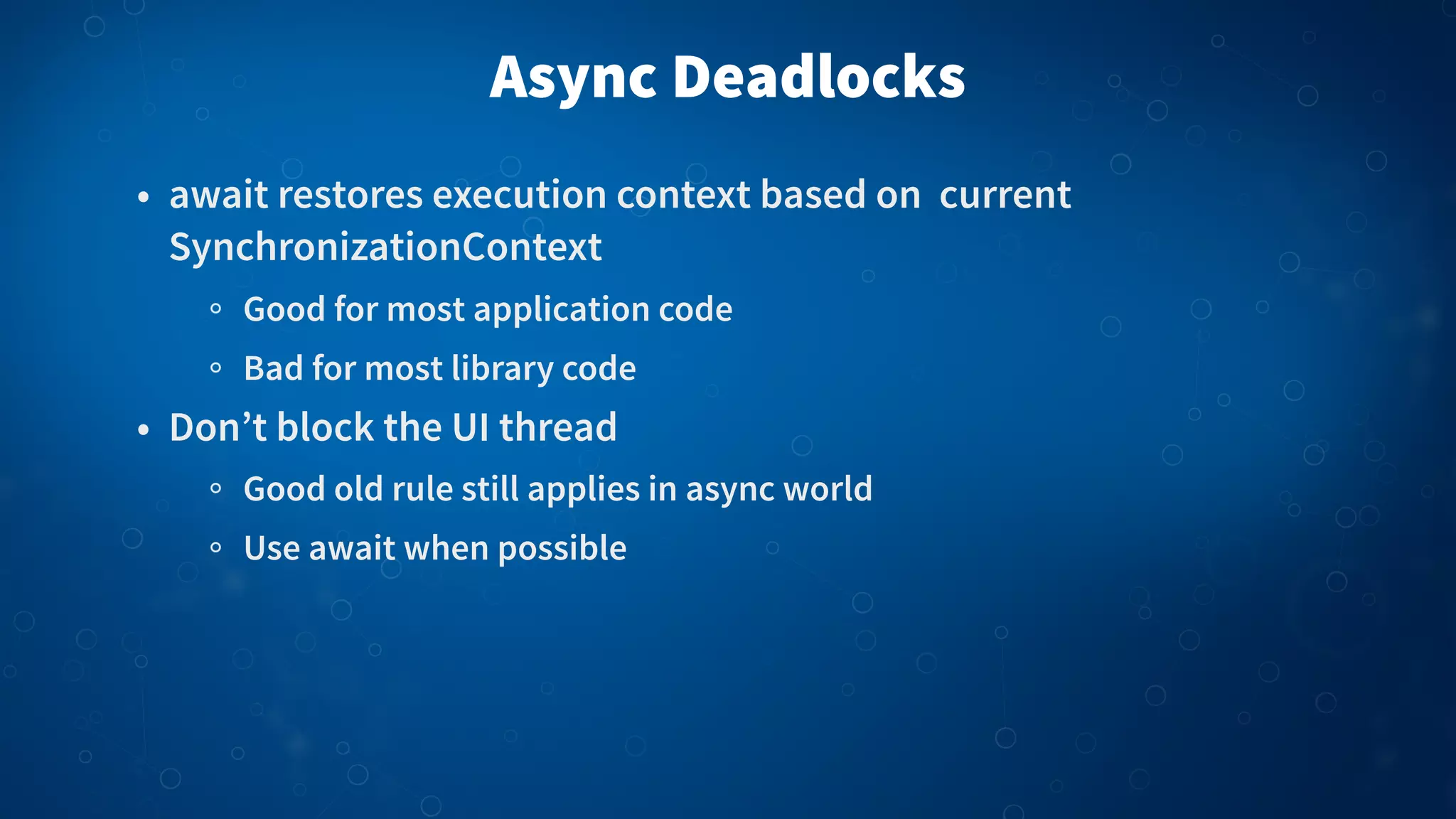
The document discusses asynchronous programming in C# using the async and await keywords. It begins by defining asynchronous events as those that occur independently of the main program flow. It then discusses how using async keeps the user interface responsive and avoids race conditions and callbacks. The key aspects of async in C# are introduced, including the async modifier and await keyword. Examples are provided of adding async to methods and event handlers. Best practices are covered such as using ConfigureAwait(false) to avoid deadlocks and naming asynchronous methods with suffixes like Async. Overall the document provides a high-level introduction to asynchronous programming with async and await in C#.







![01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Example: Calculating a Price Asynchronously public async Task<int> CalculatePriceAsync (Item[] items) { int price; // Calculate price asynchronously and return the value return price; } public override void ViewDidLoad () { button.TouchDown += async (sender, e) => { // This is asynchronous handler }; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usingasyncinyourmobileapps-mareksafar-130429085021-phpapp01/75/Using-Async-in-your-Mobile-Apps-Marek-Safar-8-2048.jpg)

![01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Calculating a Price Asynchronously public async Task<int> CalculatePriceAsync (Item[] items) { using (var cmd = CreateSqlCommand (Calculations.TotalPrice, items)) { using (var reader = await cmd.ExecuteReaderAsync ()) { int price = ReadPrice (reader); return price; } } } public override void ViewDidLoad () { button.TouchDown += async (sender, e) => { var price = await CalculatePriceAsync (items); priceLabel.Text = price.ToString (); }; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usingasyncinyourmobileapps-mareksafar-130429085021-phpapp01/75/Using-Async-in-your-Mobile-Apps-Marek-Safar-10-2048.jpg)


![01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Async Language Features public async Task RealAsync () { // This is real async heavy code (only 7 awaits someone else will // certainly do better) var test = new TestClass (await CallAsync () | await CallAsync ()) { Latitude = await GetLatitudeAsync (await AnotherAsync ()), Roles = from role in await GetRolesAsync () where role == "agent" select role }; .... test [await CallAsync ()] = new int[] { 33, await GetIntAsync () }; ... }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usingasyncinyourmobileapps-mareksafar-130429085021-phpapp01/75/Using-Async-in-your-Mobile-Apps-Marek-Safar-13-2048.jpg)




![01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Exception Throwing public async Task<int> CalculatePriceAsync (Item[] items) { if (items == null) { // Throw before suspension throw new ArgumentNullException ("items"); } ... var price = await CalculatePriceAsync (items); if (price < 0) { // Throw after suspension throw new ArgumentException ("Invalid items"); } ... }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usingasyncinyourmobileapps-mareksafar-130429085021-phpapp01/75/Using-Async-in-your-Mobile-Apps-Marek-Safar-18-2048.jpg)


![01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Async Deadlock Example public async Task<int> CalculatePriceAsync (Item[] items) { using (var cmd = CreateSqlCommand (Calculations.TotalPrice, items)) { using (var r = await cmd.ExecuteReaderAsync ()) { ..... } } } // The method itself cannot be async public override bool FinishedLaunching (UIApplication app, NSDictionary options) { .... int price = CalculatePriceAsync (items).Result; // Synchronous wait // This line won’t be reached if flow suspension occurred }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usingasyncinyourmobileapps-mareksafar-130429085021-phpapp01/75/Using-Async-in-your-Mobile-Apps-Marek-Safar-22-2048.jpg)

![01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Async Deadlock Fixed public async Task<int> CalculatePriceAsync (Item[] items) { using (var cmd = CreateSqlCommand (Calculations.TotalPrice, items)) { using (var r = await cmd.ExecuteReaderAsync ().ConfigureAwait (false)) { // The context is not restored but that’s fine for no UI method } } } // The method itself cannot be async public override bool FinishedLaunching (UIApplication app, NSDictionary options) { .... int price = CalculatePriceAsync (items).Result; // Synchronous wait // Program continues when the wait is signalled }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usingasyncinyourmobileapps-mareksafar-130429085021-phpapp01/75/Using-Async-in-your-Mobile-Apps-Marek-Safar-24-2048.jpg)





