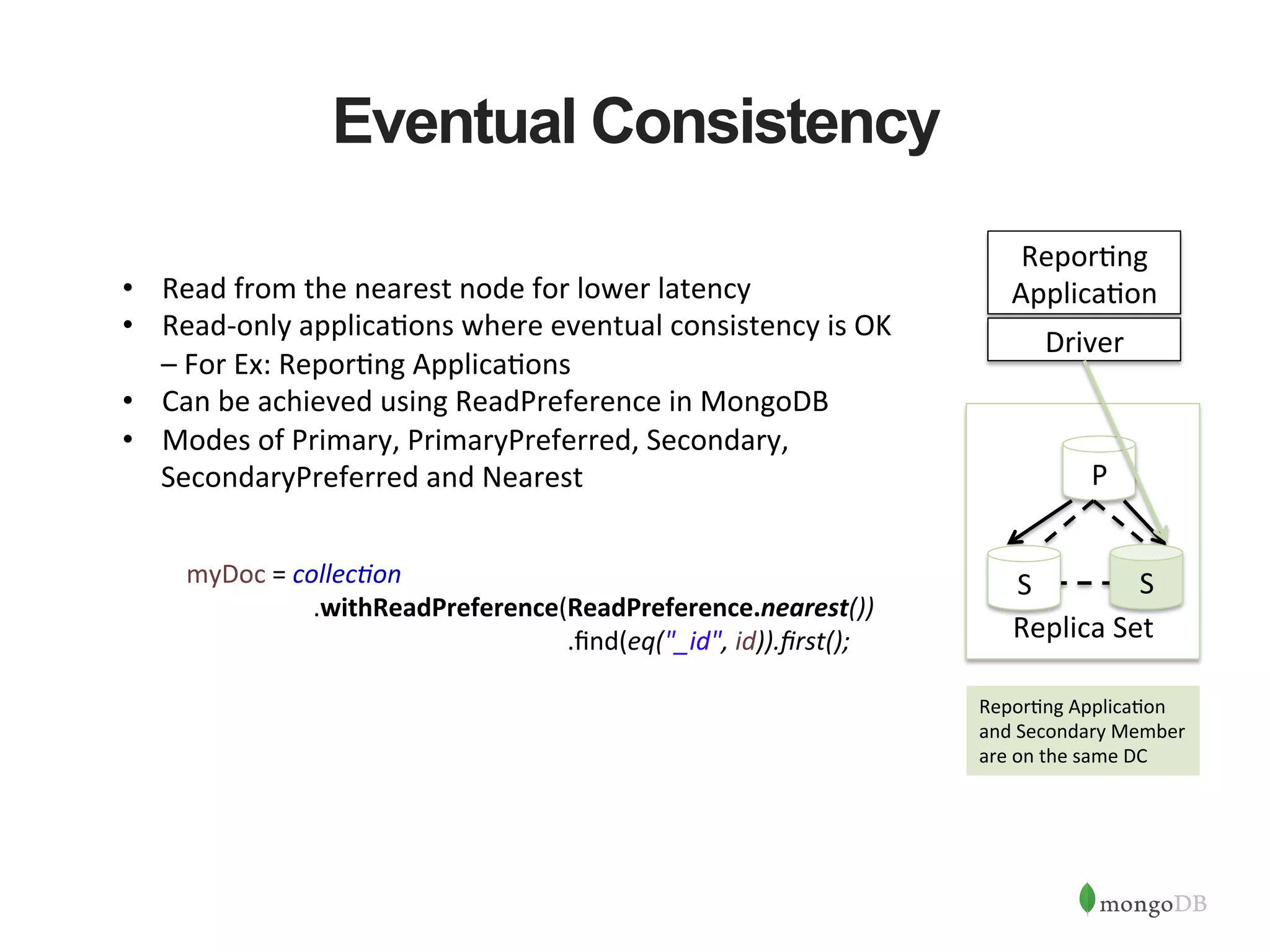
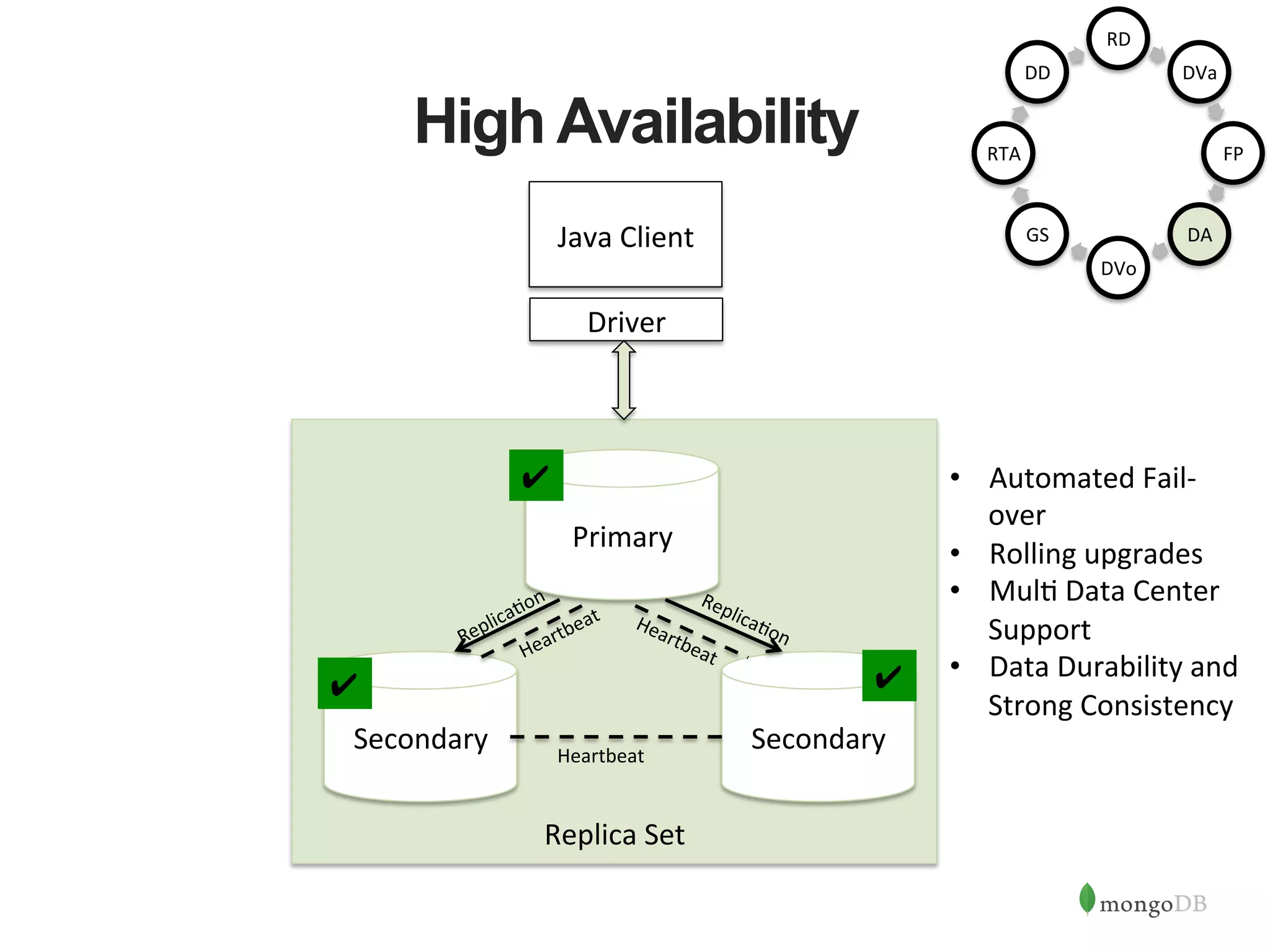
![HA Best Practices • HA against DC failures and ac1ve-‐ac1ve => 5 Nodes across 3 DCs • For Writes => Majority Nodes Need to be in Ac1ve State • For Reads => Secondary Reads can con1nue • Majority Inac1ve => Force Reconfig to con1nue Writes rs:SECONDARY> config = { "_id" : "rs", "members" : [ ... {"host":"localhost:27018", "_id":1} ... ] ... } rs:SECONDARY> rs.reconfig(config, {force:true}) { "ok" : 1 } rs:PRIMARY> Replica Set Removed Removed Primary Java Client Driver ✔ ✗ ✗](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingjavaapplicationsonmongodb-150923184742-lva1-app6892/75/Webinar-Building-Your-First-App-with-MongoDB-and-Java-28-2048.jpg)
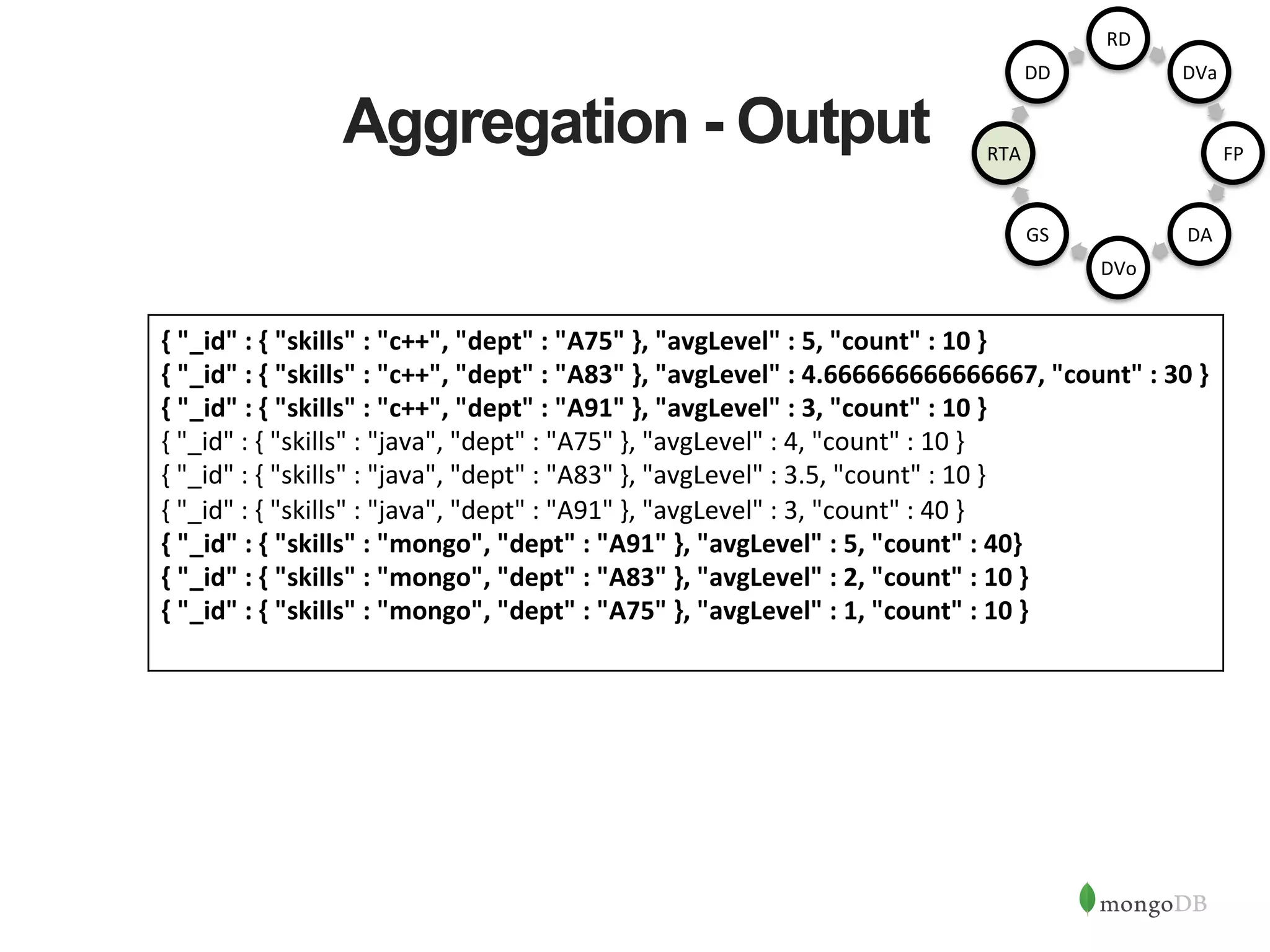
![Aggregation of Data import sta1c com.mongodb.client.model.Accumulators.avg; import sta1c com.mongodb.client.model.Accumulators.sum; import sta1c com.mongodb.client.model.Aggregates.group; import sta1c com.mongodb.client.model.Aggregates.sort; import sta1c com.mongodb.client.model.Aggregates.unwind; import sta1c com.mongodb.client.model.Aggregates.out; … public void deptForSkills() { Document group = new Document(); group.append("skills", "$skills.name"); group.append("dept", "$info.dept"); AggregateIterable<Document> iter = collec6on.aggregate(Arrays .asList(unwind("$skills"), group(group, avg("avgLevel", "$skills.level"), sum("count", 1)), sort(new Document().append( "_id.skills", 1).append( "avgLevel", -‐1)), out("skills"))); } RD DVa FP DA DVo GS RTA DD { "_id" : 5, "name" : "John Snow", "skills" : [ { "name" : "java", "level" : 3, "cerAfied" : true }, { "name" : "mongo", "level" : 5 } ], "info" : { "dept" : "A91", "yearsexp" : 3, "gps" : [-‐74.00597, 40.71427], "locaAon" : "New York" } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingjavaapplicationsonmongodb-150923184742-lva1-app6892/75/Webinar-Building-Your-First-App-with-MongoDB-and-Java-29-2048.jpg)