Embed presentation
Downloaded 29 times





This document discusses functions in C including syntax, declaration, definition, calling functions, actual and formal parameters, call by value, call by reference, and the difference between call by value and call by reference. It explains that functions allow breaking programs into smaller, reusable pieces of code. Parameters passed by value are copied so changes within the function don't affect the original variable, while parameters passed by reference use the address of the original variable so any changes made within the function also change the variable outside the function.
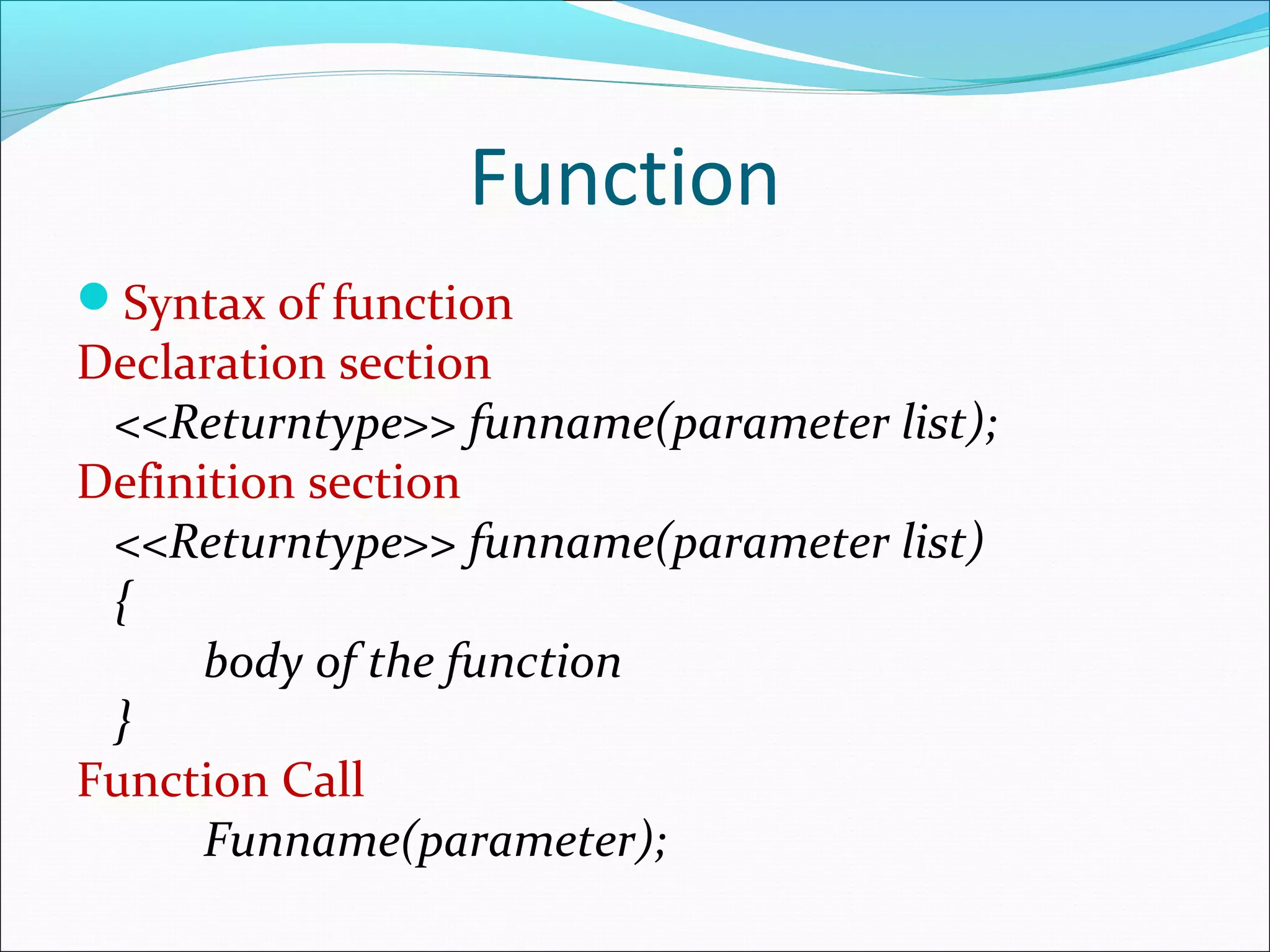
Discusses the syntax of functions including declaration, definition, and function call in C programming.
Provides an example of a function in C with a declaration and definition, showcasing how to call a function.
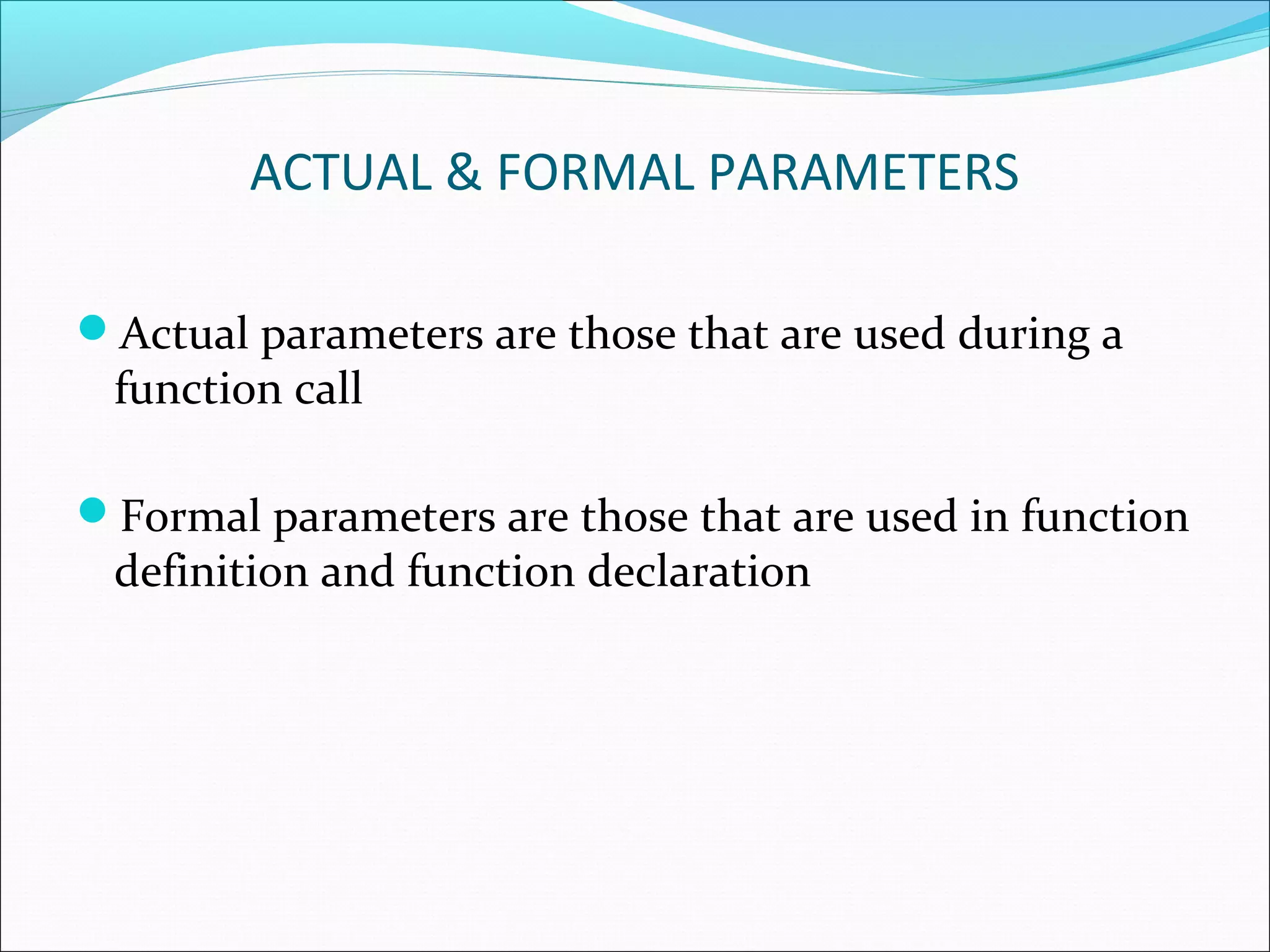
Explains the difference between actual parameters (used during calls) and formal parameters (used in definitions and declarations).
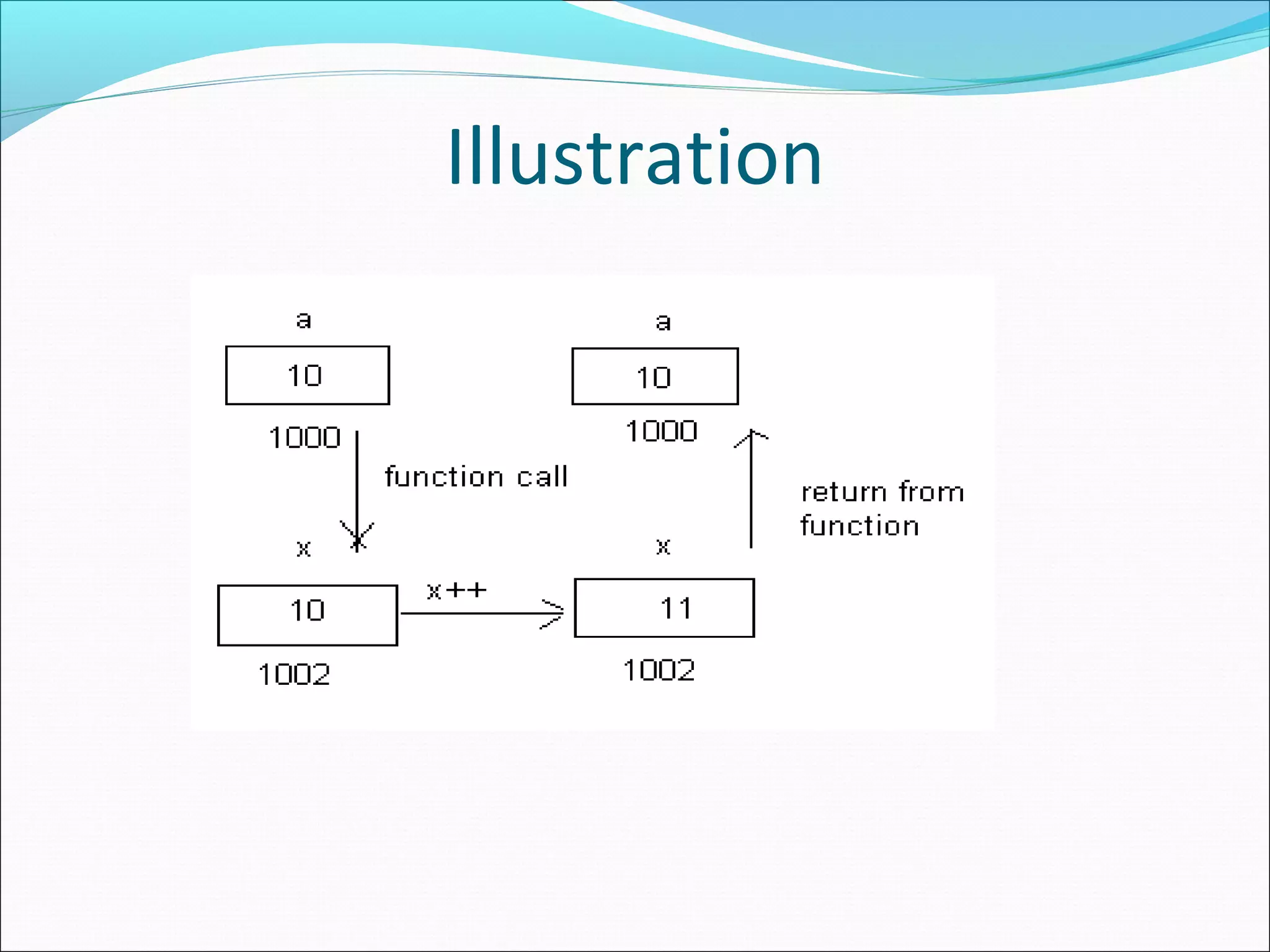
Describes the call by value method, where function parameters are passed by value, and changes are local to the function.
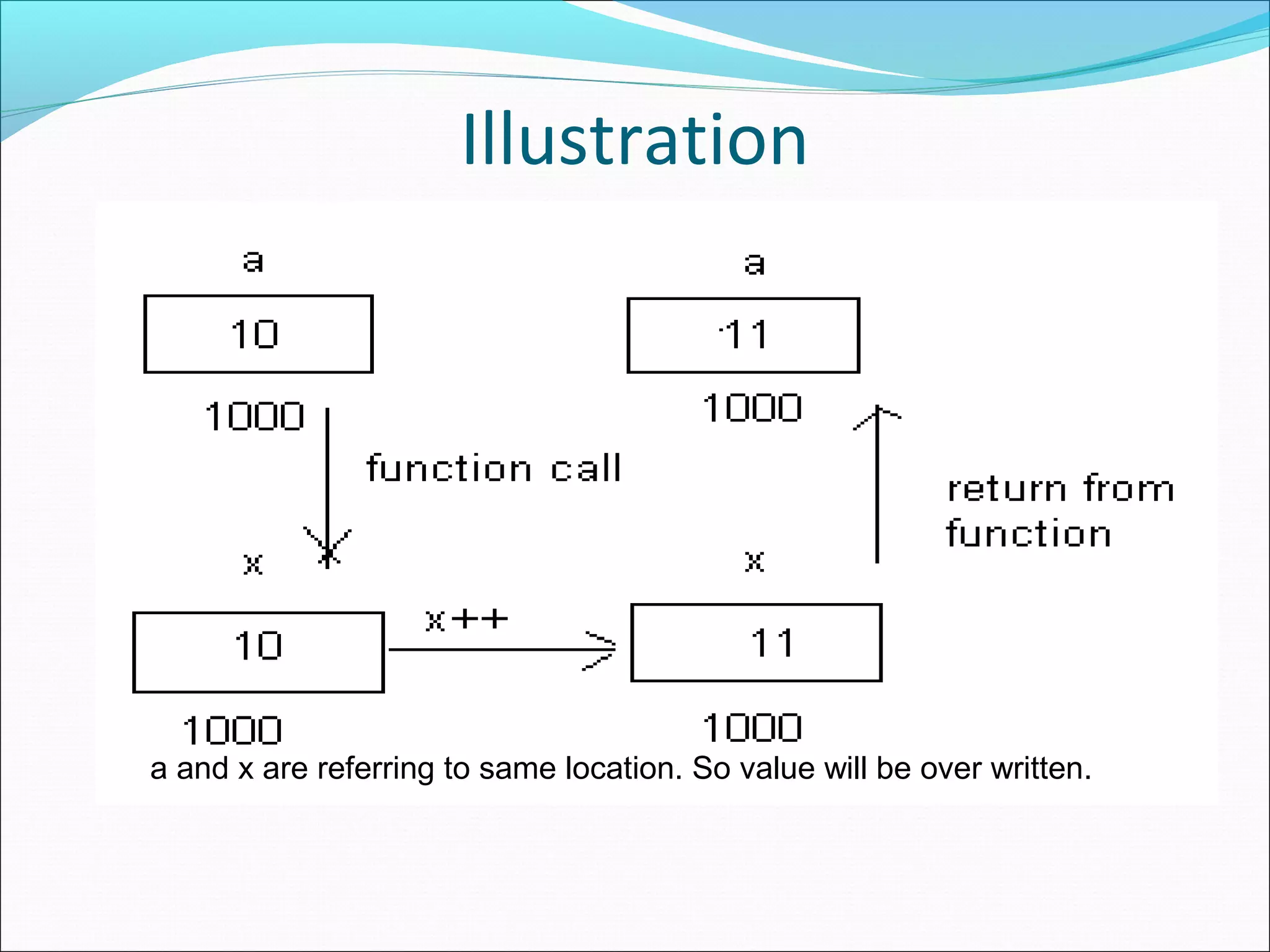
Explains call by reference, where address of variables is passed to the function, allowing changes to affect the original variable.
Illustrates how call by reference allows a variable's value to be overwritten as both point to the same memory location.
Continues the illustration of call by reference, emphasizing the effect of modifications on the original variable.
Contrasts call by value and call by reference highlighting how changes in parameters affect the original data.







