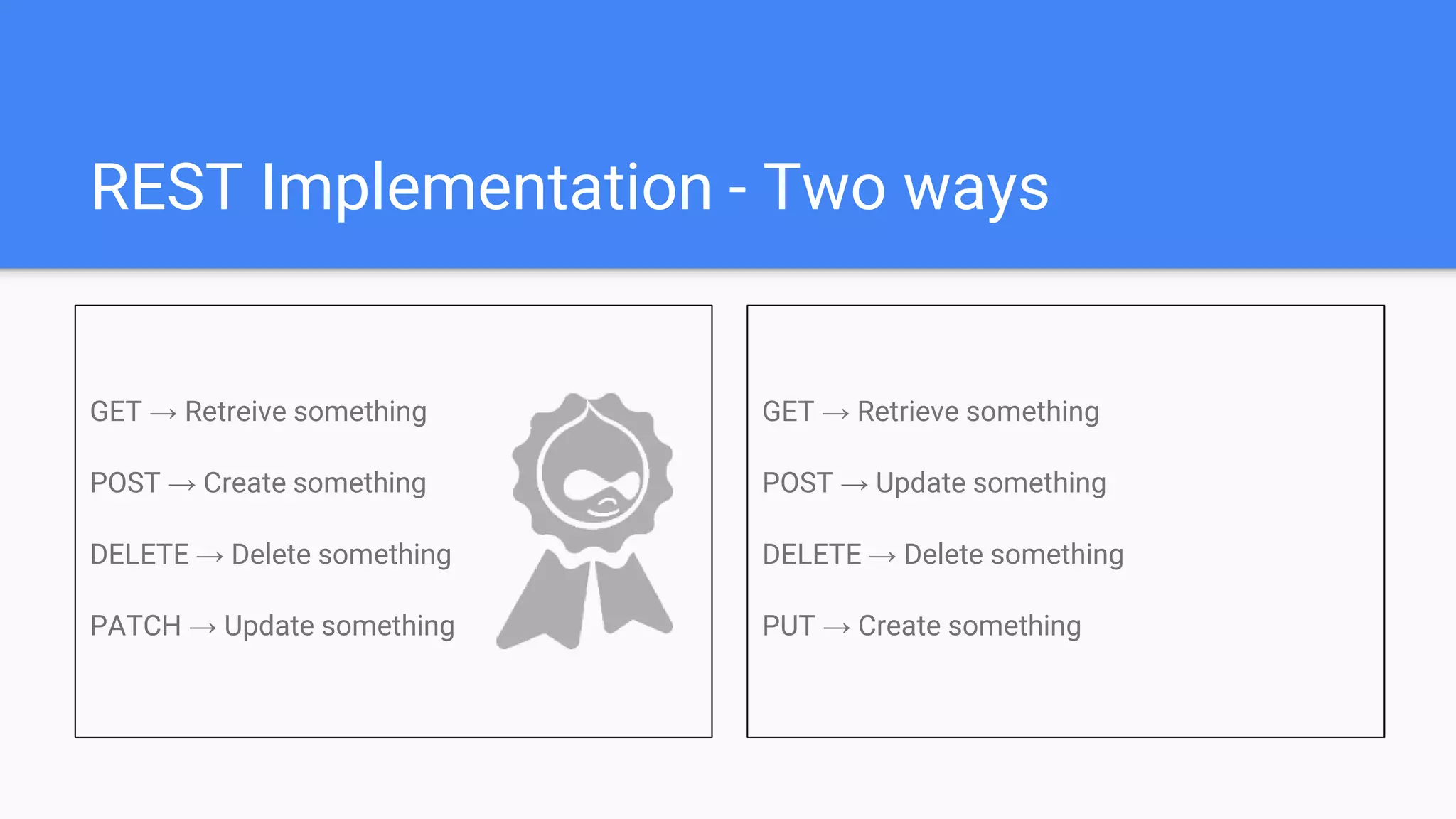
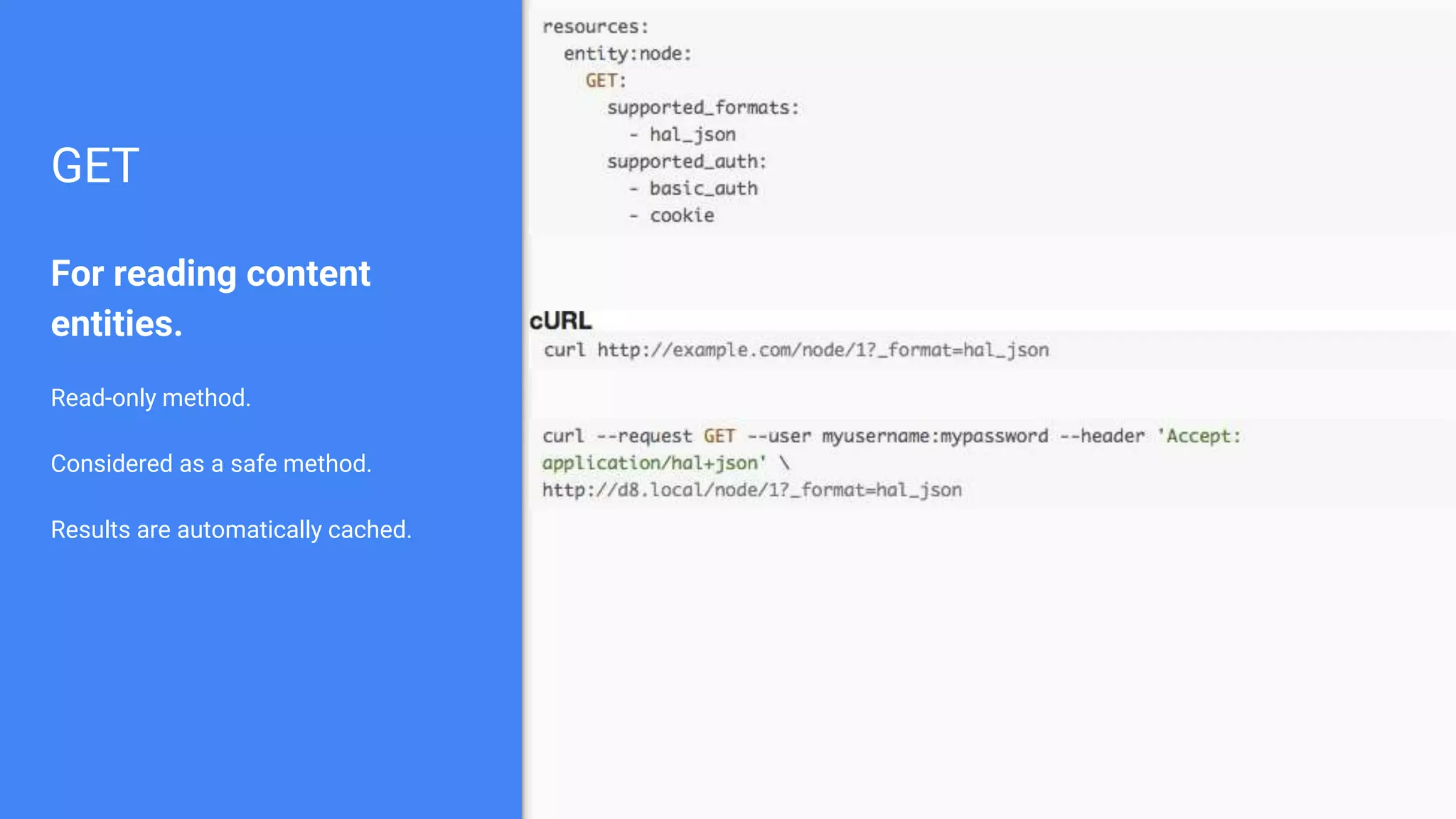
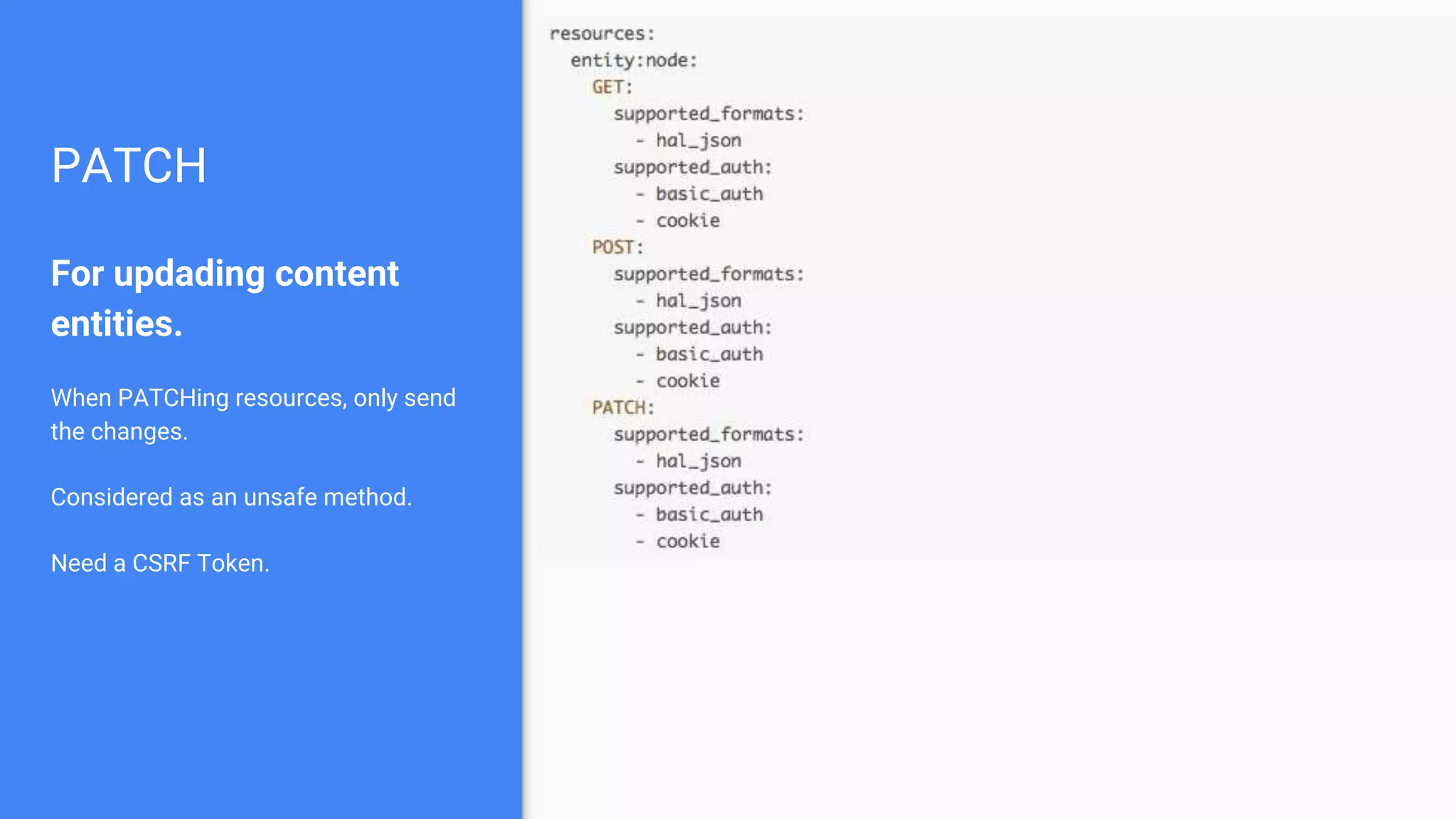
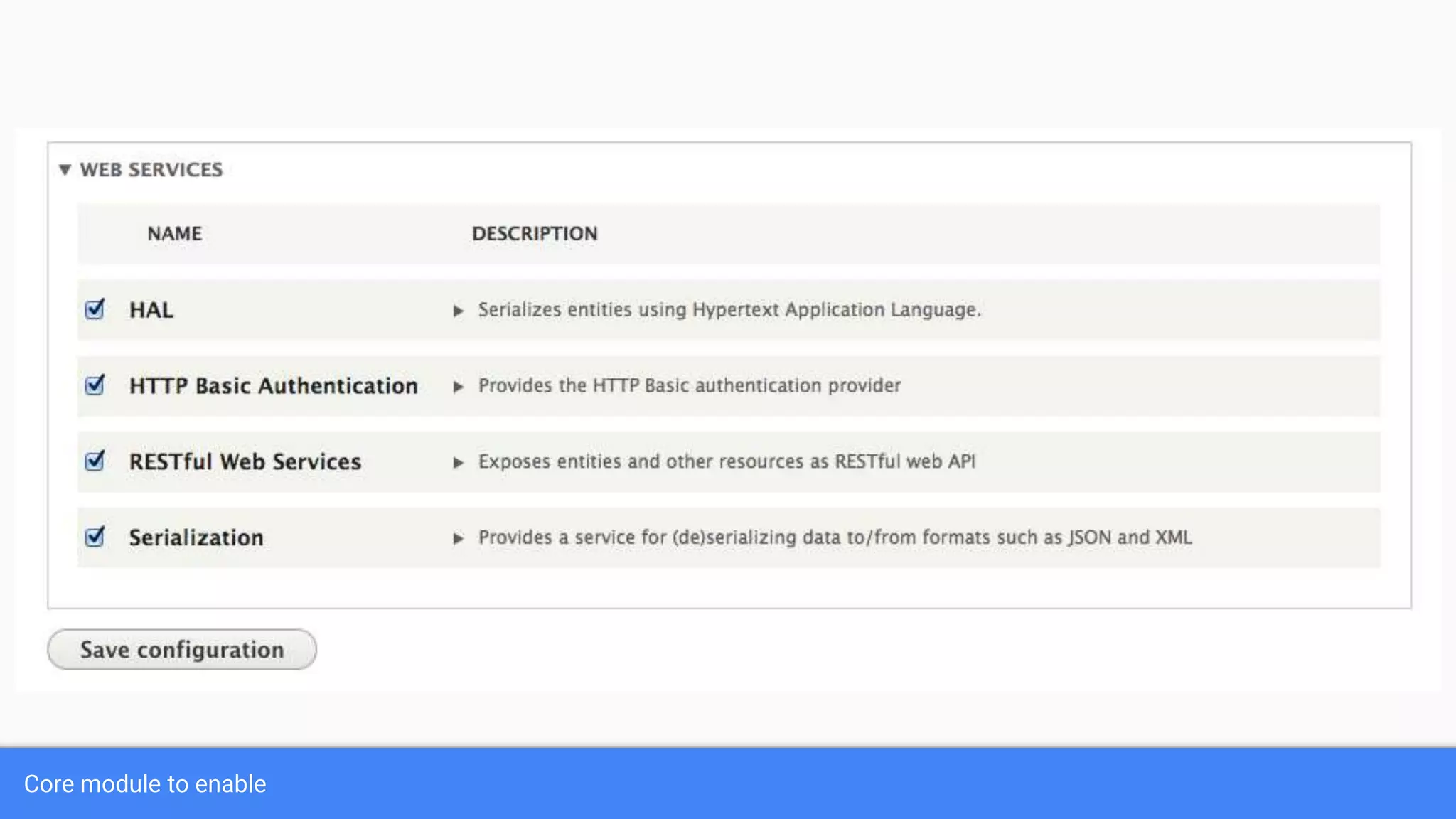
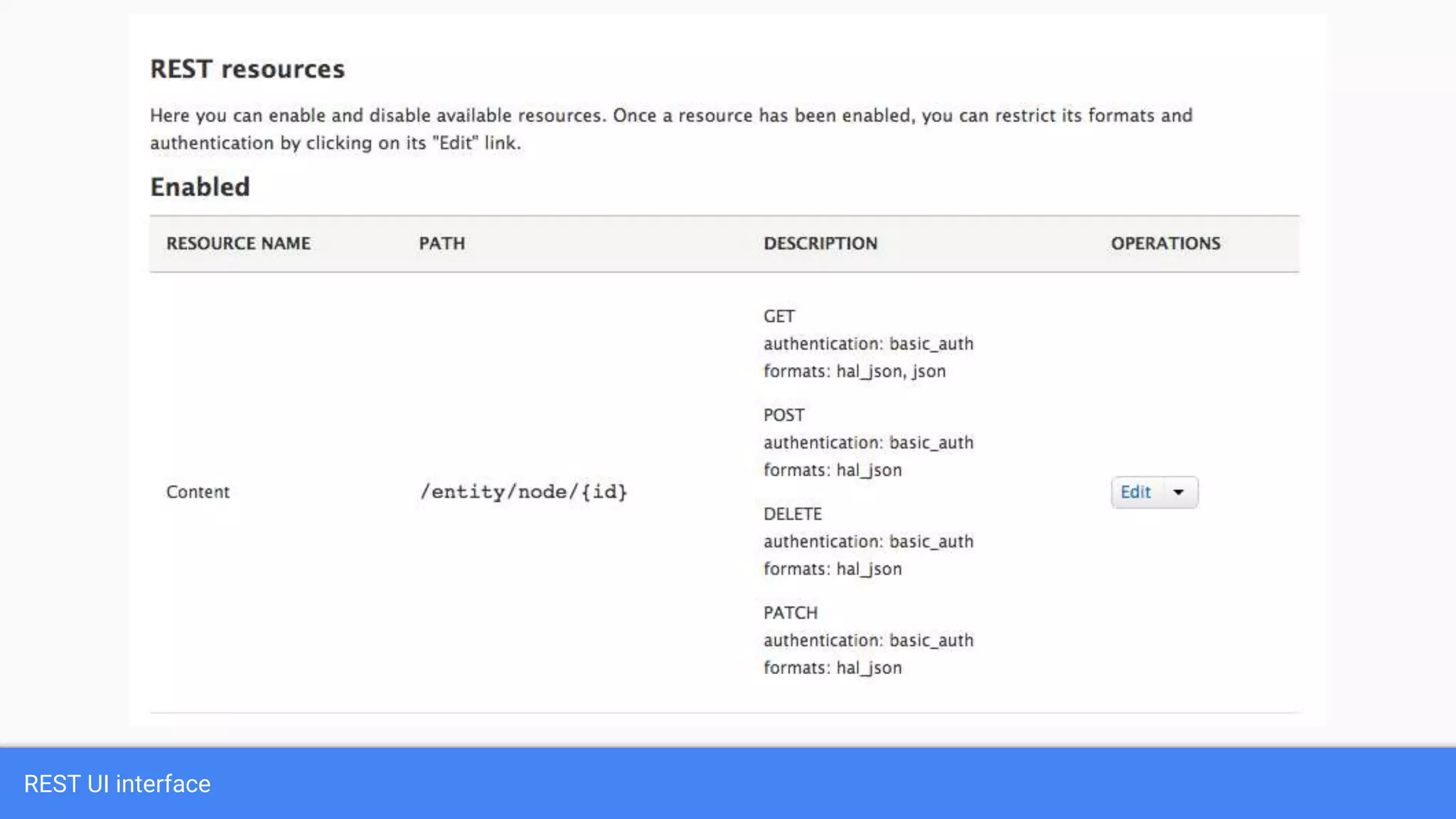
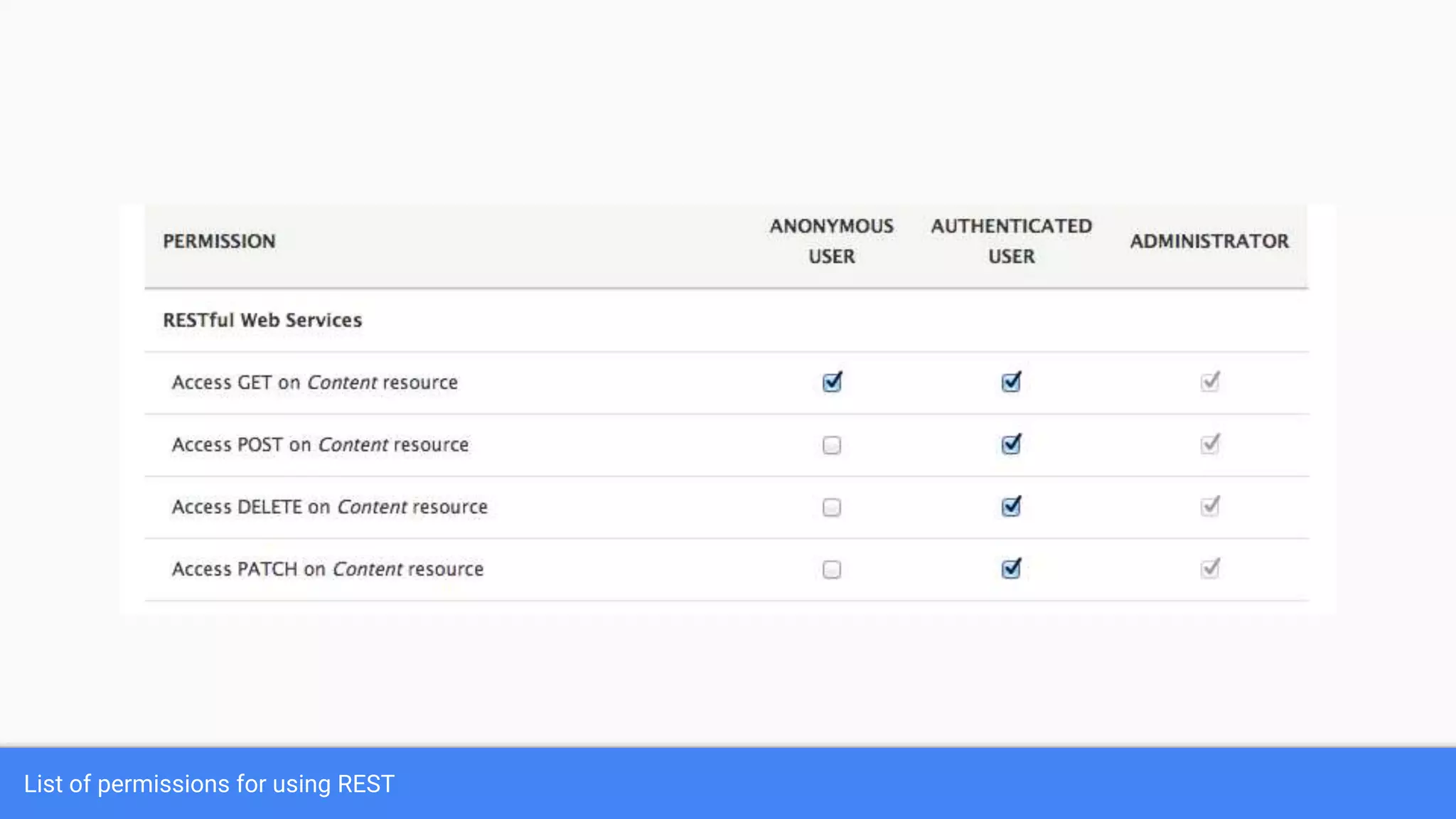
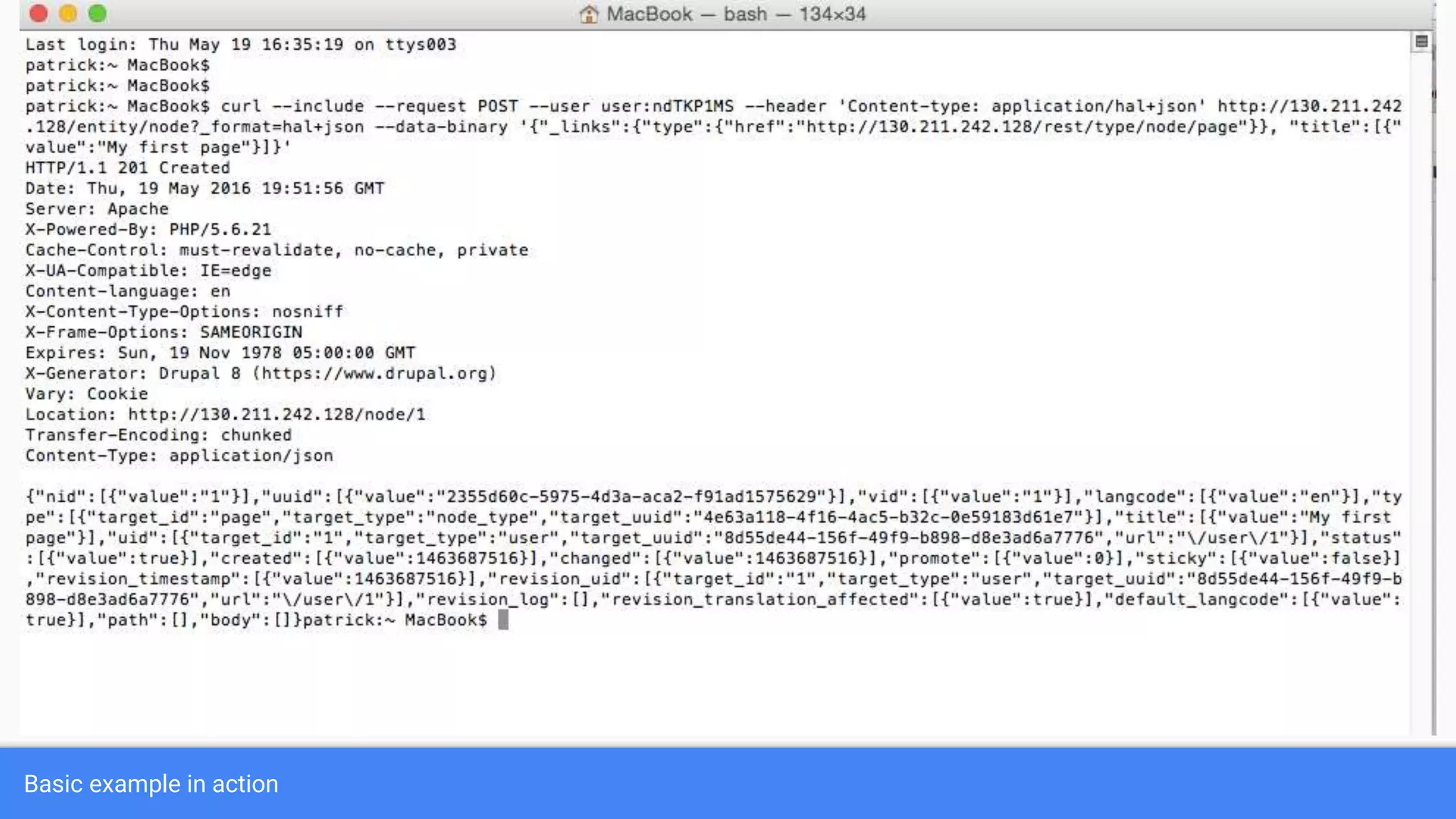
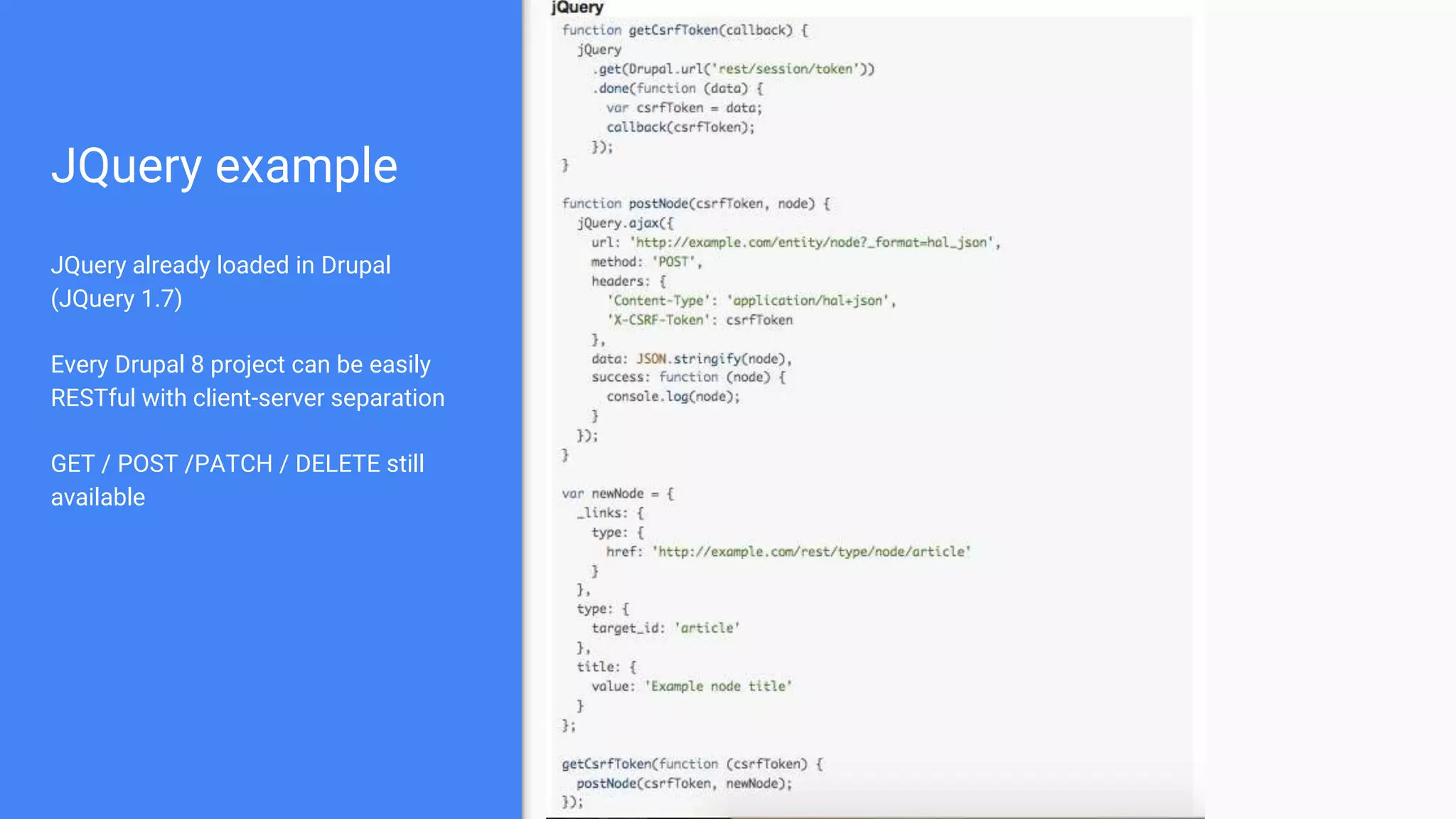
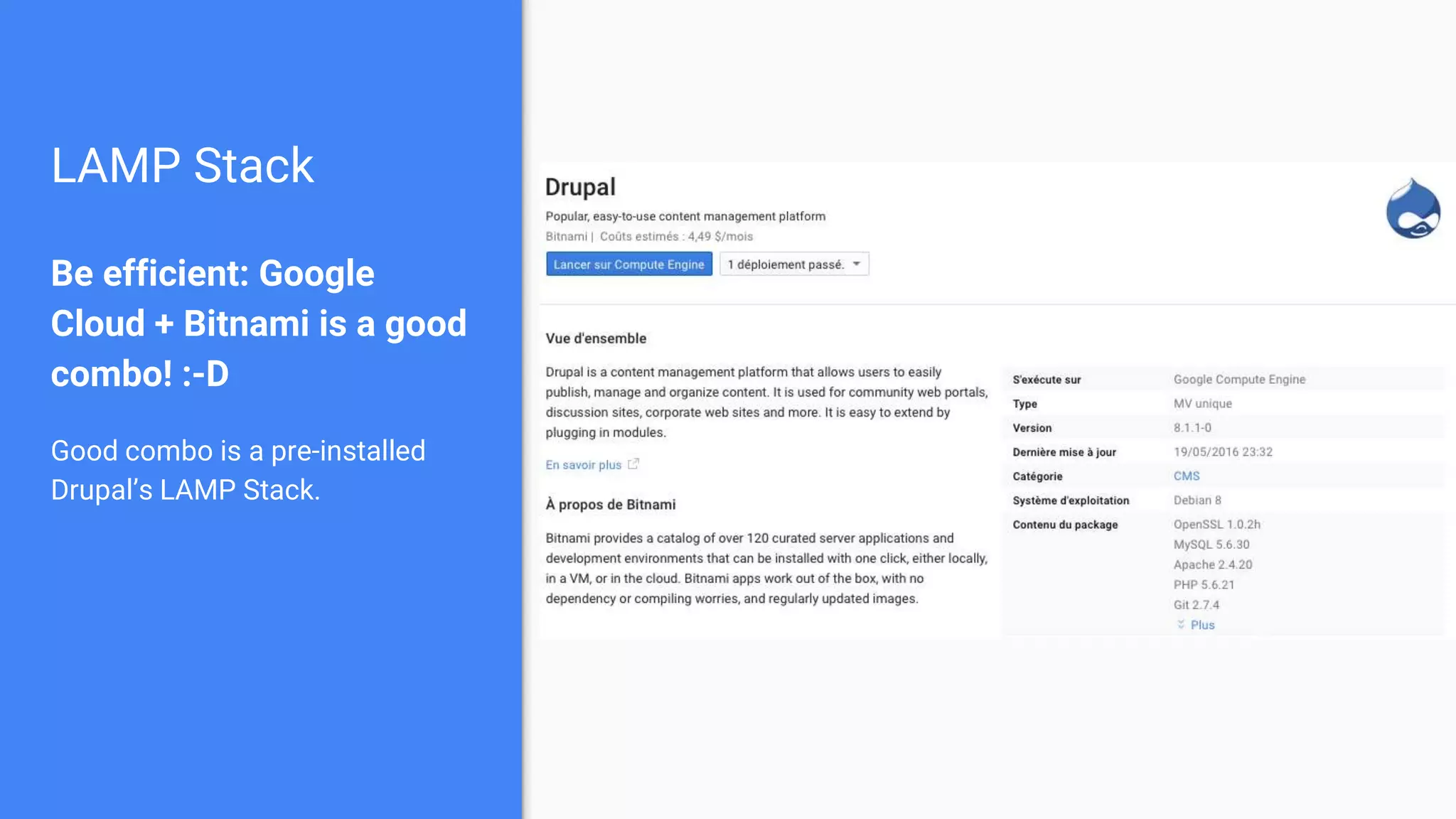
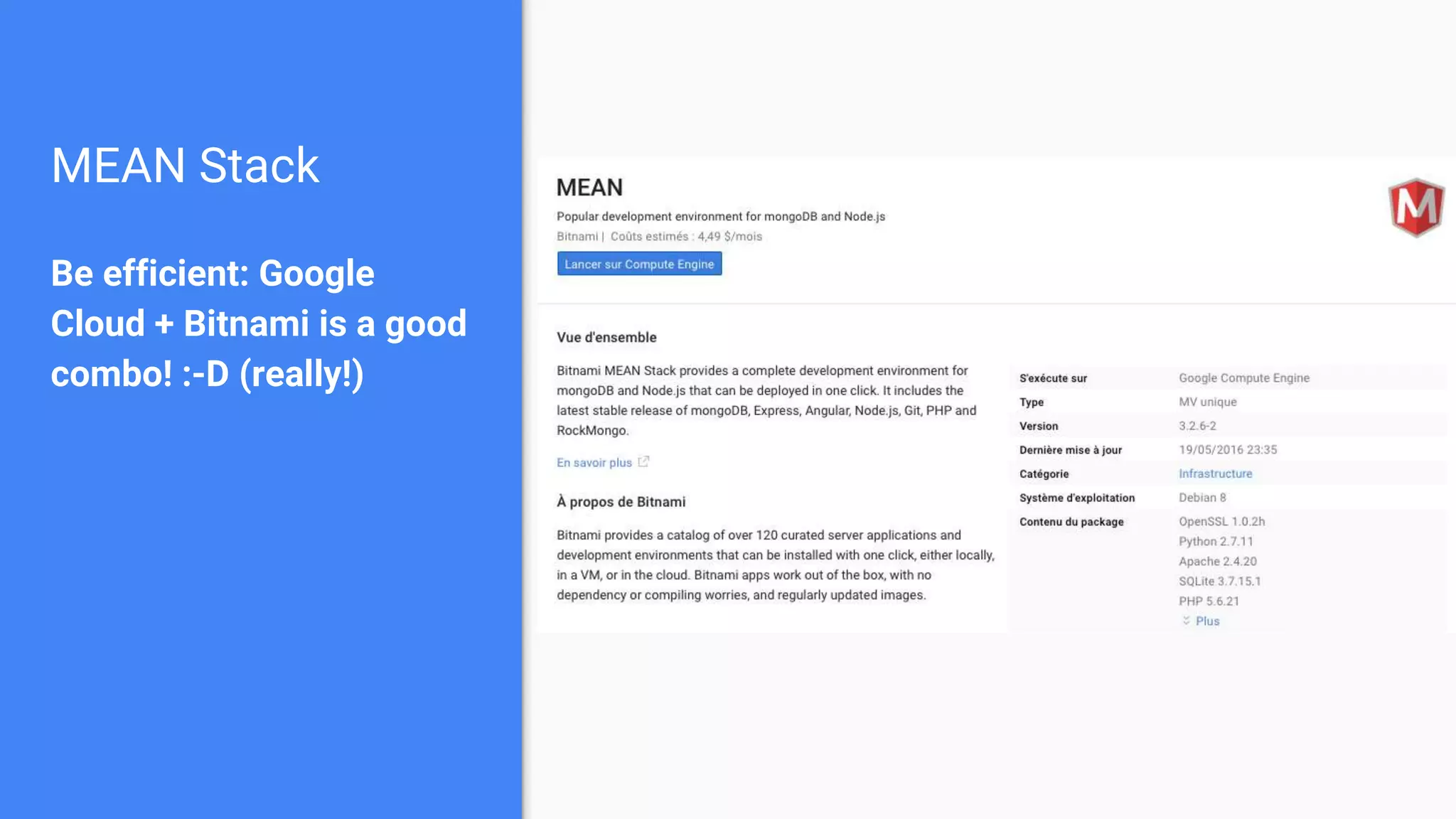
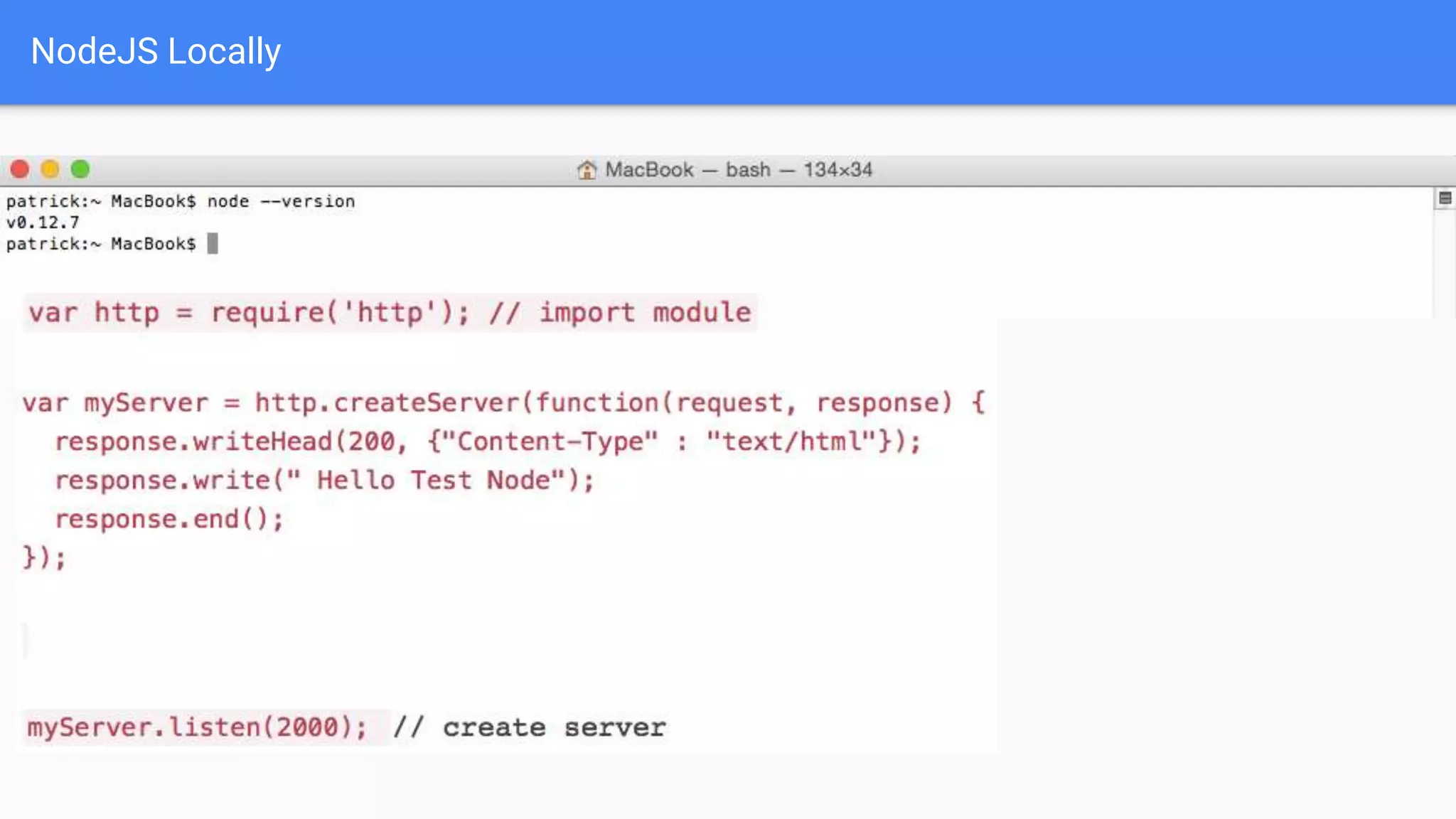
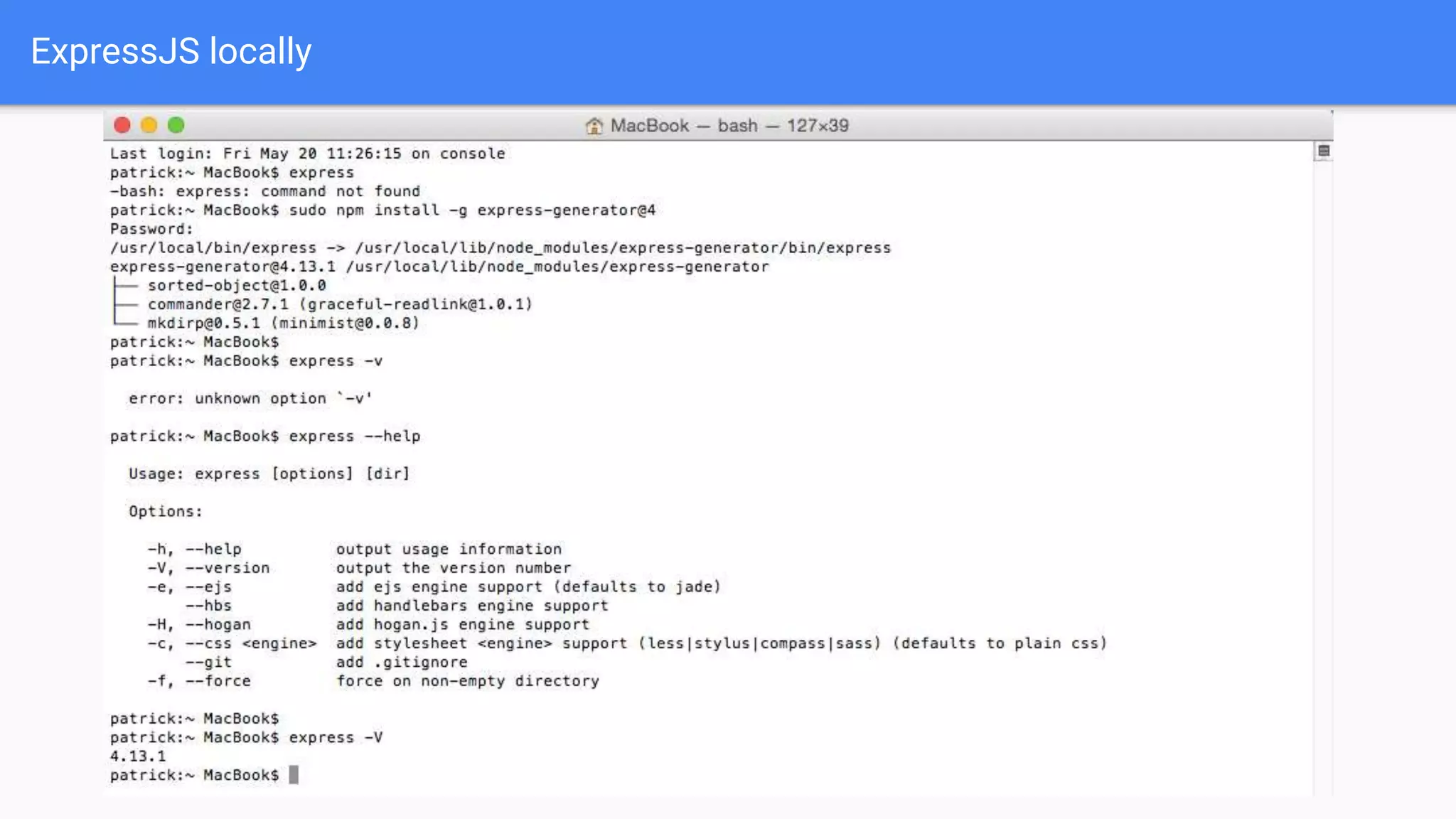
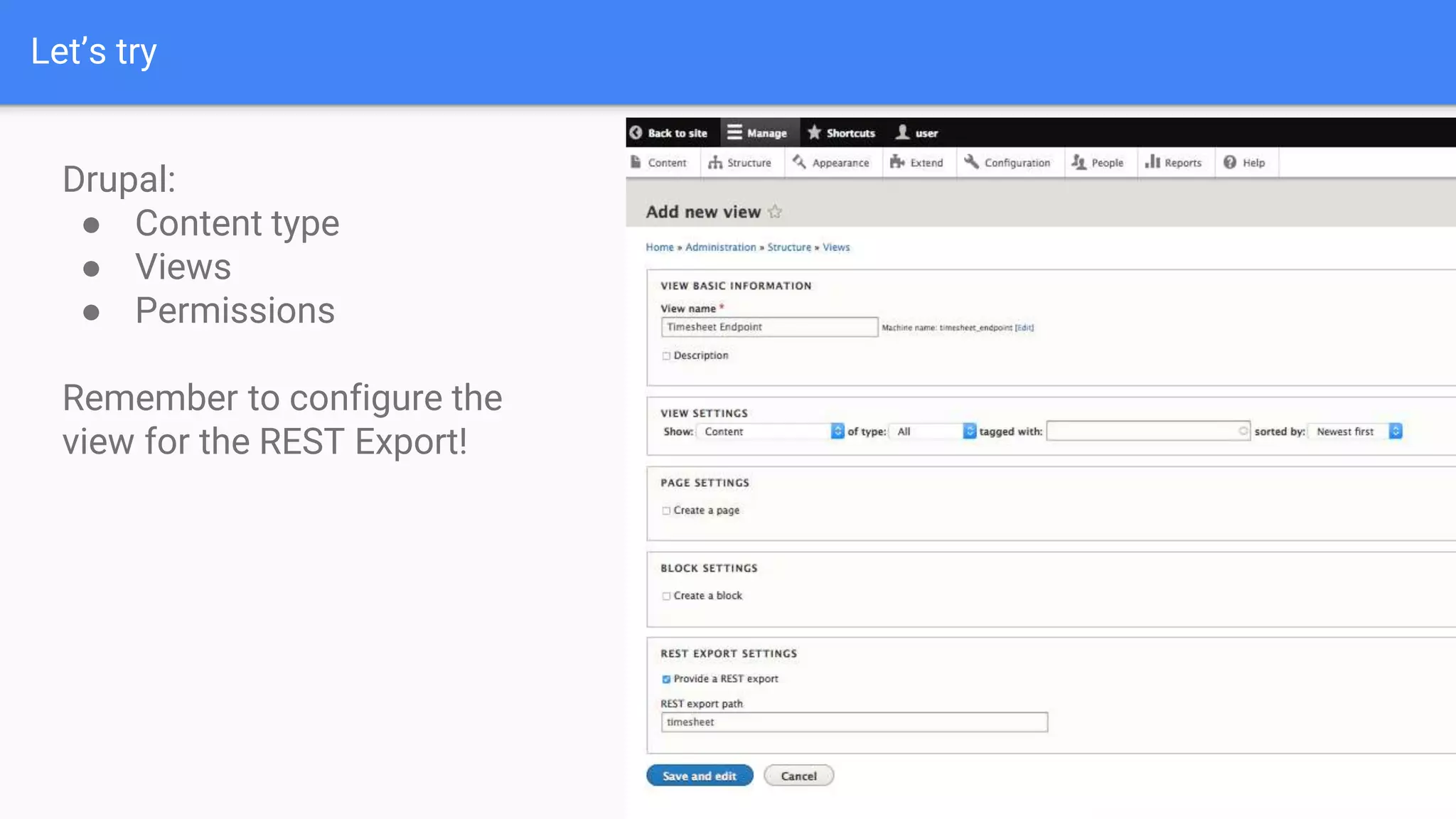
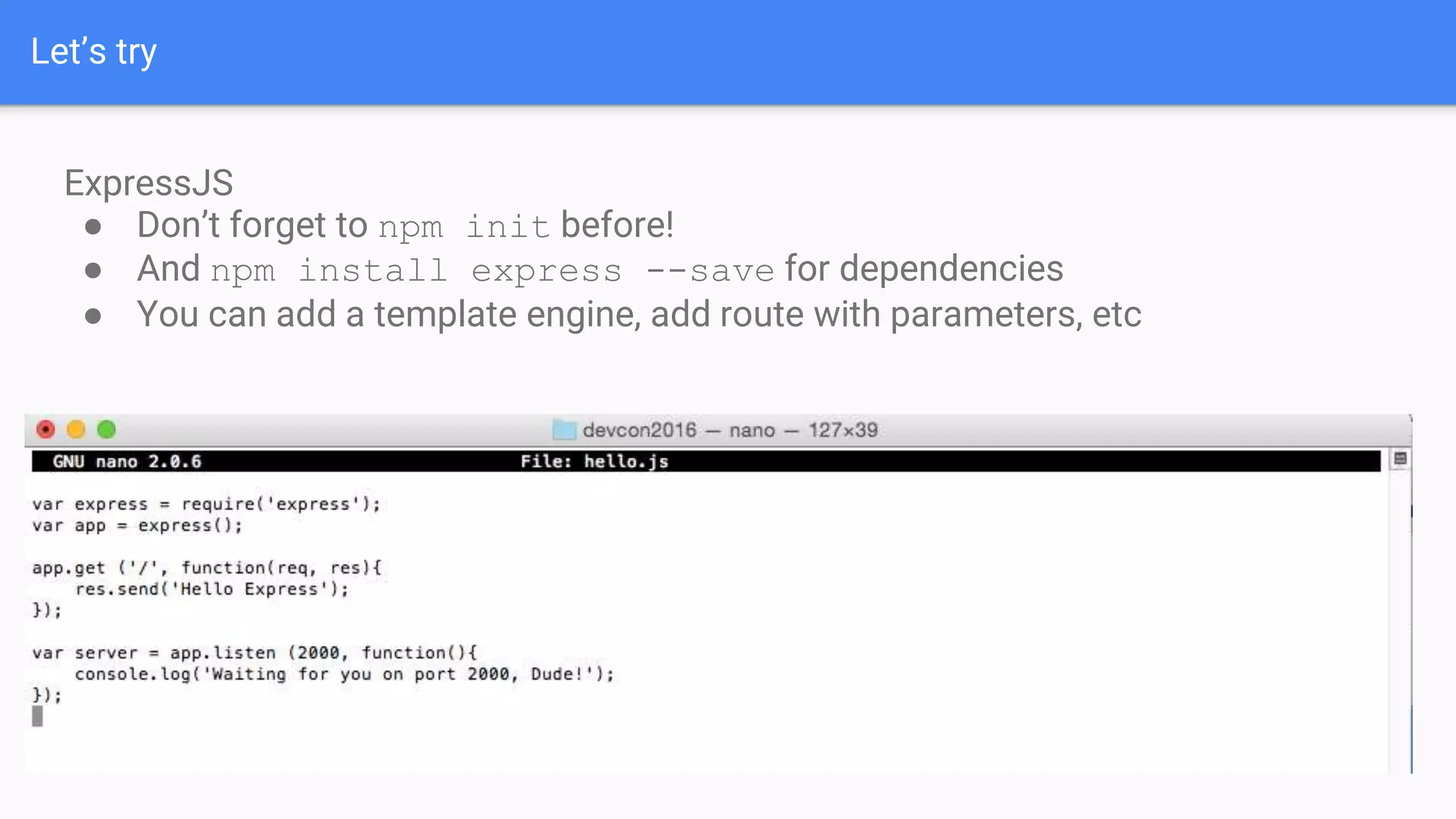
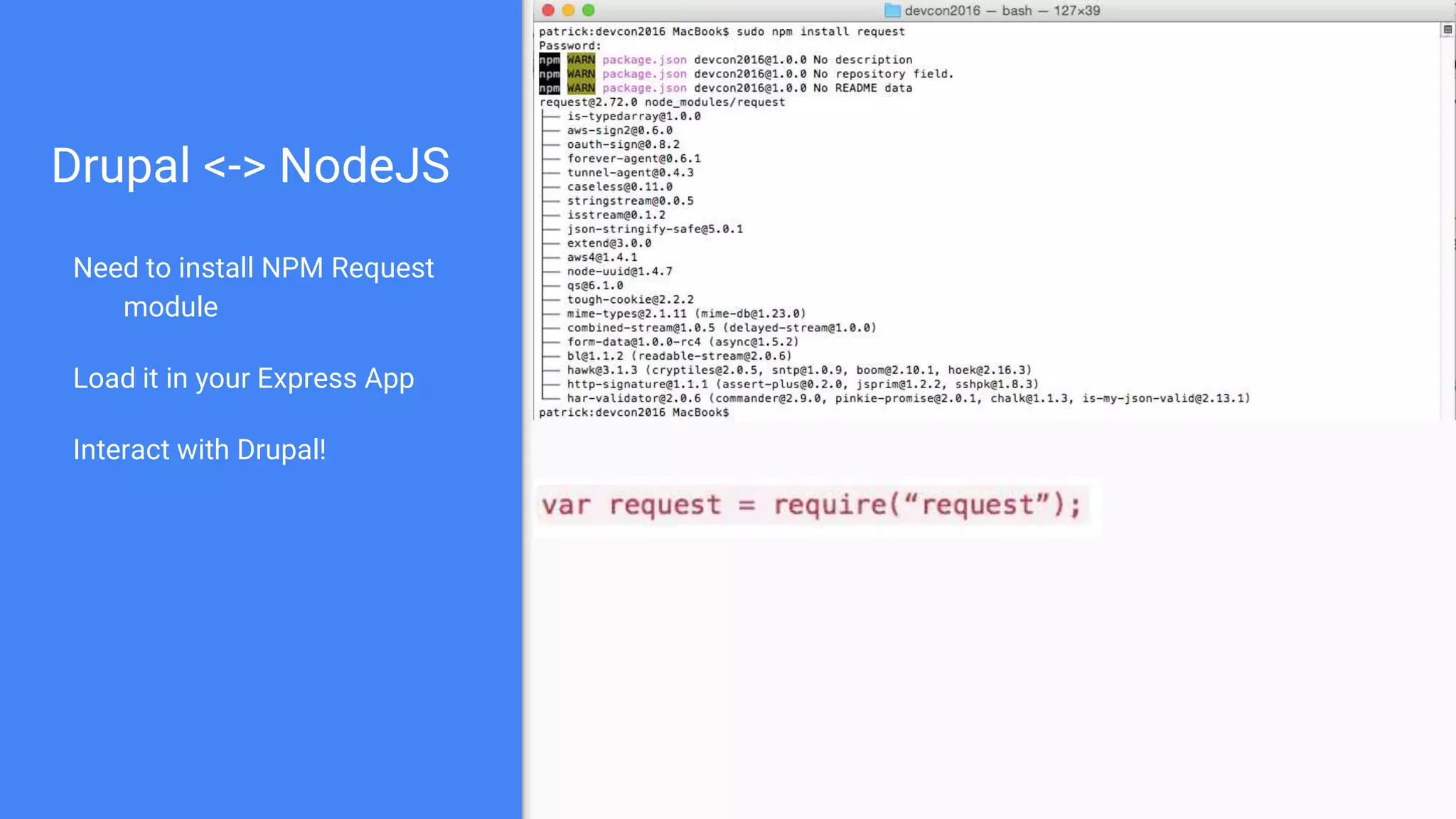
Drupal 8 allows for building RESTful applications by making it possible for other applications to read and update information on a Drupal site via the web. The RESTful Web Services API in Drupal 8 allows specifying supported HTTP verbs and serialization formats for each REST resource. A basic example demonstrates reading and writing data from a Drupal installation using REST, and an advanced example shows building a timesheet application with a NodeJS/Express frontend separated from the Drupal backend.