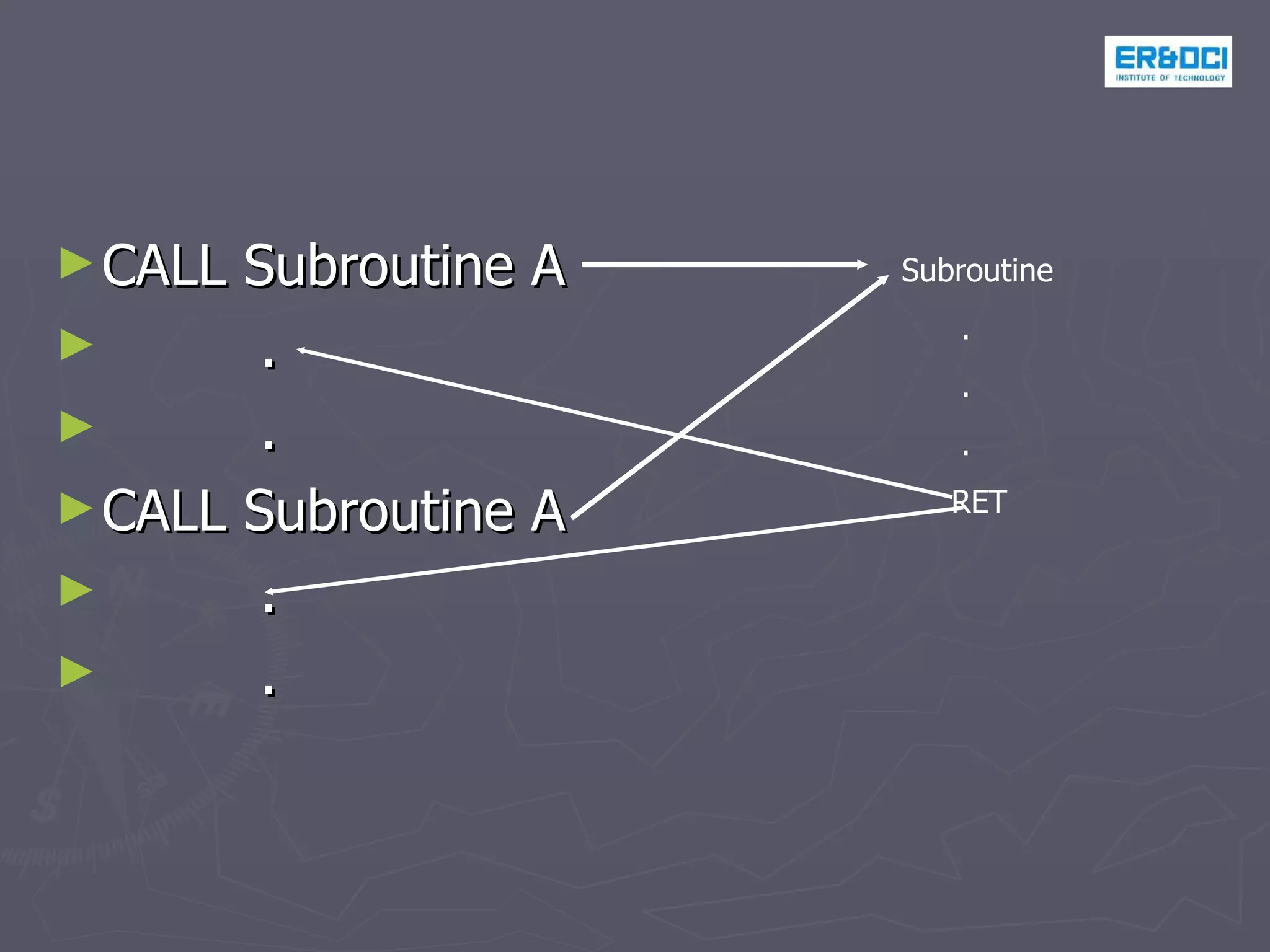
The document discusses stack and subroutines in assembly language programs. It explains that stack is used to store return addresses and save register contents. Subroutines allow breaking programs into modules and use CALL and RET instructions. An example program adds two numbers stored in memory locations and returns the result.







![Sub Routine Eg. .DATA num1 dw 22 num2 dw 32 result dw 0 .CODE addnum proc mov ax, [num1] mov bx, [num2] add ax, bx mov [result], ax ret addnum endp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stackandsubroutine-111106021148-phpapp02/75/Stack-and-subroutine-9-2048.jpg)




![* Write an ALP to perform simple unsigned Multiplication. The two 16 bit numbers r 1121H and 1301H.Store the product in the location whose offset adrs is 8100H. TITLE Multiplication DOS SEG .MODEL Small .STACK 100H DATA Num1 DW 1121H Num2 DW 1301H .CODE Main PROC MOV AX, num1 ;Bring the first number to AX MOV BX, num2 ;Bring second MUL AX,BX ;Multiply the contents of AX and BX MOV [8100H],AX ;store the result at 8100H MOV AX,4C00H ;Return to DOS INT 21 H Main ENDP END Main](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stackandsubroutine-111106021148-phpapp02/75/Stack-and-subroutine-14-2048.jpg)

![* Write an ALP to find the greatest number in a given series of 8-bit numbers. The length of the series is stored in a location whose 16 bit offst adrs is 8100H.the series begins from the location whose offset adrs is 8102H.Store the result in the location whose 16-bit offset adrs is 8150H. TITLE Find the max. in a given series of data DOS SEG .MODEL Small .STACK 100H .DATA List db 20,45,13,15,04,72 .CODE Main PROC MOV AX,@data ;initialise DS Register MOV DS, AX MOV SI,[8102H] ;initialize SI register MOV AL,00H MOV CX,OFFSET 8100H;Length of series in CX BACK CMP AL,[SI] ;is next element>max JNC LAB MOV AL,[SI] LAB INC SI LOOP BACK ;repeat until CX=0 MOV [8150H],AL MOV AX,4C00H ;return to DOS INT 21 H Main ENDP END main](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stackandsubroutine-111106021148-phpapp02/75/Stack-and-subroutine-16-2048.jpg)
![* Write an ALP to find the sum of series of data. The length of the array is stored in a location whose 16-bit offset address is 8100H.the series begins from the location, whose offset 16-bit adrs is 8102H.store the result in location whose 16-bit offset is 8150H. .DATA list db 07,82,17,59,A3,3E Main PROC MOV AX,@data MOV DS,AX MOV DX,00H MOV CX,[8100H] MOV SI,OFFSET list BACK ADD DL,[SI] ADC DH,0 INC SI LOOP BACK MOV [8150],DX MOV AX,4C00H Main ENDP END main](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stackandsubroutine-111106021148-phpapp02/75/Stack-and-subroutine-17-2048.jpg)
