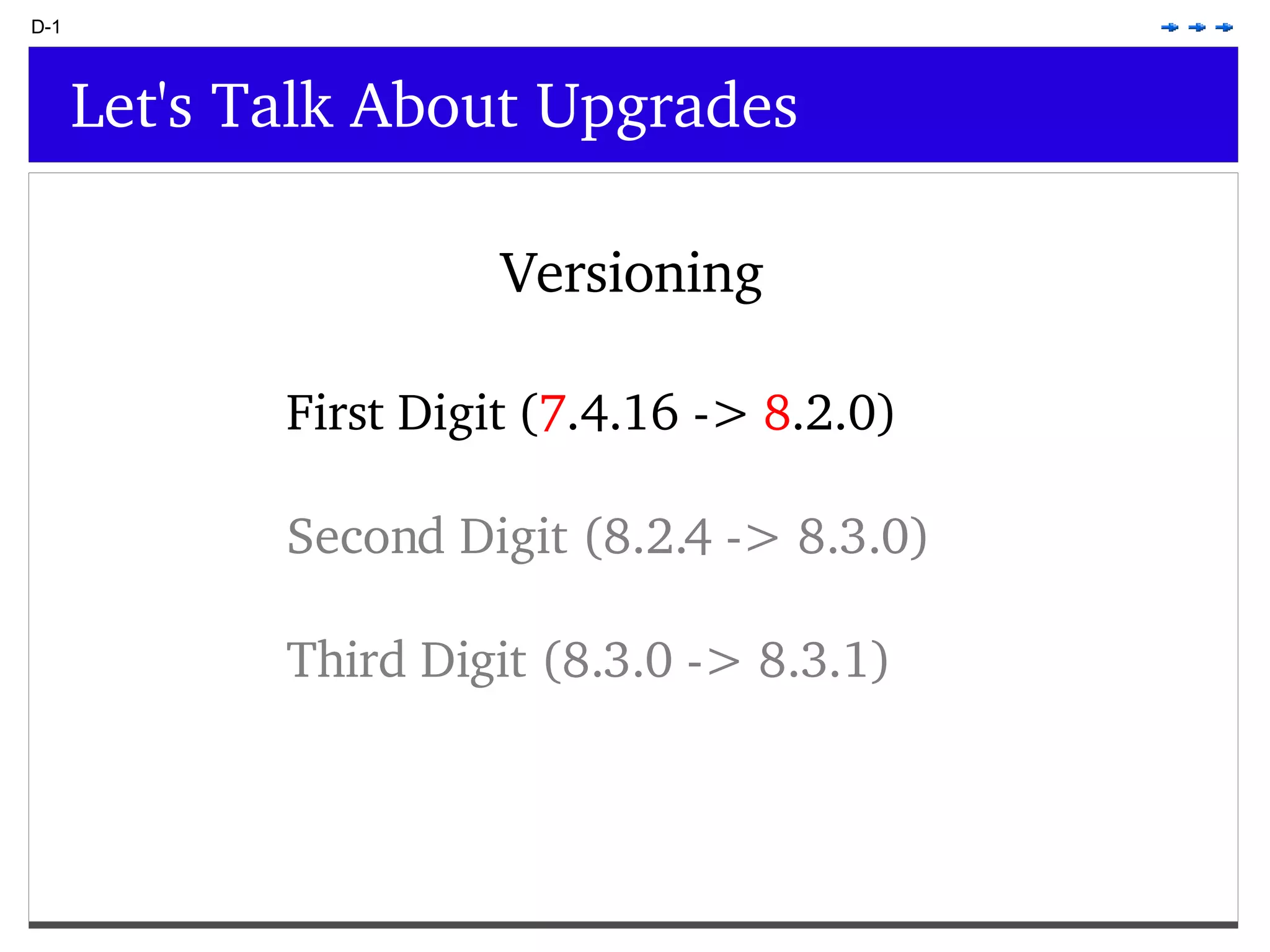
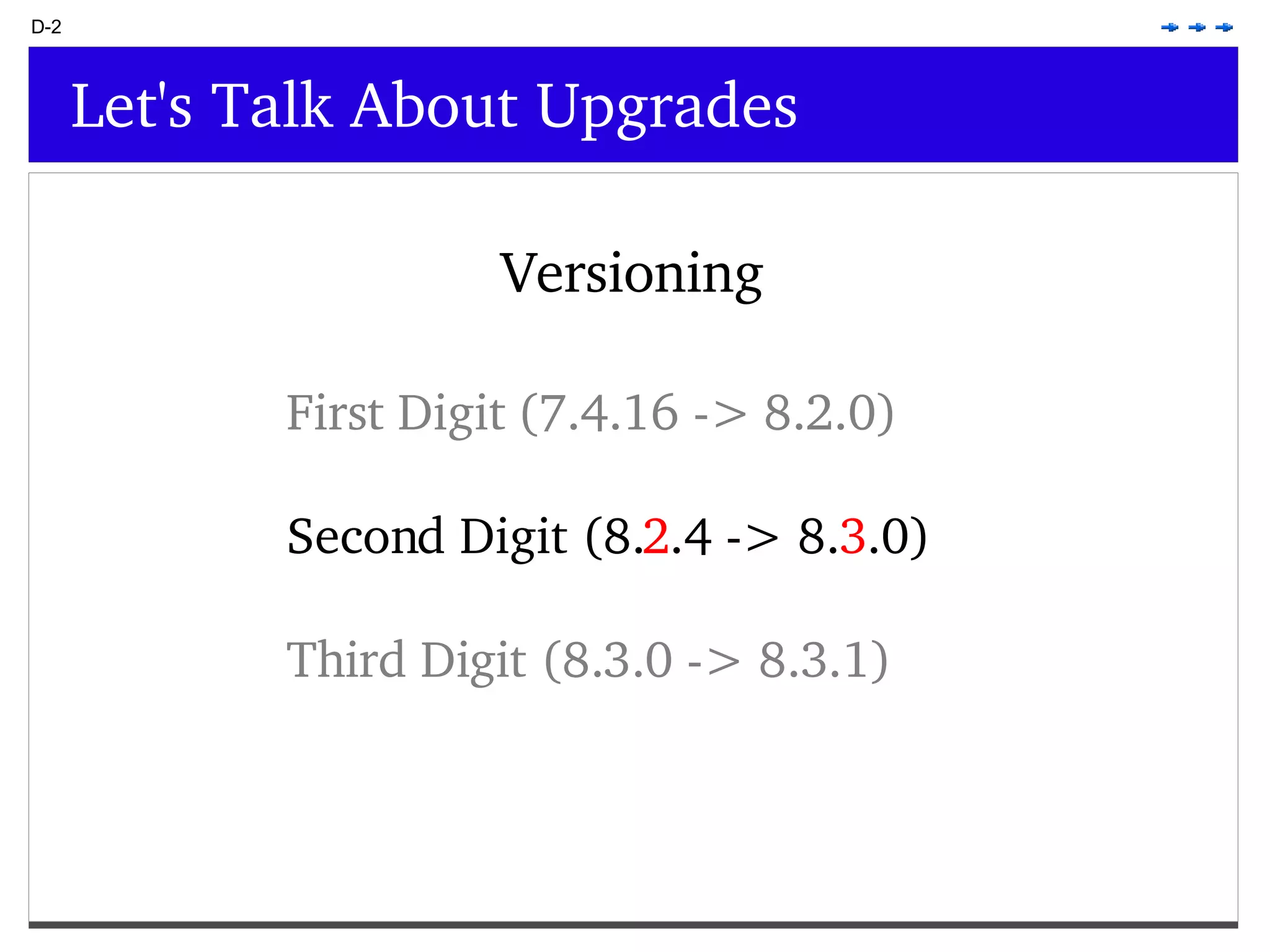
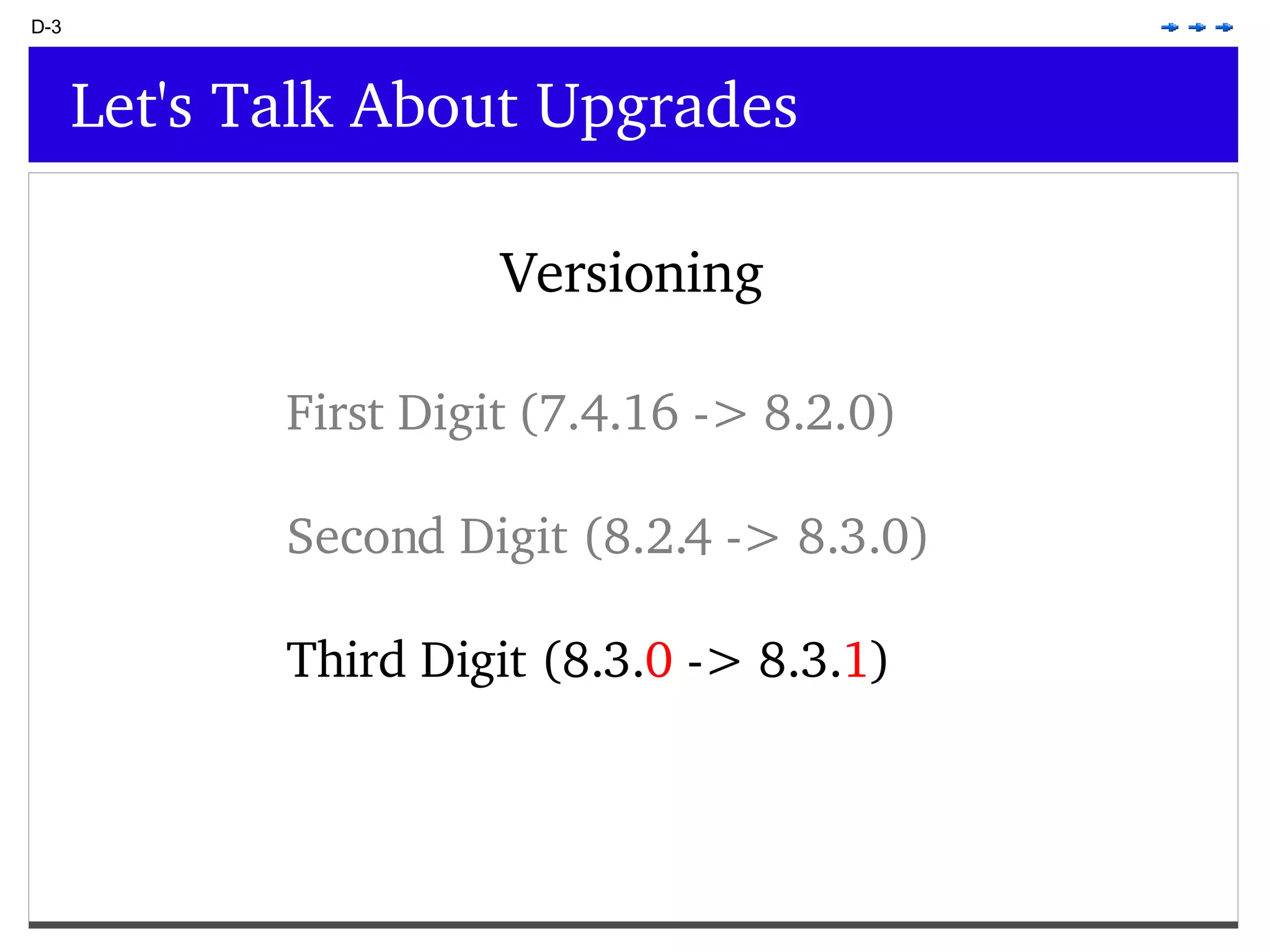
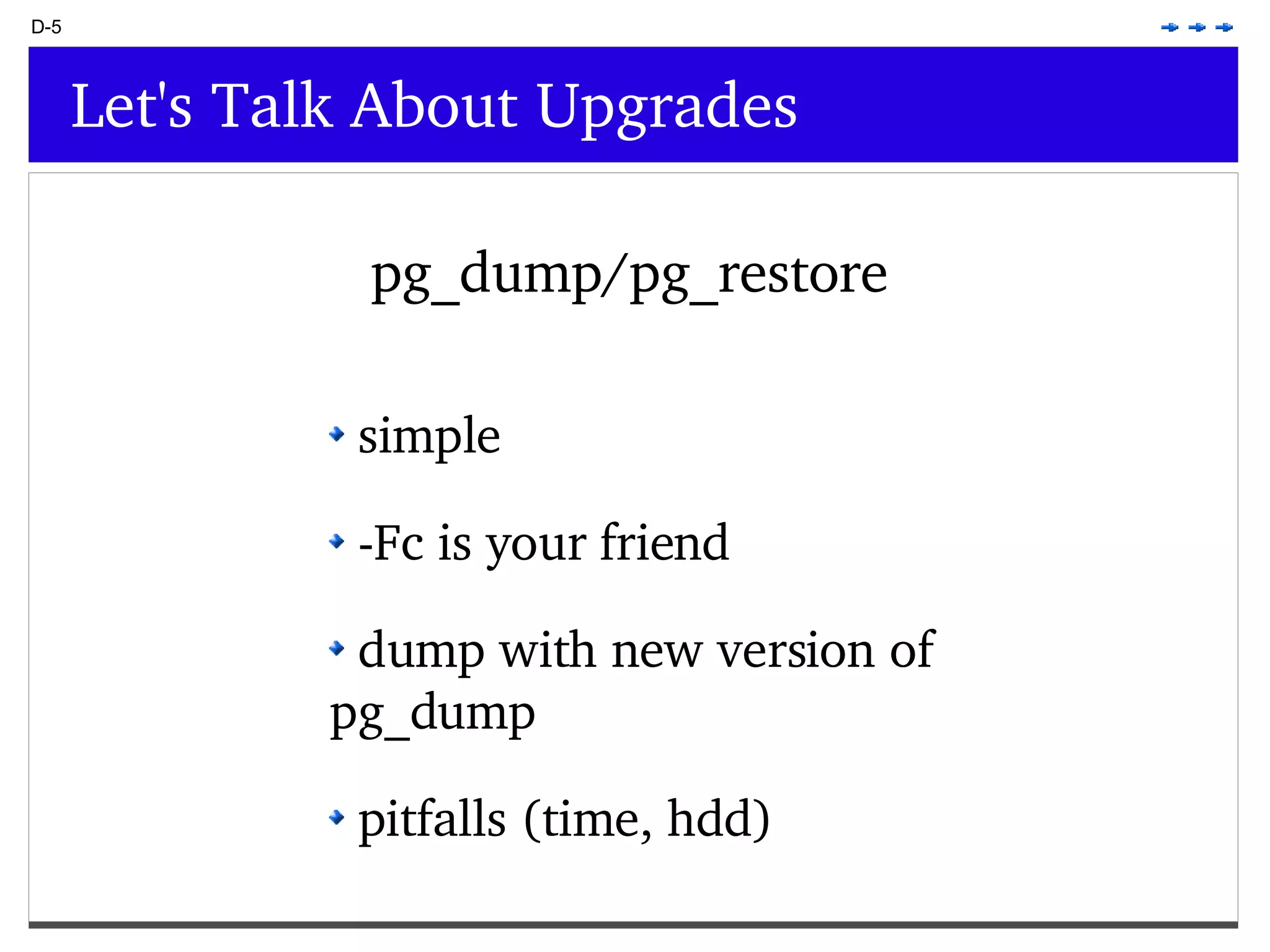
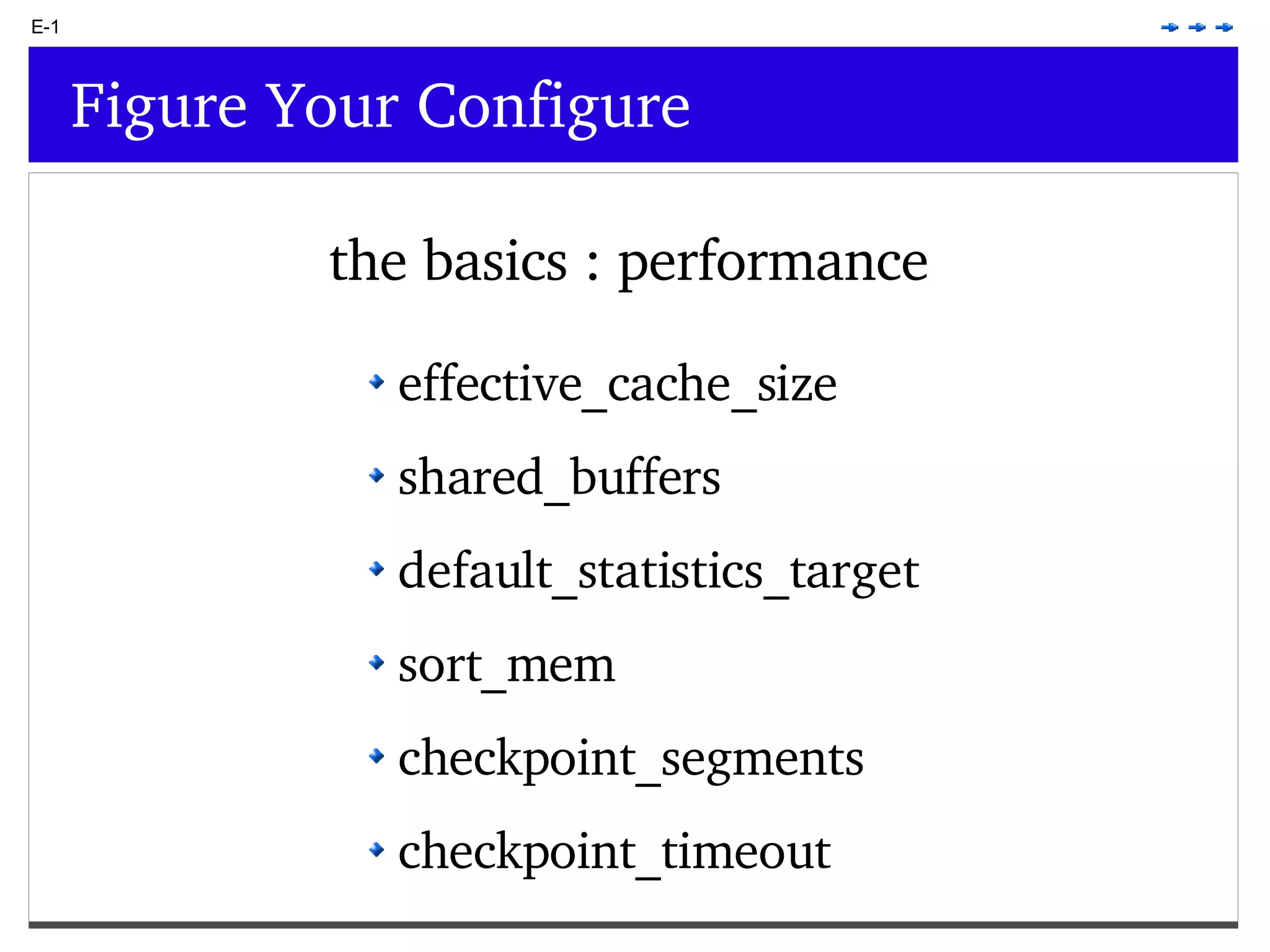
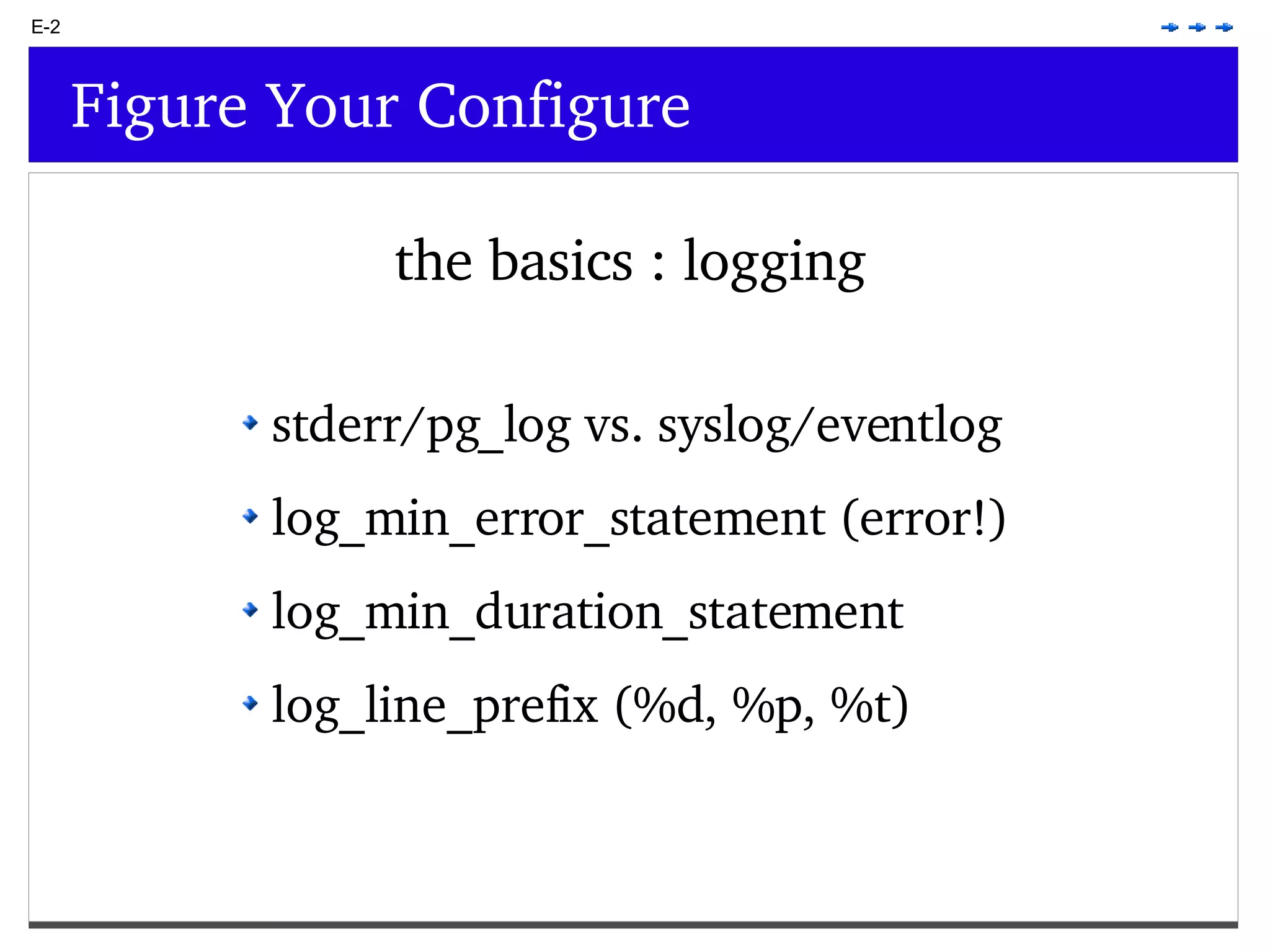
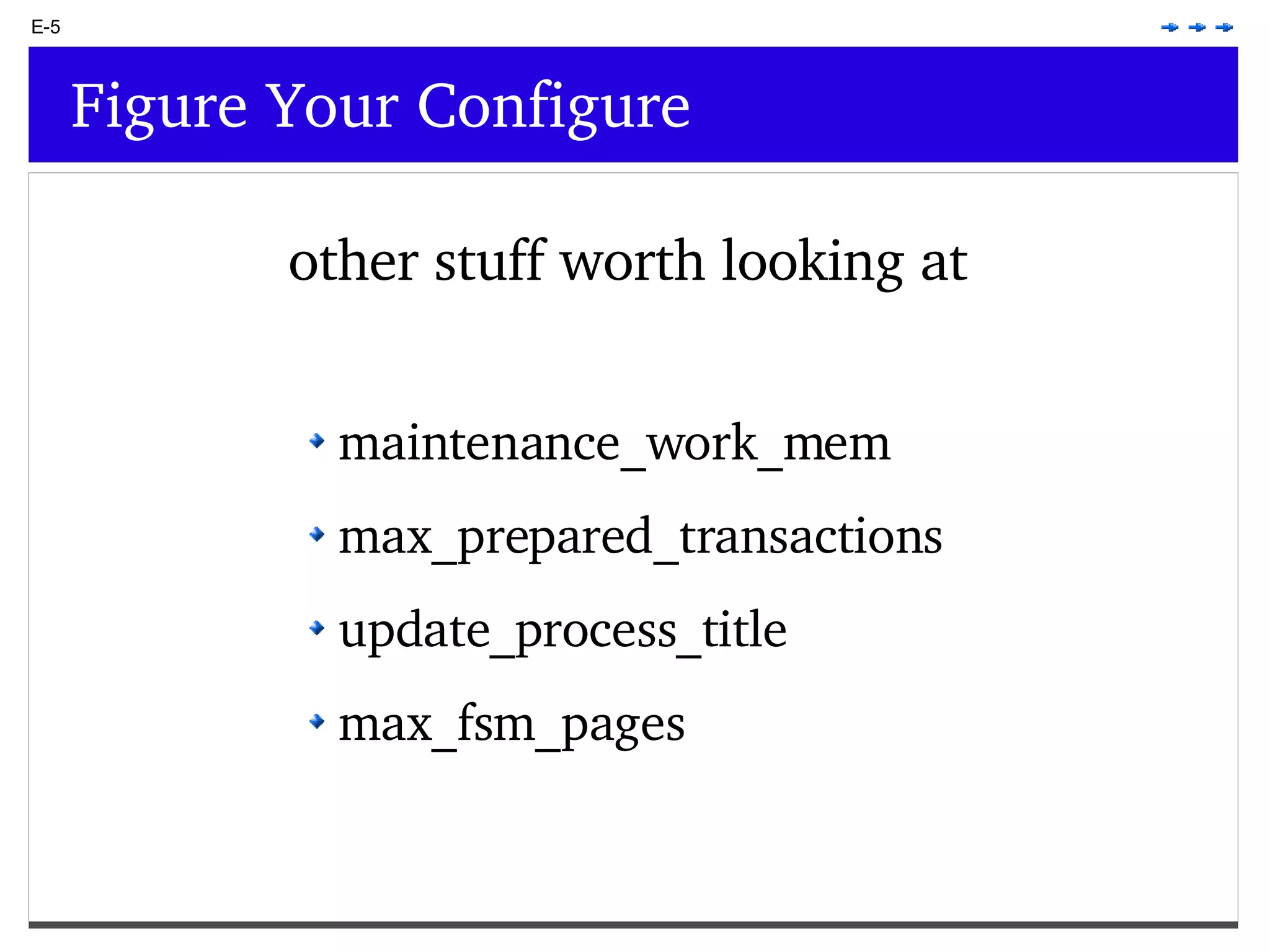
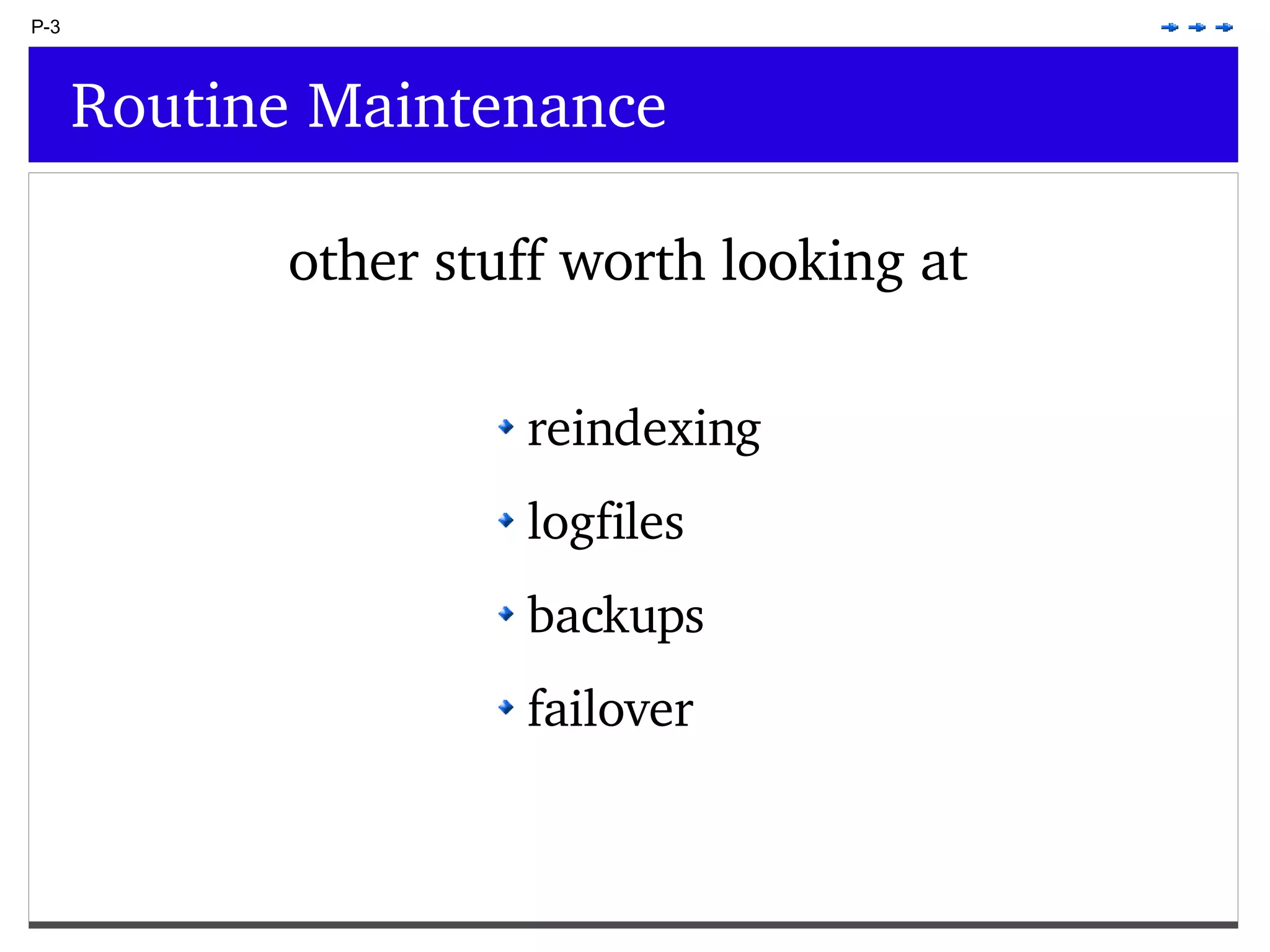
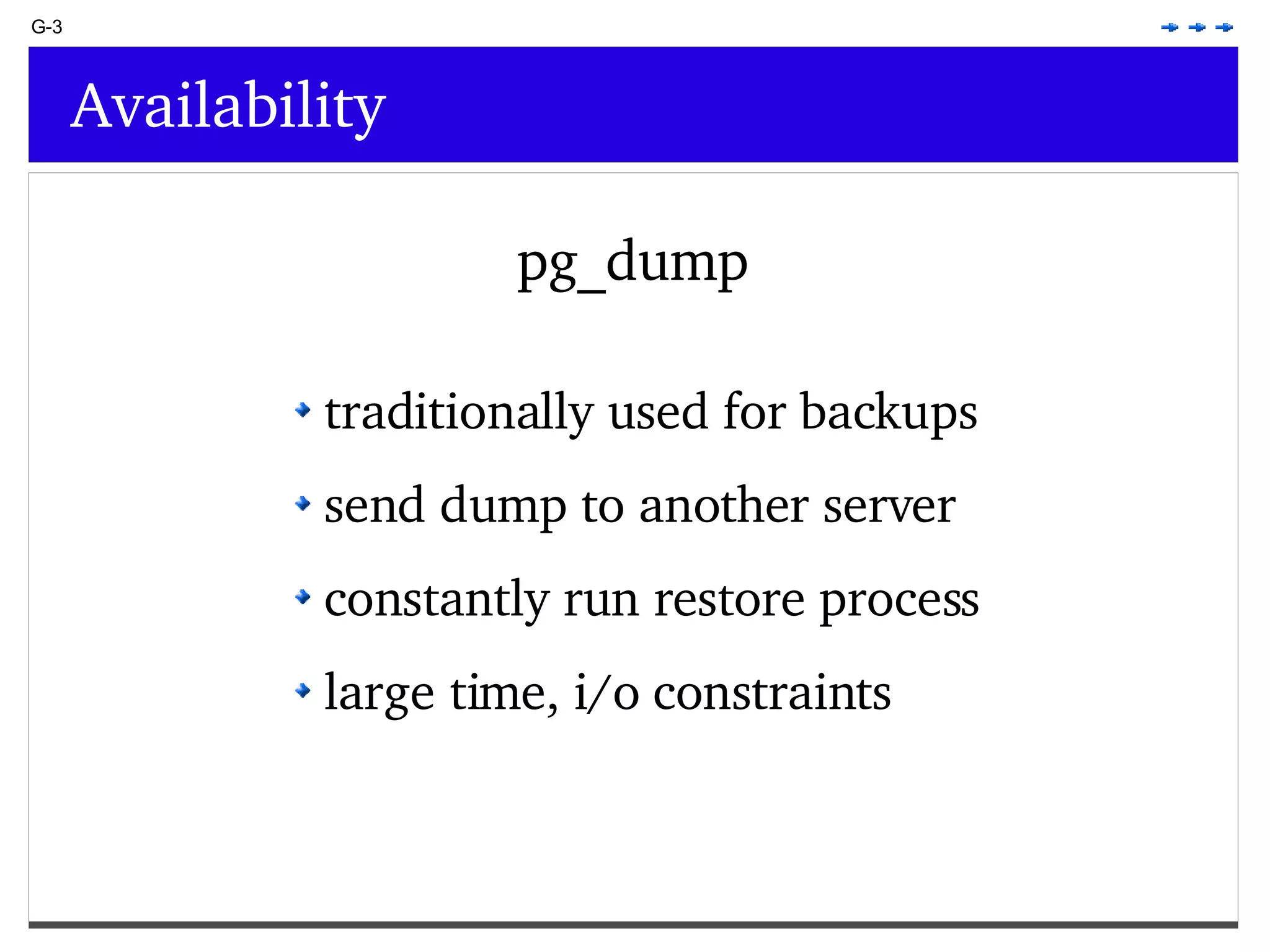
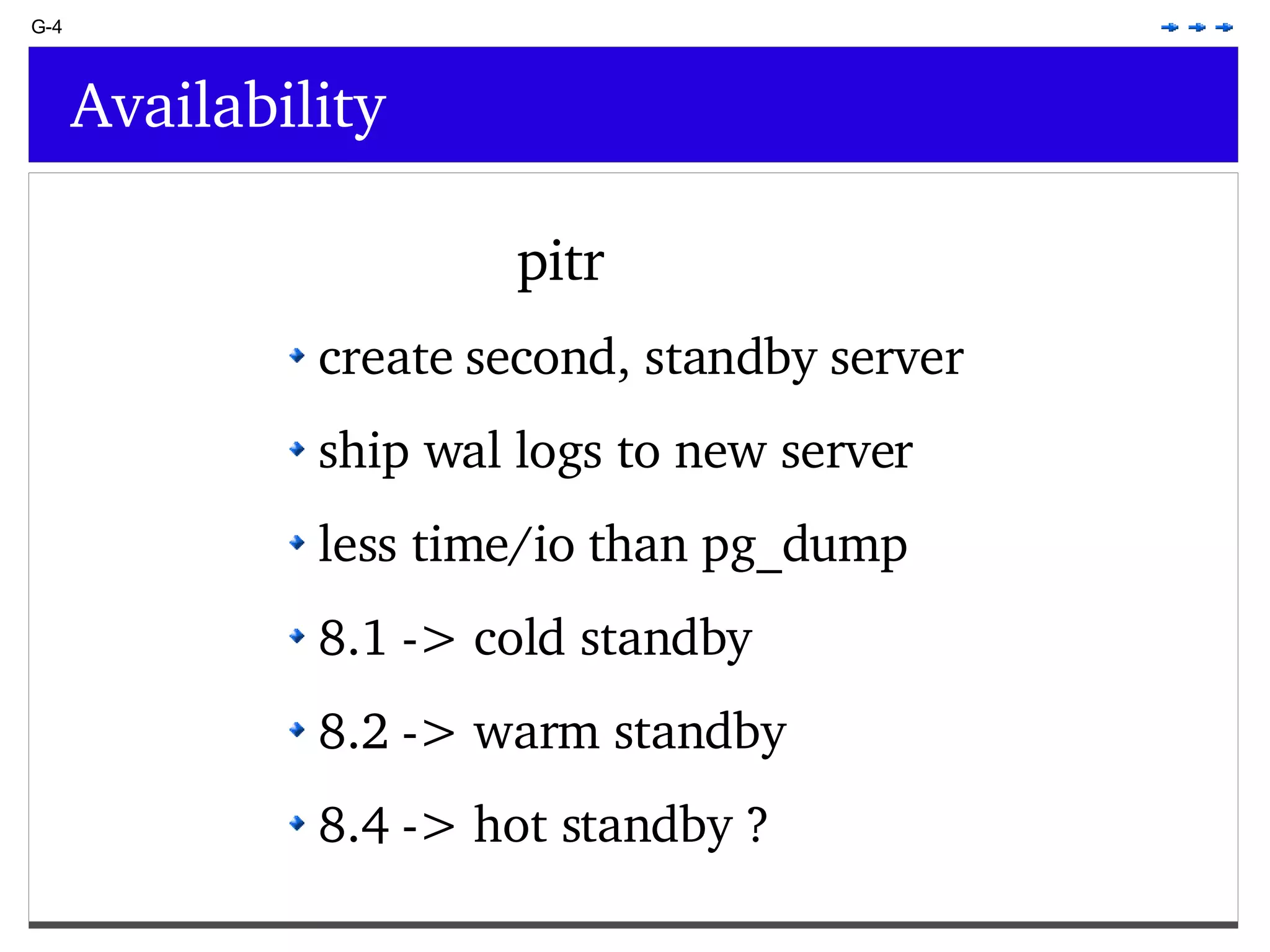
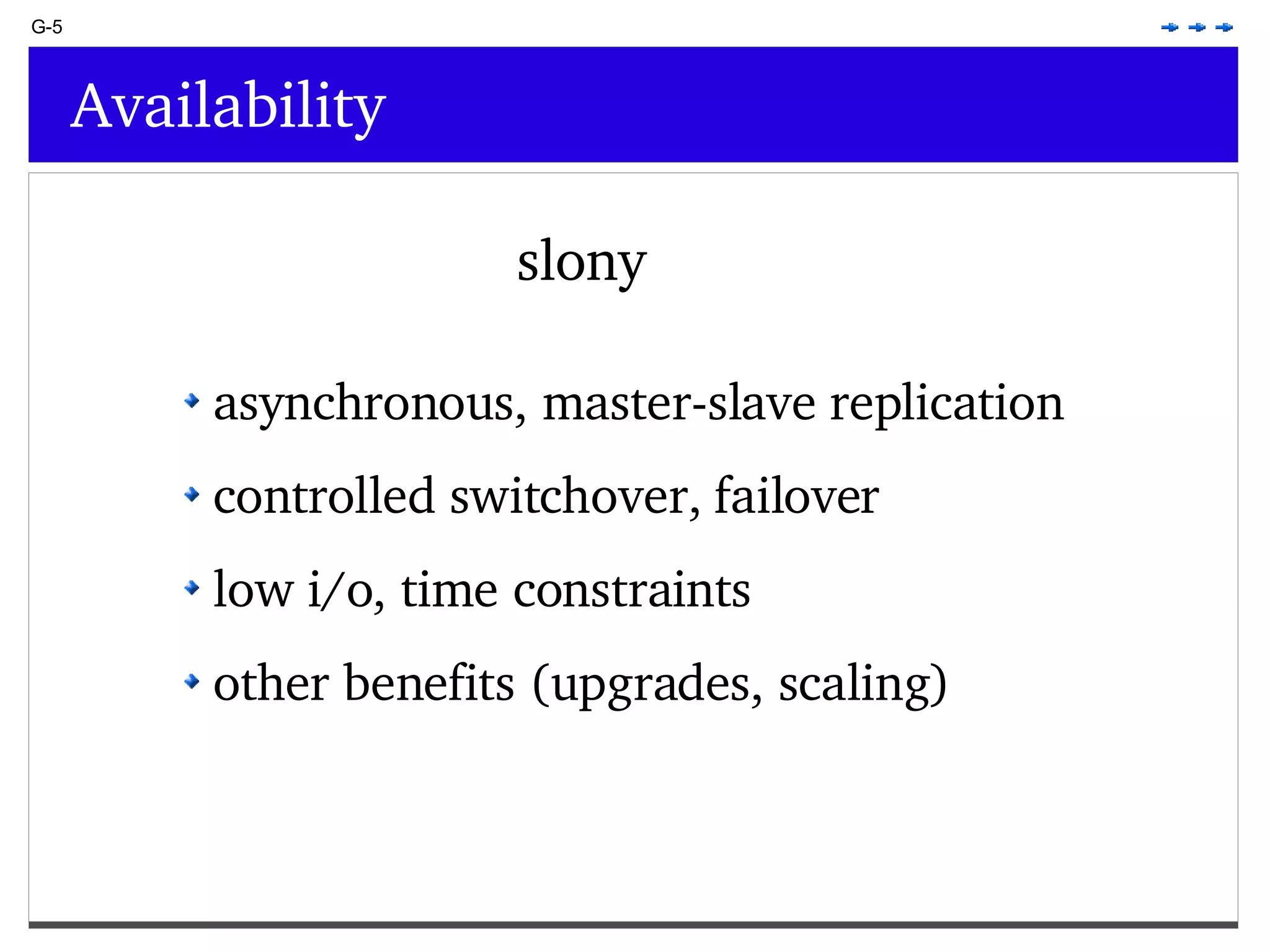
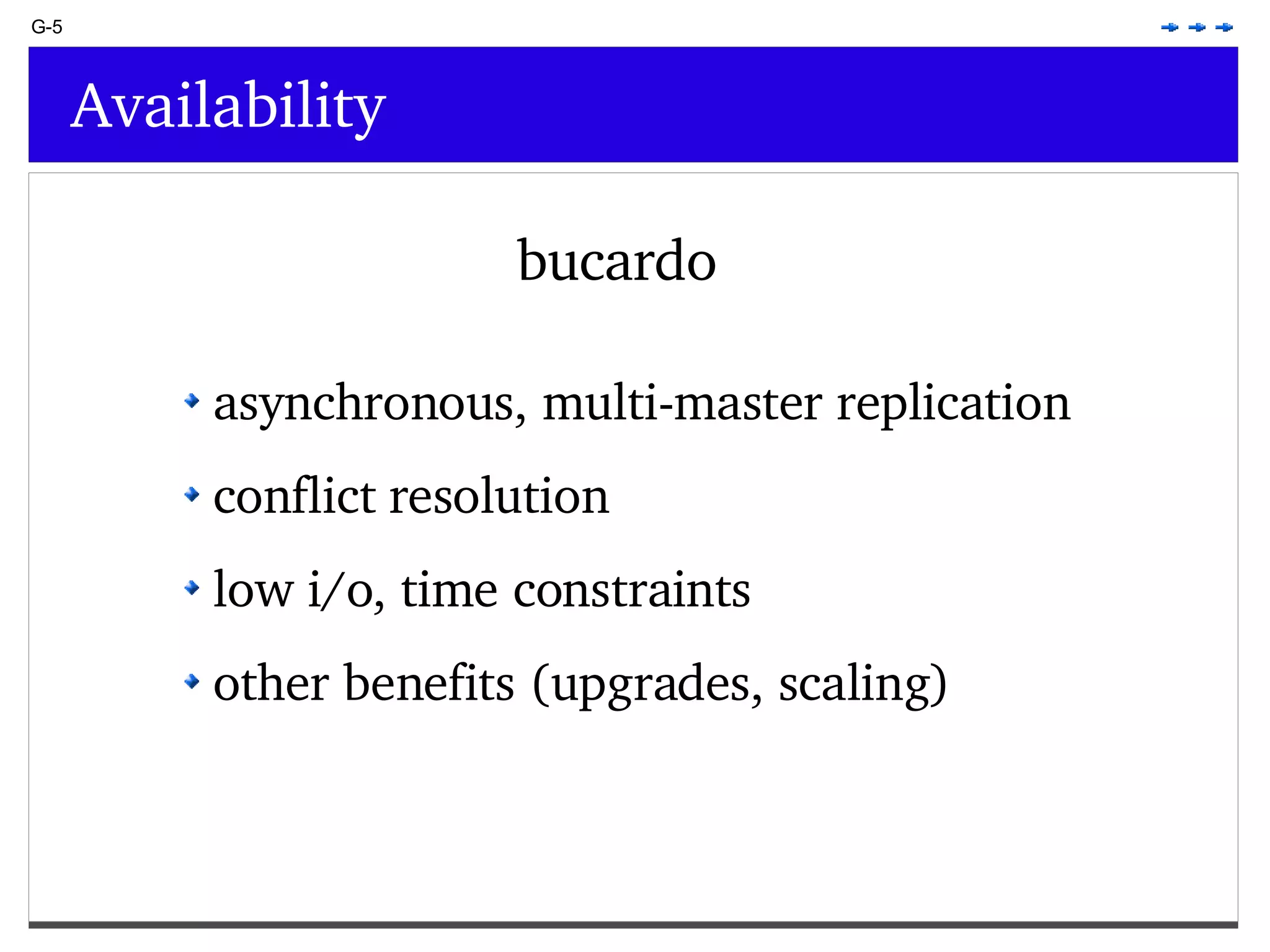
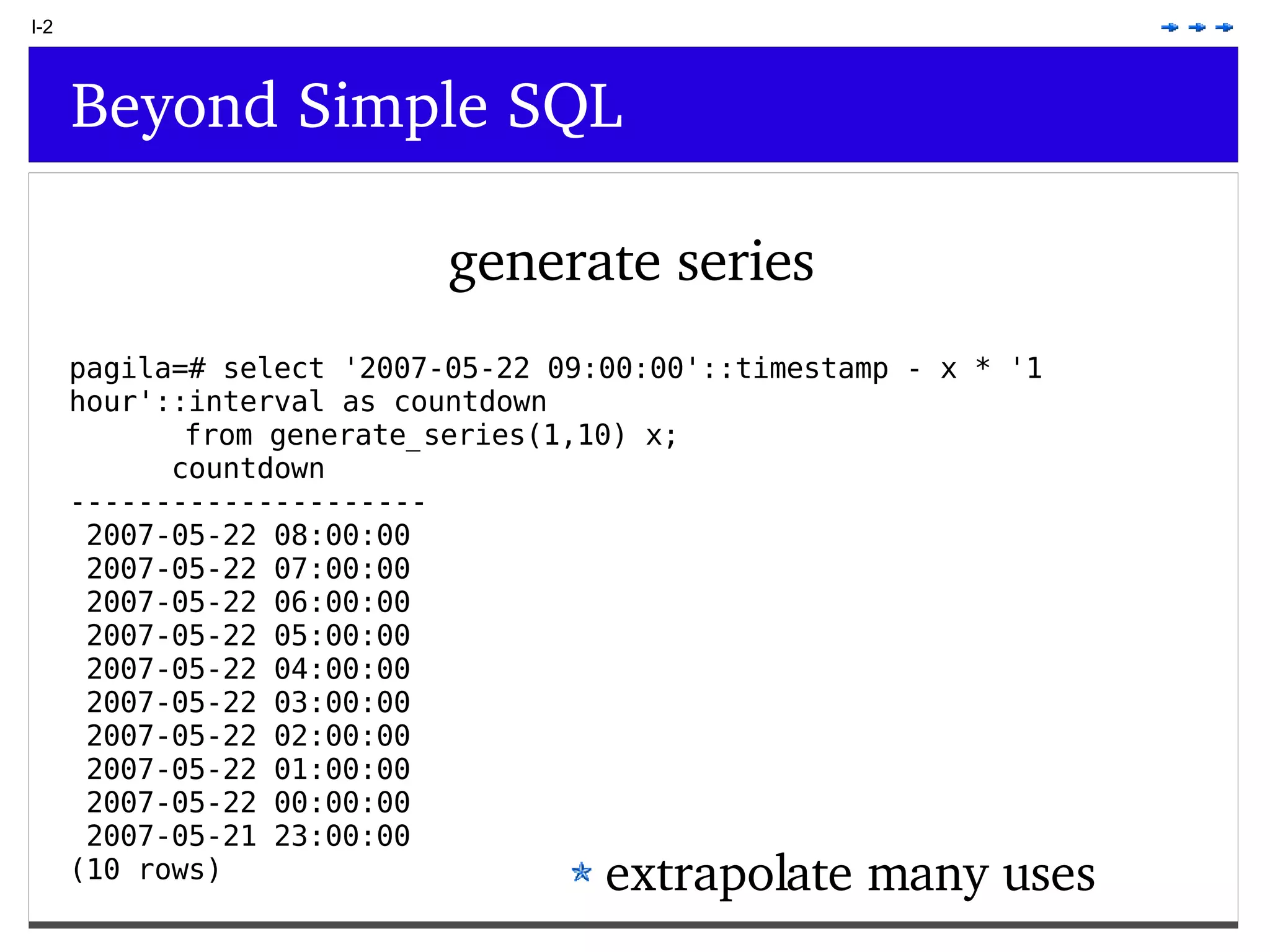
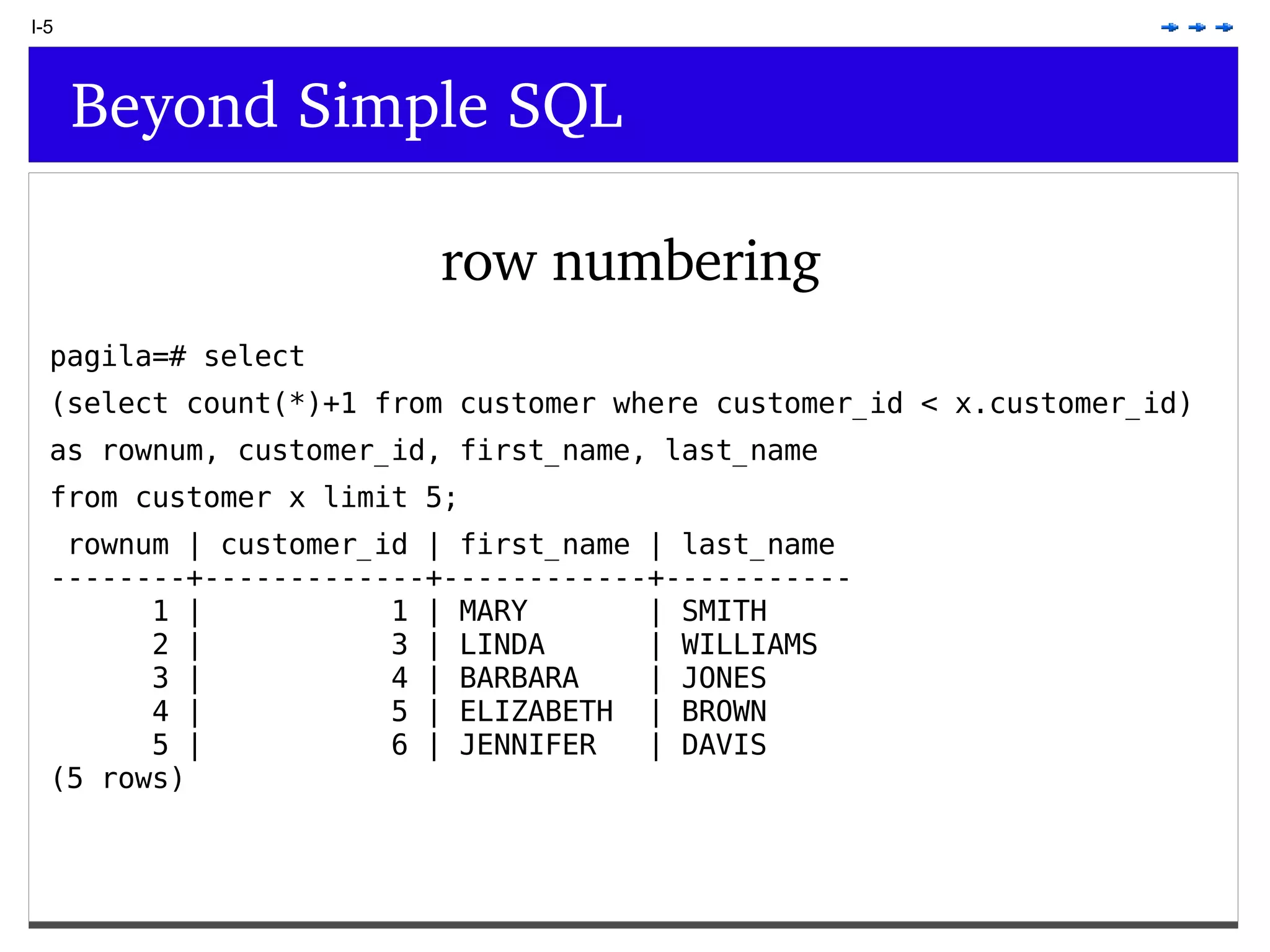
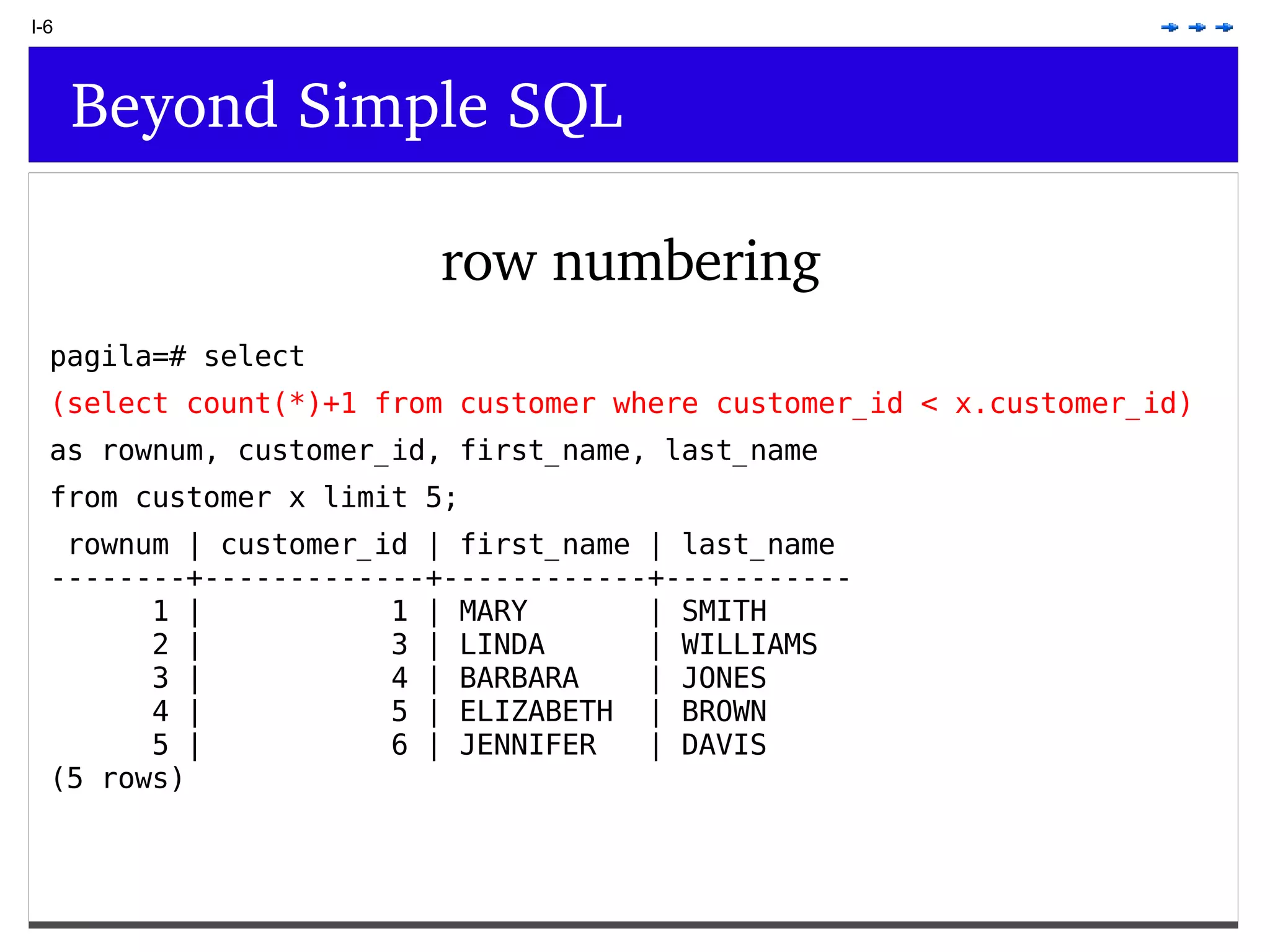
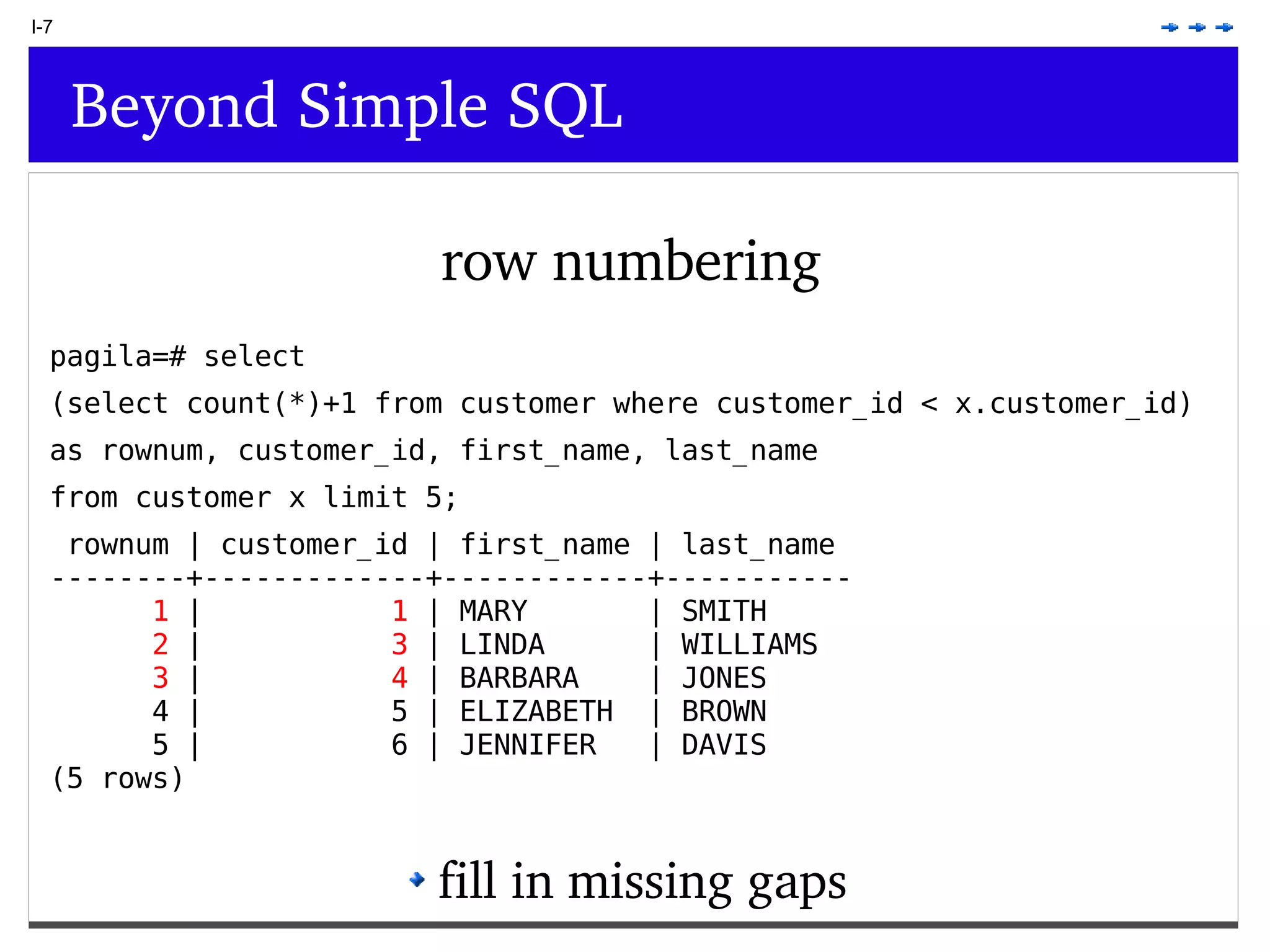
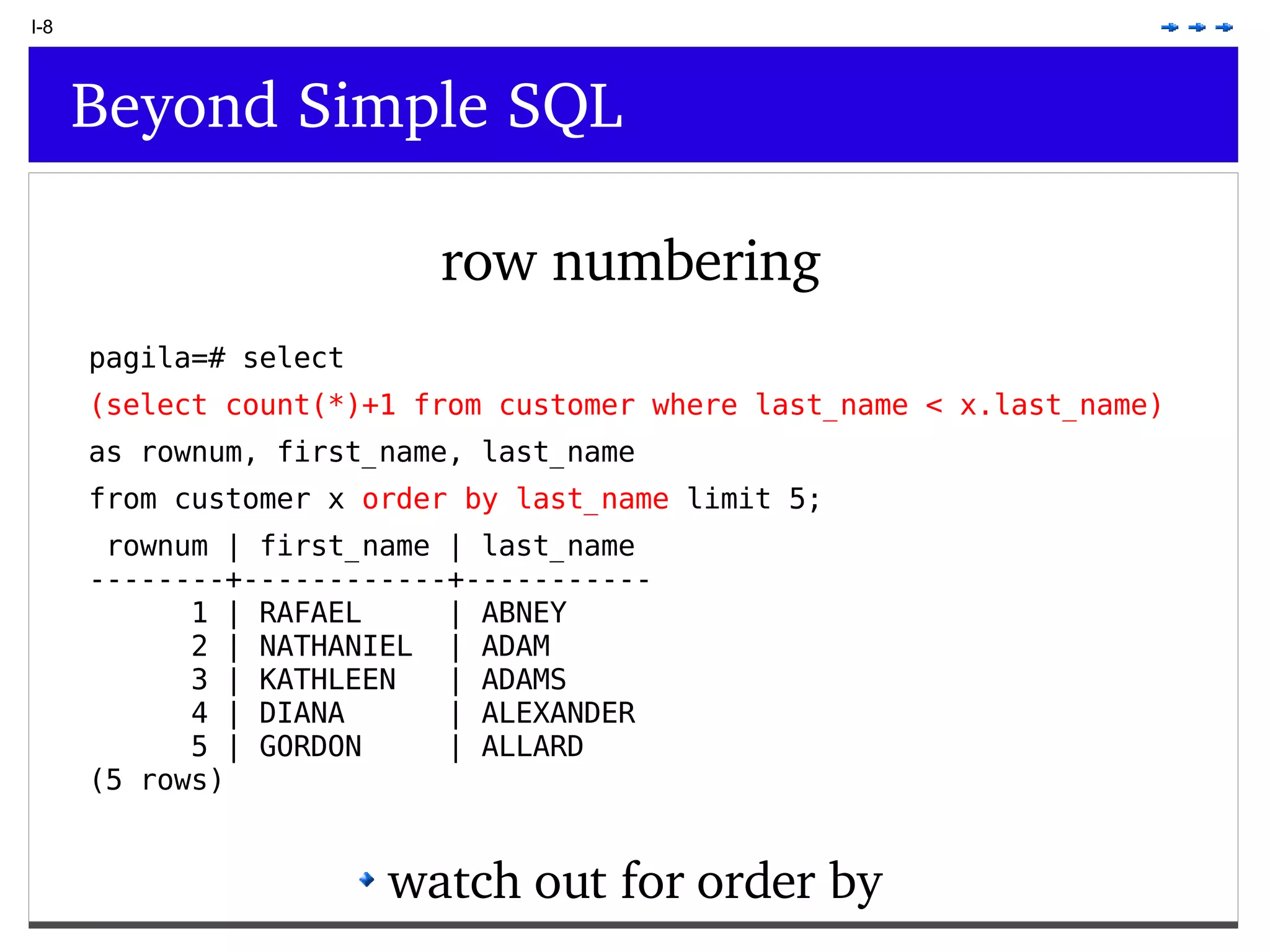
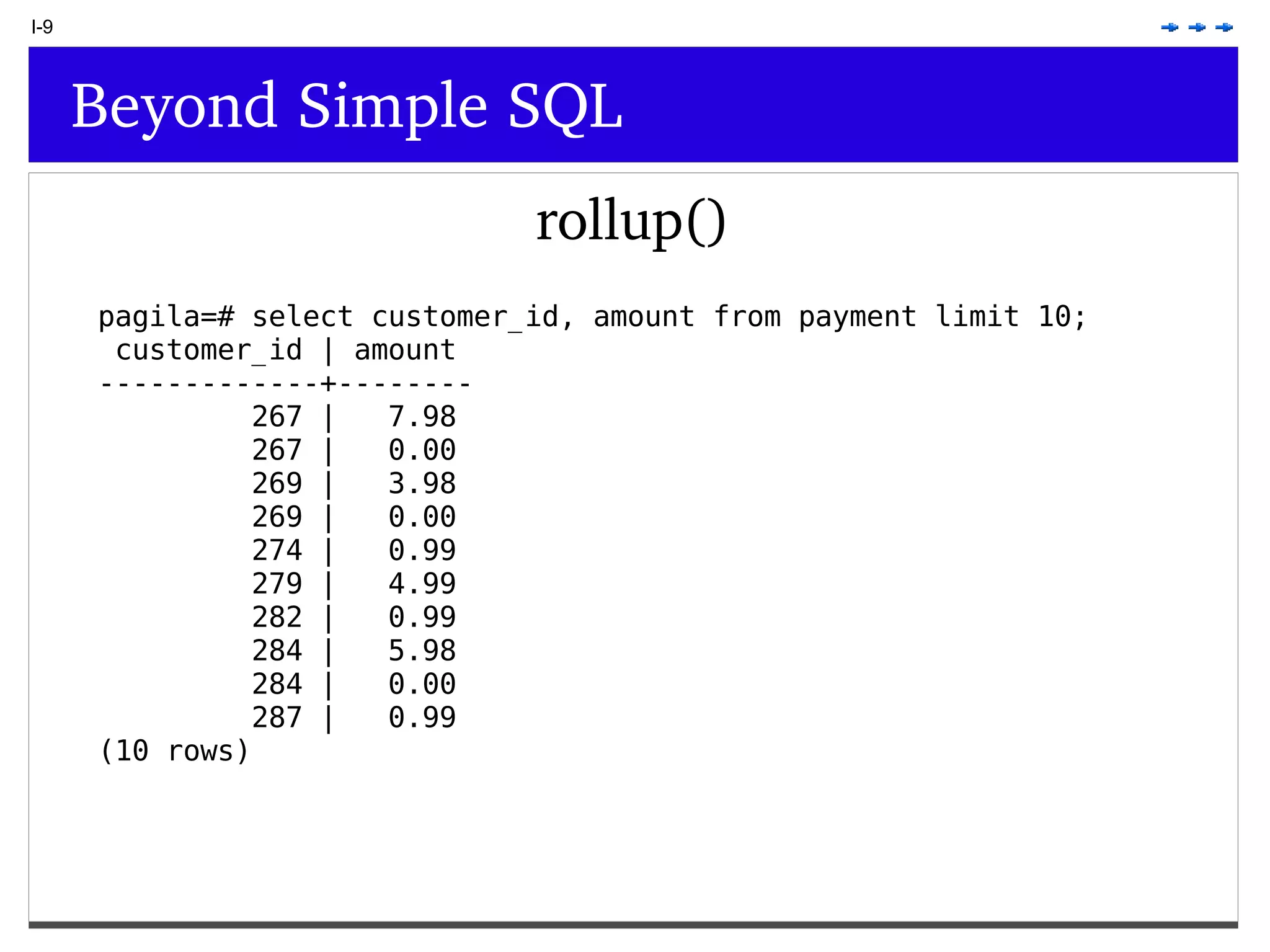
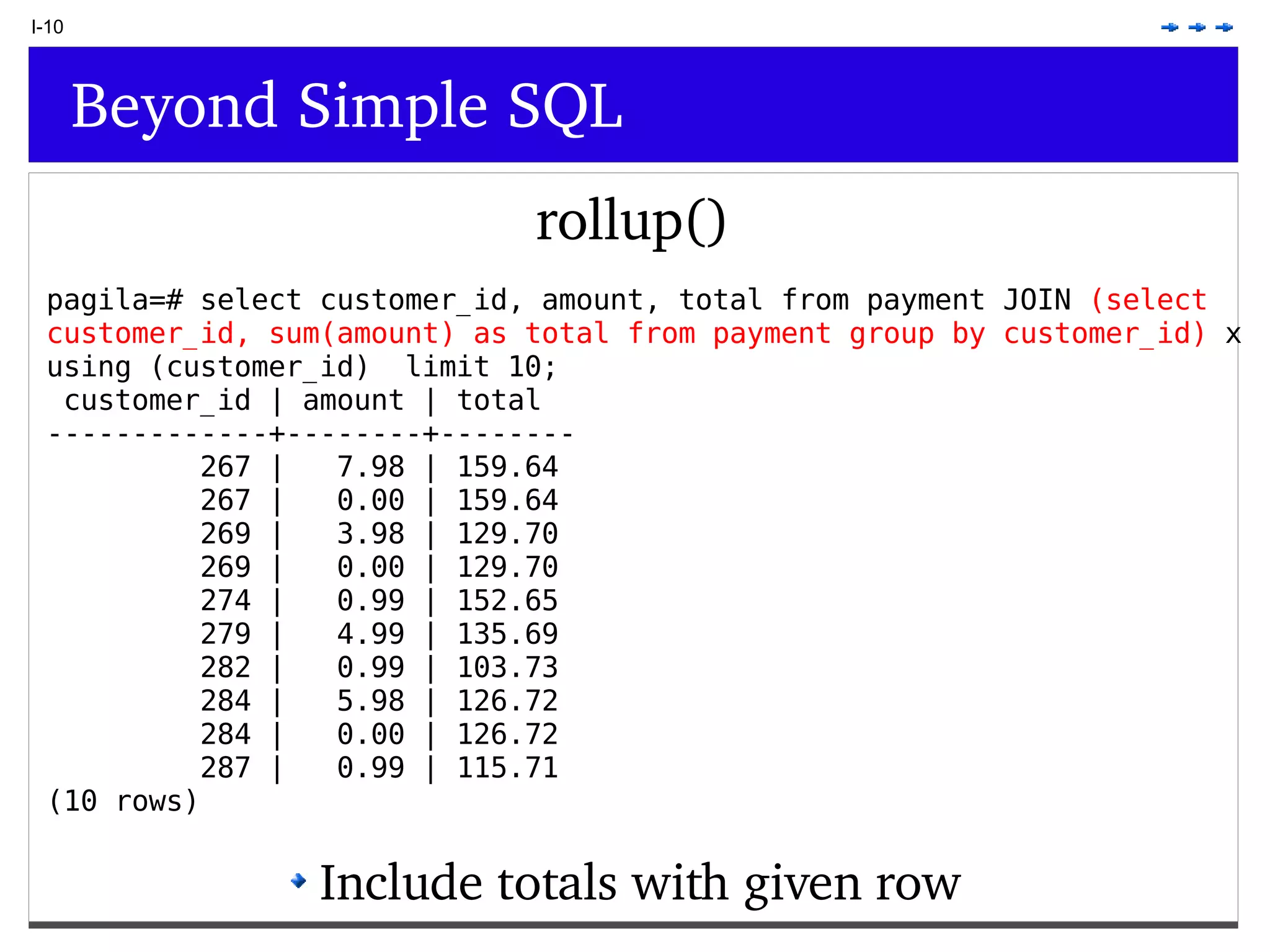
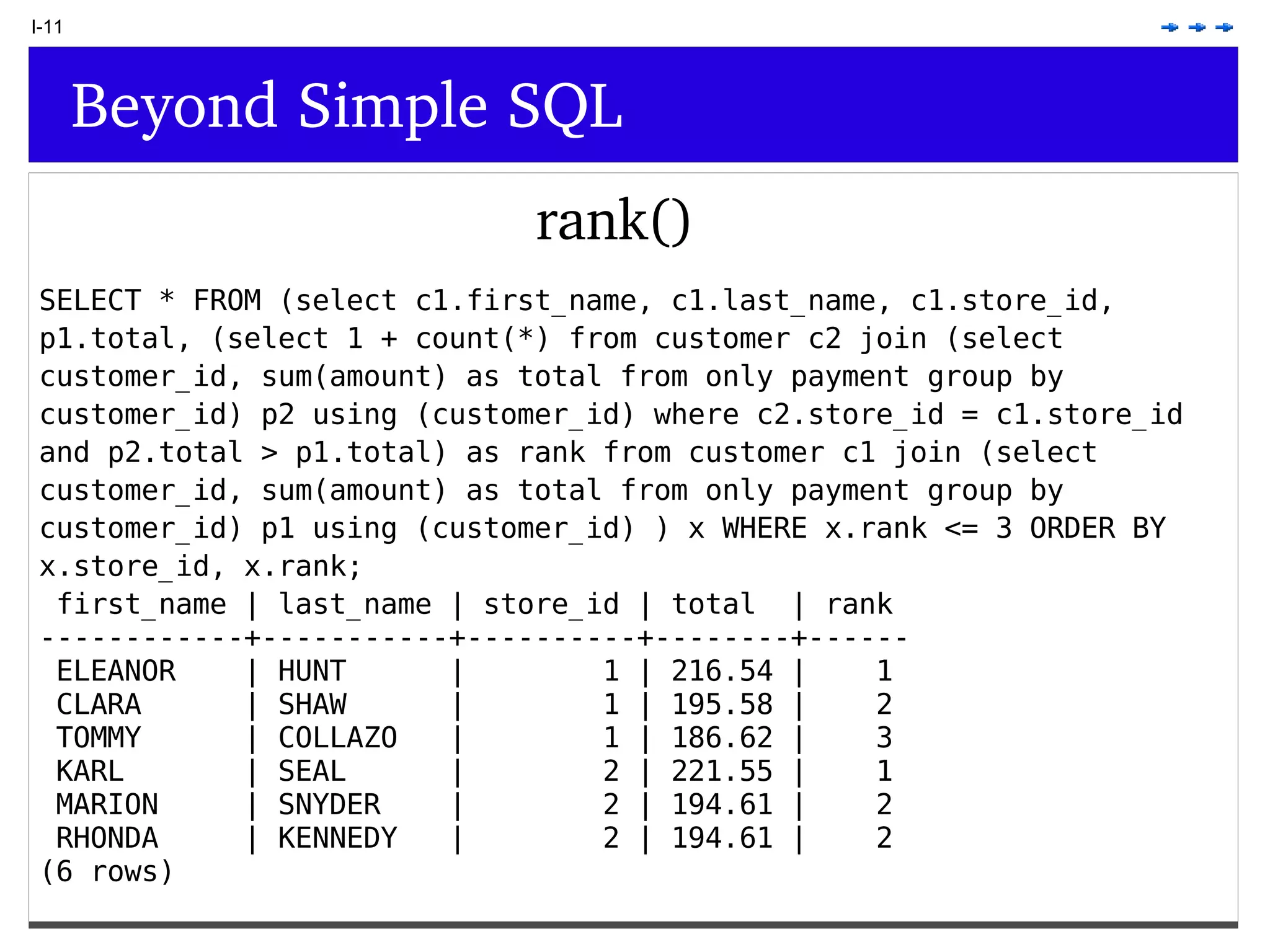
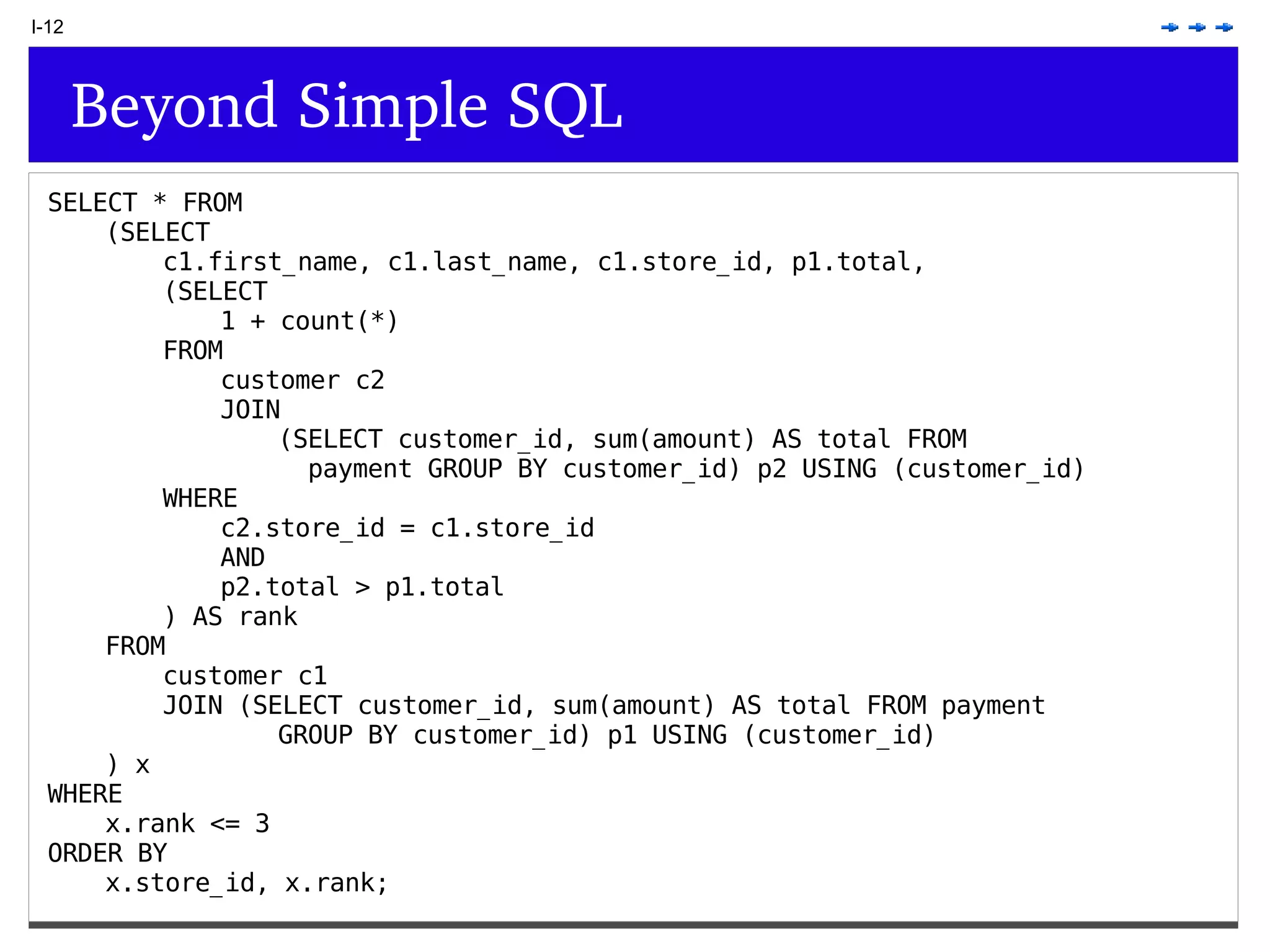
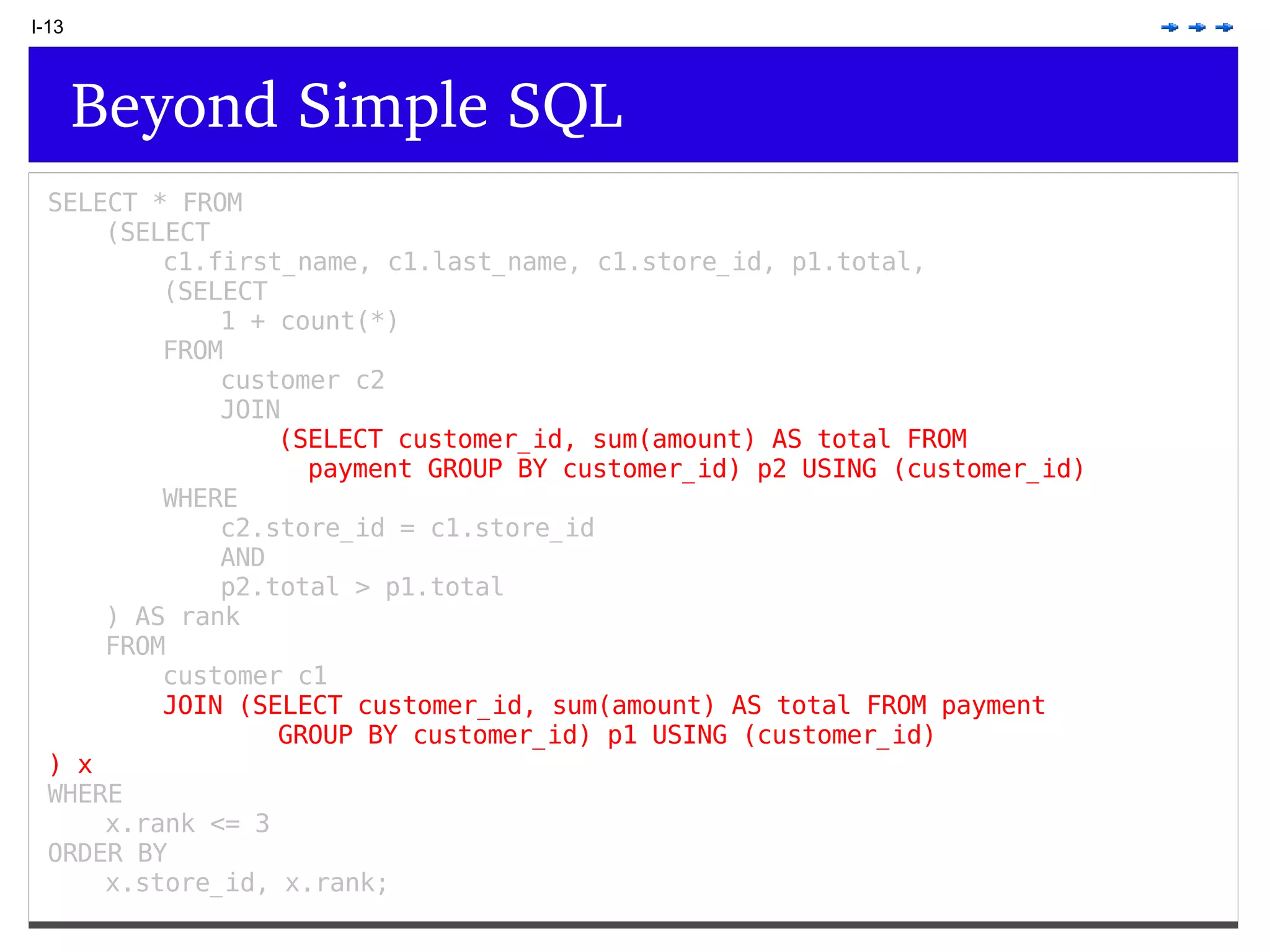
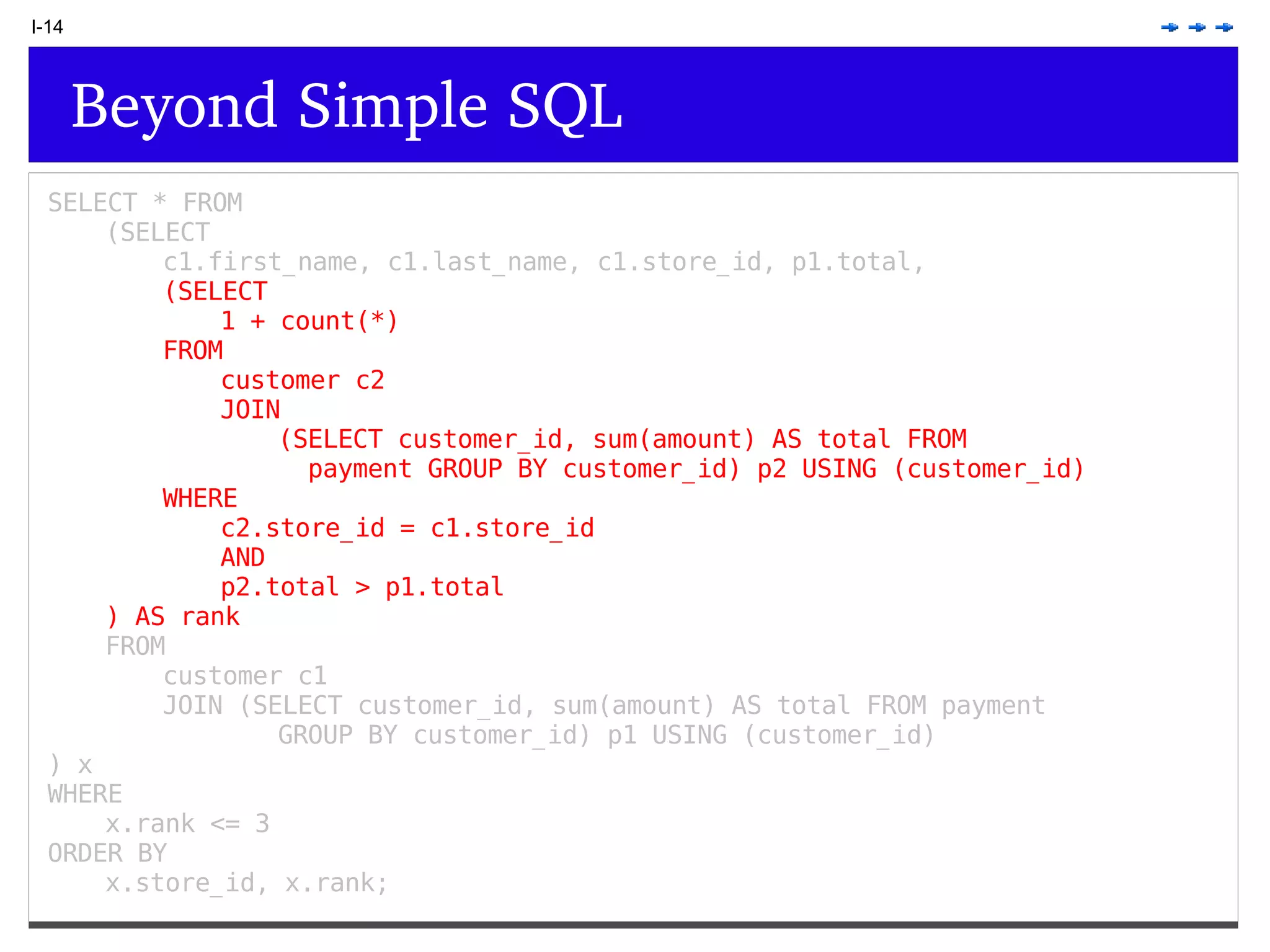
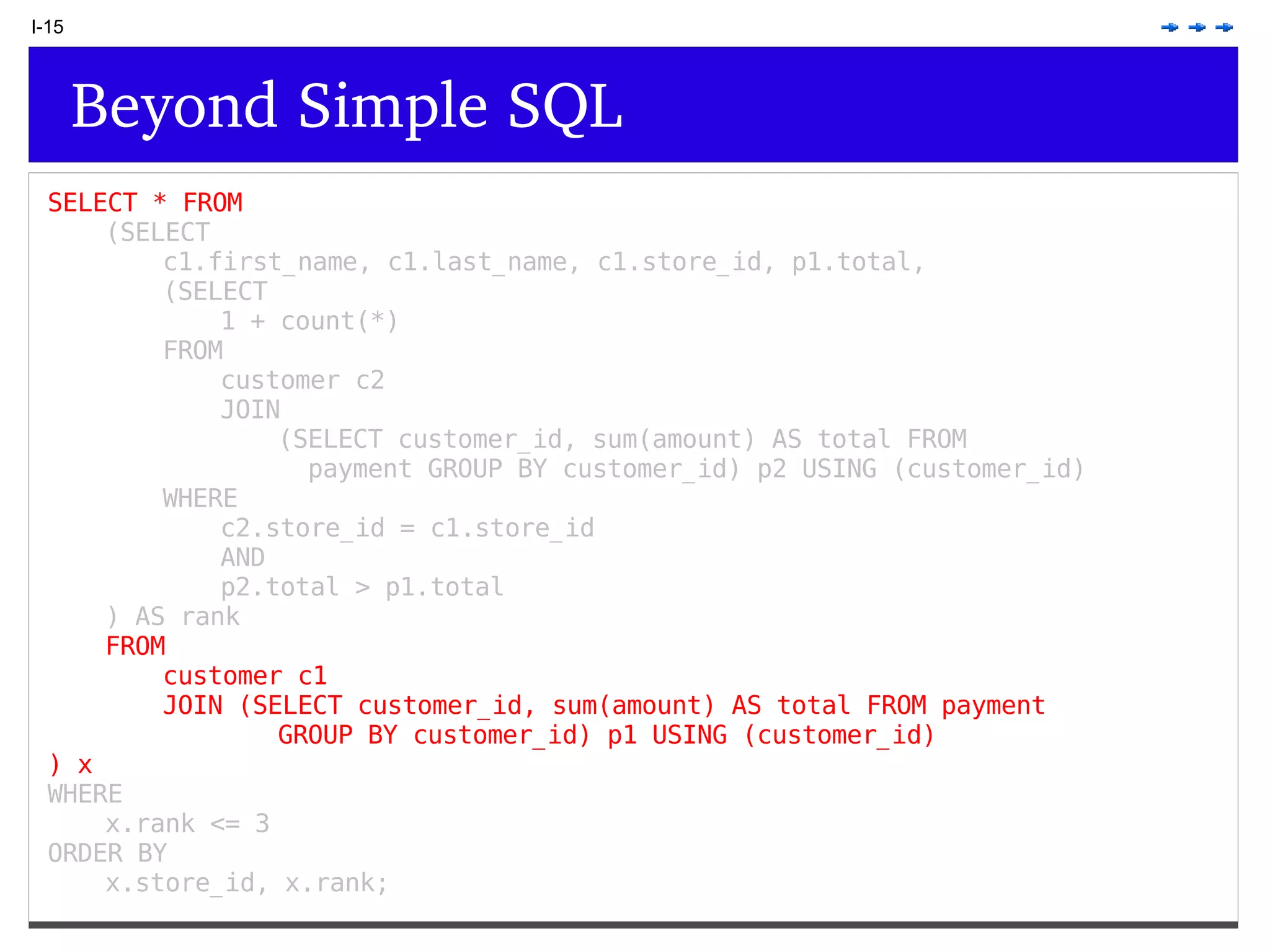
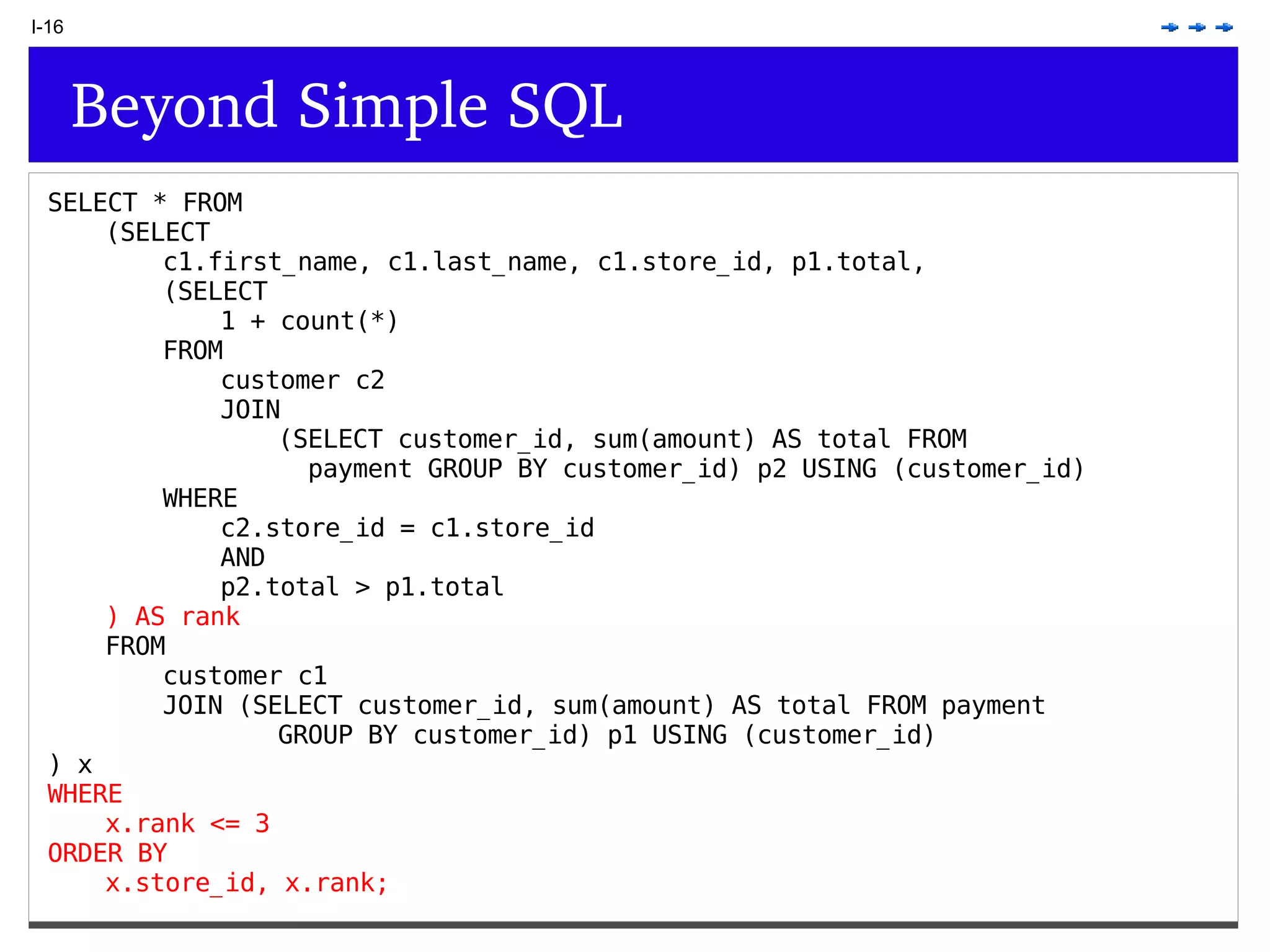
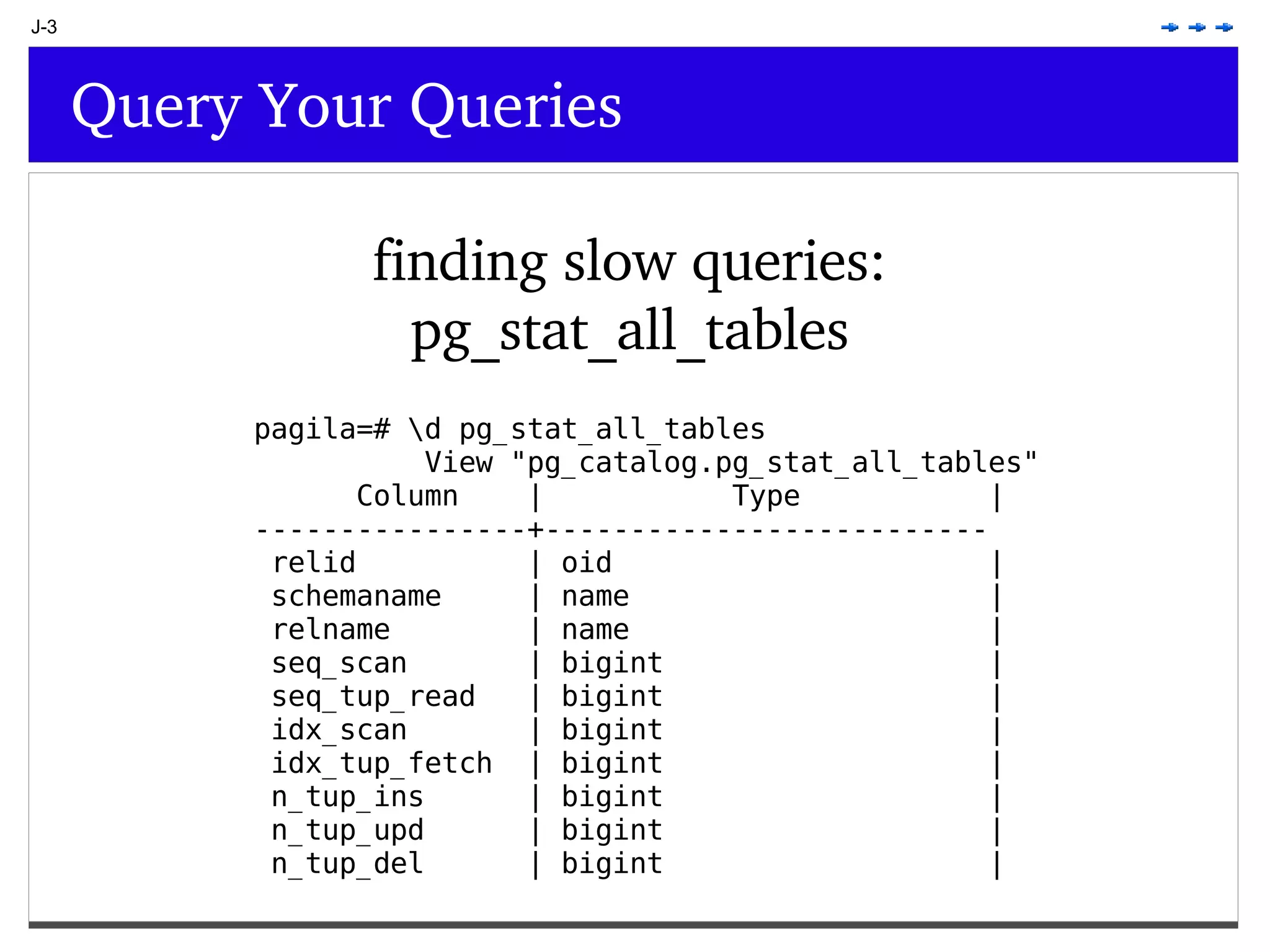
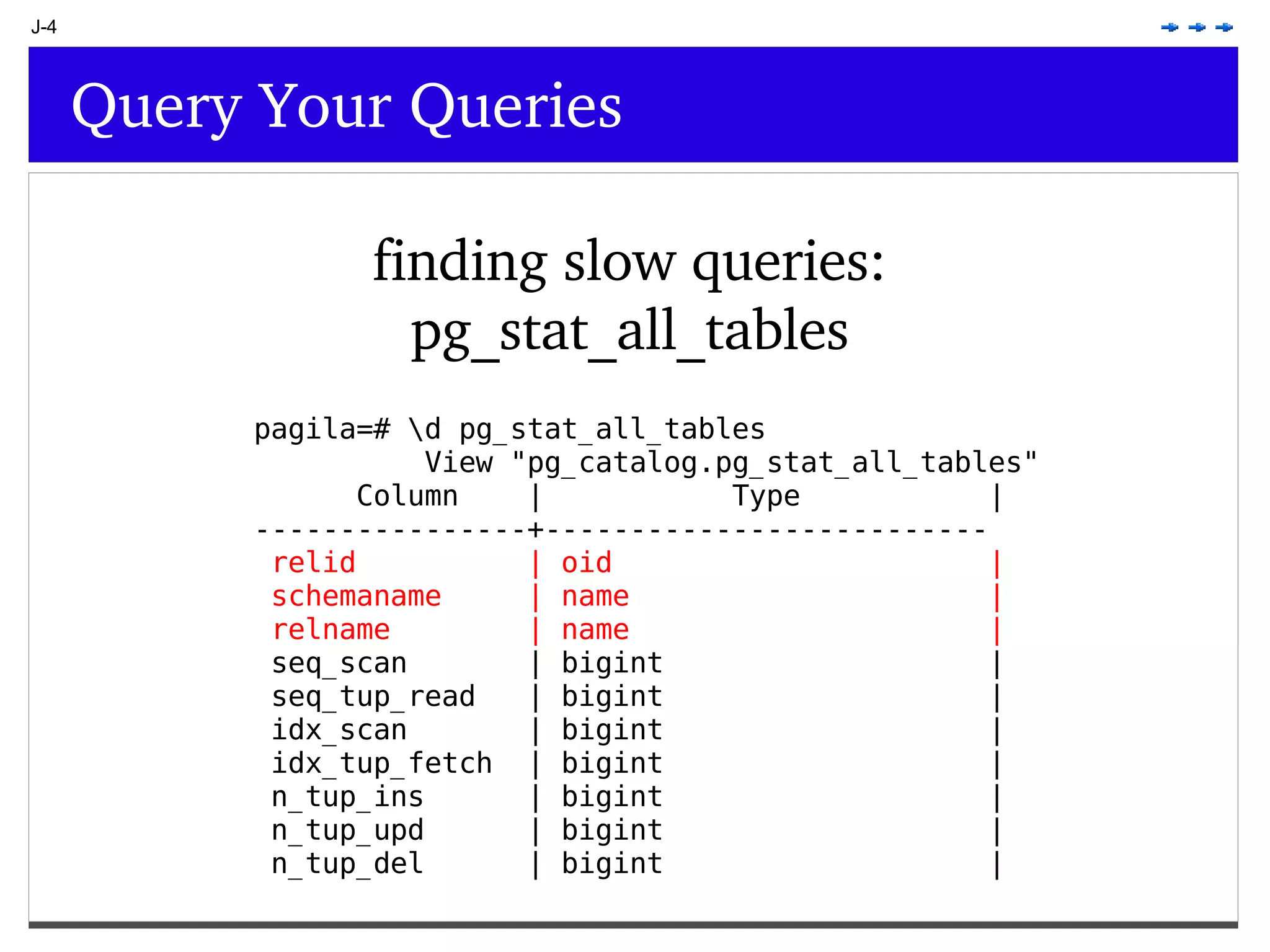
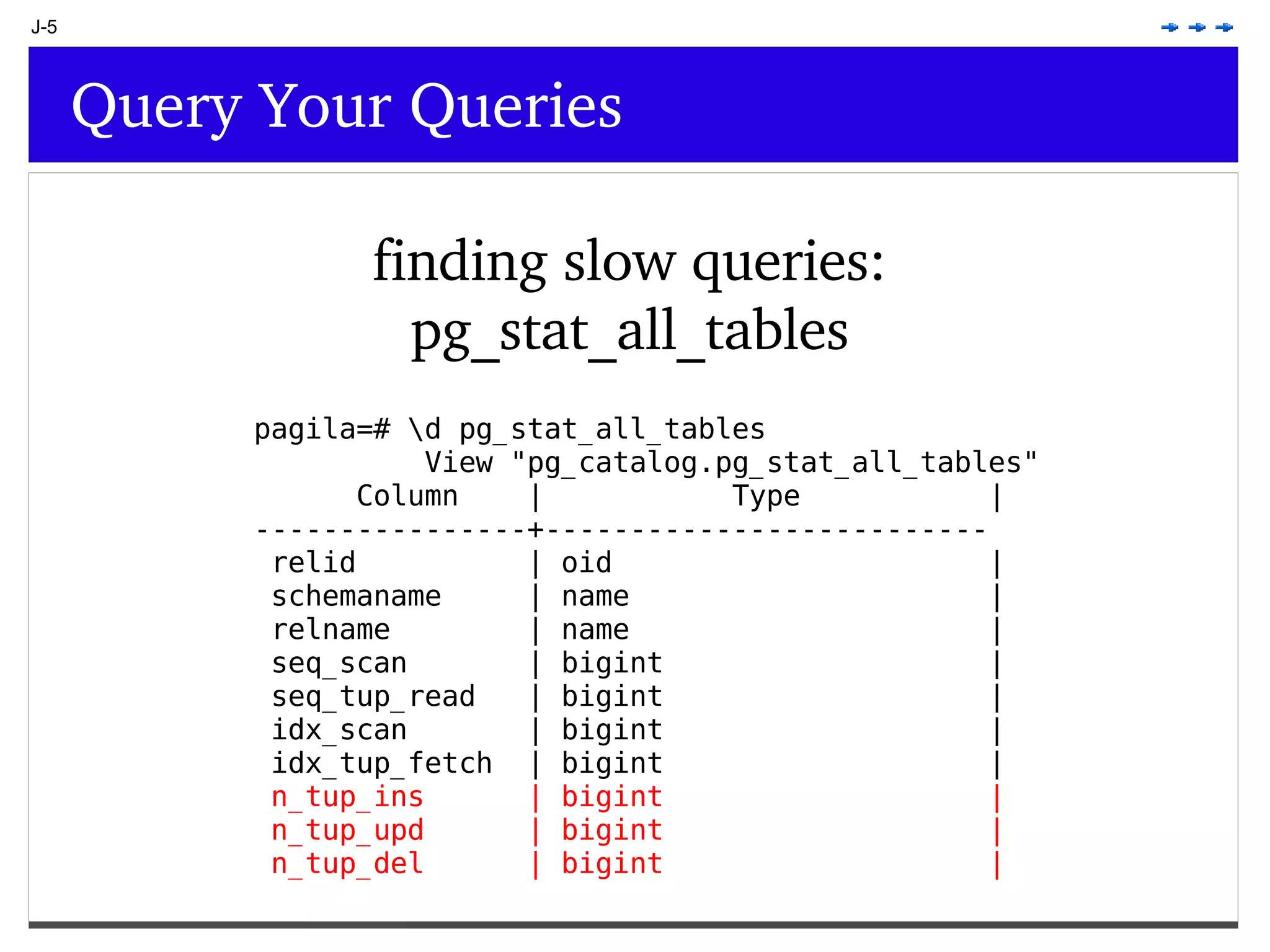
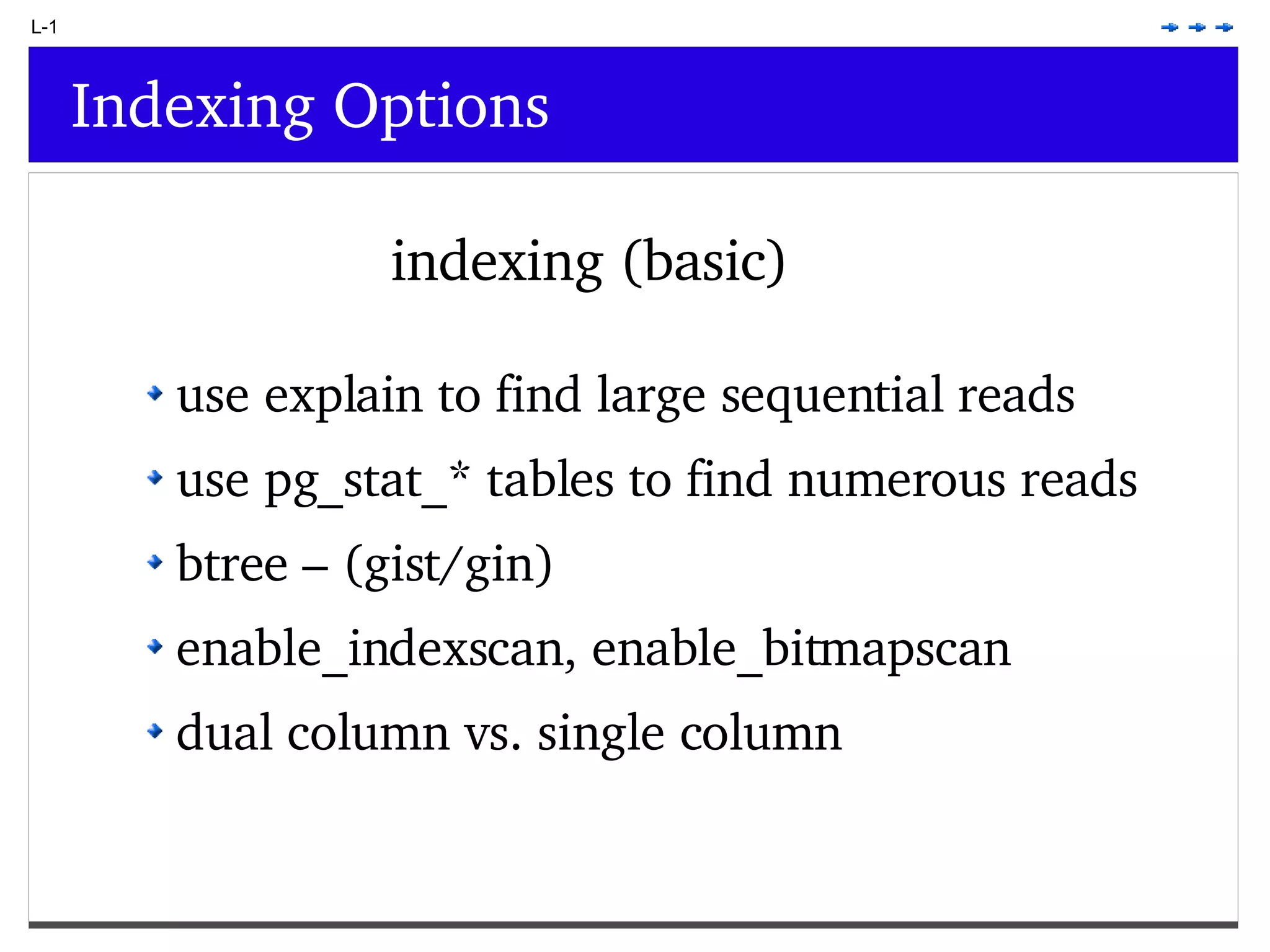
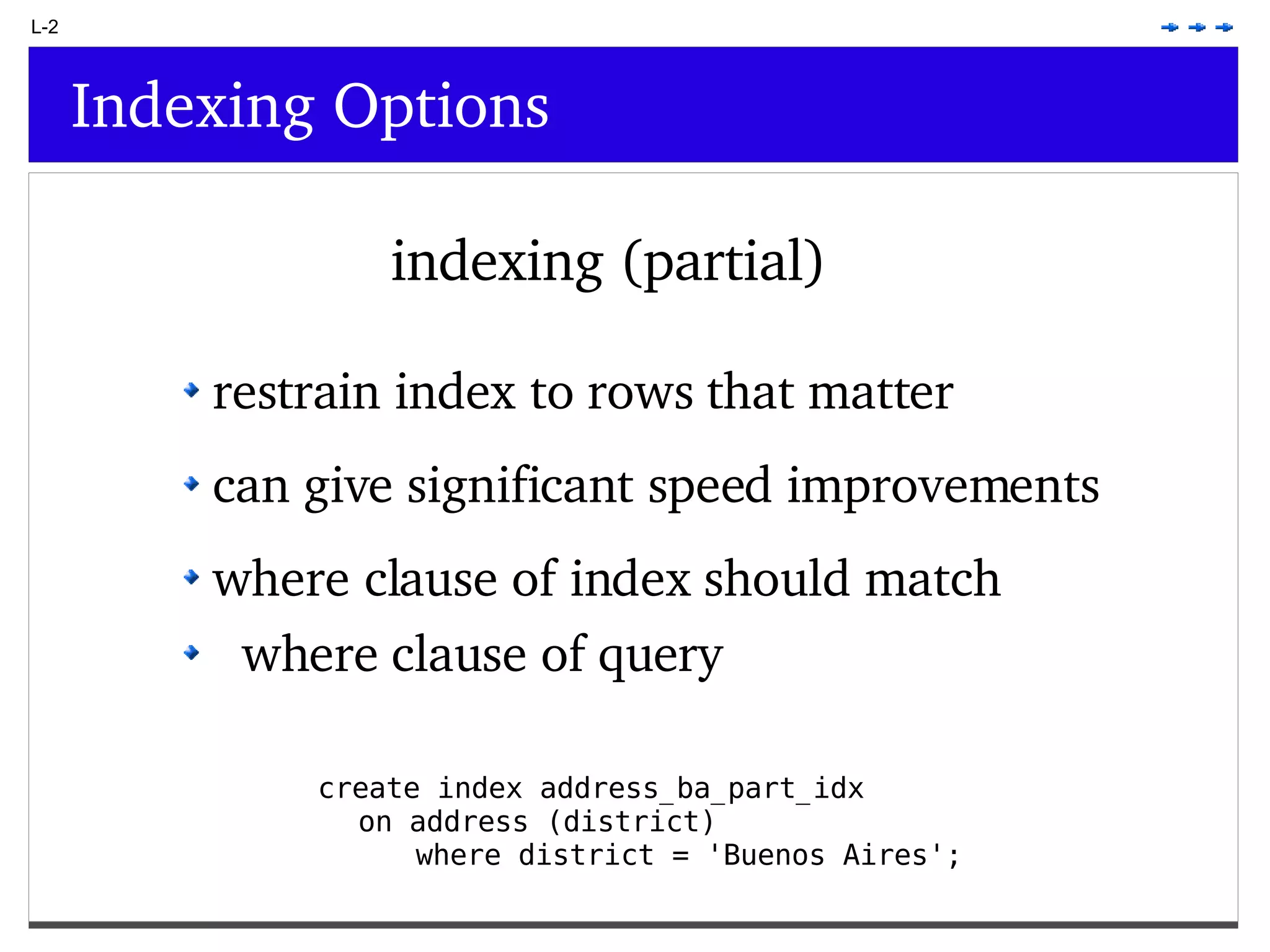
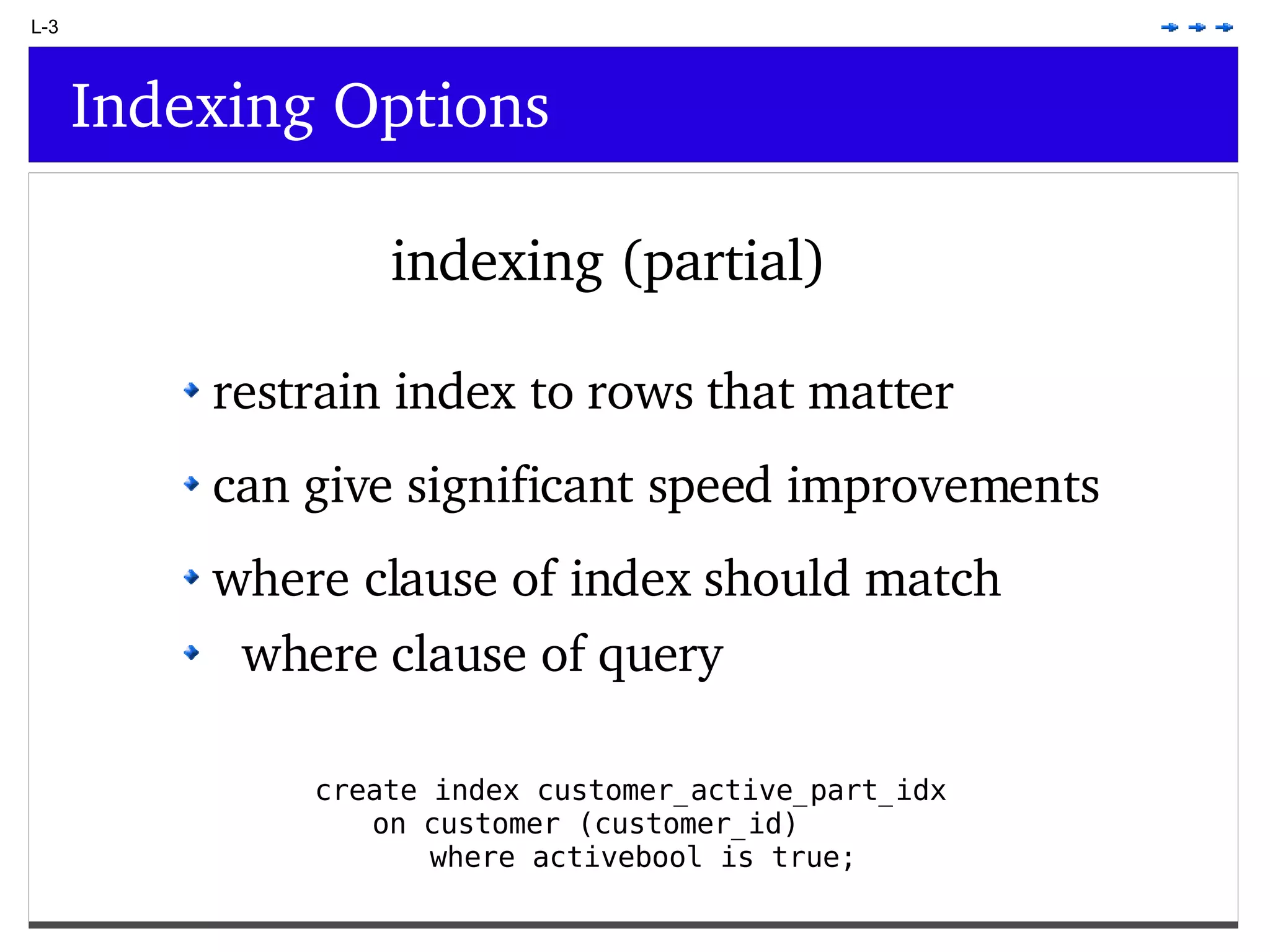
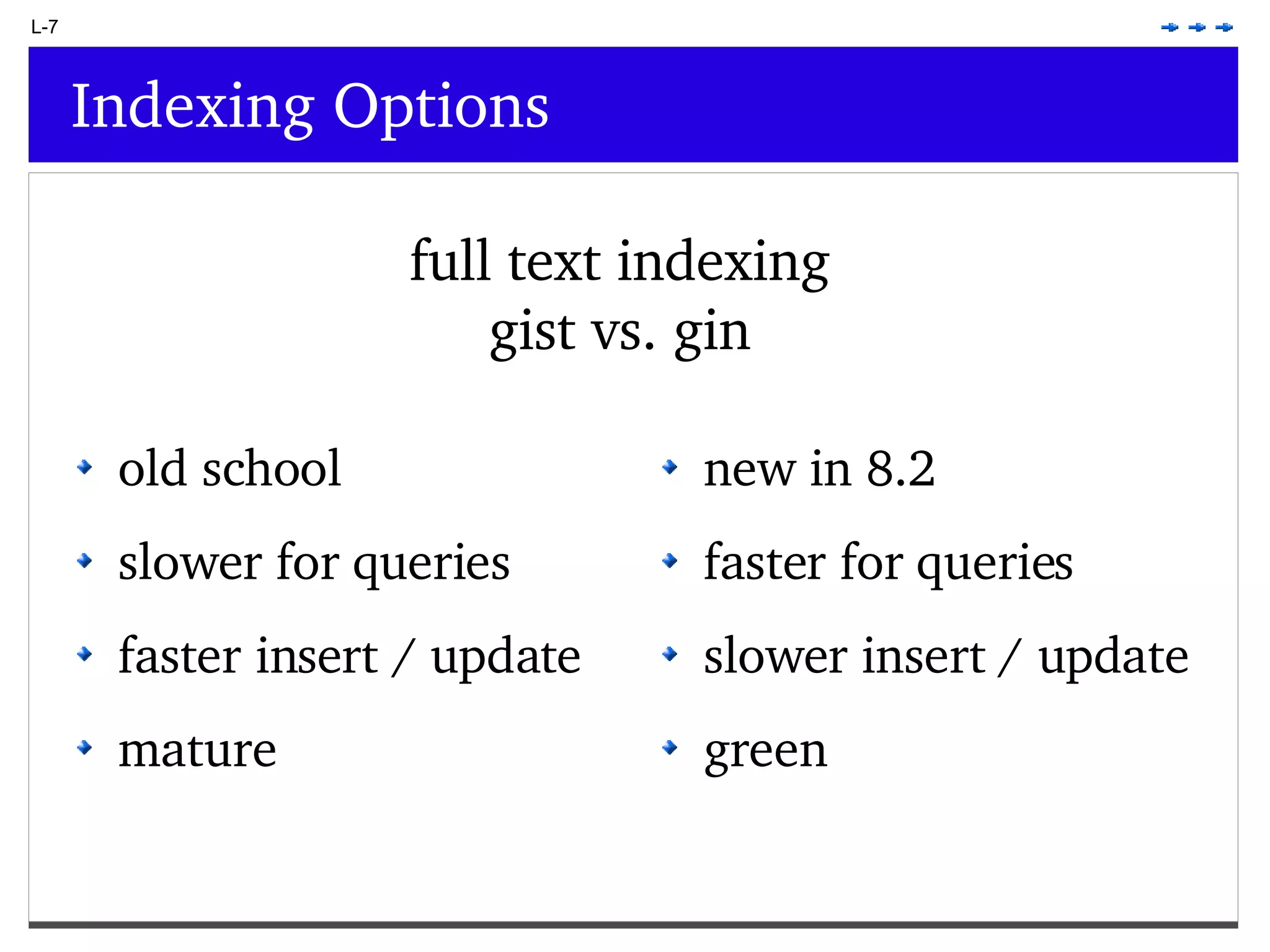
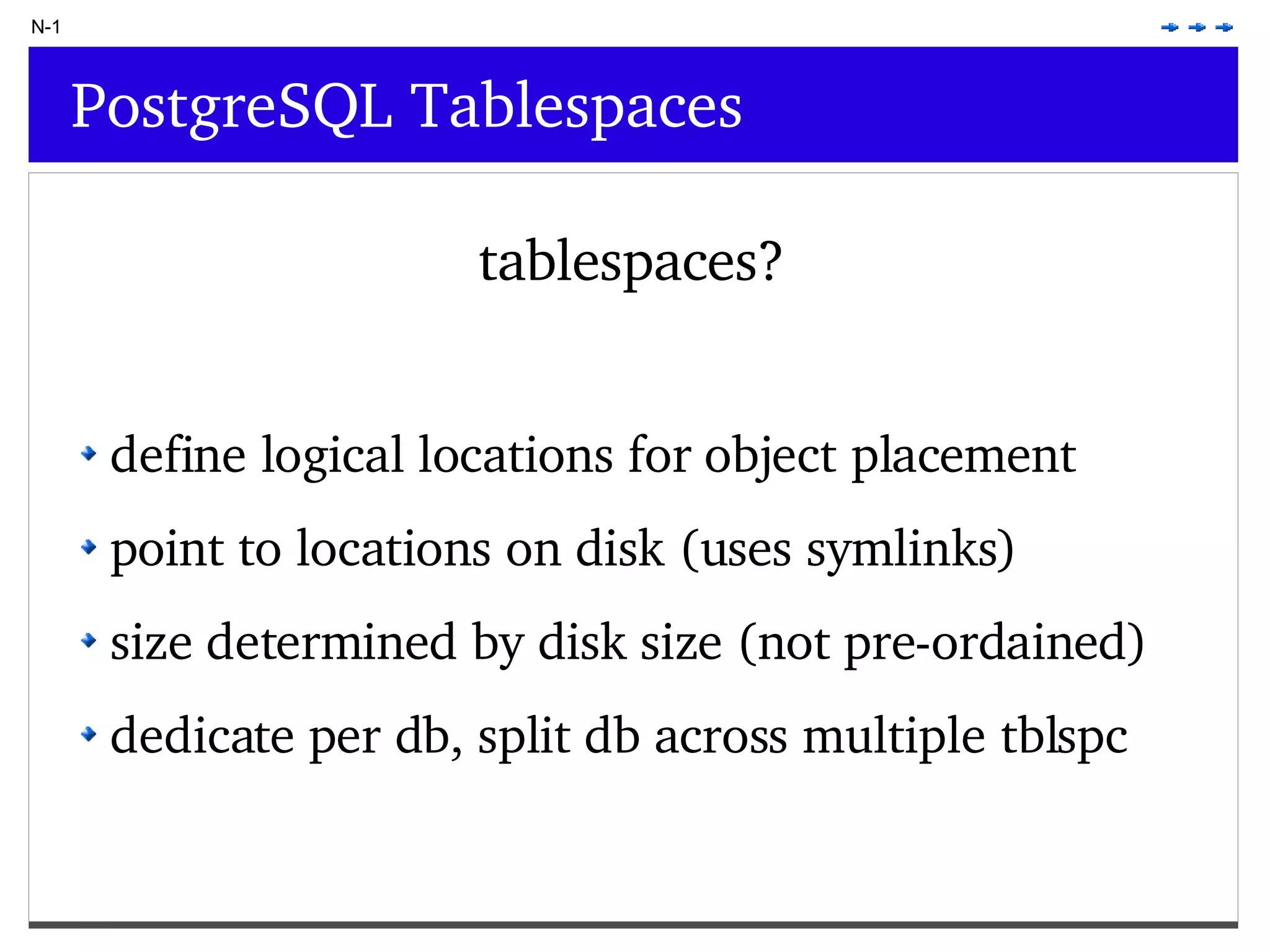
This document provides an overview of PostgreSQL topics including: - Installation and configuration best practices such as using package management and configuring logging - Routine maintenance activities like vacuuming and backups - Upgrades and the differences between major, minor, and bugfix versions - Advanced SQL topics like window functions, common table expressions, and querying slow queries