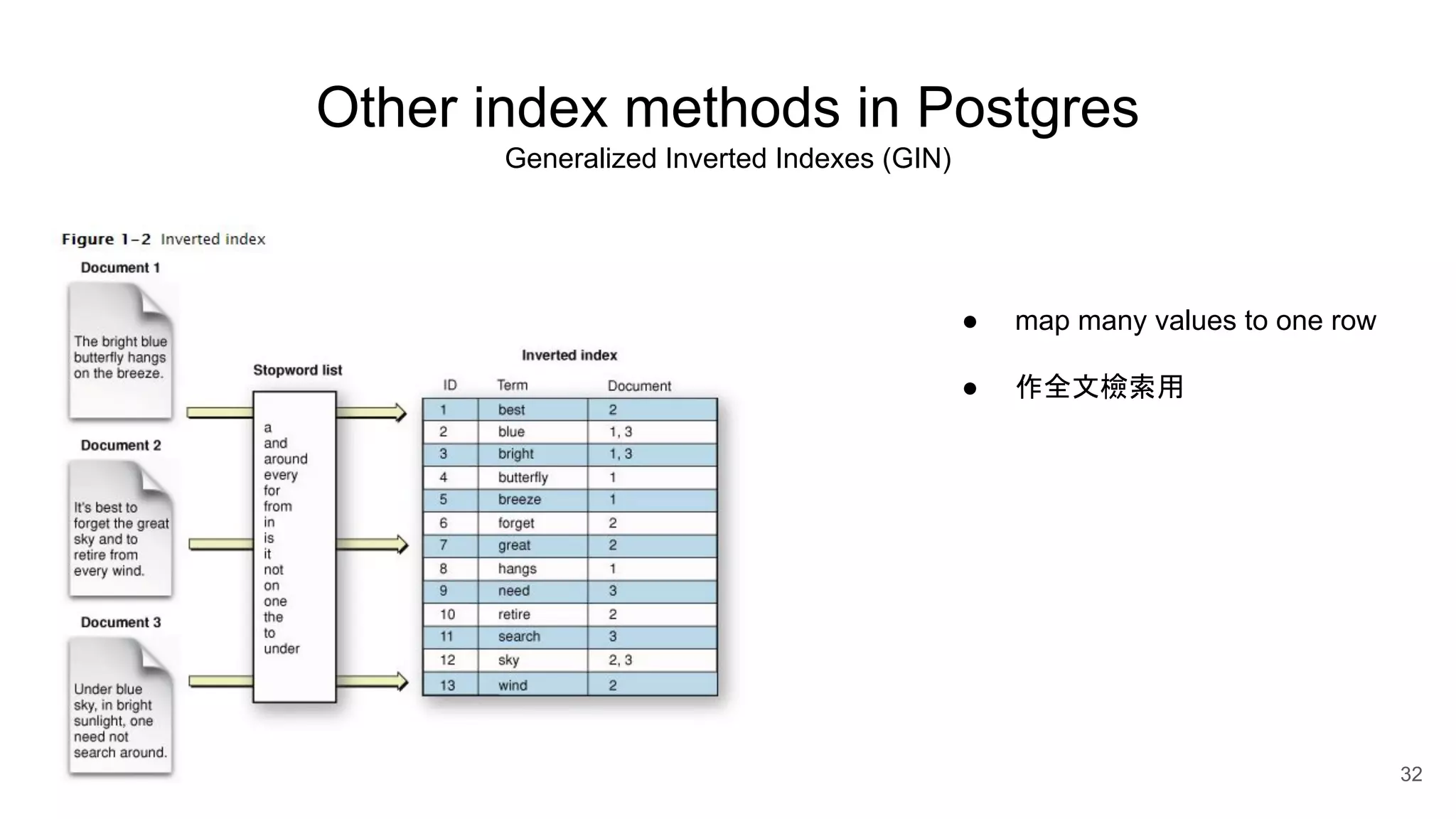
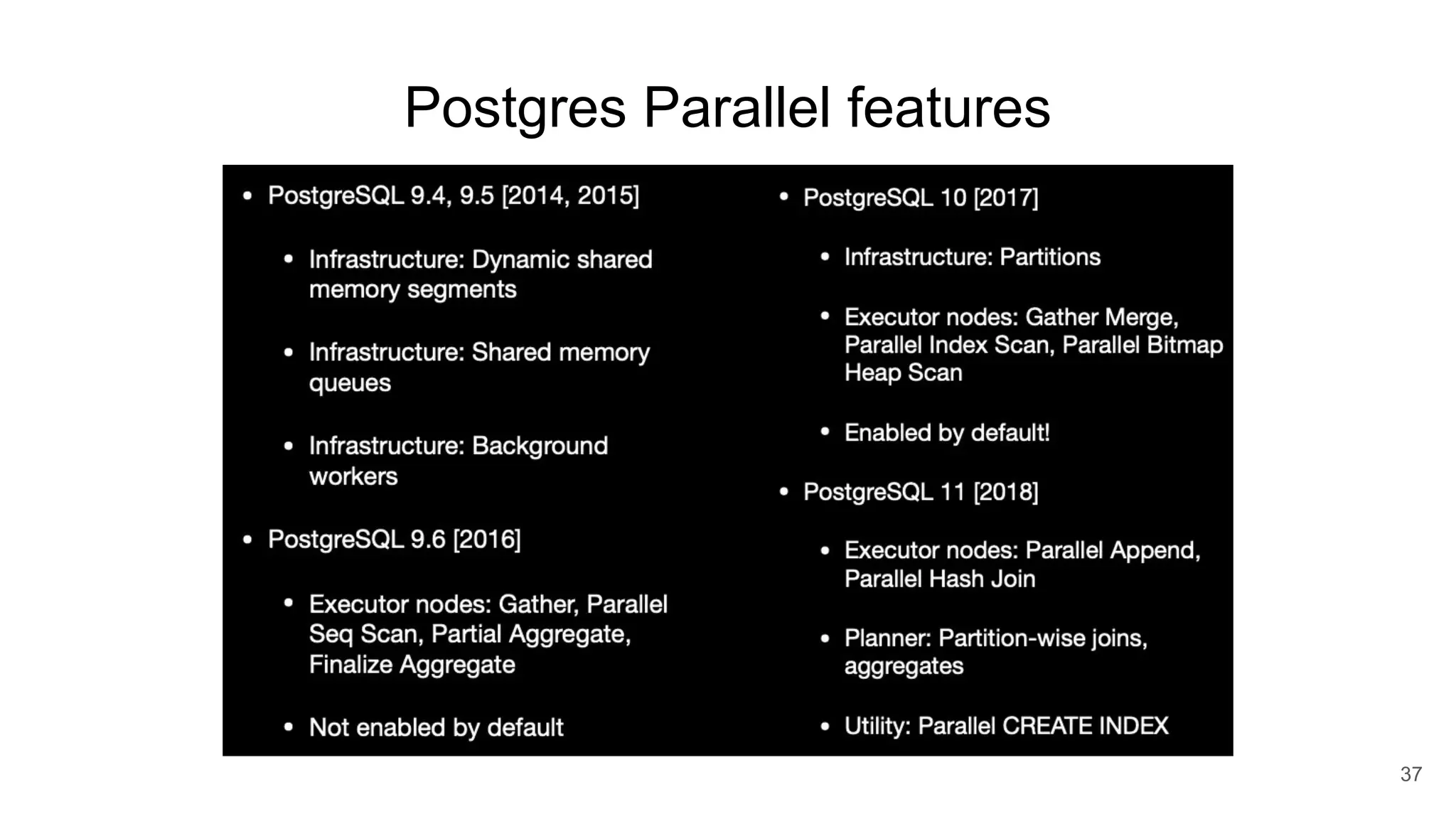
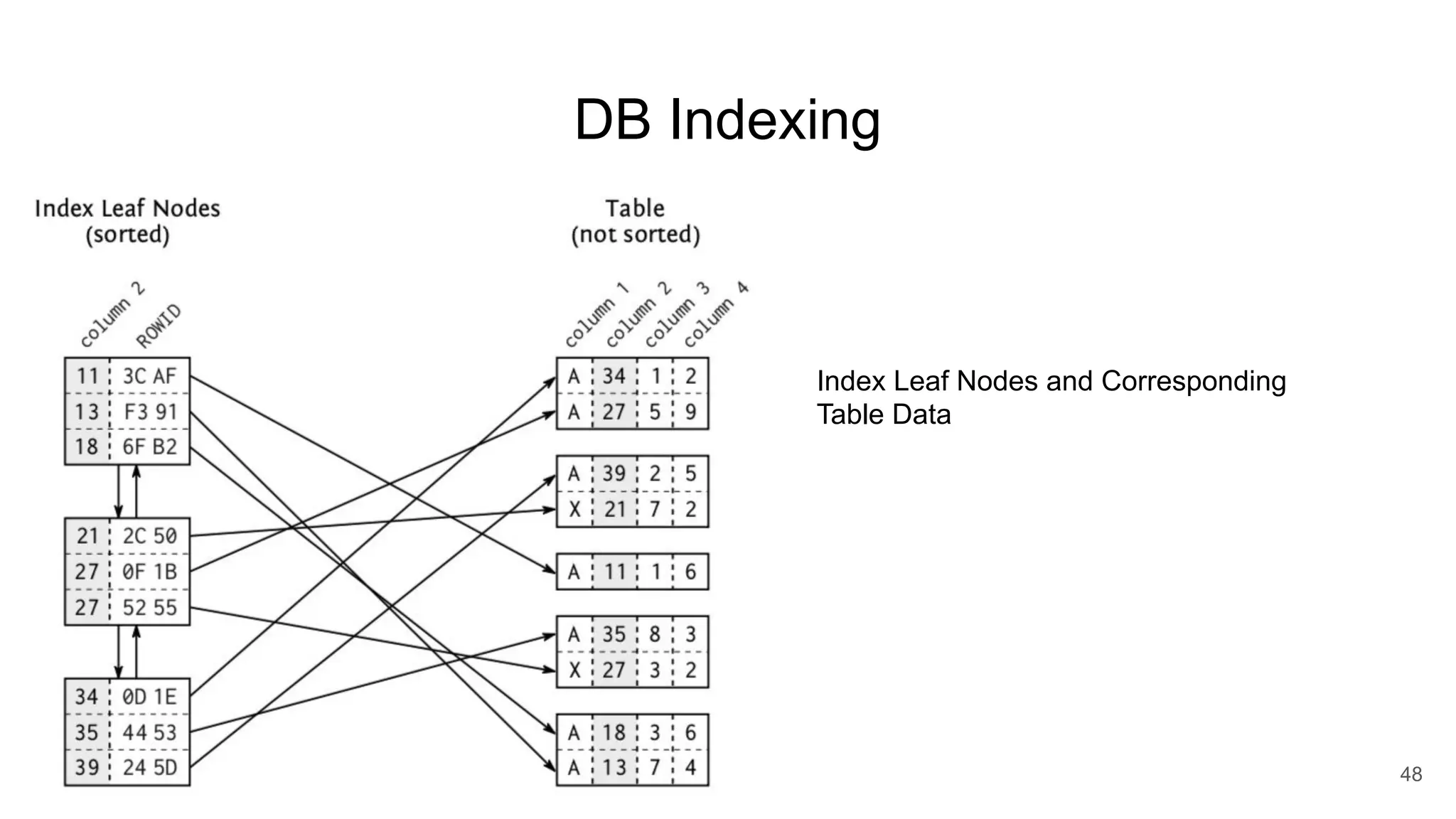
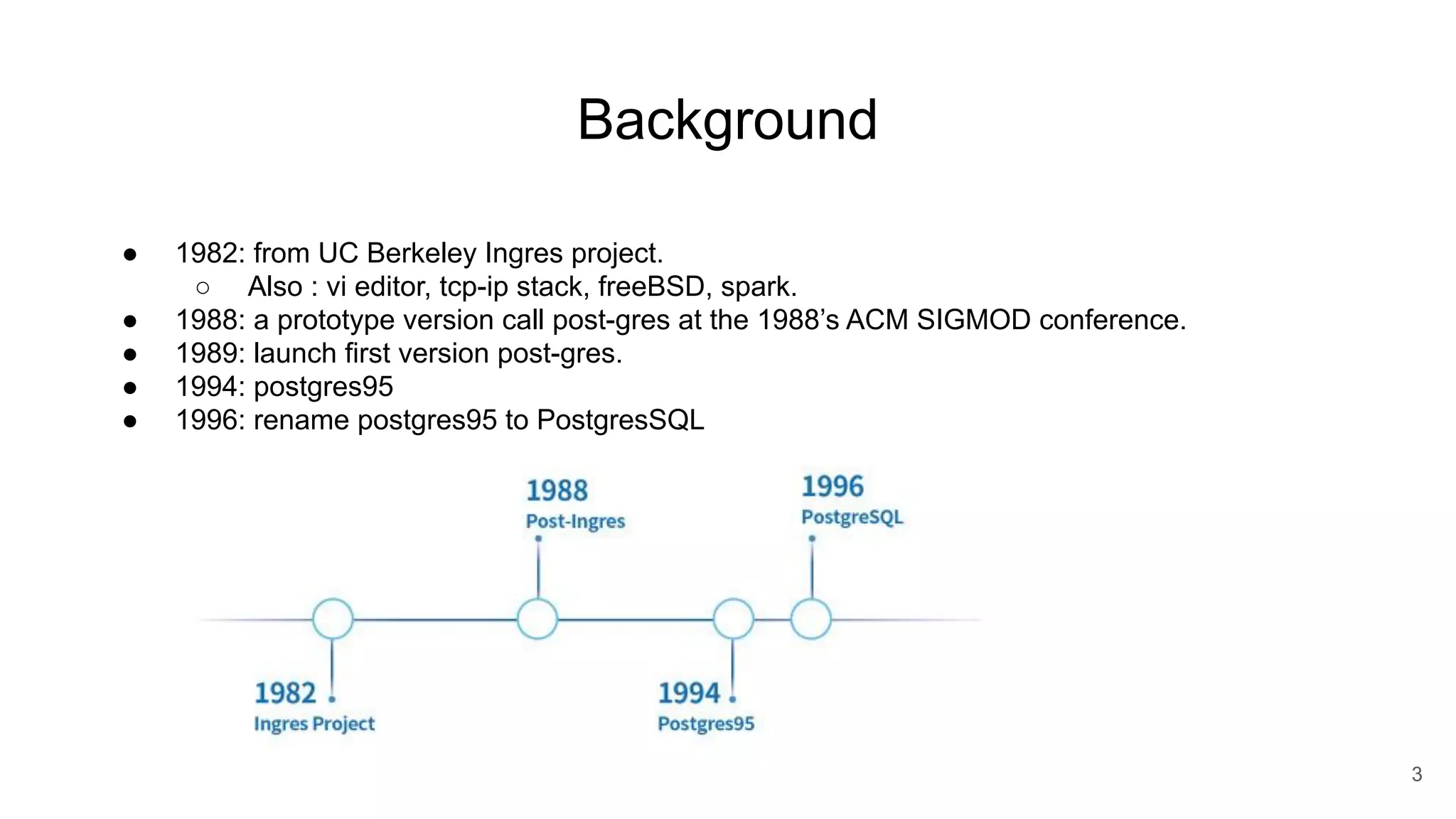
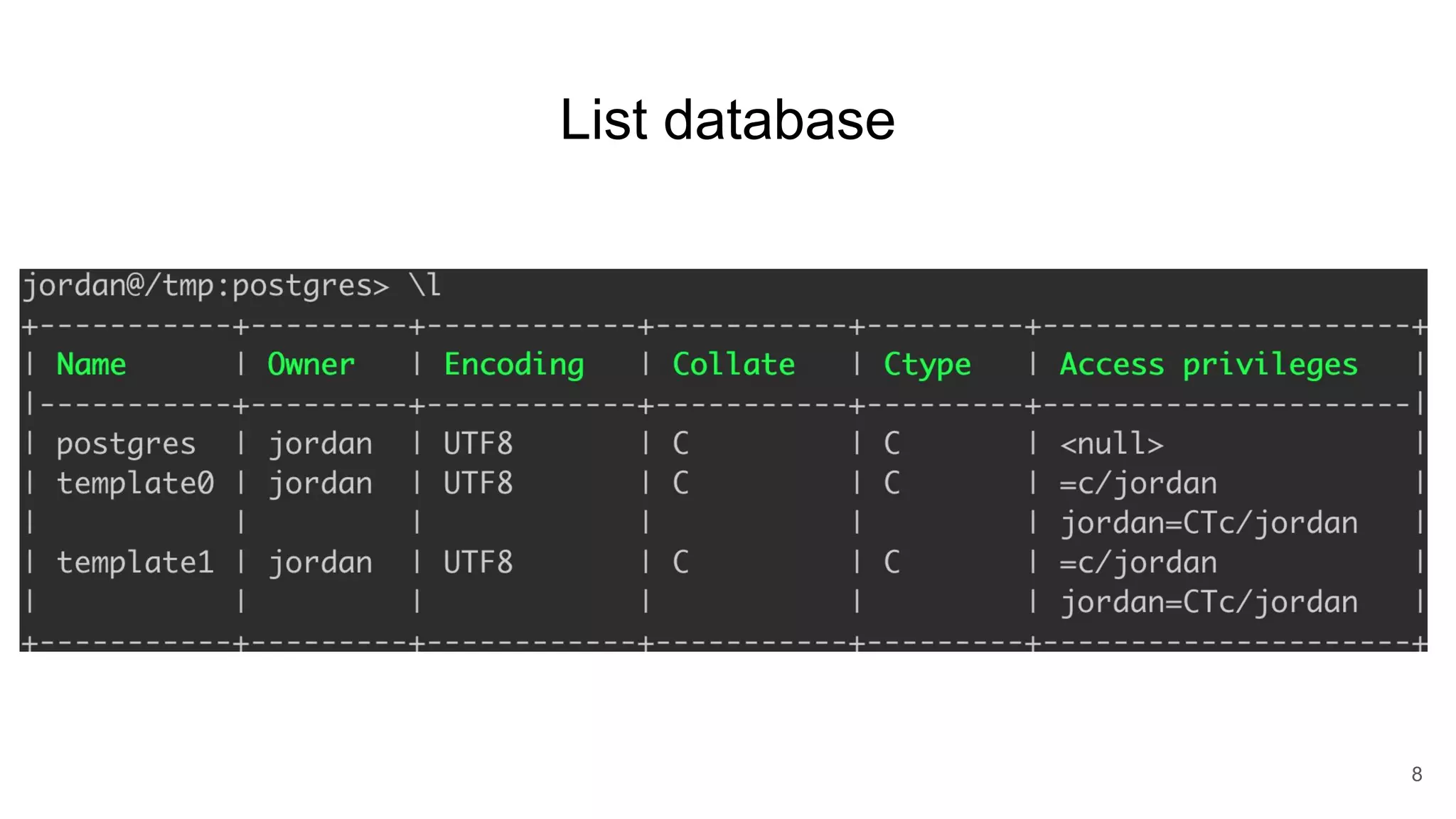
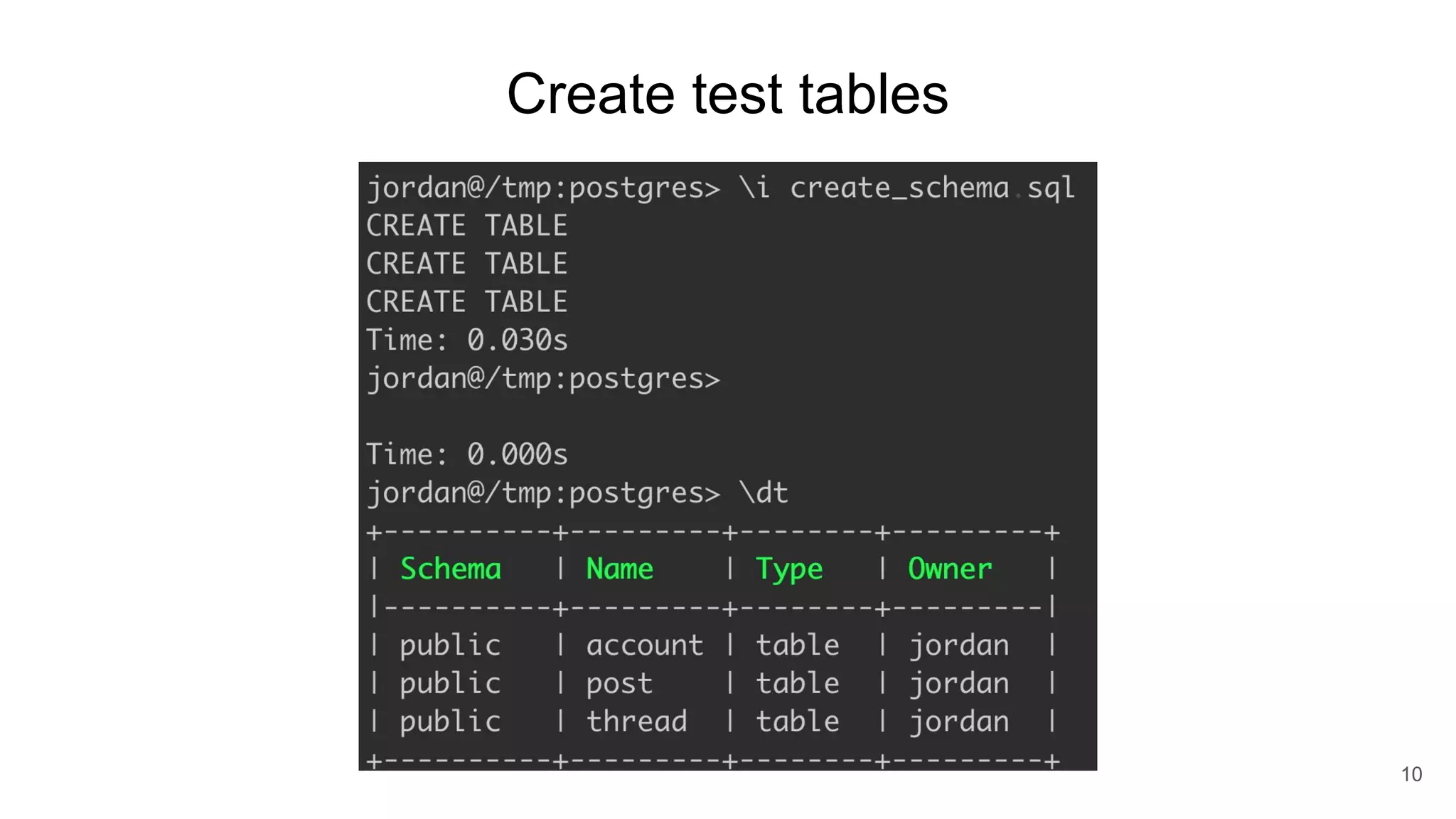
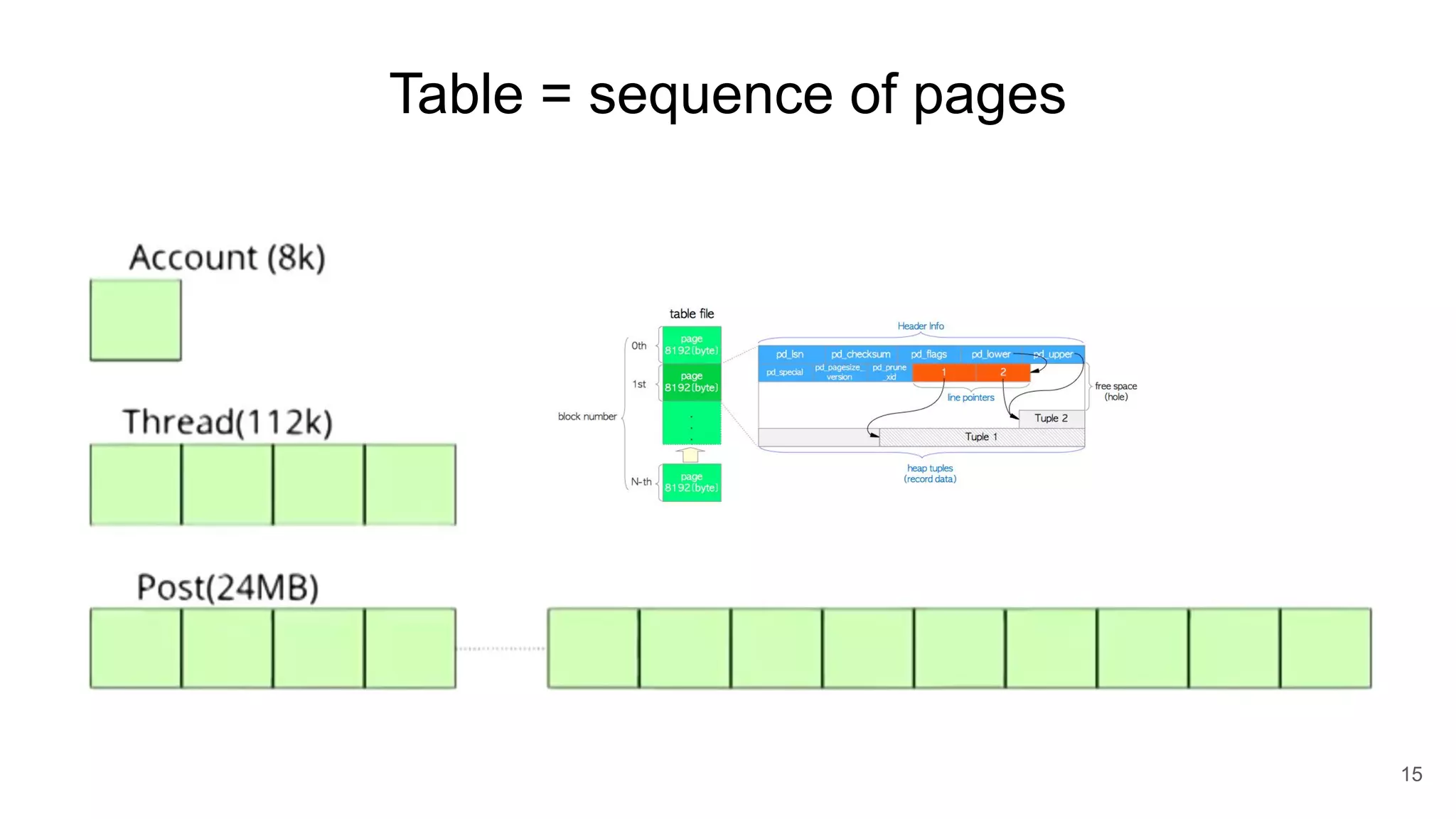
Postgres has evolved from its origins as an academic project in the 1980s. It uses indexes like a book index to quickly find data by pointing to specific rows. As more data is added, updated, or deleted, indexes also need updating to accurately reflect the table data. Toward handling big data, Postgres supports parallelism, database partitioning, and sharding to distribute data across multiple machines.













![Bitmap Index Scan ● 讀取 index(es) ● 動態建立 bitmap (array) ● Boolean 運算 ● 最後才實際到 pages 拿資料 ● 由於是以 physical order 到 page 拿資 料,若有 order by, 則會需要額外的 sort operation [source] 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postgresindexingandtowardbigdataapplication-200215064747/75/Postgres-indexing-and-toward-big-data-application-23-2048.jpg)