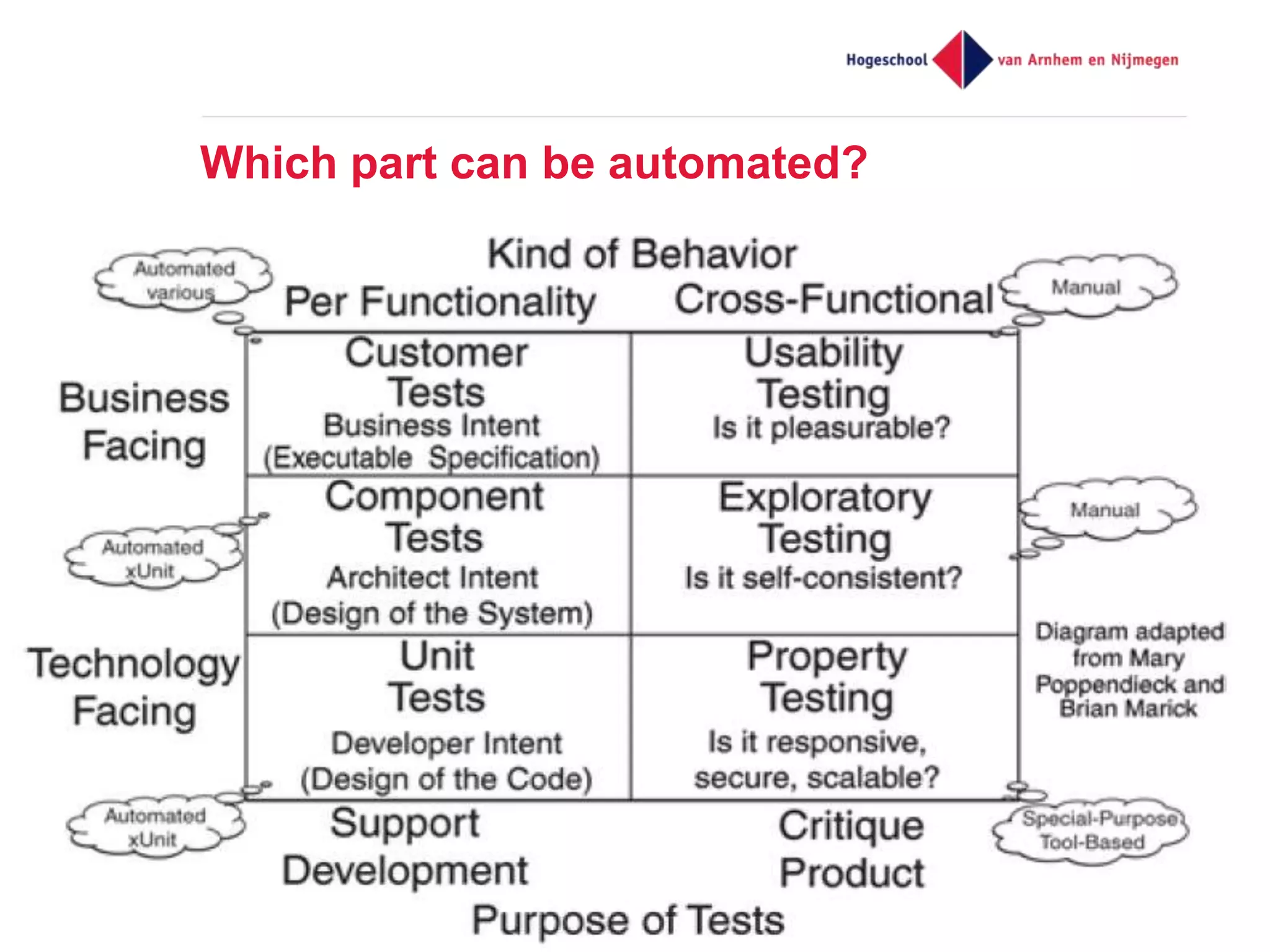
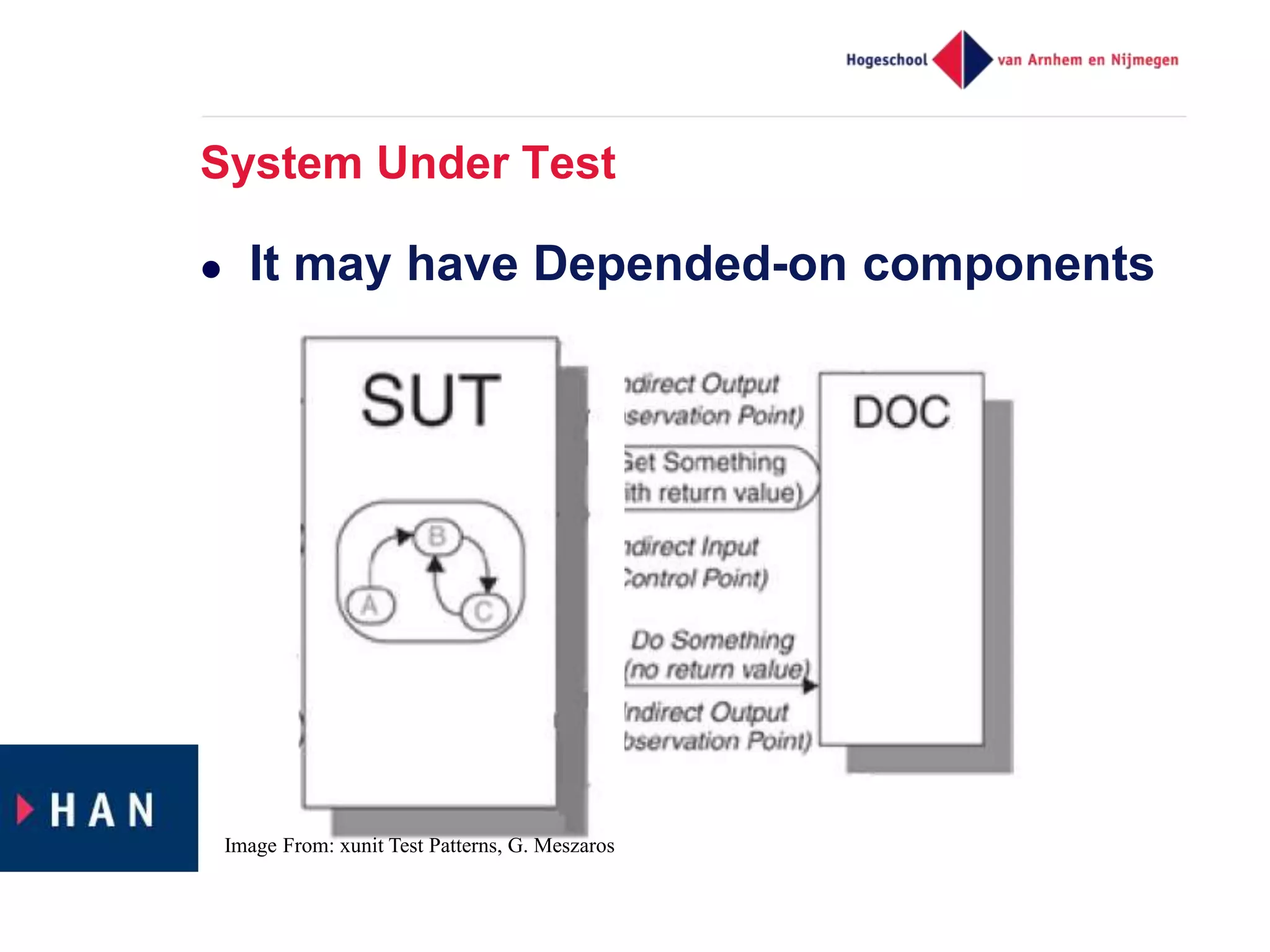
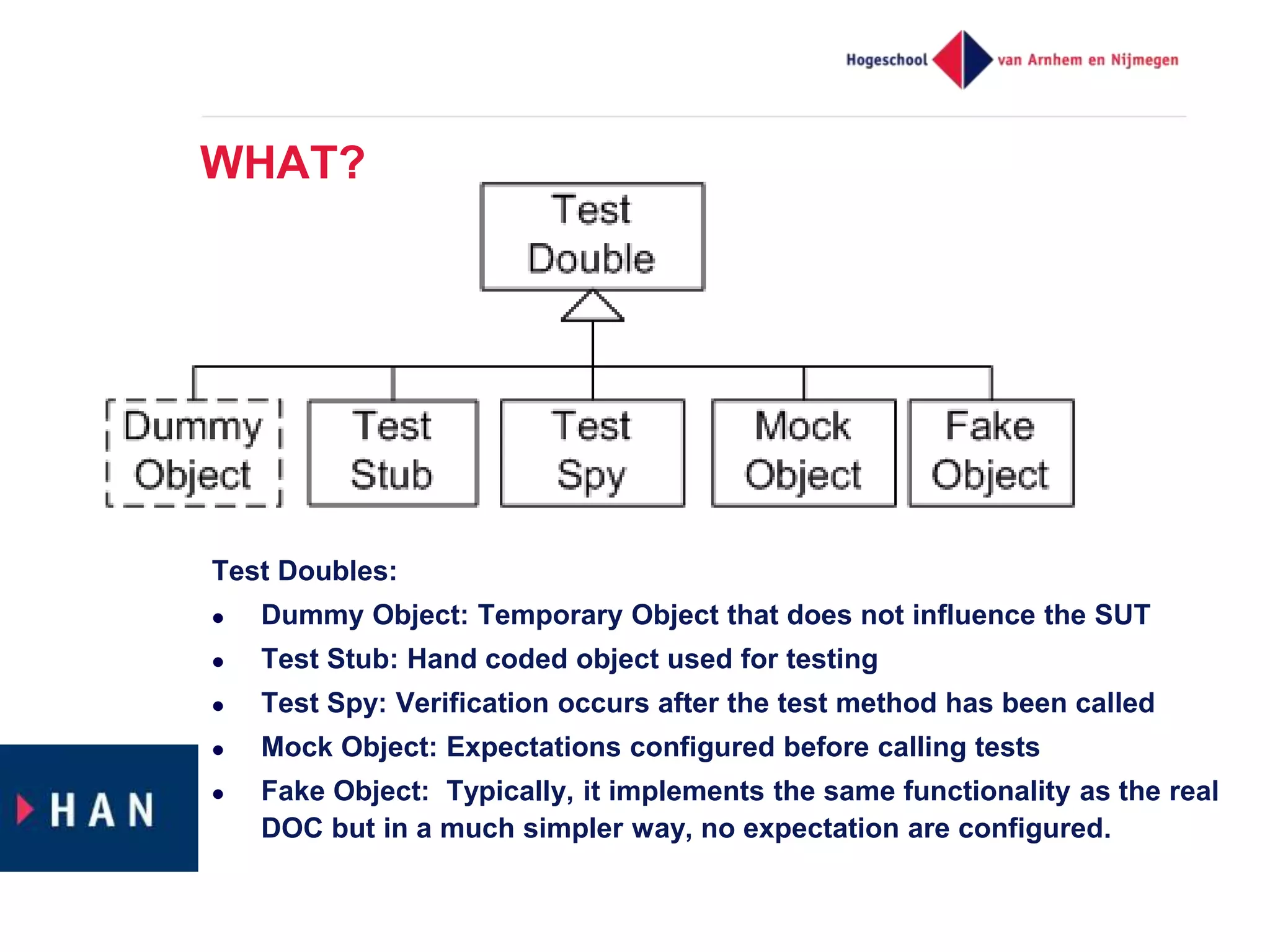
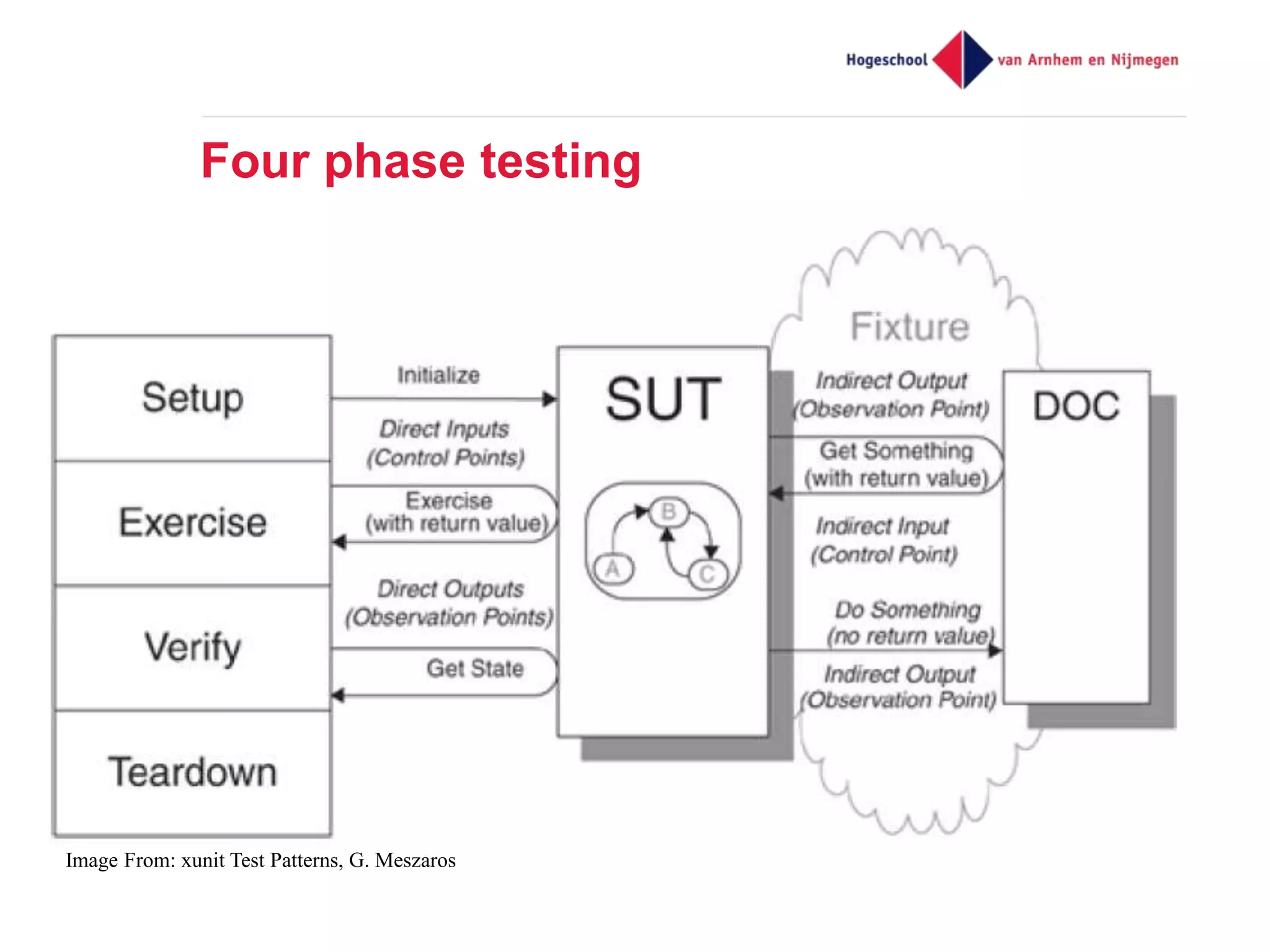
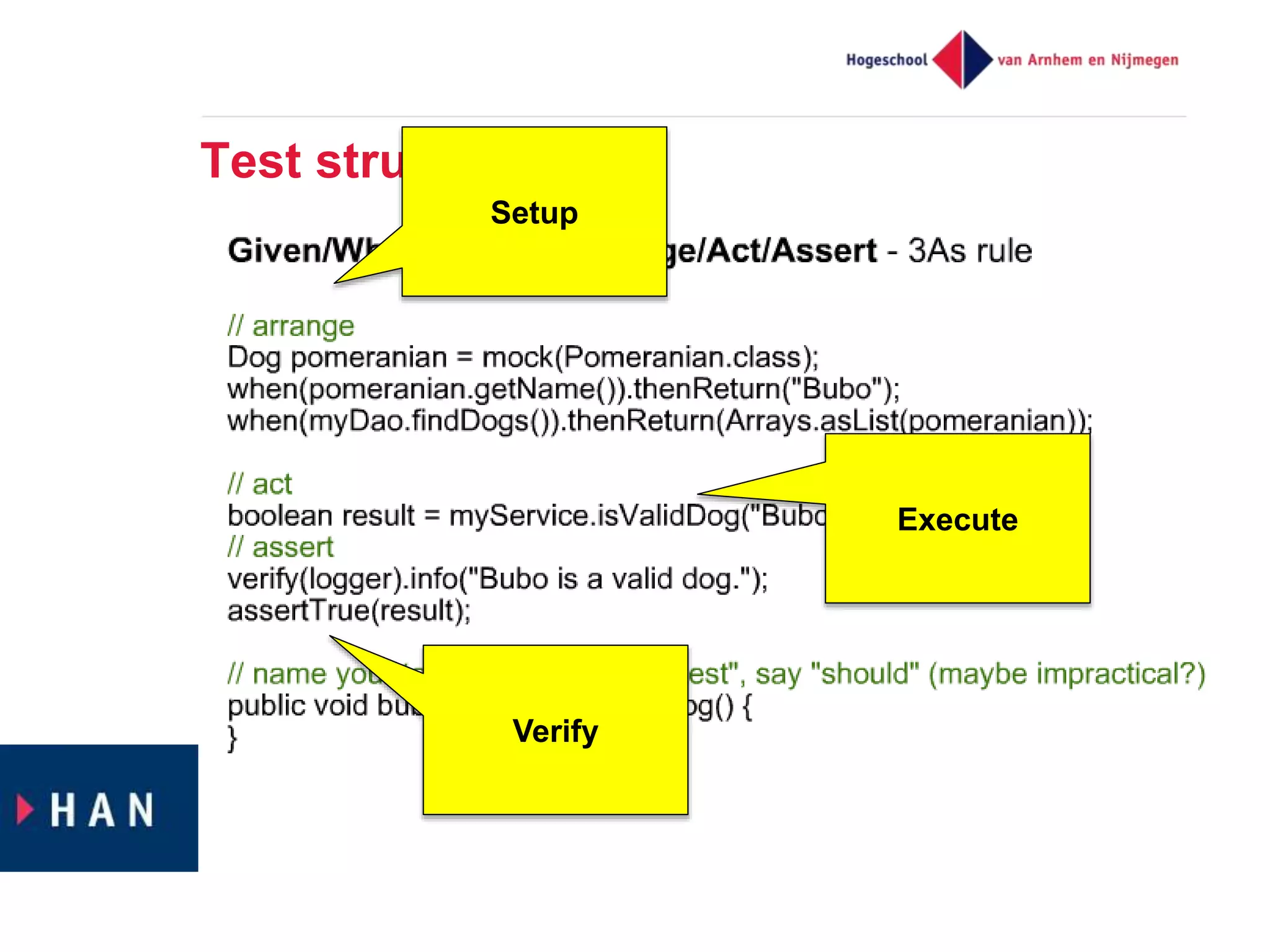
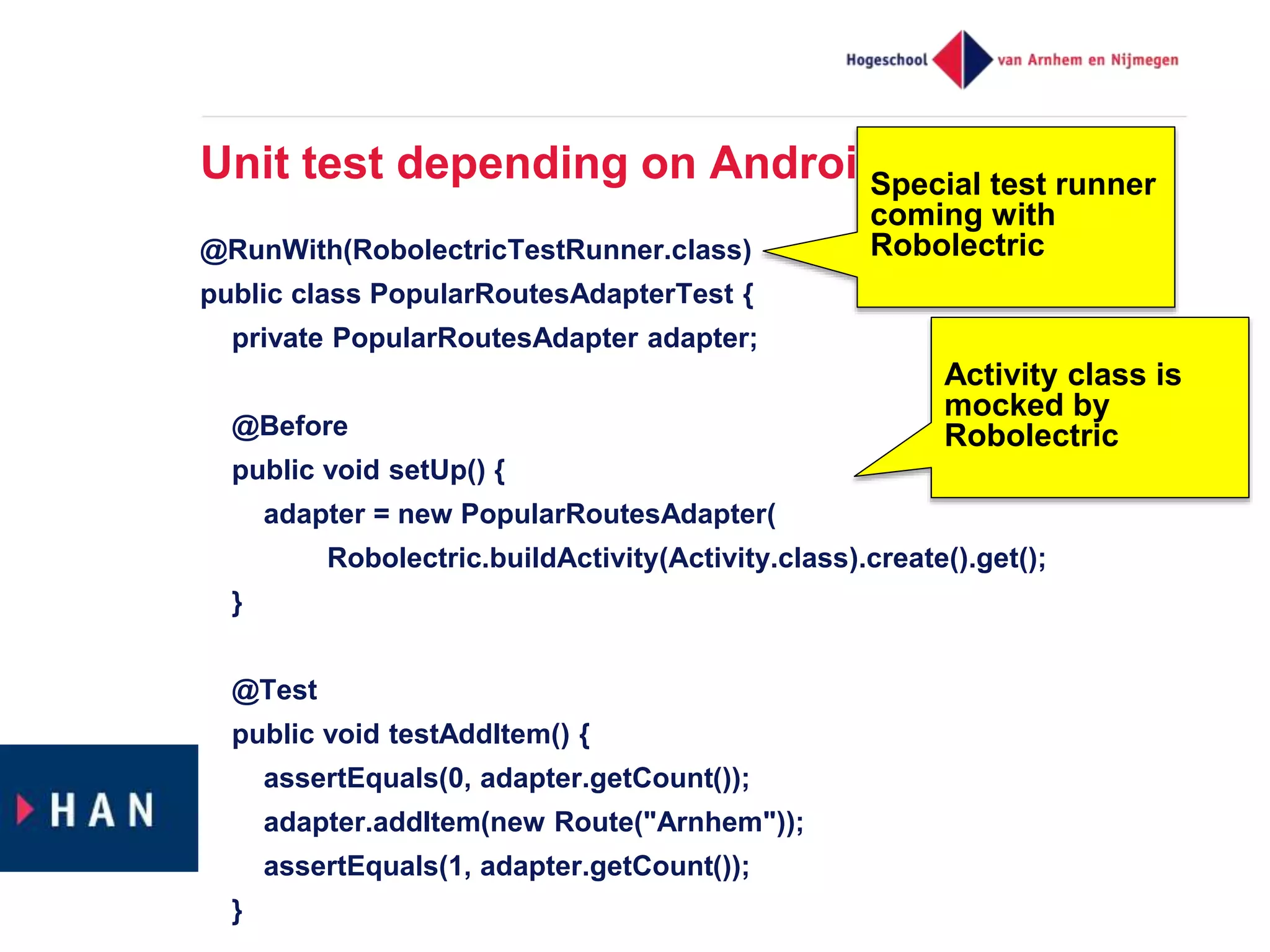
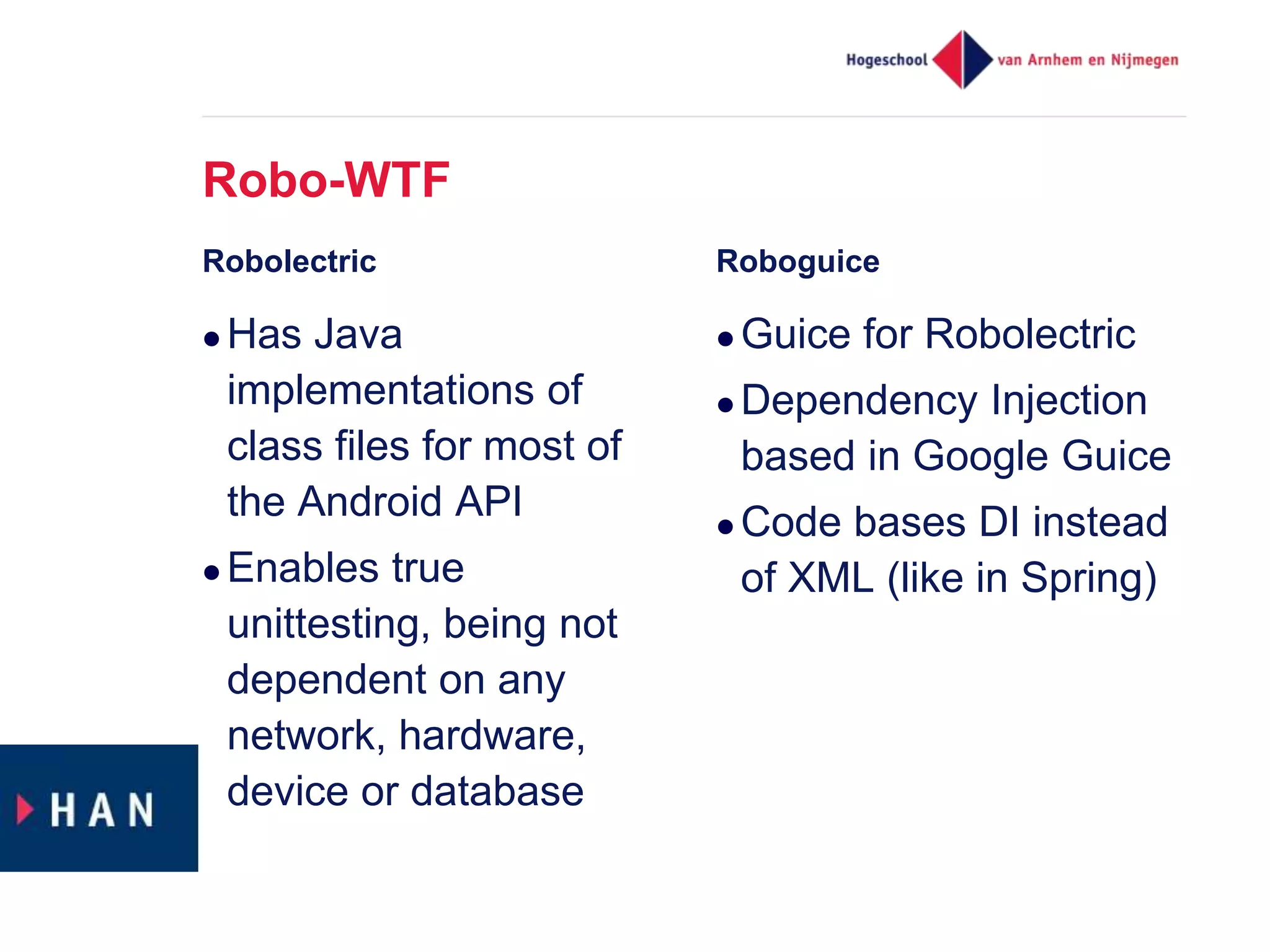
The document discusses effective unit testing strategies for Android, emphasizing the importance of automation, writing tests first, and utilizing various test doubles like mocks and stubs. It highlights the use of frameworks such as Mockito and Robolectric to facilitate testing while addressing common issues like slow tests and dependencies on specific platforms. The document concludes with recommendations for good testing practices and resources for further reading.