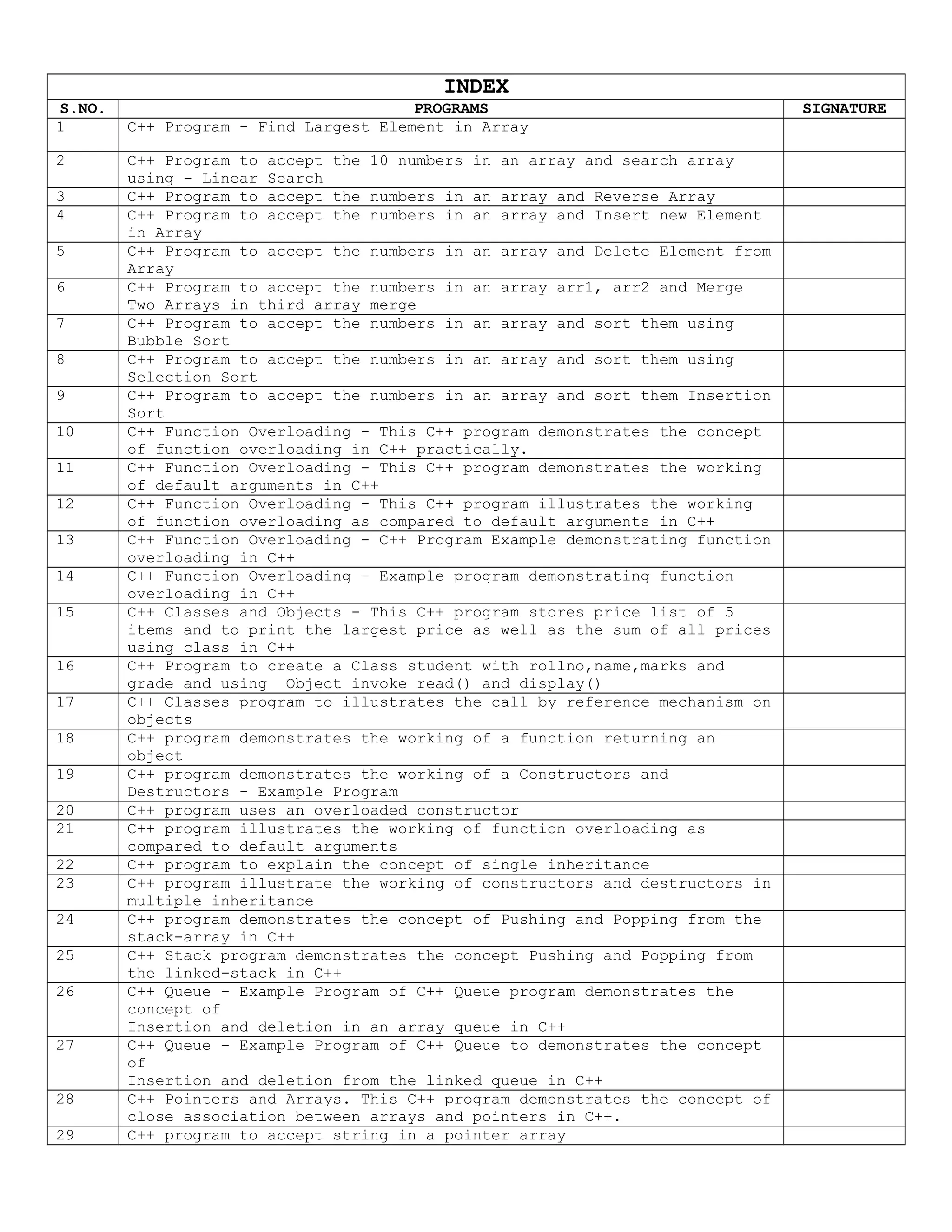
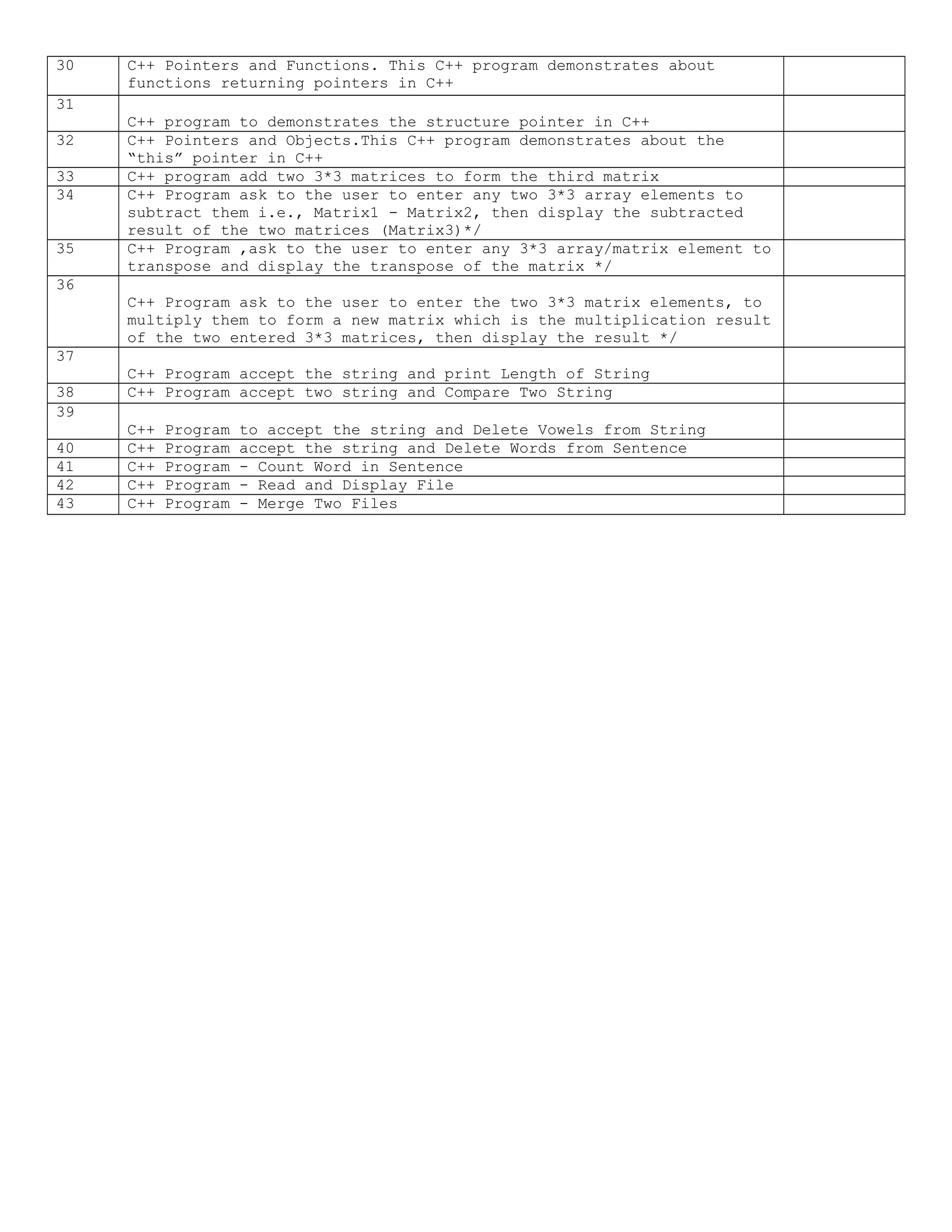
This document appears to be a student project report submitted to a secondary school. It includes an acknowledgements section thanking guidance received. It also includes a certificate section signed by a computer science faculty member. The bulk of the document is an index listing 25 C++ programs with brief descriptions and signatures. The programs cover topics like arrays, sorting, functions, classes, pointers and file handling. In total, this report submitted a series of C++ programs to fulfill a school programming assignment.


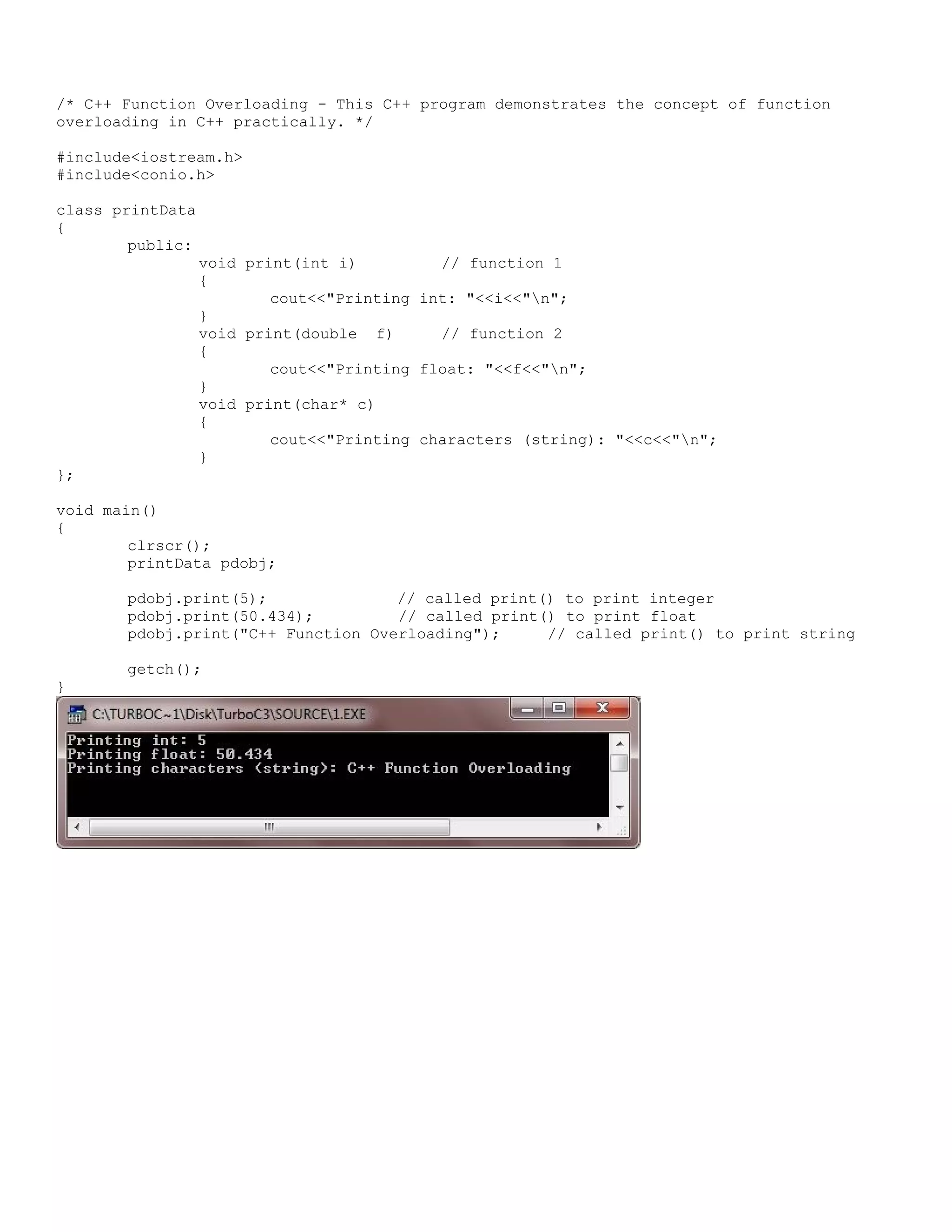
![/* C++ Program - Find Largest Element in Array */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { clrscr(); int large, arr[50], size, i; cout<<"Enter Array Size (max 50) : "; cin>>size; cout<<"Enter array elements : "; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { cin>>arr[i]; } cout<<"Searching for largest number ...nn"; large=arr[0]; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { if(large<arr[i]) { large=arr[i]; } } cout<<"Largest Number = "<<large; getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-6-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program to accept the 10 numbers in an array and search array using - Linear Search */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { clrscr(); int arr[10], i, num, n, c=0, pos; cout<<"Enter the array size : "; cin>>n; cout<<"Enter Array Elements : "; for(i=0; i<n; i++) { cin>>arr[i]; } cout<<"Enter the number to be search : "; cin>>num; for(i=0; i<n; i++) { if(arr[i]==num) { c=1; pos=i+1; break; } } if(c==0) { cout<<"Number not found..!!"; } else { cout<<num<<" found at position "<<pos; } getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-7-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program to accept the numbers in an array and Reverse Array */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { clrscr(); int arr[50], size, i, j, temp; cout<<"Enter array size : "; cin>>size; cout<<"Enter array elements : "; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { cin>>arr[i]; } j=i-1; // now j will point to the last element i=0; // and i will be point to the first element while(i<j) { temp=arr[i]; arr[i]=arr[j]; arr[j]=temp; i++; j--; } cout<<"Now the Reverse of the Array is : n"; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { cout<<arr[i]<<" "; } getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-8-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program to accept the numbers in an array and Insert new Element in Array */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { clrscr(); int arr[50], size, insert, i, pos; cout<<"Enter Array Size : "; cin>>size; cout<<"Enter array elements : "; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { cin>>arr[i]; } cout<<"Enter element to be insert : "; cin>>insert; cout<<"At which position (Enter index number) ? "; cin>>pos; // now create a space at the required position for(i=size; i>pos; i--) { arr[i]=arr[i-1]; } arr[pos]=insert; cout<<"Element inserted successfully..!!n"; cout<<"Now the new array is : n"; for(i=0; i<size+1; i++) { cout<<arr[i]<<" "; } getch();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-9-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program to accept the numbers in an array and Delete Element from Array */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { clrscr(); int arr[50], size, i, del, count=0; cout<<"Enter array size : "; cin>>size; cout<<"Enter array elements : "; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { cin>>arr[i]; } cout<<"Enter element to be delete : "; cin>>del; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { if(arr[i]==del) { for(int j=i; j<(size-1); j++) { arr[j]=arr[j+1]; } count++; break; } } if(count==0) { cout<<"Element not found..!!"; } else { cout<<"Element deleted successfully..!!n"; cout<<"Now the new array is :n"; for(i=0; i<(size-1); i++) { cout<<arr[i]<<" "; } } getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-10-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program to accept the numbers in an array arr1, arr2 and Merge Two Arrays in third array merge */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { clrscr(); int arr1[50], arr2[50], size1, size2, size, i, j, k, merge[100]; cout<<"Enter Array 1 Size : "; cin>>size1; cout<<"Enter Array 1 Elements : "; for(i=0; i<size1; i++) { cin>>arr1[i]; } cout<<"Enter Array 2 Size : "; cin>>size2; cout<<"Enter Array 2 Elements : "; for(i=0; i<size2; i++) { cin>>arr2[i]; } for(i=0; i<size1; i++) { merge[i]=arr1[i]; } size=size1+size2; for(i=0, k=size1; k<size && i<size2; i++, k++) { merge[k]=arr2[i]; } cout<<"Now the new array after merging is :n"; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { cout<<merge[i]<<" "; } getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-11-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program to accept the numbers in an array and sort them using Bubble Sort */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { clrscr(); int n, i, arr[50], j, temp; cout<<"Enter total number of elements :"; cin>>n; cout<<"Enter "<<n<<" numbers :"; for(i=0; i<n; i++) { cin>>arr[i]; } cout<<"Sorting array using bubble sort technique...n"; for(i=0; i<(n-1); i++) { for(j=0; j<(n-i-1); j++) { if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]) { temp=arr[j]; arr[j]=arr[j+1]; arr[j+1]=temp; } } } cout<<"Elements sorted successfully..!!n"; cout<<"Sorted list in ascending order :n"; for(i=0; i<n; i++) { cout<<arr[i]<<" "; } getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-12-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program to accept the numbers in an array and sort them using Selection Sort */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { clrscr(); int size, arr[50], i, j, temp; cout<<"Enter Array Size : "; cin>>size; cout<<"Enter Array Elements : "; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { cin>>arr[i]; } cout<<"Sorting array using selection sort...n"; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { for(j=i+1; j<size; j++) { if(arr[i]>arr[j]) { temp=arr[i]; arr[i]=arr[j]; arr[j]=temp; } } } cout<<"Now the Array after sorting is :n"; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { cout<<arr[i]<<" "; } getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-13-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program to accept the numbers in an array and sort them Insertion Sort */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { clrscr(); int size, arr[50], i, j, temp; cout<<"Enter Array Size : "; cin>>size; cout<<"Enter Array Elements : "; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { cin>>arr[i]; } cout<<"Sorting array using selection sort ... n"; for(i=1; i<size; i++) { temp=arr[i]; j=i-1; while((temp<arr[j]) && (j>=0)) { arr[j+1]=arr[j]; j=j-1; } arr[j+1]=temp; } cout<<"Array after sorting : n"; for(i=0; i<size; i++) { cout<<arr[i]<<" "; } getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-14-2048.jpg)
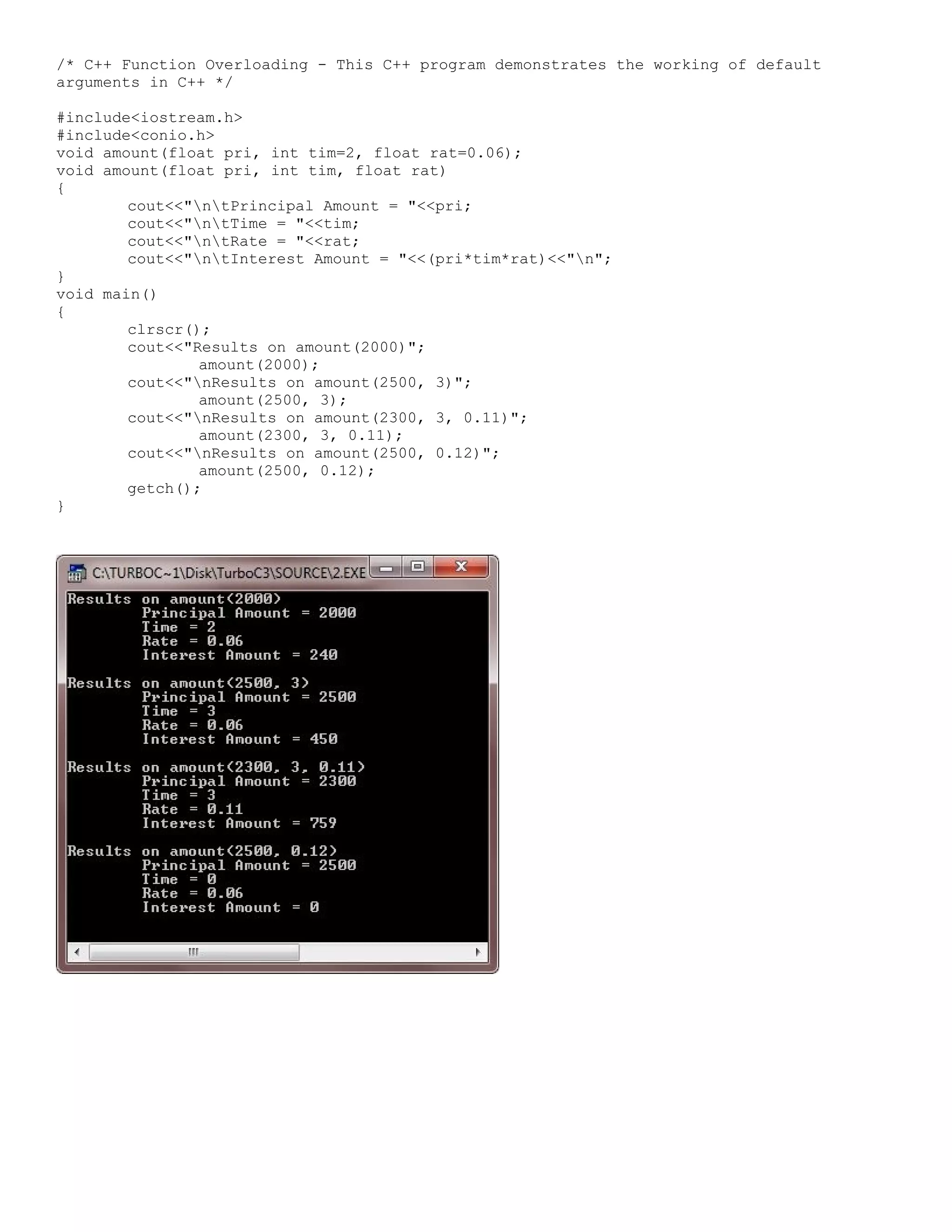



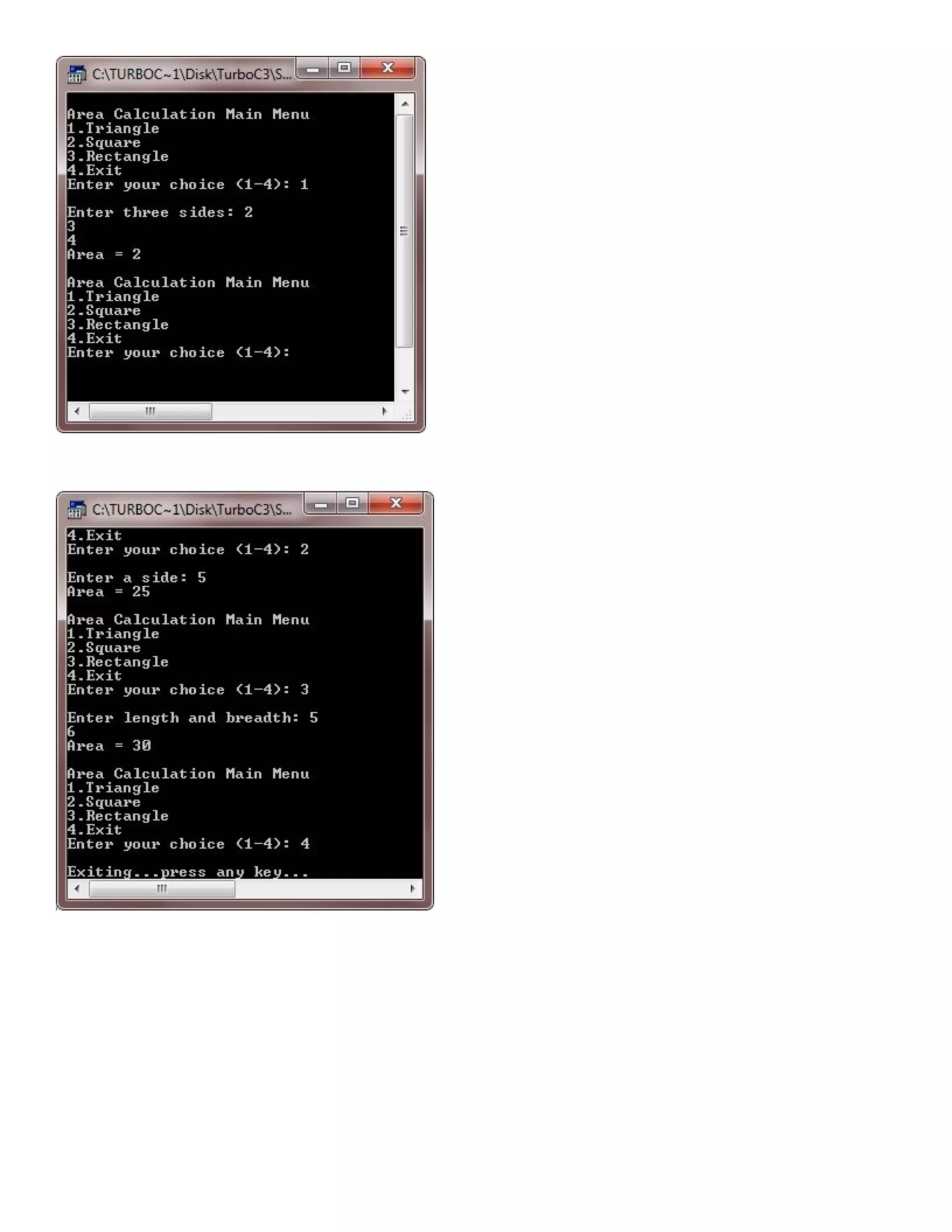

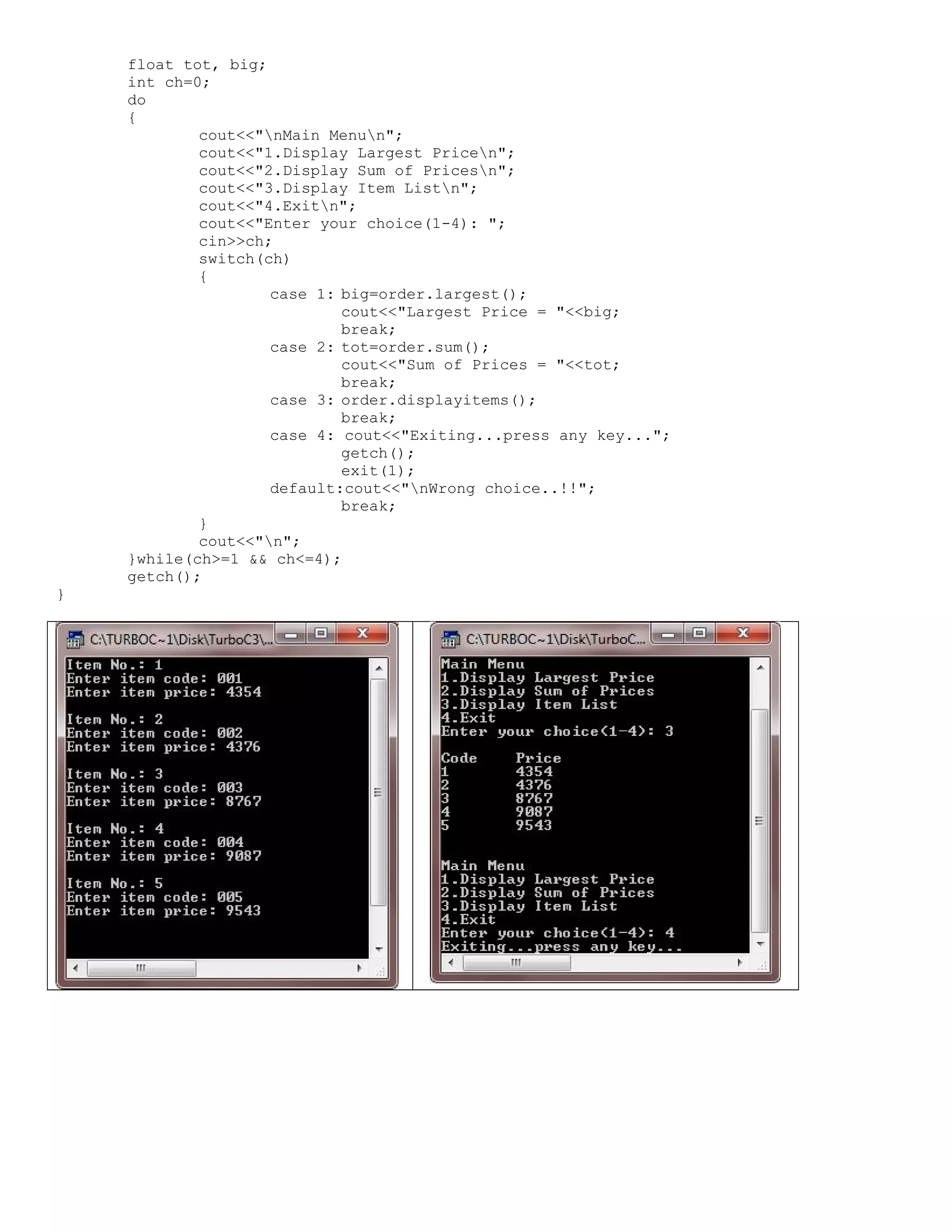
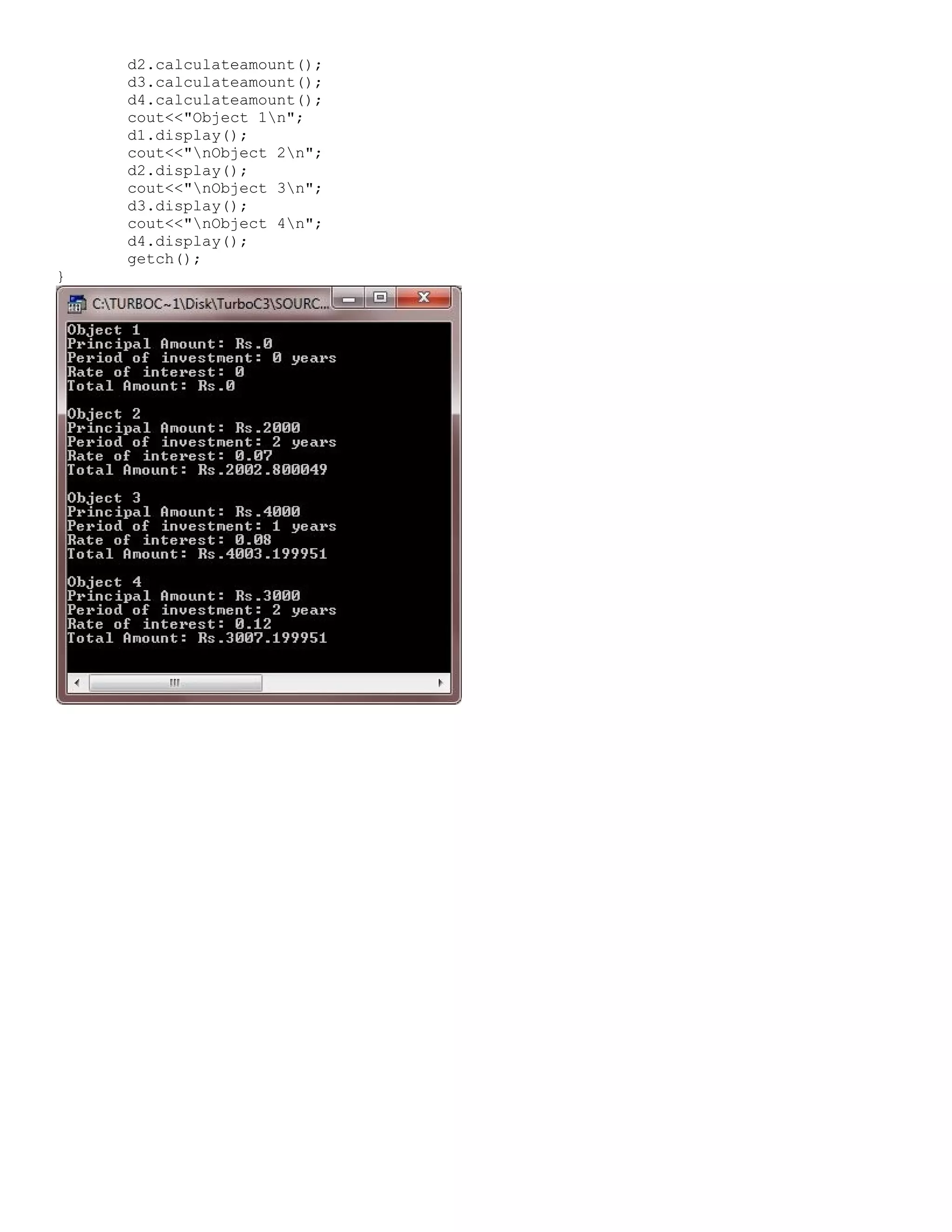
![* C++ Classes and Objects - This C++ program stores price list of 5 items and to print the largest price as well as the sum of all prices using class in C++ */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> #include<stdlib.h> class ITEM { int itemcode[5]; float itprice[5]; public: void initialize(void); float largest(void); float sum(void); void displayitems(void); }; void ITEM::initialize(void) { for(int i=0; i<5; i++) { cout<<"Item No.: "<<(i+1); cout<<"nEnter item code: "; cin>>itemcode[i]; cout<<"Enter item price: "; cin>>itprice[i]; cout<<"n"; } } float ITEM::largest(void) { float larg=itprice[0]; for(int i=1; i<5; i++) { if(larg<itprice[i]) { larg=itprice[i]; } } return larg; } float ITEM::sum(void) { float sum=0; for(int i=0; i<5; i++) { sum = sum + itprice[i]; } return sum; } void ITEM::displayitems(void) { cout<<"nCodetPricen"; for(int i=0; i<5; i++) { cout<<itemcode[i]<<"t"; cout<<itprice[i]<<"n"; } } void main() { clrscr(); ITEM order; order.initialize();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-23-2048.jpg)
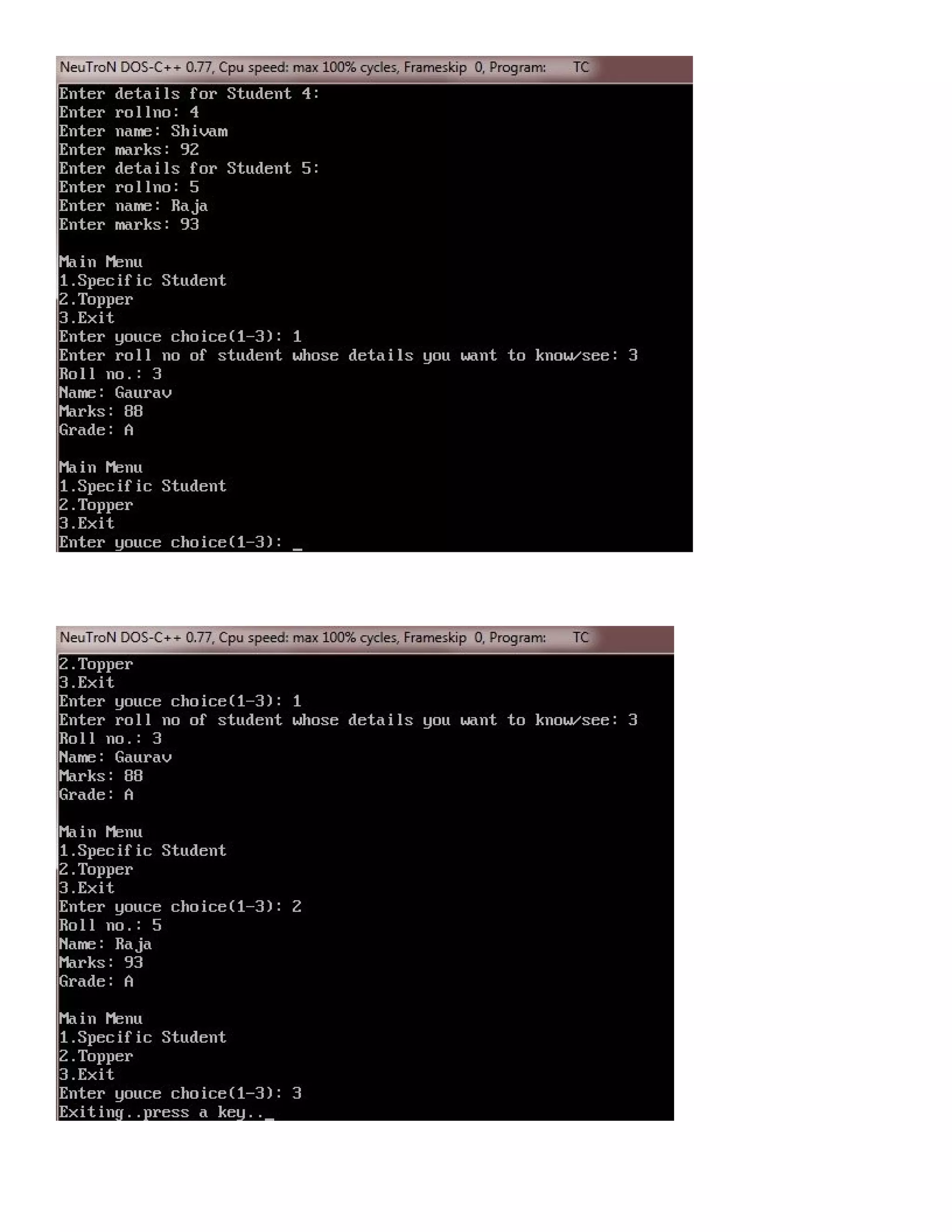
![/* C++ Program to create a Class student with rollno,name,marks and grade and using Object invoke read() and display() */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<stdio.h> class STUDENT { private: int rollno; char name[40]; float marks; char grade; public: void read() // mutator { cout<<"nEnter rollno: "; cin>>rollno; cout<<"Enter name: "; gets(name); cout<<"Enter marks: "; cin>>marks; } void display() // accessor { calculategrade(); cout<<"Roll no.: "<<rollno<<"n"; cout<<"Name: "<<name<<"n"; cout<<"Marks: "<<marks<<"n"; cout<<"Grade: "<<grade<<"n"; } int getrollno() // accessor { return rollno; } float getmarks() // accessor { return marks; } void calculategrade() // mutator { if(marks>=80) { grade = 'A'; } else if(marks>=60) { grade = 'B'; } else if(marks>=40) { grade = 'C'; } else { grade = 'F'; } } }; void main() { clrscr();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-25-2048.jpg)
![STUDENT tw[5]; for(int i=0; i<5; i++) { cout<<"nEnter details for Student "<<i+1<<": "; tw[i].read(); } int choice, rno, pos=-1, highmarks=0; do { cout<<"nMain Menun"; cout<<"1.Specific Studentn"; cout<<"2.Toppern"; cout<<"3.Exitn"; cout<<"Enter youce choice(1-3): "; cin>>choice; switch(choice) { case 1: cout<<"Enter roll no of student whose details you want to know/see: "; cin>>rno; for(i=0; i<5; i++) { if(tw[i].getrollno()==rno) { tw[i].display(); break; } } if(i==5) { cout<<"Invalid rollno..!!"; } break; case 2: for(i=0; i<5; i++) { if(tw[i].getmarks()>highmarks) { pos=i; highmarks=tw[i].getmarks(); } } tw[pos].display(); break; case 3: cout<<"Exiting..press a key.."; getch(); exit(1); default: cout<<"Wrong choice..!!"; break; } }while(choice>=1 && choice<=3); getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-26-2048.jpg)
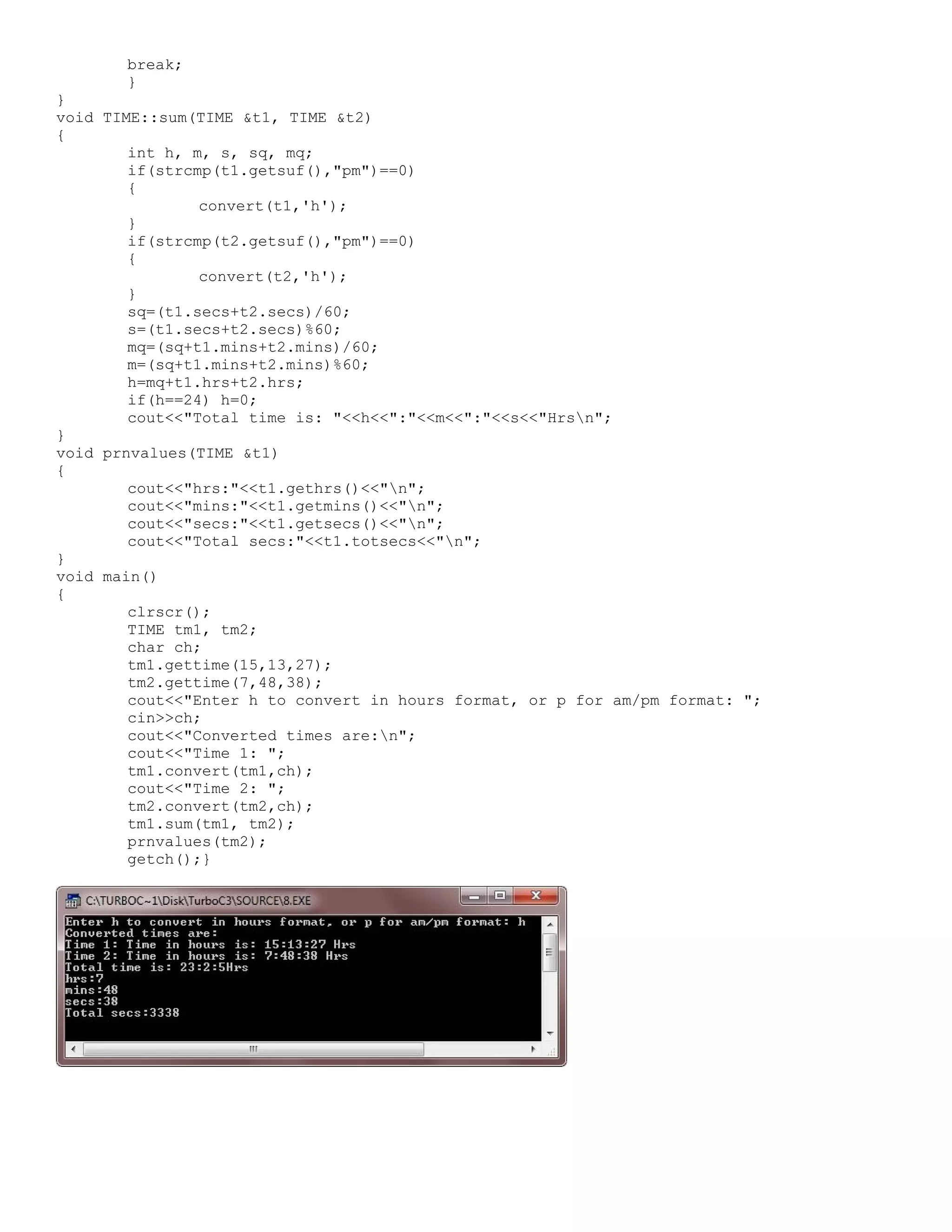
![/* C++ Classes program to illustrates the call by reference mechanism on objects */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> class TIME { int hrs, mins, secs; char suf[4]; public: int totsecs; void gettime(int h, int m, int s) { hrs=h; mins=m; secs=s; totsecs=(hrs*60)+(mins*60)+secs; strcpy(suf, "Hrs"); } void puttime(void) { cout<<"Time is: "<<hrs<<":"<<mins<<":"<<secs<<" "<<suf<<"n"; } char *getsuf() { return suf; } void convert(TIME &t, char ch); void sum(TIME &t1, TIME &t2); int gethrs() { return hrs; } int getmins() { return mins; } int getsecs() { return secs; } }; void TIME::convert(TIME &t, char ch) { switch(ch) { case 'h': if(strcmp(t.suf, "Hrs")!=0) { t.hrs=(strcmp(t.suf, "am")==0)?t.hrs:t.hrs+12; strcpy(t.suf,"Hrs"); } cout<<"Time in hours is: "<<t.hrs<<":"<<t.mins<<":"<<t.secs<<" "<<t.suf<<"n"; break; case 'p': if(strcmp(t.suf,"Hrs")==0) { (t.hrs>12)?strcpy(t.suf,"pm"):strcpy(t.suf,"am"); t.hrs=((t.hrs>12)?(t.hrs-12):t.hrs); } cout<<"Time in am/pm is: "<<t.hrs<<":"<<t.mins<<":"<<t.secs<<" "<<t.suf<<"n"; break; default: cout<<"Wrong choice..!!";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-28-2048.jpg)





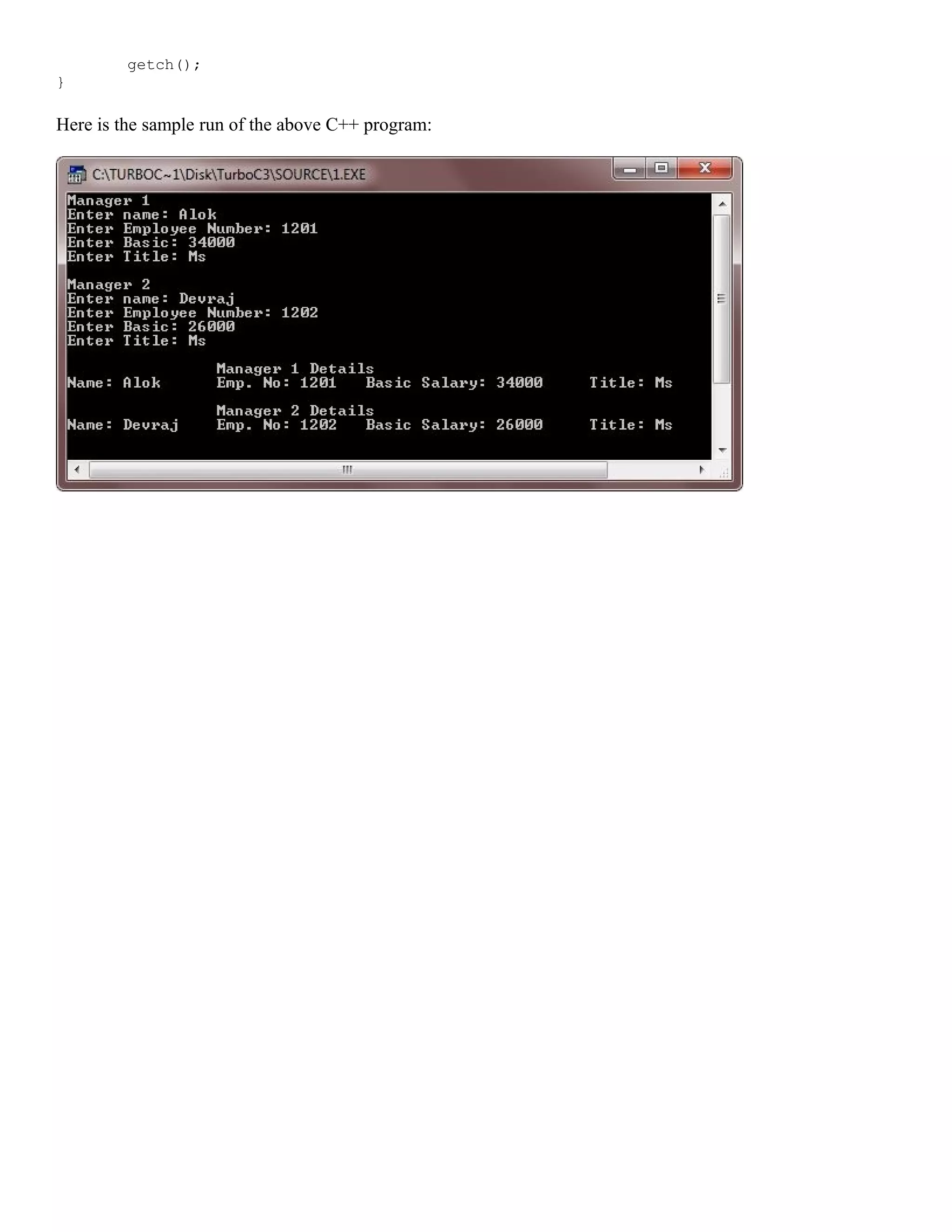
![/* C++ program to explain the concept of single inheritance */ #include<iostream.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> class EMPLOYEE { private: char name[30]; unsigned long enumb; public: void getdata() { cout<<"Enter name: "; gets(name); cout<<"Enter Employee Number: "; cin>>enumb; } void putdata() { cout<<"Name: "<<name<<"t"; cout<<"Emp. No: "<<enumb<<"t"; cout<<"Basic Salary: "<<basic; } protected: float basic; void getbasic() { cout<<"Enter Basic: "; cin>>basic; } }; class MANAGER:public EMPLOYEE { private: char title[30]; public: void getdata() { EMPLOYEE::getdata(); getbasic(); cout<<"Enter Title: "; gets(title); } void putdata() { EMPLOYEE::putdata(); cout<<"tTitle: "<<title<<"n"; } }; void main() { clrscr(); MANAGER m1, m2; cout<<"Manager 1n"; m1.getdata(); cout<<"nManager 2n"; m2.getdata(); cout<<"nttManager 1 Detailsn"; m1.putdata(); cout<<"nttManager 2 Detailsn"; m2.putdata();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-37-2048.jpg)


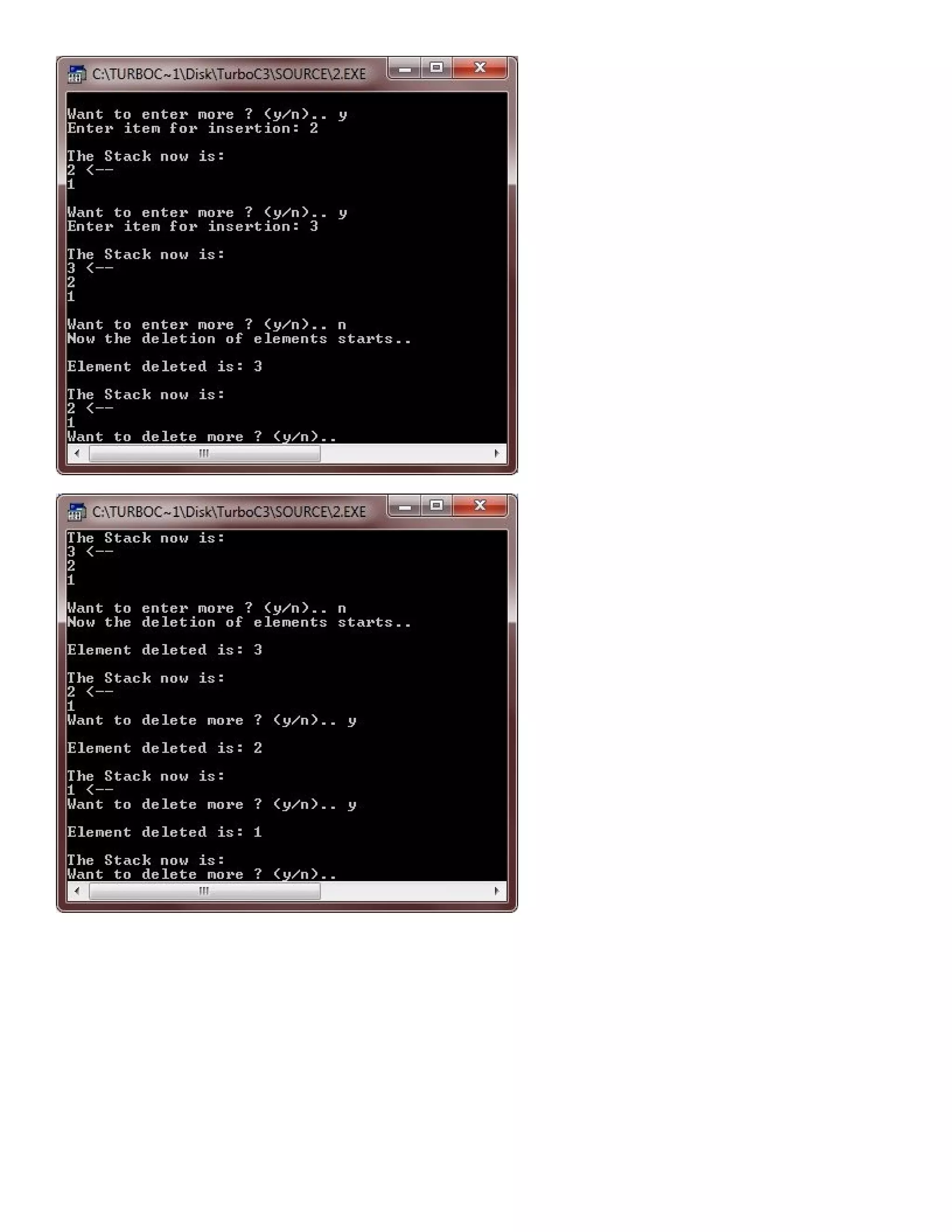
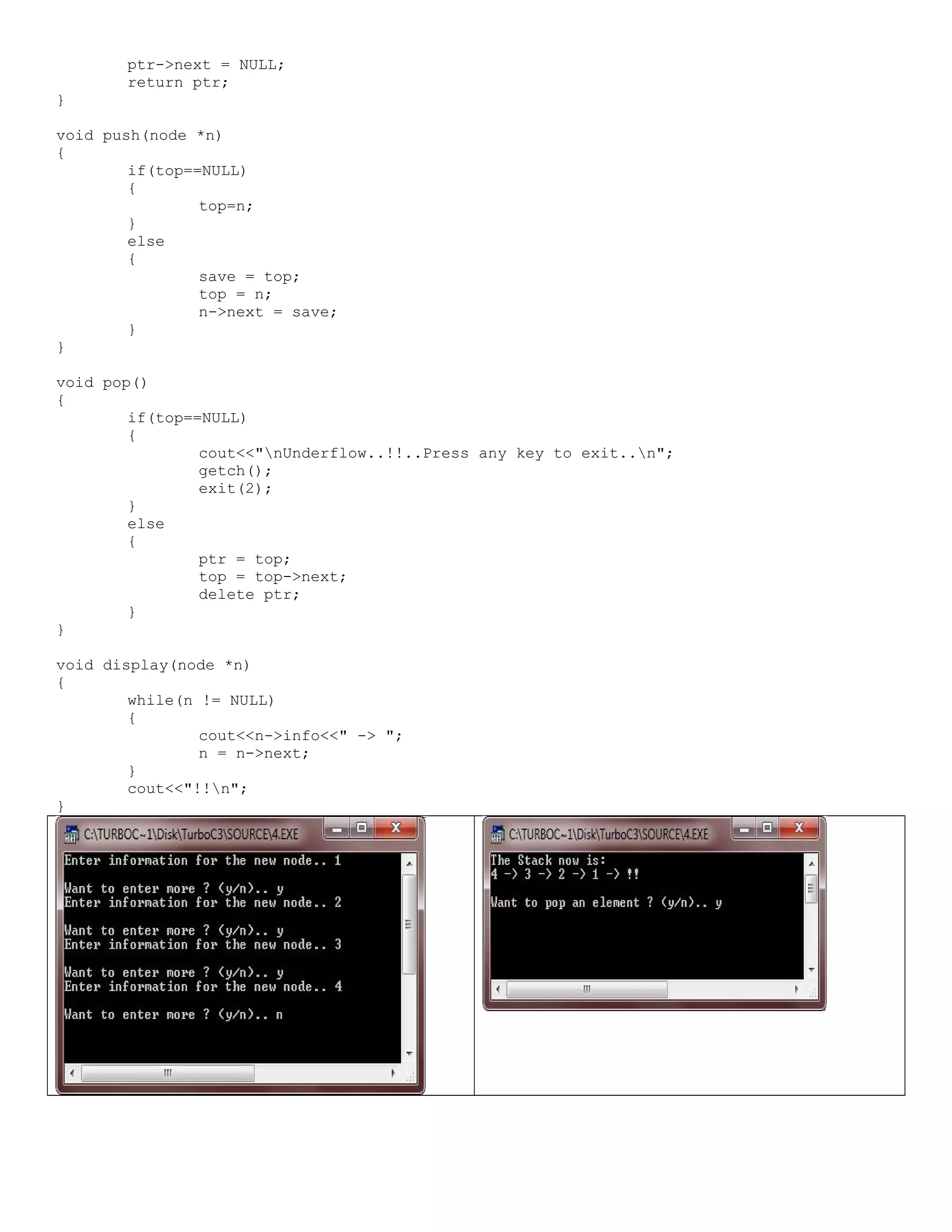
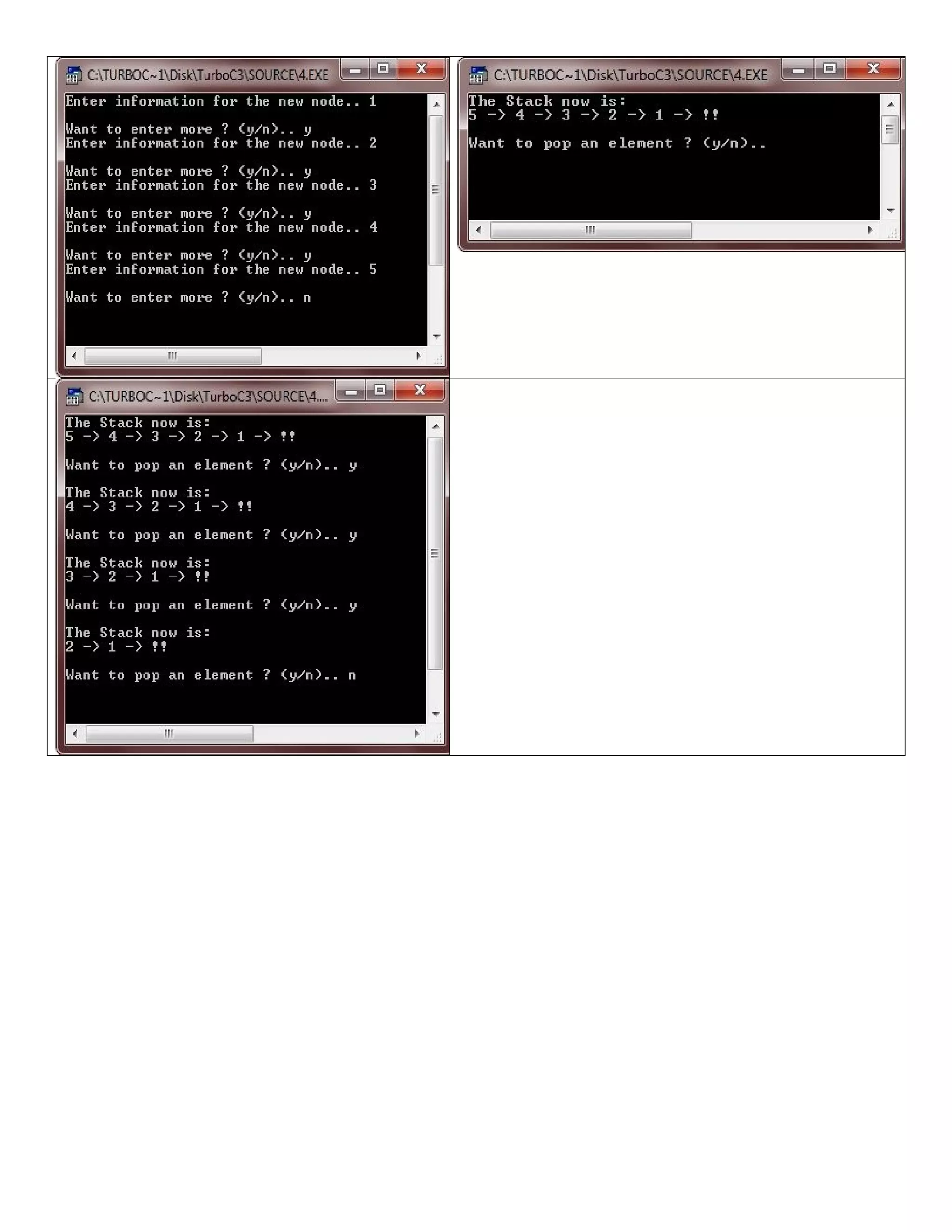
![/* C++ program demonstrates the concept of Pushing and Popping from the stack-array in C+ + */ #include<iostream.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<conio.h> int pop(int [], int &); int push(int [], int &, int); void display(int [], int); const int SIZE = 50; void main() { clrscr(); int stack[SIZE], item, top=-1, res; char ch='y'; while(ch=='y' || ch=='Y') { cout<<"Enter item for insertion: "; cin>>item; res = push(stack, top, item); if(res == -1) { cout<<"Overflow..!!..Aborting..Press a key to exit..n"; getch(); exit(1); } cout<<"nThe Stack now is:n"; display(stack, top); cout<<"nWant to enter more ? (y/n).. "; cin>>ch; } cout<<"Now the deletion of elements starts..n"; ch='y'; while(ch=='y' || ch=='Y') { res = pop(stack, top); if(res==-1) { cout<<"nUnderflow..!!..Aborting..!!..Press a key to exit..n"; getch(); exit(2); } else { cout<<"nElement deleted is: "<<res<<endl; cout<<"nThe Stack now is:n"; display(stack, top); } cout<<"Want to delete more ? (y/n).. "; cin>>ch; } getch(); } int push(int stack[], int &top, int elem) { if(top == SIZE-1) { return -1; } else](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-41-2048.jpg)
![{ top++; stack[top] = elem; } return 0; } int pop(int stack[], int &top) { int ret; if(top==-1) { return -1; } else { ret=stack[top]; top--; } return ret; } void display(int stack[], int top) { if(top==-1) { return; } cout<<stack[top]<<" <-- "<<"n"; for(int i=top-1; i>=0; i--) { cout<<stack[i]<<"n"; } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-42-2048.jpg)


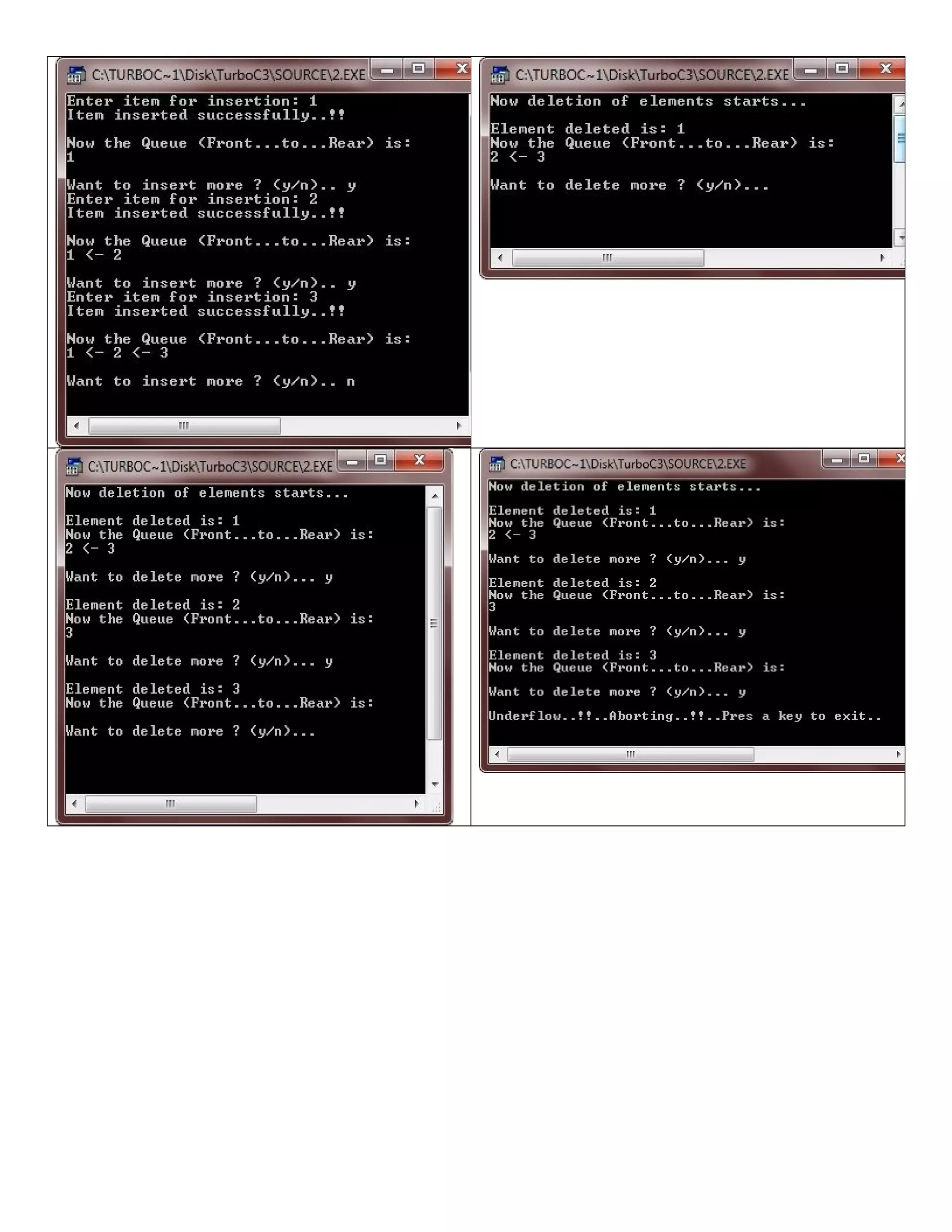
![/* C++ Queue - Example Program of C++ Queue program demonstrates the concept of Insertion and deletion in an array queue in C++ */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> #include<stdlib.h> int delete_from_queue(int []); int insert_in_queue(int [], int); void display(int [], int, int); const int SIZE = 50; int queue[SIZE]; int front=-1; int rear=-1; void main() { clrscr(); int item, check; char ch='y'; while(ch=='y' || ch=='Y') { cout<<"Enter item for insertion: "; cin>>item; check = insert_in_queue(queue, item); if(check == -1) { cout<<"nOverflow..!!..Aborting..!!..Press a key to exit..n"; getch(); exit(1); } cout<<"Item inserted successfully..!!n"; cout<<"nNow the Queue (Front...to...Rear) is:n"; display(queue, front, rear); cout<<"nWant to insert more ? (y/n).. "; cin>>ch; } clrscr(); cout<<"Now deletion of elements starts...n"; ch='y'; while(ch=='y' || ch=='Y') { check = delete_from_queue(queue); if(check == -1) { cout<<"nUnderflow..!!..Aborting..!!..Pres a key to exit..n"; getch(); exit(2); } else { cout<<"nElement deleted is: "<<check<<"n"; cout<<"Now the Queue (Front...to...Rear) is:n"; display(queue, front, rear); } cout<<"nWant to delete more ? (y/n)... "; cin>>ch; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-47-2048.jpg)
![getch(); } int insert_in_queue(int queue[], int elem) { if(rear == SIZE-1) { return -1; } else if(rear == -1) { front = rear = 0; queue[rear] = elem; } else { rear++; queue[rear] = elem; } return 0; } int delete_from_queue(int queue[]) { int retn; if(front == -1) { return -1; } else { retn = queue[front]; if(front == rear) { front = rear = -1; } else { front++; } } return retn; } void display(int queue[], int front, int rear) { if(front == -1) { return; } for(int i=front; i<rear; i++) { cout<<queue[i]<<" <- "; } cout<<queue[rear]<<"n"; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-48-2048.jpg)


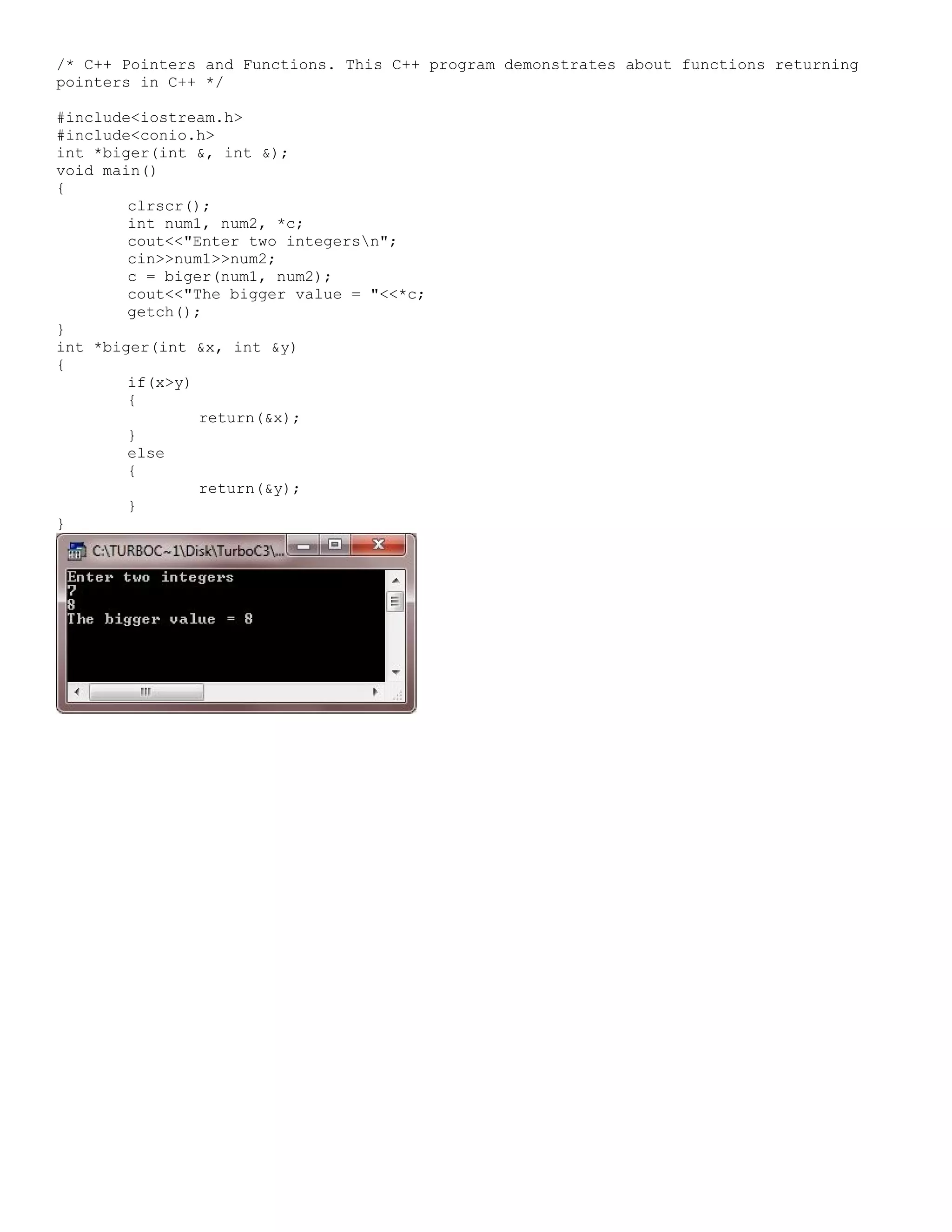
![/* C++ Pointers and Arrays. This C++ program demonstrates the concept of close association between arrays and pointers in C++. */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { clrscr(); int *iptr[5]; int fa=65, fb=66, fc=67, fd=68, fe=69; int i; // initialize array pointers by making them point to 5 different ints iptr[0] = &fa; iptr[1] = &fb; iptr[2] = &fc; iptr[3] = &fd; iptr[4] = &fe; // now prints the values being pointed to by the pointers for(i=0; i<5; i++) { cout<<"The pointer iptr["<<i<<"] points to "<<*iptr[i]<<"n"; } cout<<"n"; // now print the addresses stored in the array cout<<"The base address of the array iptr of pointers is "<<iptr<<"n"; for(i=0; i<5; i++) { cout<<"The address stored in iptr["<<i<<"] is "<<iptr[i]<<"n"; } getch(); } Here is the sample run of the above C++ program](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-53-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ program to accept string in a pointer array */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> void main() { clrscr(); char *names[] = {"Sachin", "Dhoni", "Sehwag", "Raina", "Yuvraj"}; int len=0; len=strlen(names[1]); // length of 2nd string cout<<"Originally:ntstring 2 is "; cout.write(names[1],len).put('n'); cout<<"tand string 4 is "; cout.write(names[3],len).put('n'); // now exchange the position of string 2 and 4 char *tptr; tptr = names[1]; names[1] = names[3]; names[3] = tptr; // now print the exchanged string cout<<"nExchanged:ntstring 2 is "; cout.write(names[1],len).put('n'); cout<<"tand string 4 is "; cout.write(names[3],len).put('n'); getch(); } Here is the sample output of the above C++ program](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-54-2048.jpg)
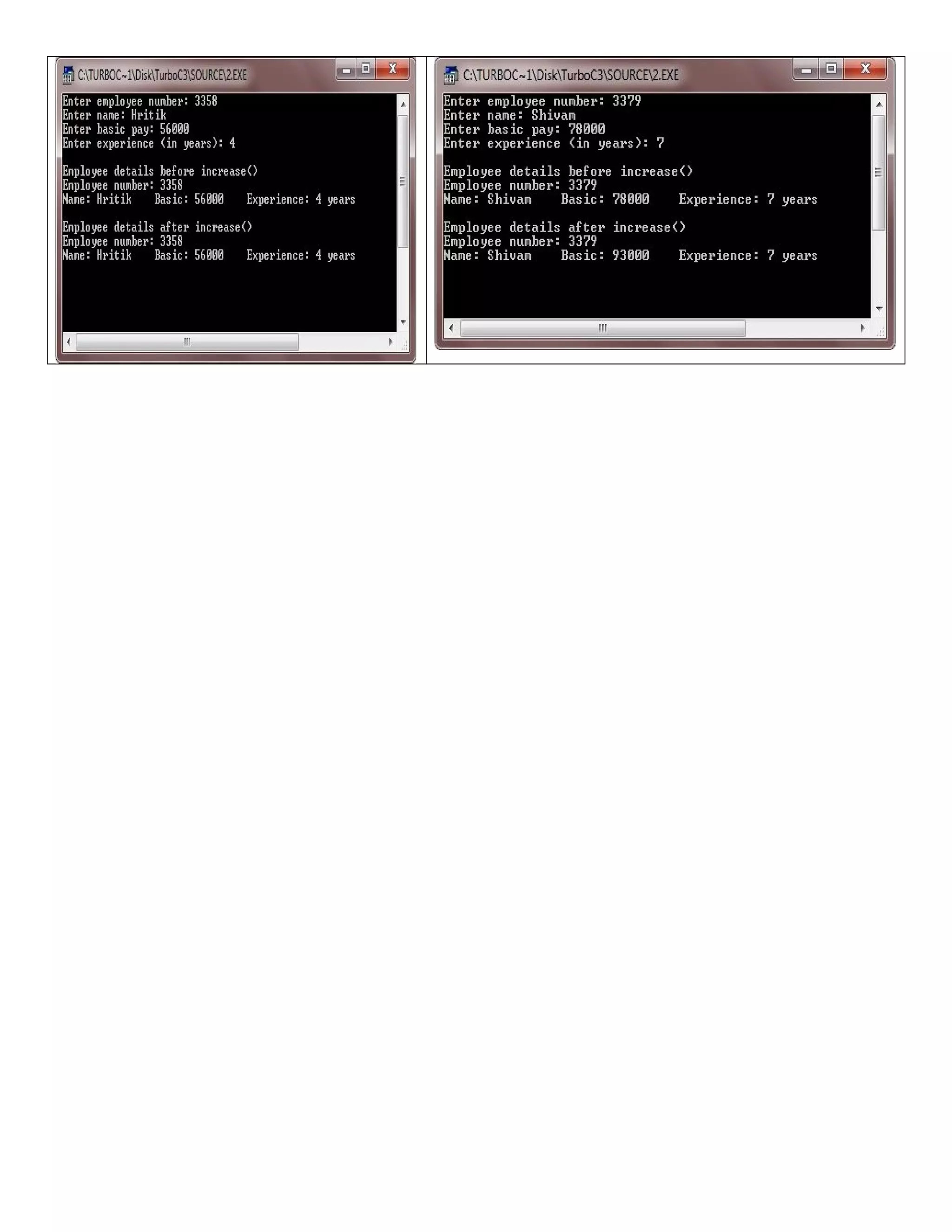
![* C++ program to demonstrates the structure pointer in C++ */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdio.h> struct emp { int empno; char empname[20]; float empbasic; float empexperience; }; void display(emp *e); void increase(emp *e); void main() { clrscr(); emp mgr, *eptr; cout<<"Enter employee number: "; cin>>mgr.empno; cout<<"Enter name: "; gets(mgr.empname); cout<<"Enter basic pay: "; cin>>mgr.empbasic; cout<<"Enter experience (in years): "; cin>>mgr.empexperience; eptr = &mgr; cout<<"nEmployee details before increase()n"; display(eptr); increase(eptr); cout<<"nEmployee details after increase()n"; display(eptr); getch(); } void display(emp *e) { int len=strlen(e->empname); cout<<"Employee number: "<<e->empno; cout<<"nName: "; cout.write(e->empname, len); cout<<"tBasic: "<<e->empbasic; cout<<"tExperience: "<<e->empexperience<<" yearsn"; } void increase(emp *e) { if(e->empexperience >= 5) { e->empbasic = e->empbasic + 15000; } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-56-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Pointers and Objects.This C++ program demonstrates about the “this” pointer in C+ +*/ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> class Salesman { char name[1200]; float total_sales; public: Salesman(char *s, float f) { strcpy(name, ""); strcpy(name, s); total_sales = f; } void prnobject(void) { cout.write(this->name, 26); // use of this pointer cout<<" has invoked prnobject().n"; } }; void main() { clrscr(); Salesman Rajat("Rajat", 21450), Ravi("Ravi", 23190), Vikrant("Vikrant", 19142); /* above statement creates three objects */ Rajat.prnobject(); Vikrant.prnobject(); Ravi.prnobject(); getch(); } Above C++ program will produce the following output :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-58-2048.jpg)
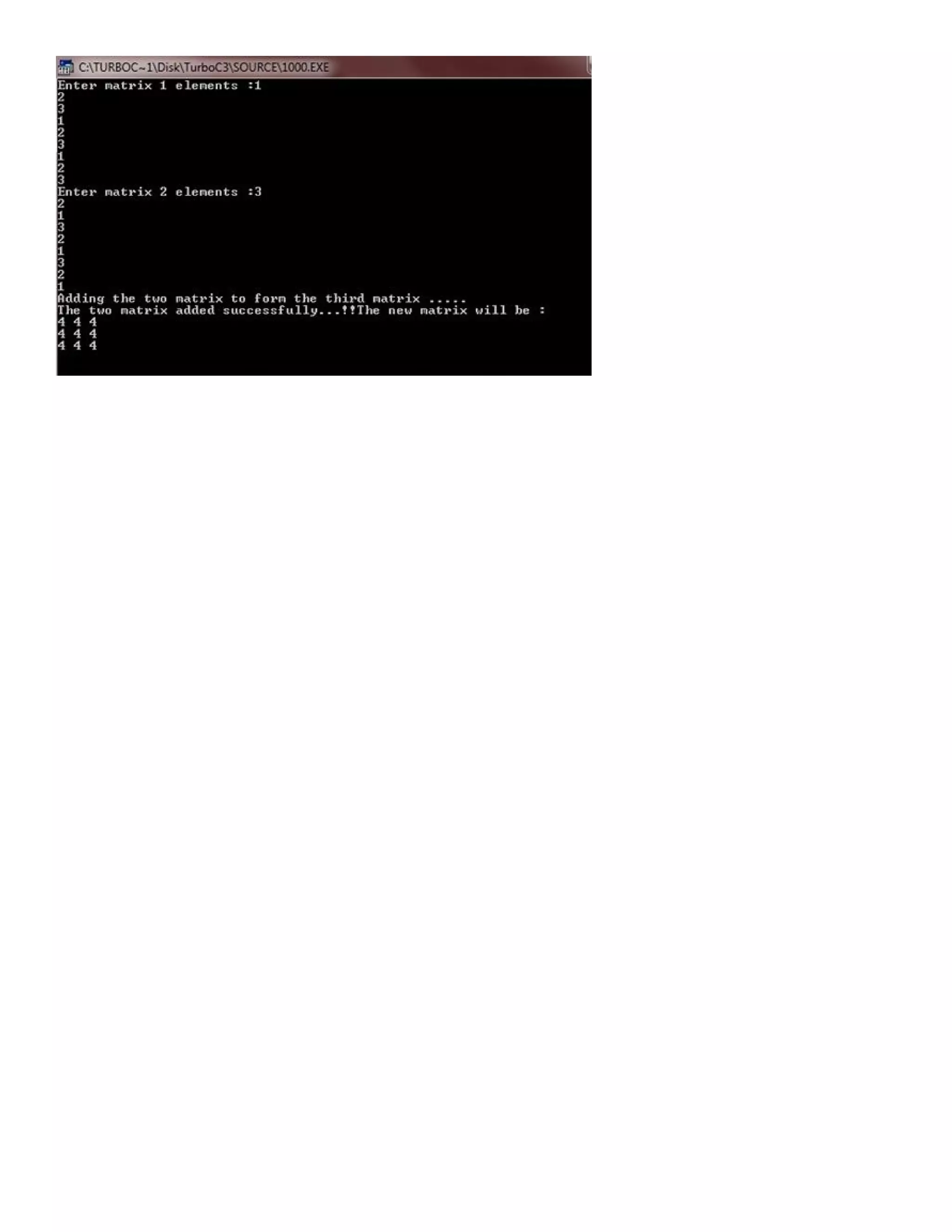
![/* C++ program add two 3*3 matrices to form the third matrix */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { clrscr(); int mat1[3][3], mat2[3][3], i, j, mat3[3][3]; cout<<"Enter matrix 1 elements :"; for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) { cin>>mat1[i][j]; } } cout<<"Enter matrix 2 elements :"; for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) { cin>>mat2[i][j]; } } cout<<"Adding the two matrix to form the third matrix .....n"; for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) { mat3[i][j]=mat1[i][j]+mat2[i][j]; } } cout<<"The two matrix added successfully...!!"; cout<<"The new matrix will be :n"; for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) { cout<<mat3[i][j]<<" "; } cout<<"n"; } getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-59-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program ask to the user to enter any two 3*3 array elements to subtract them i.e., Matrix1 - Matrix2, then display the subtracted result of the two matrices (Matrix3)*/ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { clrscr(); int arr1[3][3], arr2[3][3], arr3[3][3], sub, i, j; cout<<"Enter 3*3 Array 1 Elements : "; for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) { cin>>arr1[i][j]; } } cout<<"Enter 3*3 Array 2 Elements : "; for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) { cin>>arr2[i][j]; } } cout<<"Subtracting array (array1-array2) ... n"; for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) { arr3[i][j]=arr1[i][j]-arr2[i][j]; } } cout<<"Result of Array1 - Array2 is :n"; for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) { cout<<arr3[i][j]<<" "; } cout<<"n"; } getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-61-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program ,ask to the user to enter any 3*3 array/matrix element to transpose and display the transpose of the matrix */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { clrscr(); int arr[3][3], i, j, arrt[3][3]; cout<<"Enter 3*3 Array Elements : "; for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) { cin>>arr[i][j]; } } cout<<"Transposing Array...n"; for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) { arrt[i][j]=arr[j][i]; } } cout<<"Transpose of the Matrix is :n"; for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) { cout<<arrt[i][j]; } cout<<"n"; } getch(); } When the above C++ program is compile and executed, it will produce the following result:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-62-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program ask to the user to enter the two 3*3 matrix elements, to multiply them to form a new matrix which is the multiplication result of the two entered 3*3 matrices, then display the result */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { clrscr(); int mat1[3][3], mat2[3][3], mat3[3][3], sum=0, i, j, k; cout<<"Enter first matrix element (3*3) : "; for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) { cin>>mat1[i][j]; } } cout<<"Enter second matrix element (3*3) : "; for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) { cin>>mat2[i][j]; } } cout<<"Multiplying two matrices...n"; for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) { sum=0; for(k=0; k<3; k++) { sum = sum + mat1[i][k] * mat2[k][j]; } mat3[i][j] = sum; } } cout<<"nMultiplication of two Matrices : n"; for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) { cout<<mat3[i][j]<<" "; } cout<<"n"; } getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-63-2048.jpg)

![/* C++ Program accept the string and print Length of String */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdio.h> void main() { clrscr(); char str[20], len; cout<<"Enter a string : "; gets(str); len=strlen(str); cout<<"Length of the string is "<<len; getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-65-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program accept two string and Compare Two String */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdio.h> void main() { clrscr(); char str1[100], str2[100]; cout<<"Enter first string : "; gets(str1); cout<<"Enter second string : "; gets(str2); if(strcmp(str1, str2)==0) { cout<<"Both the strings are equal"; } else { cout<<"Both the strings are not equal"; } Getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-66-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program to accept the string and Delete Vowels from String */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdio.h> void main() { clrscr(); char str[20]; int len, i, j; cout<<"Enter a string : "; gets(str); len=strlen(str); for(i=0; i<len; i++) { if(str[i]=='a' || str[i]=='e' || str[i]=='i' || str[i]=='o' || str[i]=='u' || str[i]=='A' || str[i]=='E' || str[i]=='I' || str[i]=='O' || str[i]=='U') { for(j=i; j<len; j++) { str[j]=str[j+1]; } len--; } } cout<<"After deleting the vowels, the string will be : "<<str; getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-67-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program accept the string and Delete Words from Sentence */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> void main() { clrscr(); int i, j = 0, k = 0, count = 0; char str[100], str1[10][20], word[20]; cout<<"Enter the String : "; gets(str); /* Converting the string into 2D Array */ for (i=0; str[i]!='0'; i++) { if (str[i]==' ') { str1[k][j] = '0'; k++; j=0; } else { str1[k][j]=str[i]; j++; } } str1[k][j] = '0'; cout<<"Enter a word to be delete : "; cin>>word; /* Comparing the string with the given word */ for (i=0; i<k+1; i++) { if (strcmp(str1[i], word) == 0) { for (j=i; j<k+1; j++) { strcpy(str1[j], str1[j + 1]); k--; } } } cout<<"The new String after deleting the word : n"; for (i=0; i<k+1; i++) { cout<<str1[i]<<" "; } getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-68-2048.jpg)

![/* C++ Program - Count Word in Sentence */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> void main() { clrscr(); char strs[100], countw=0, strw[15], i; cout<<"Write a sentence : "; gets(strs); int len=strlen(strs); for(i=0; i<len; i++) { if(strs[i]==' ') { countw++; } } cout<<"Total number of words in the sentence is "<<countw+1; getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-70-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program - Read and Display File */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> #include<fstream.h> #include<stdlib.h> void main() { clrscr(); ifstream ifile; char s[100], fname[20]; cout<<"Enter file name to read and display its content (like file.txt) : "; cin>>fname; ifile.open(fname); if(!ifile) { cout<<"Error in opening file..!!"; getch(); exit(0); } while(ifile.eof()==0) { ifile>>s; cout<<s<<" "; } cout<<"n"; ifile.close(); getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-71-2048.jpg)
![/* C++ Program to Merge Two Files */ #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> #include<fstream.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> void main() { clrscr(); ifstream ifiles1, ifiles2; ofstream ifilet; char ch, fname1[20], fname2[20], fname3[30]; cout<<"Enter first file name (with extension like file1.txt) : "; gets(fname1); cout<<"Enter second file name (with extension like file2.txt) : "; gets(fname2); cout<<"Enter name of file (with extension like file3.txt) which will store the contents of the two files (fname1 and fname1) : "; gets(fname3); ifiles1.open(fname1); ifiles2.open(fname2); if(ifiles1==NULL || ifiles2==NULL) { perror("Error Message "); cout<<"Press any key to exit...n"; getch(); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } ifilet.open(fname3); if(!ifilet) { perror("Error Message "); cout<<"Press any key to exit...n"; getch(); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } while(ifiles1.eof()==0) { ifiles1>>ch; ifilet<<ch; } while(ifiles2.eof()==0) { ifiles2>>ch; ifilet<<ch; } cout<<"The two files were merged into "<<fname3<<" file successfully..!!"; ifiles1.close(); ifiles2.close(); ifilet.close(); getch(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cplusfiles2017-171111160552/75/programming-in-C-report-72-2048.jpg)
