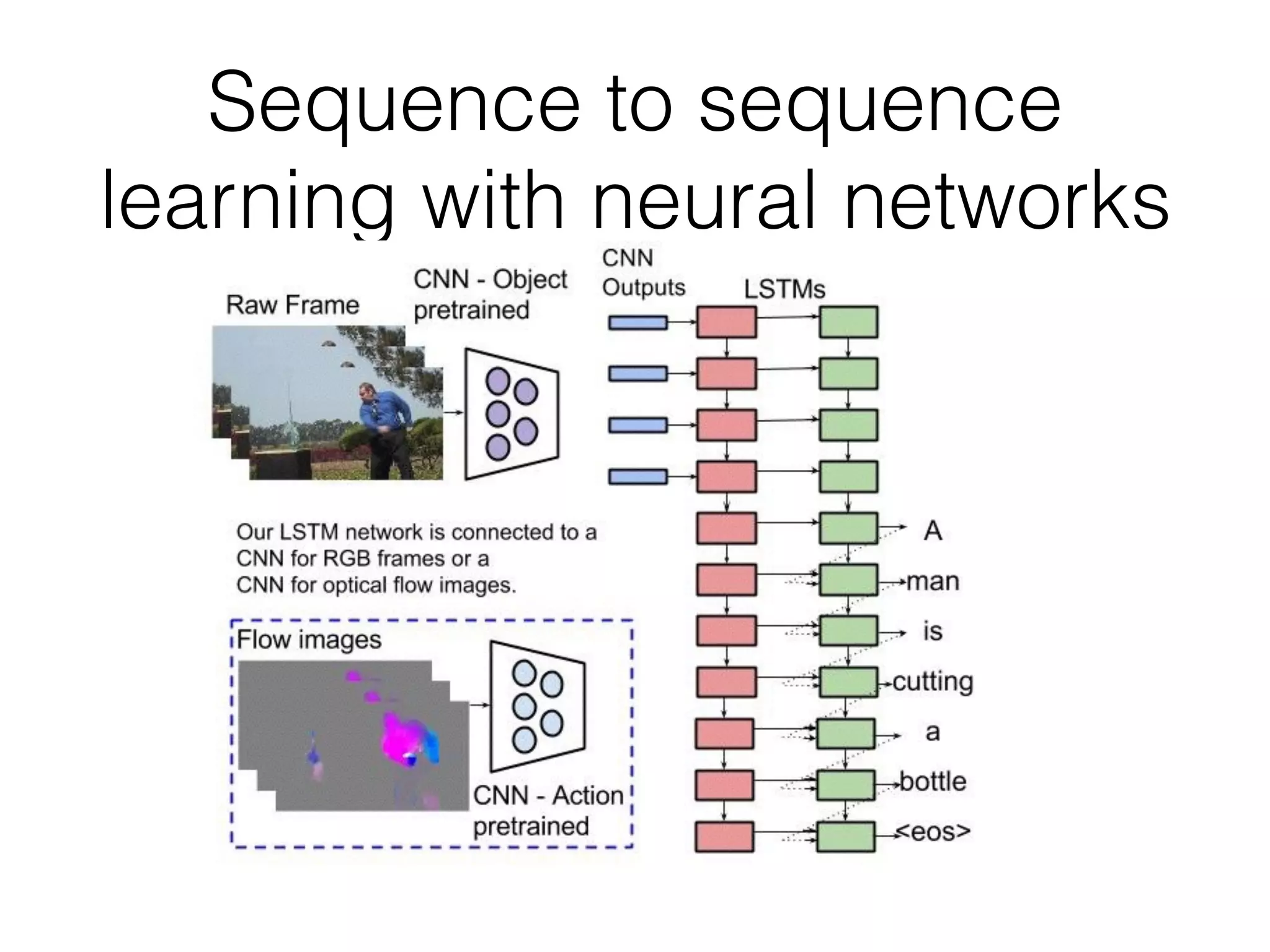
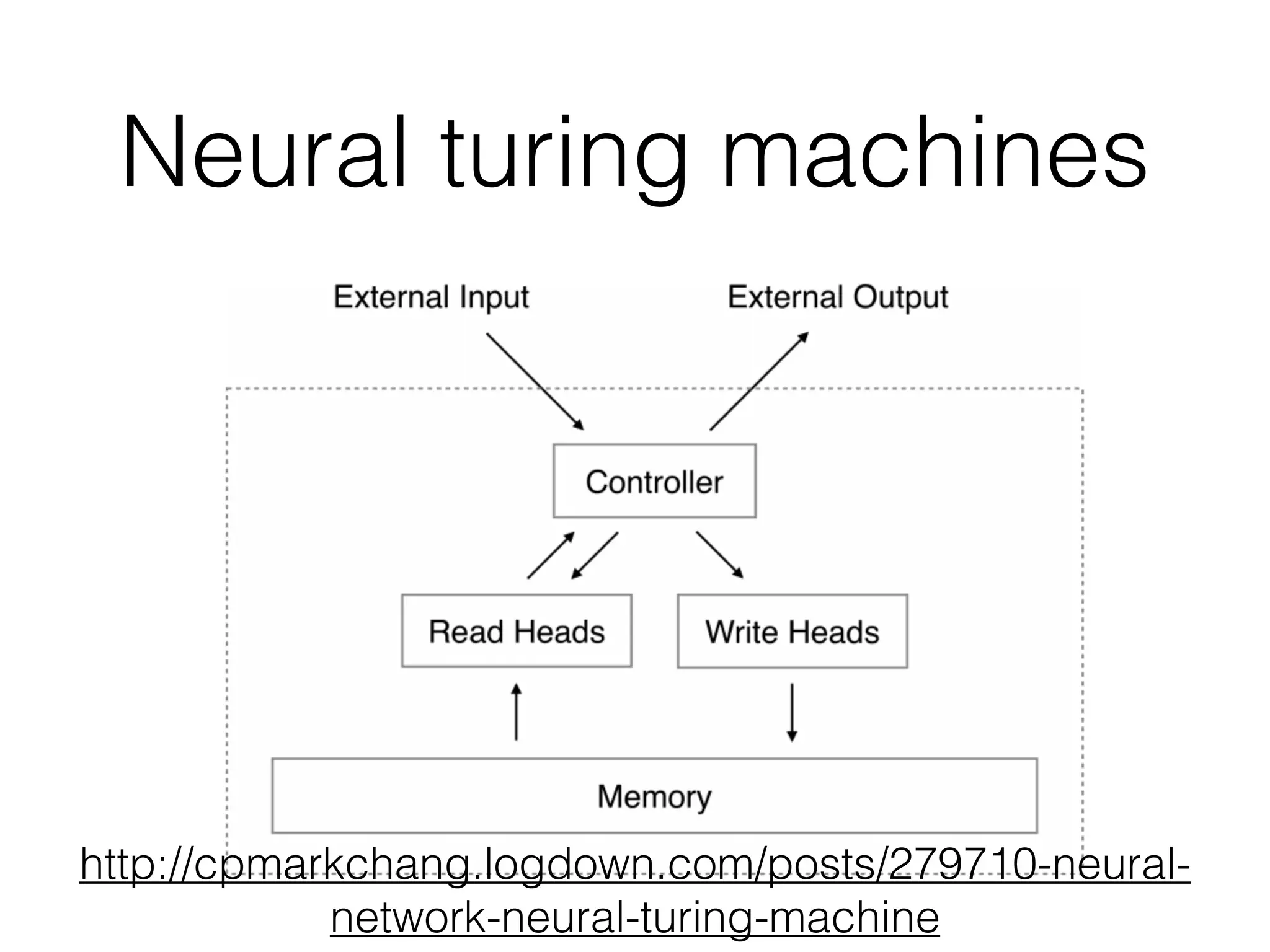
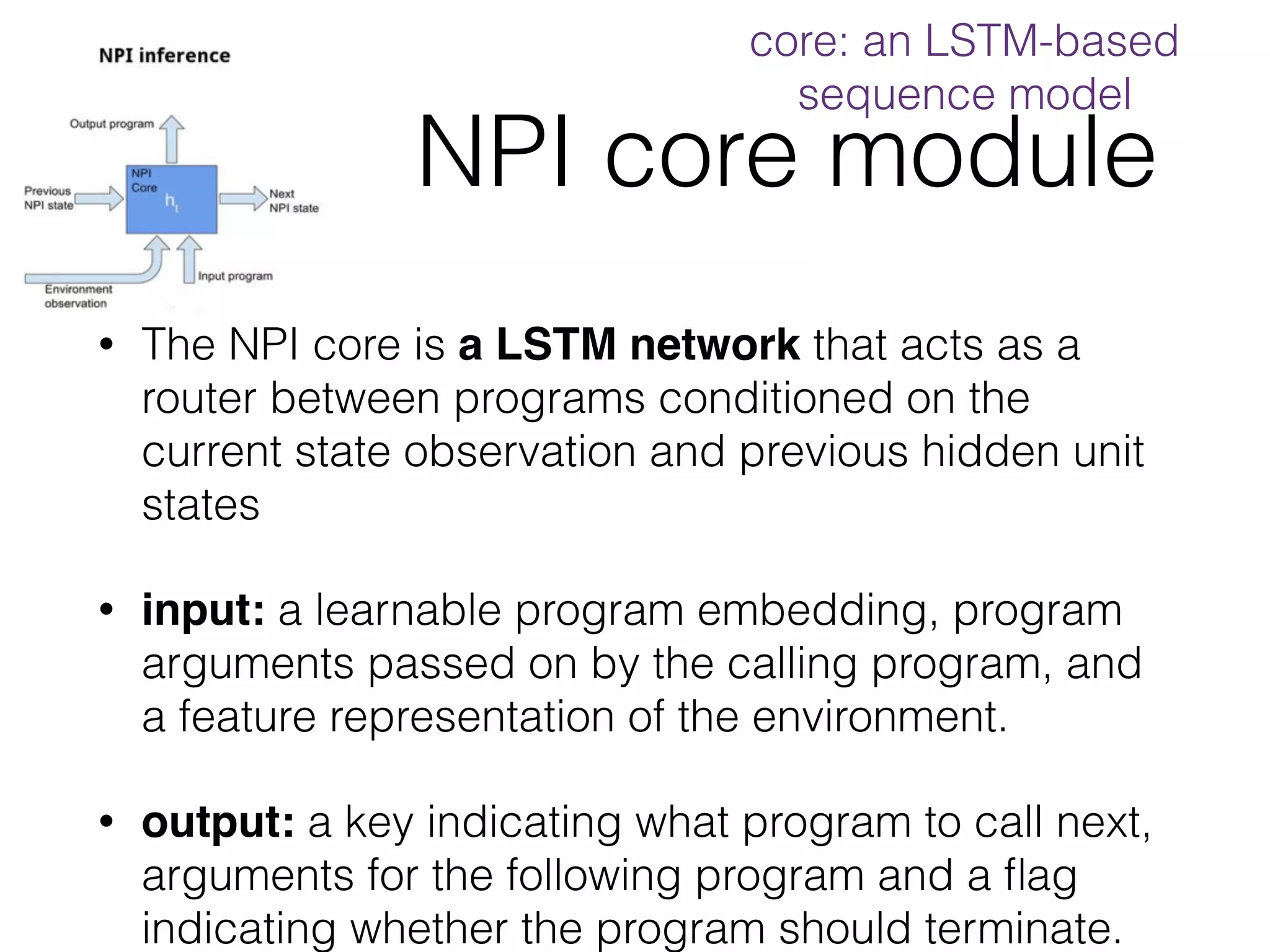
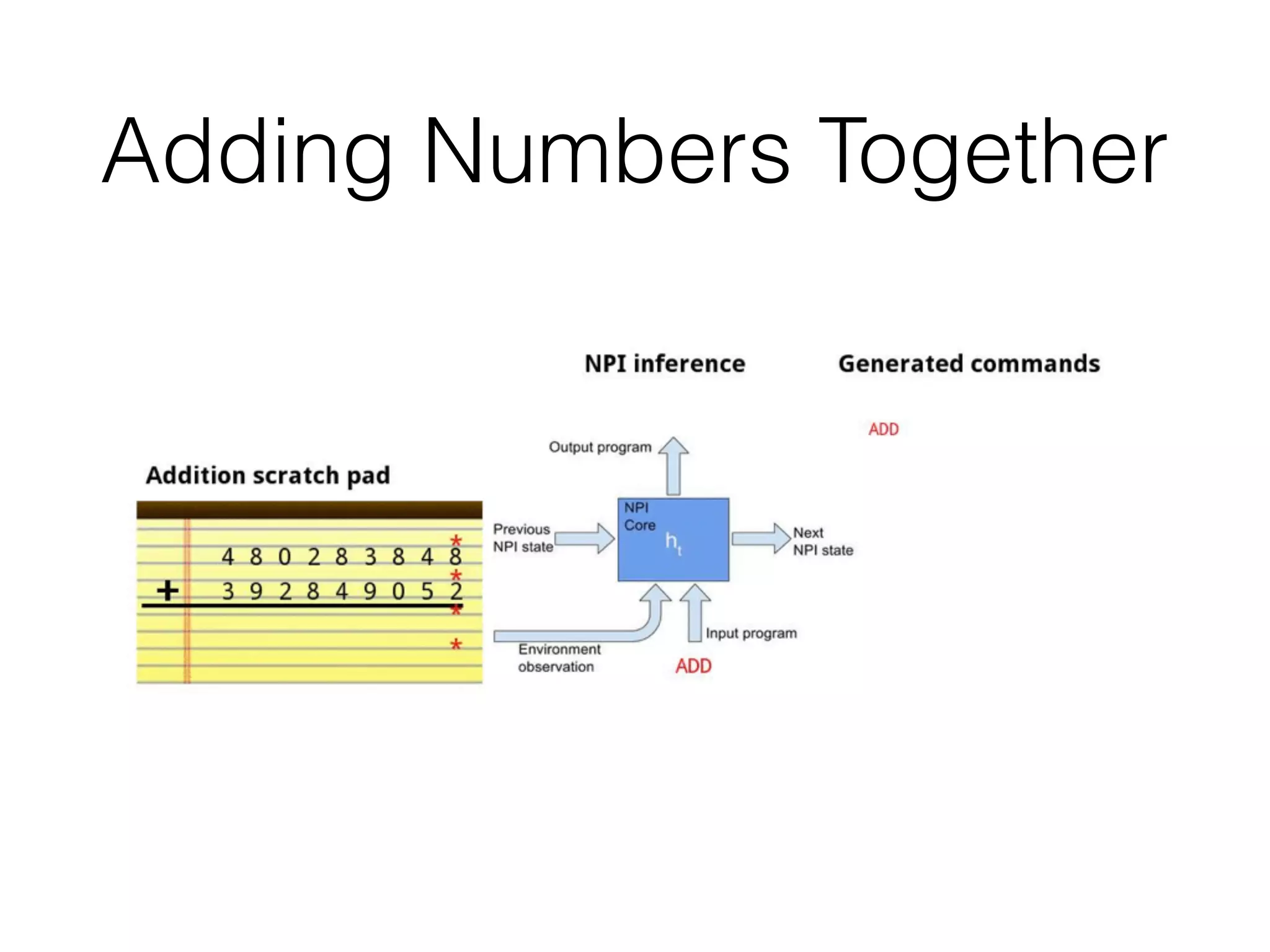
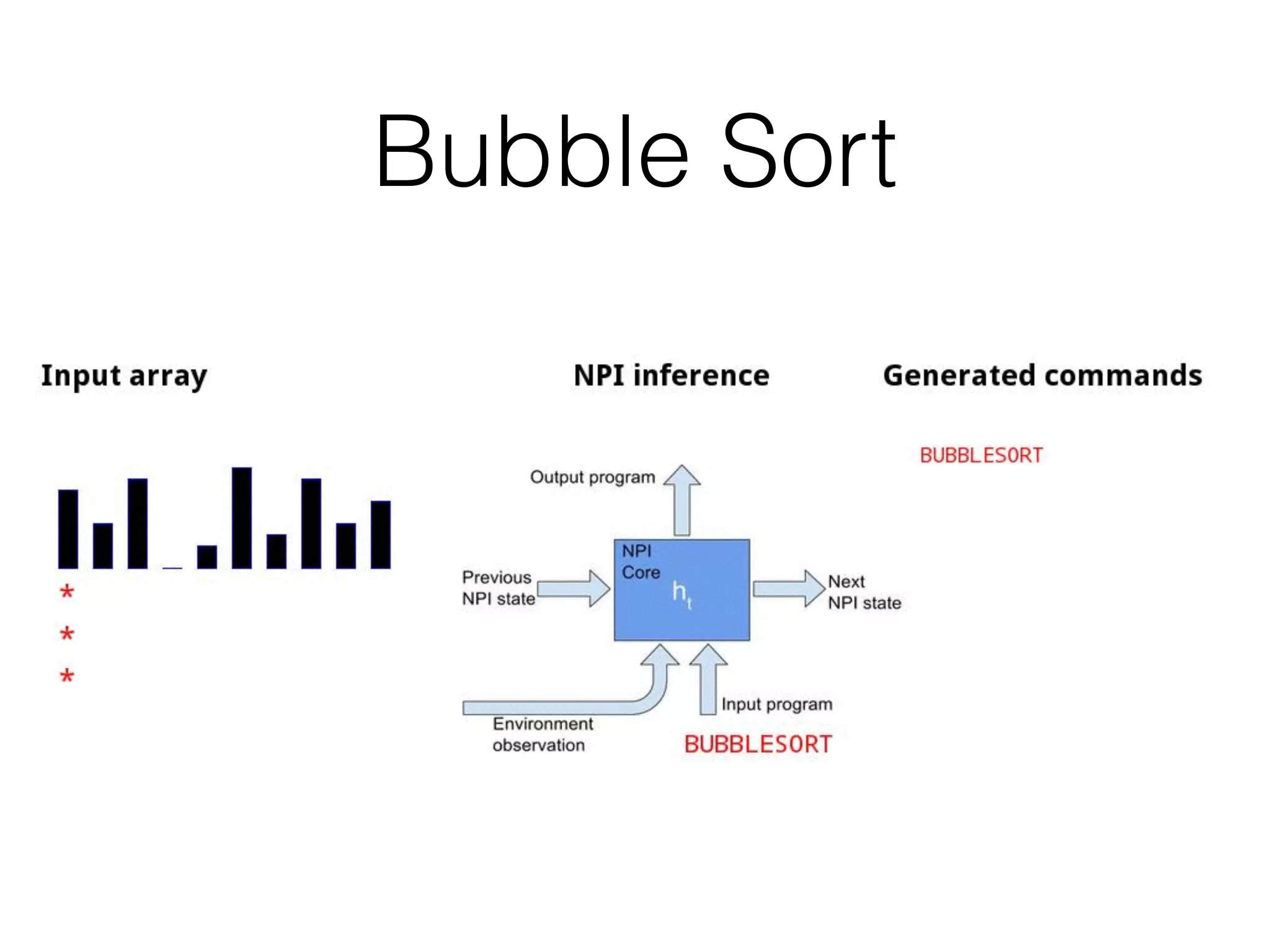
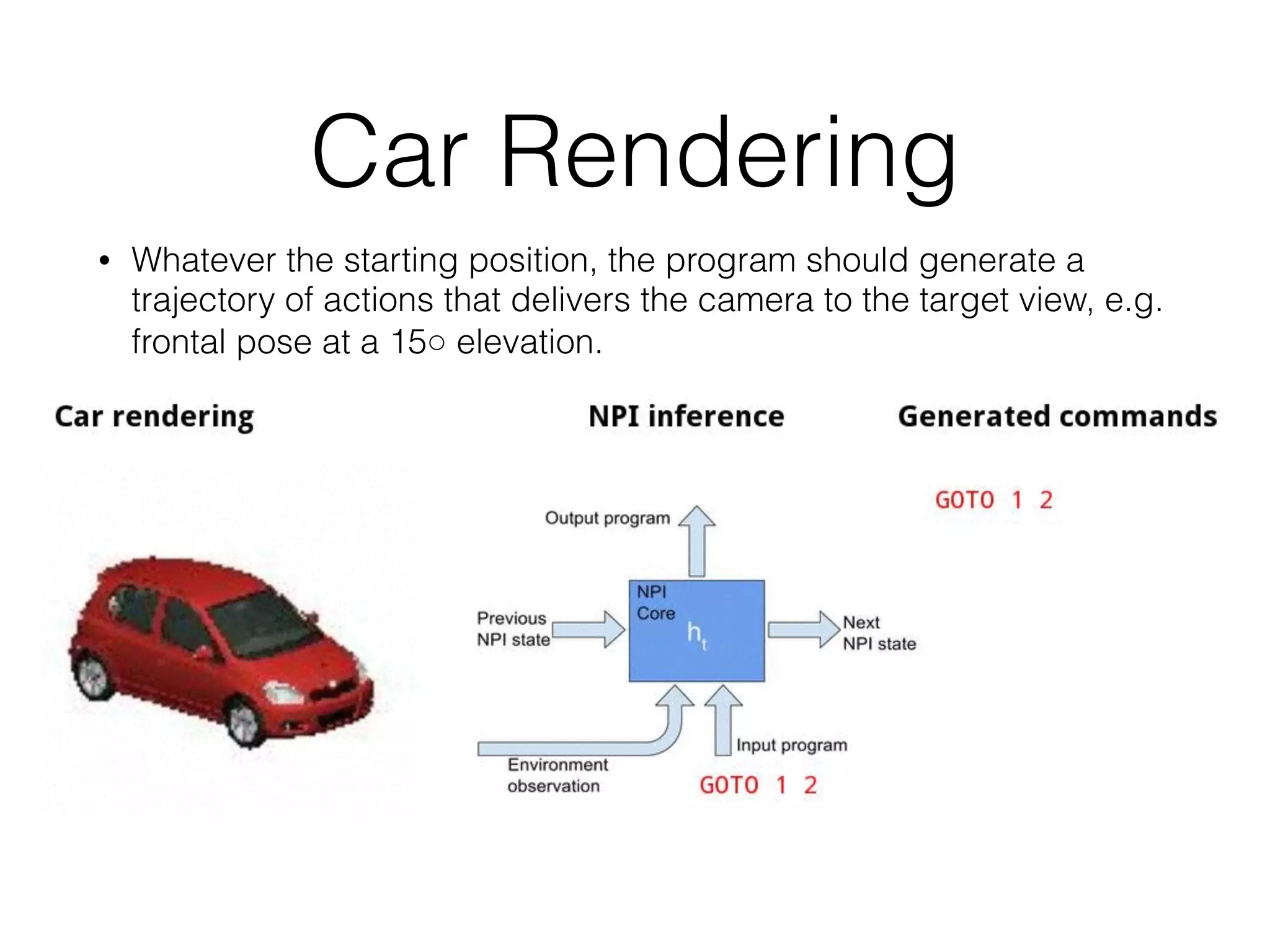
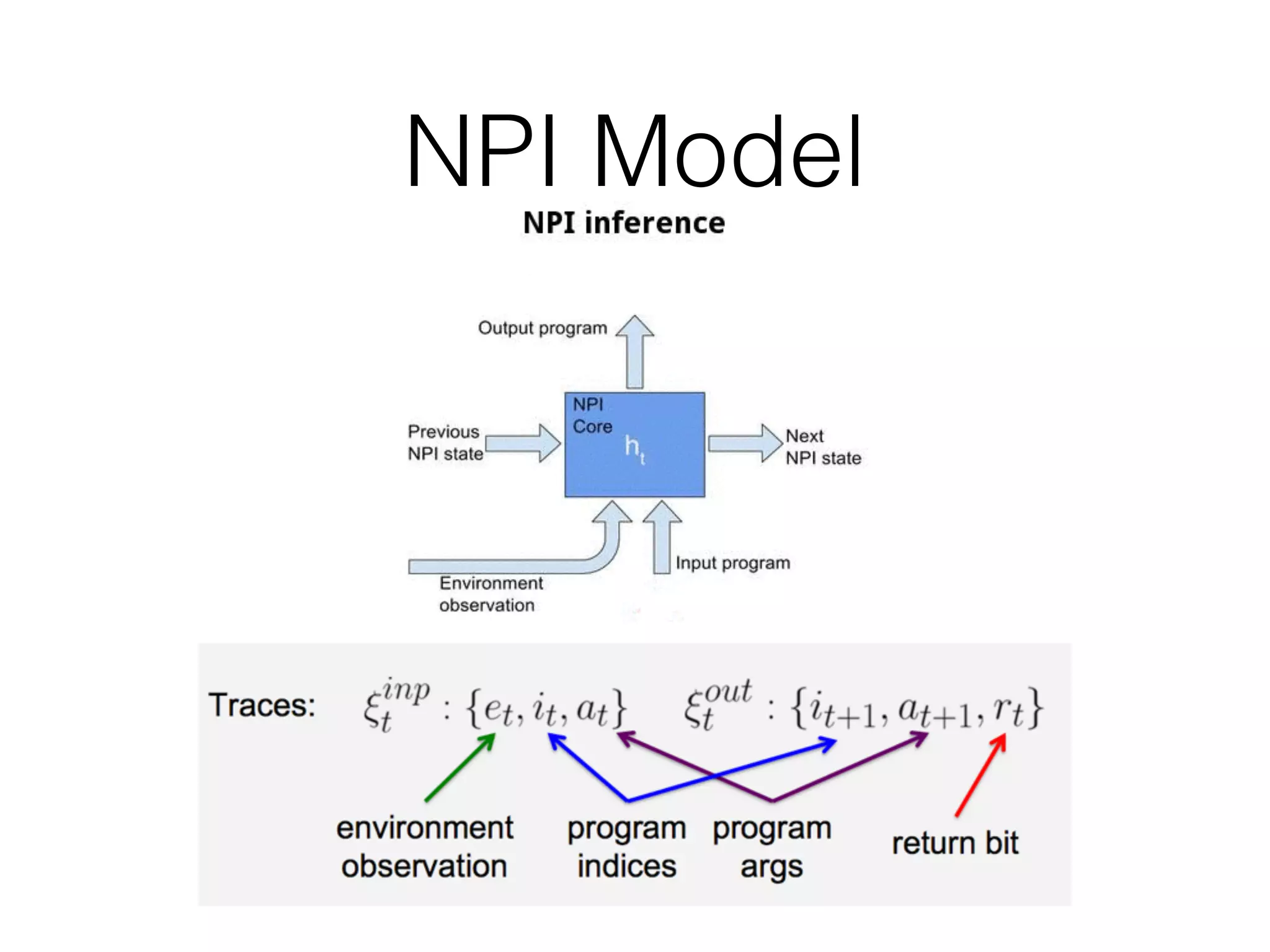
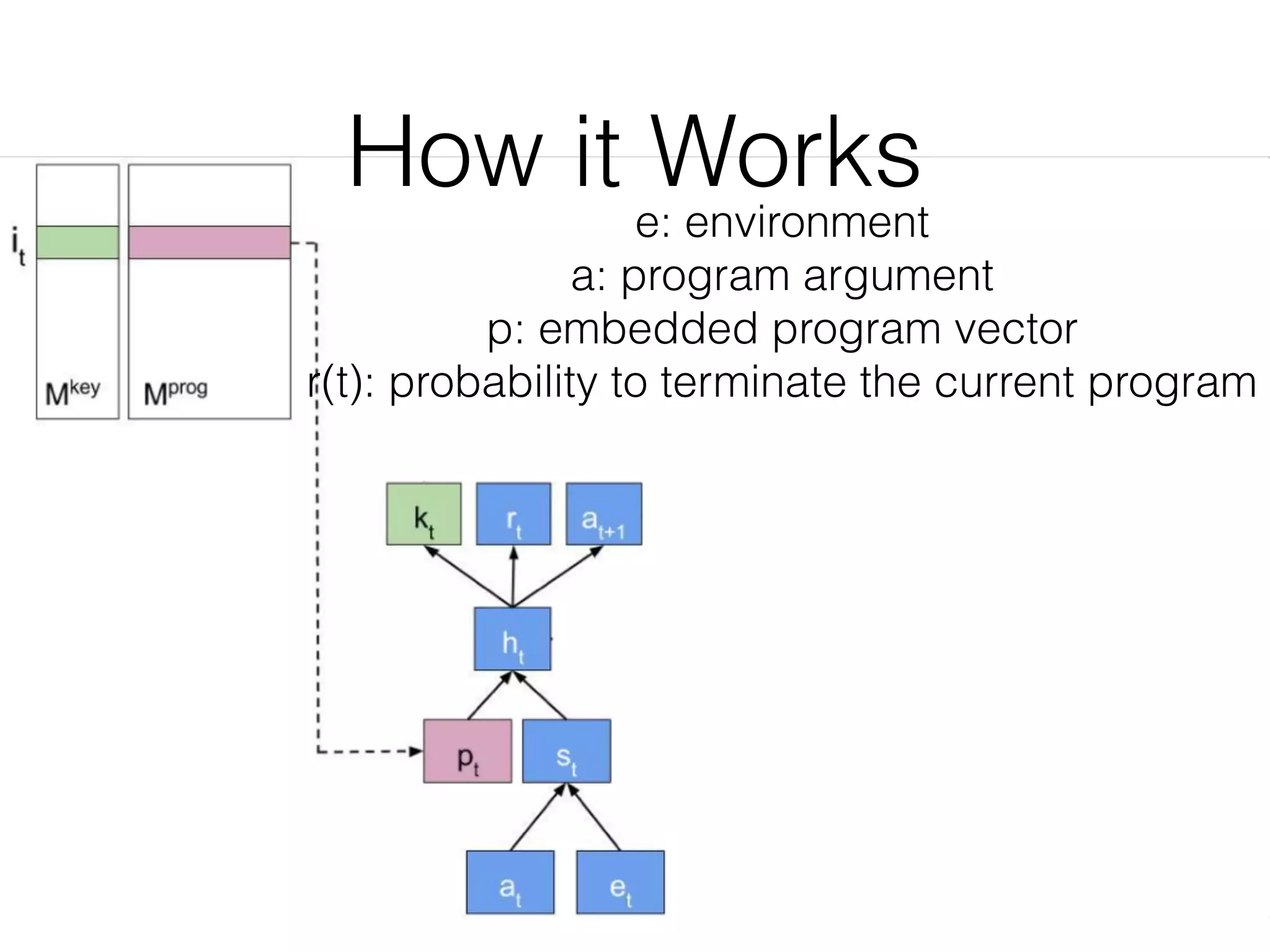
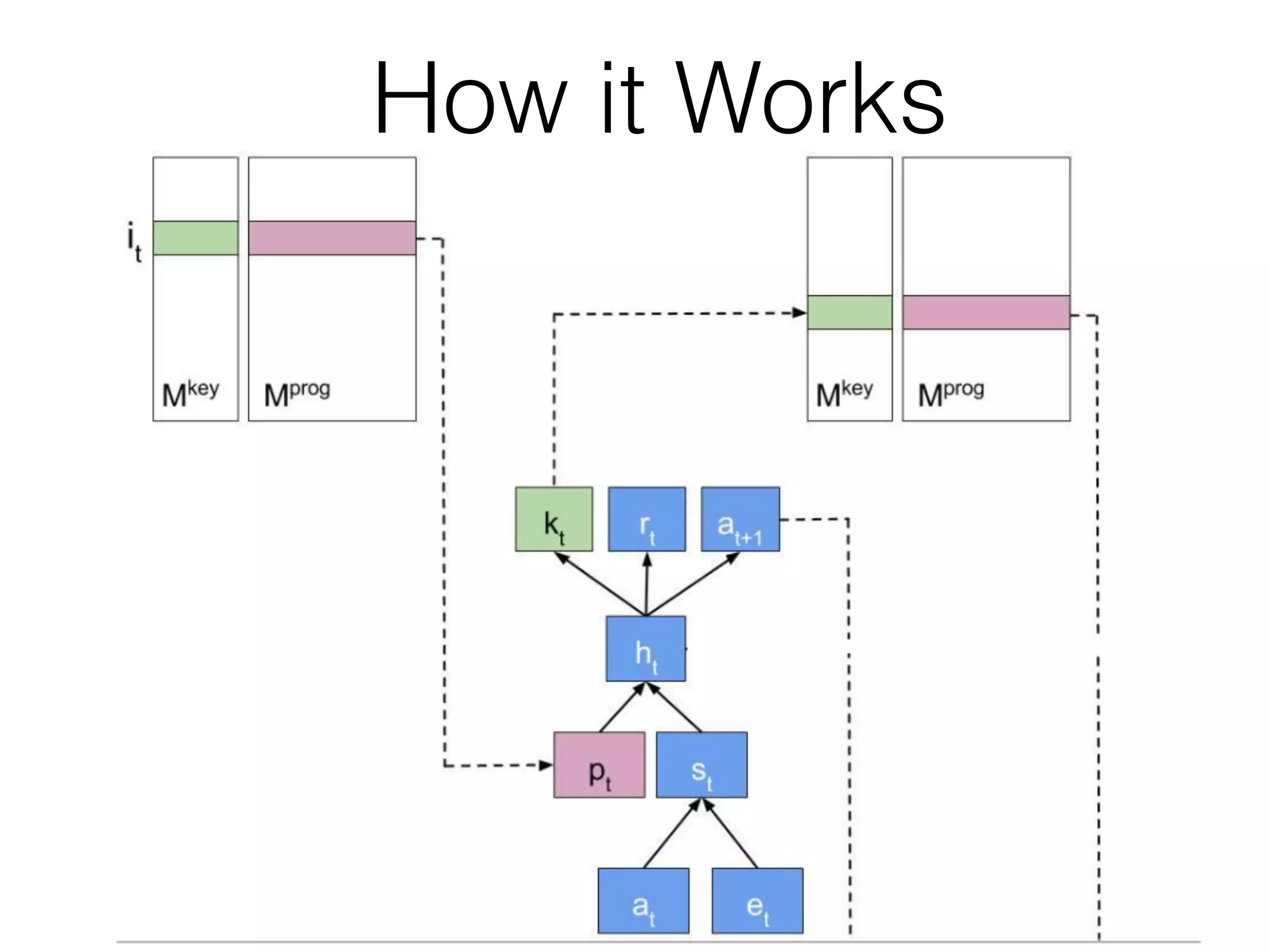
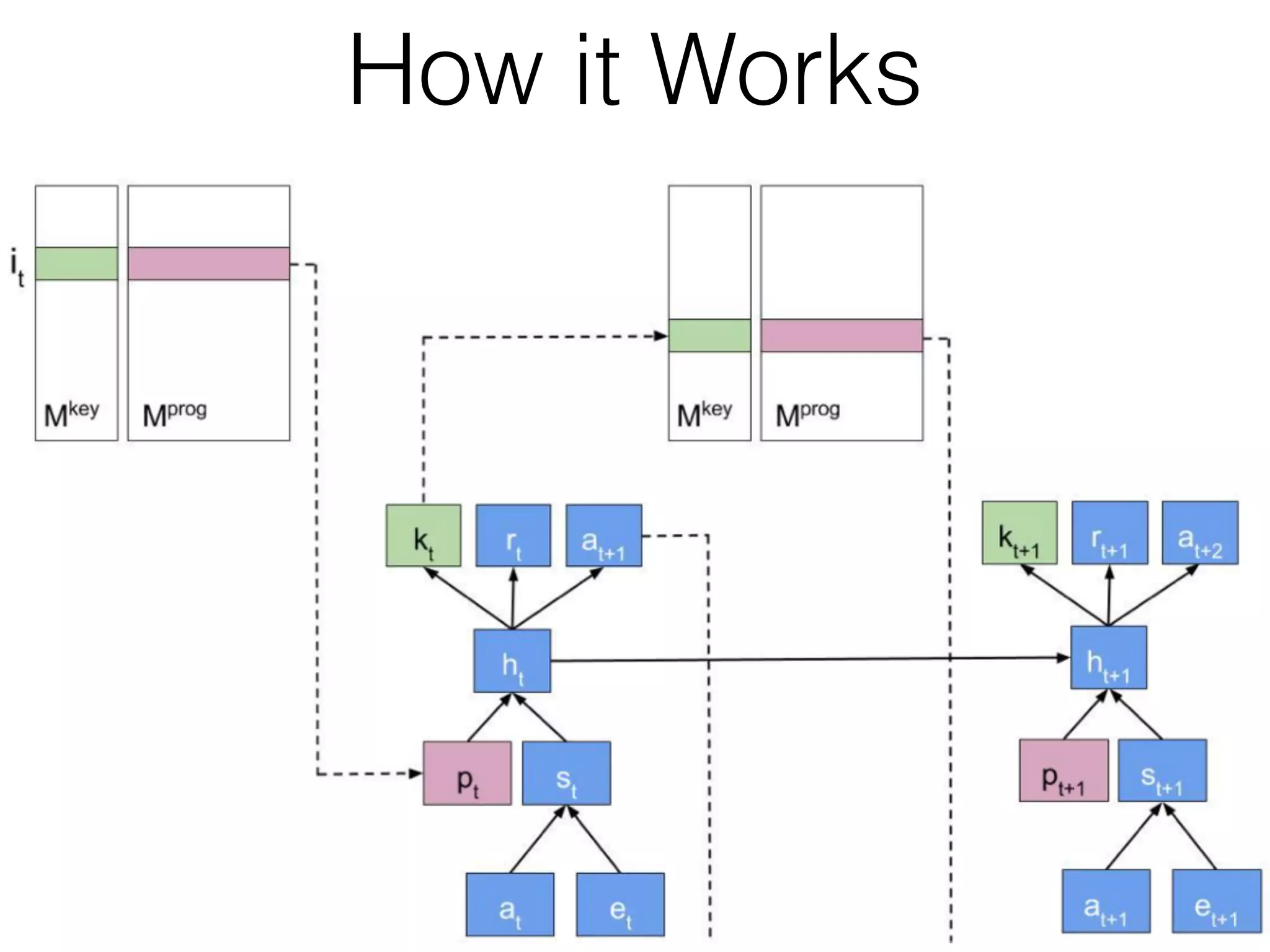
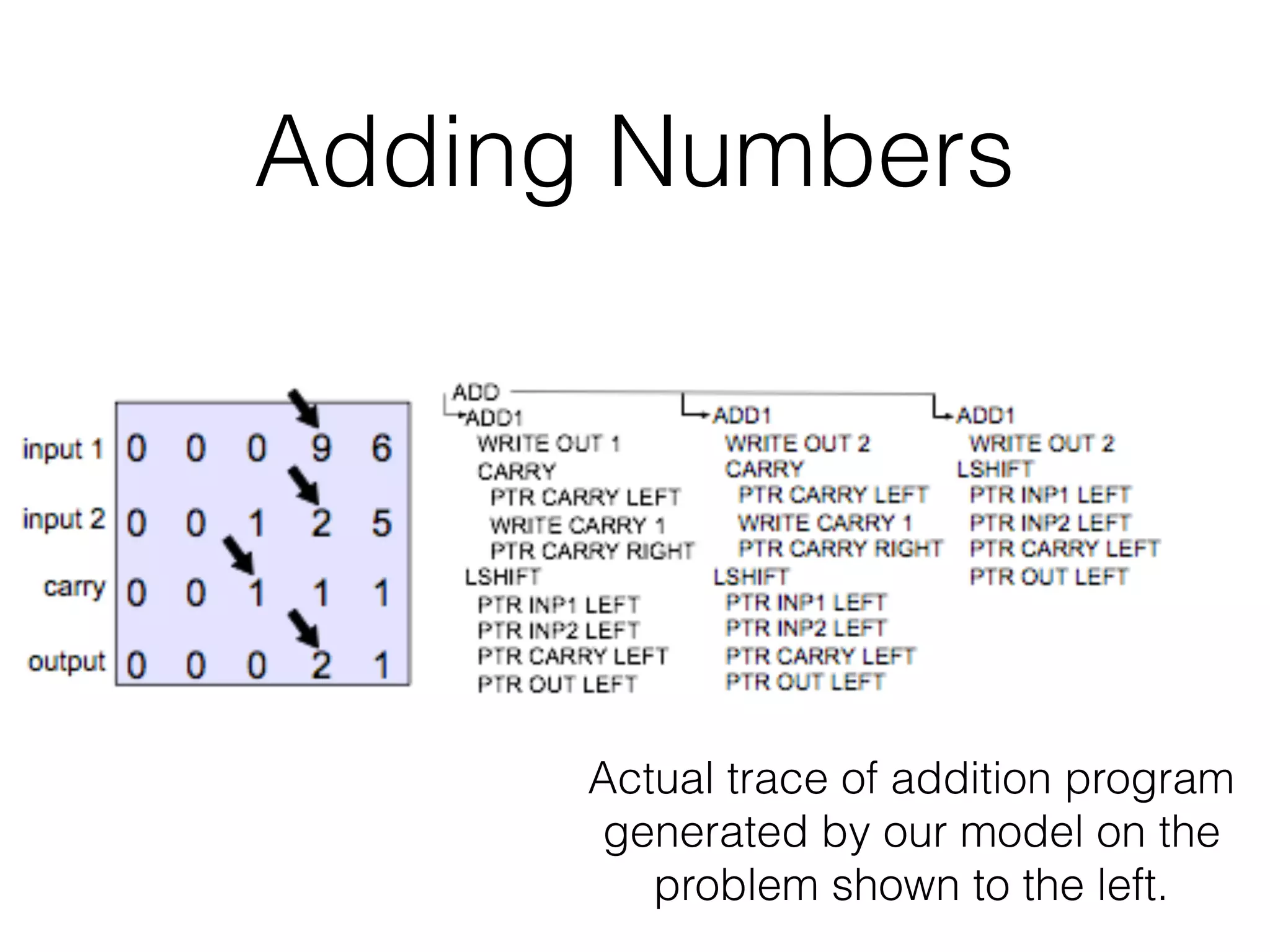
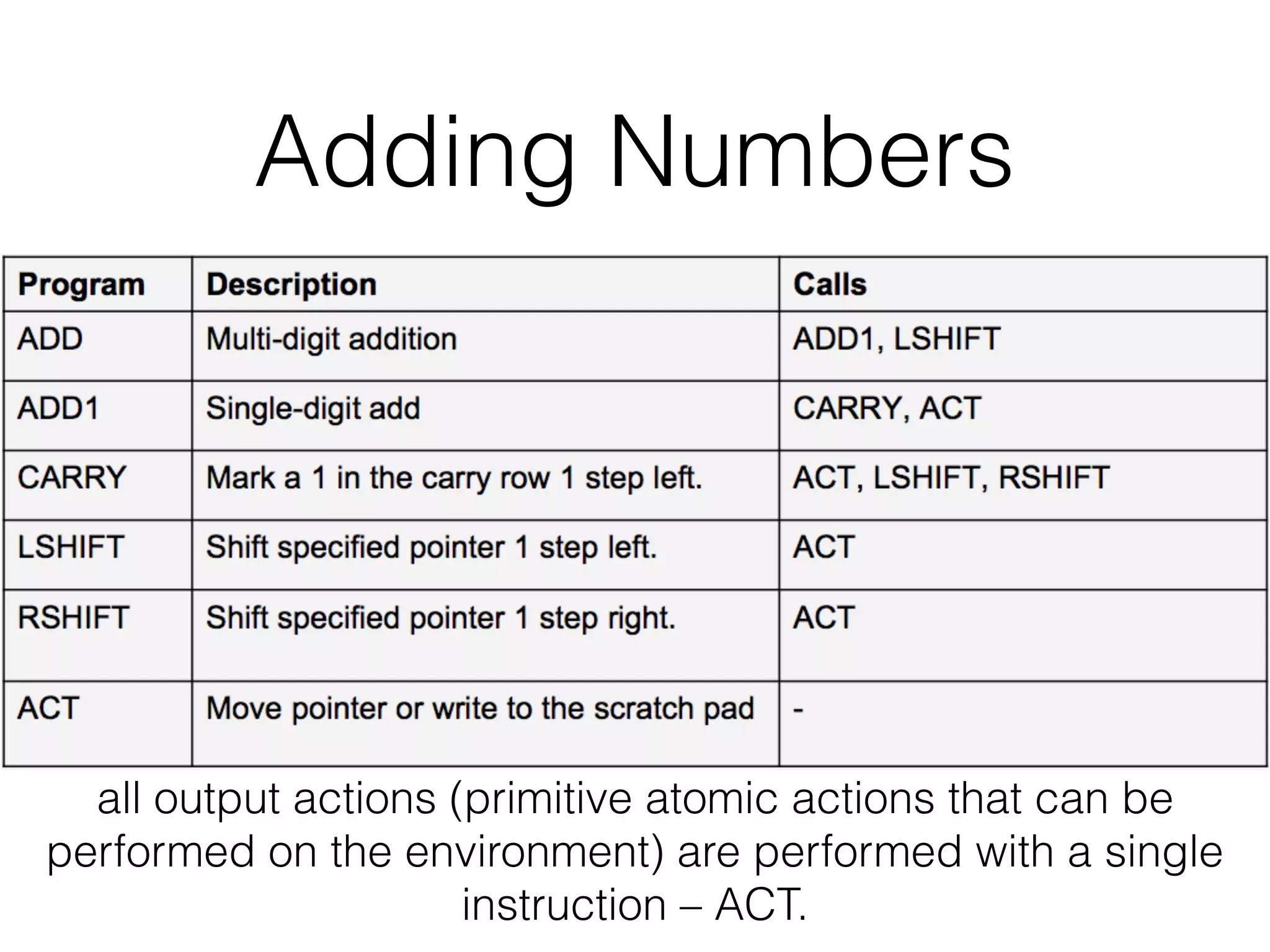
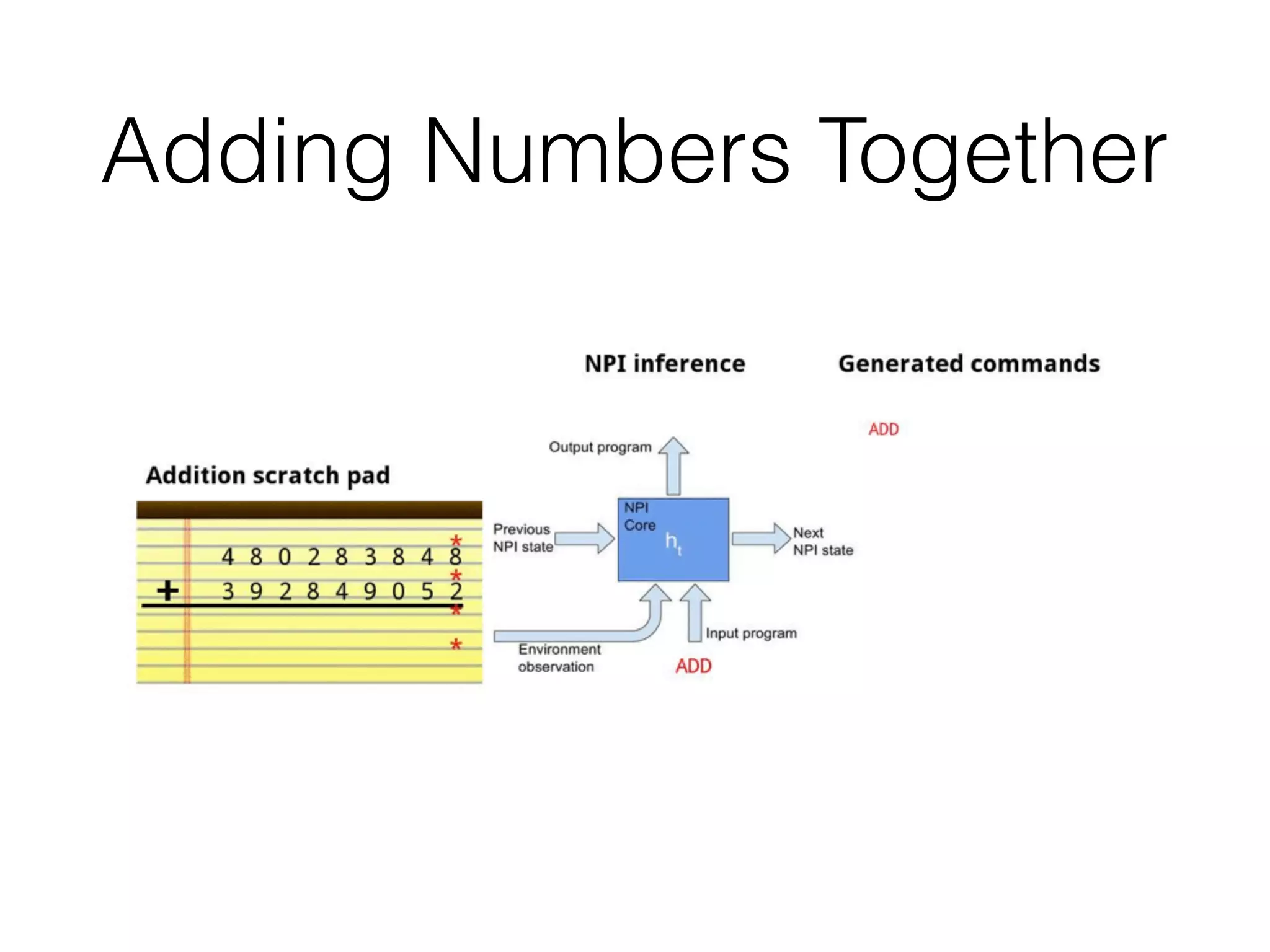
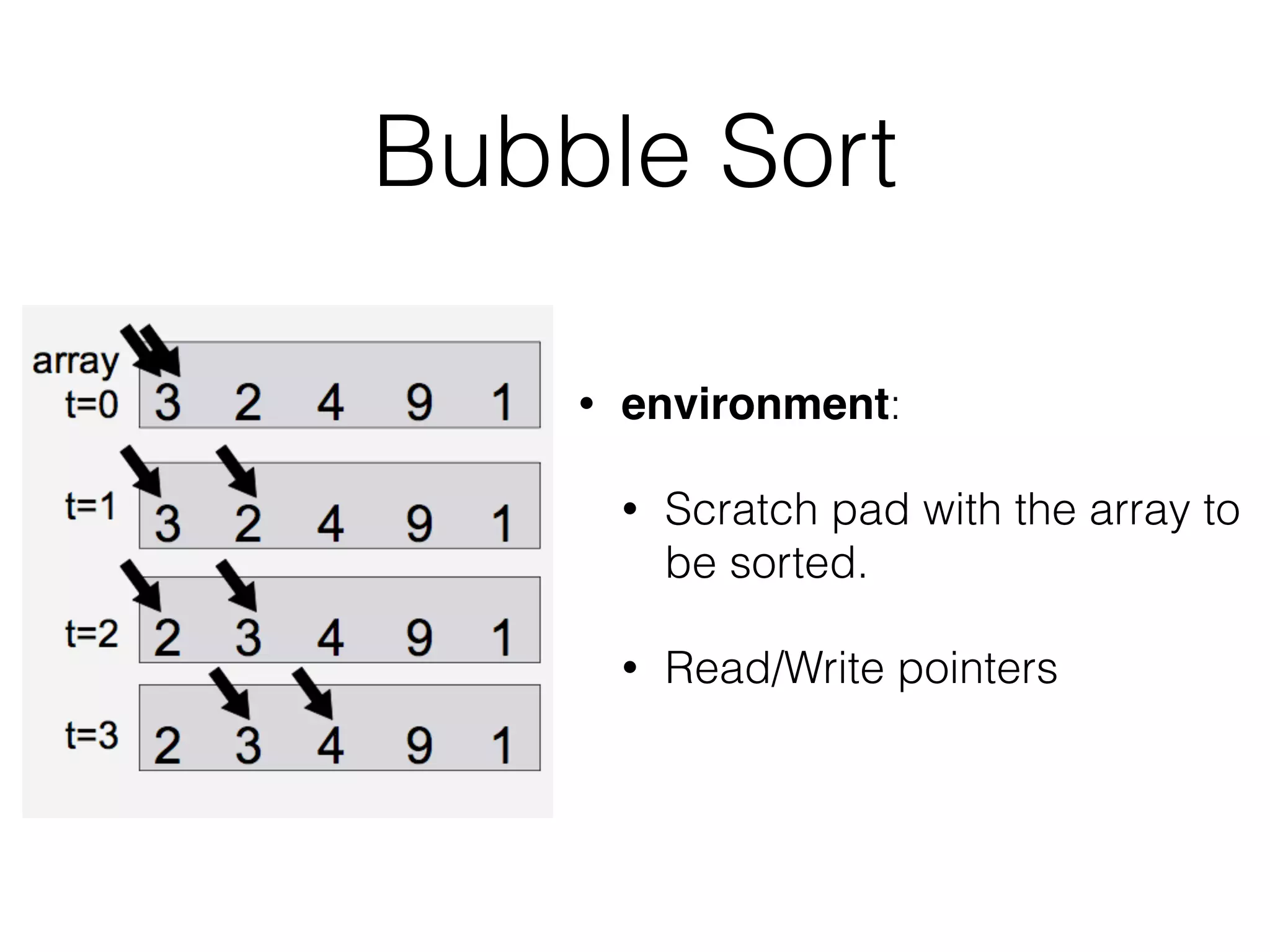
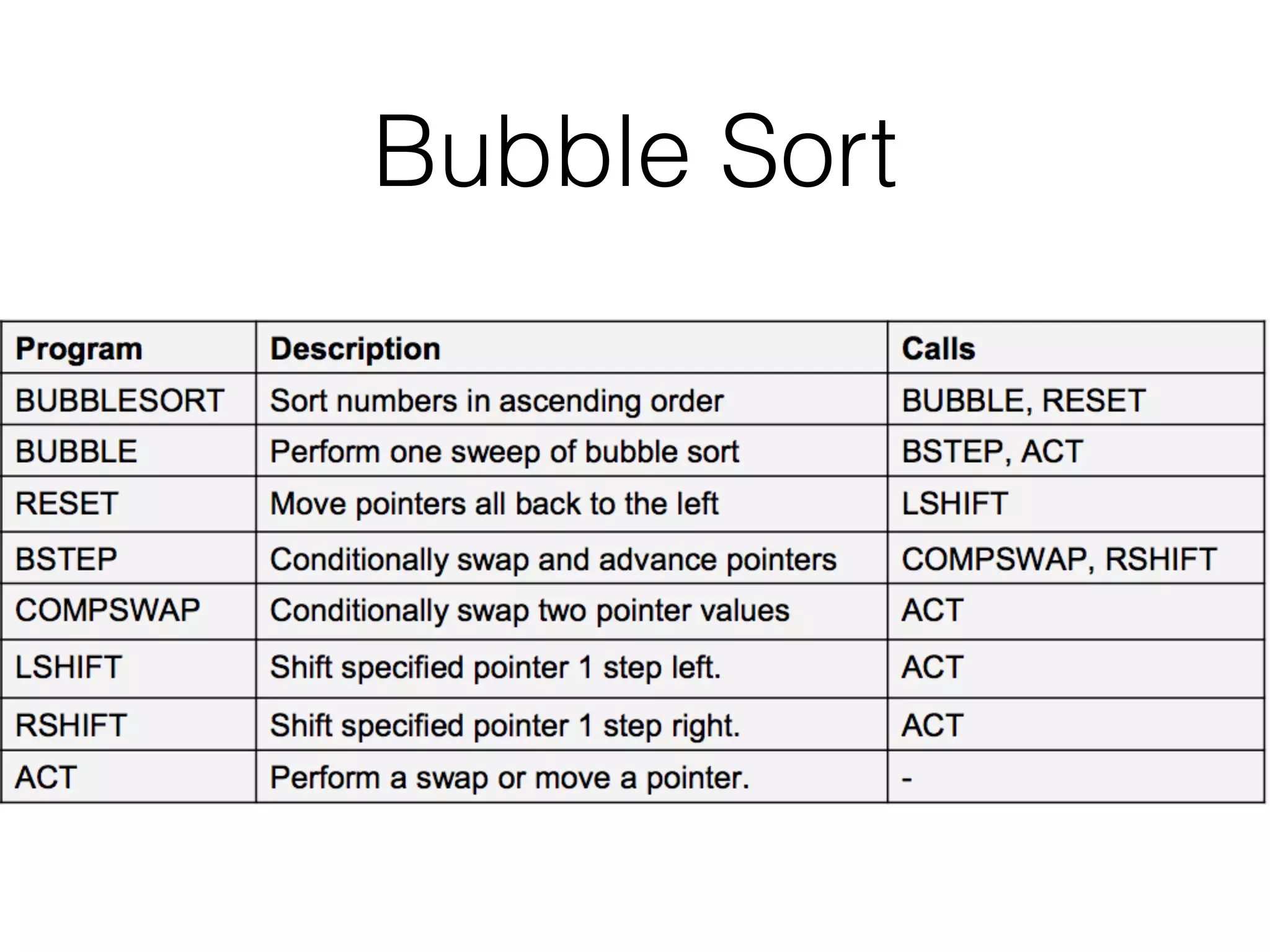
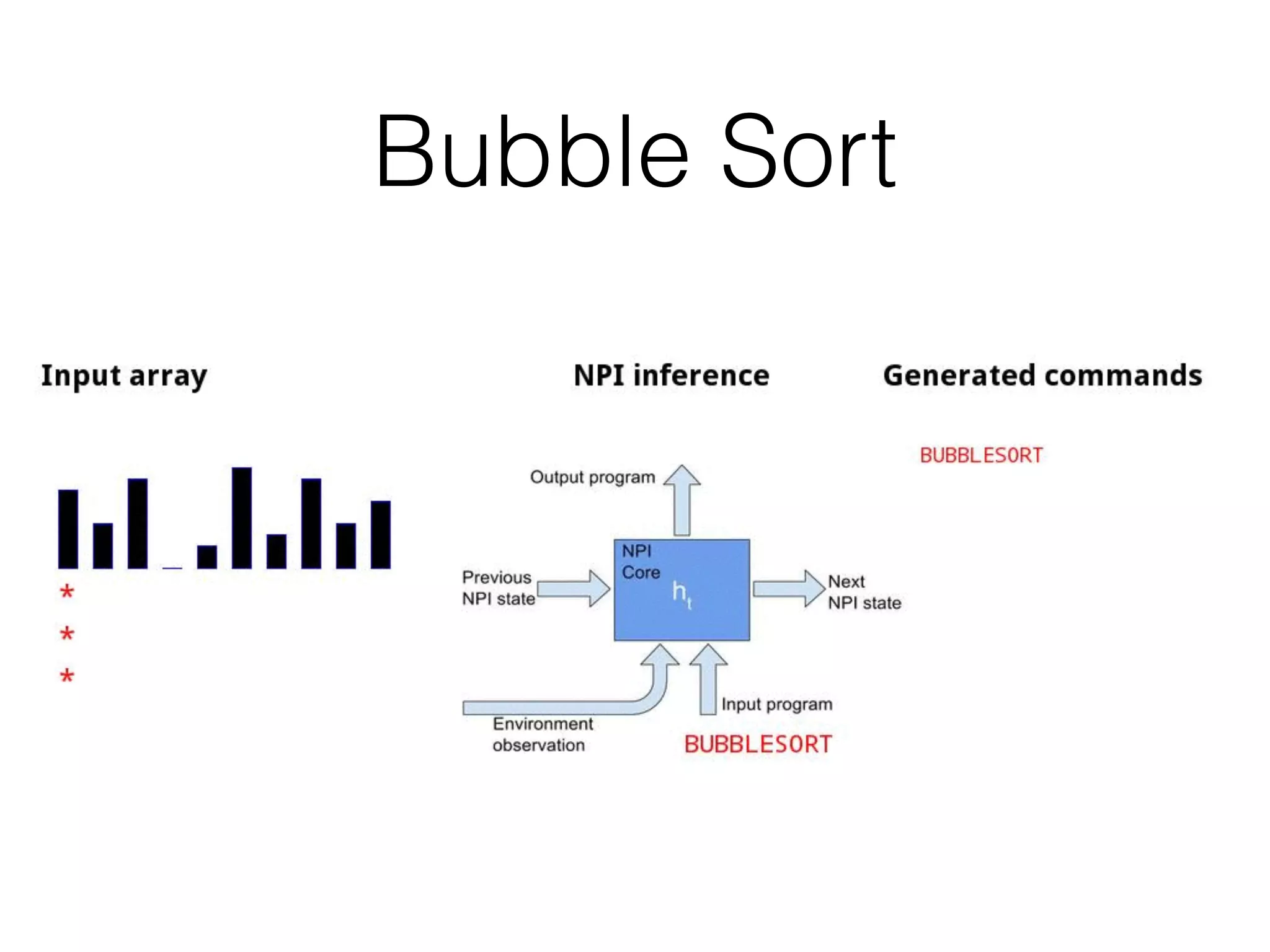
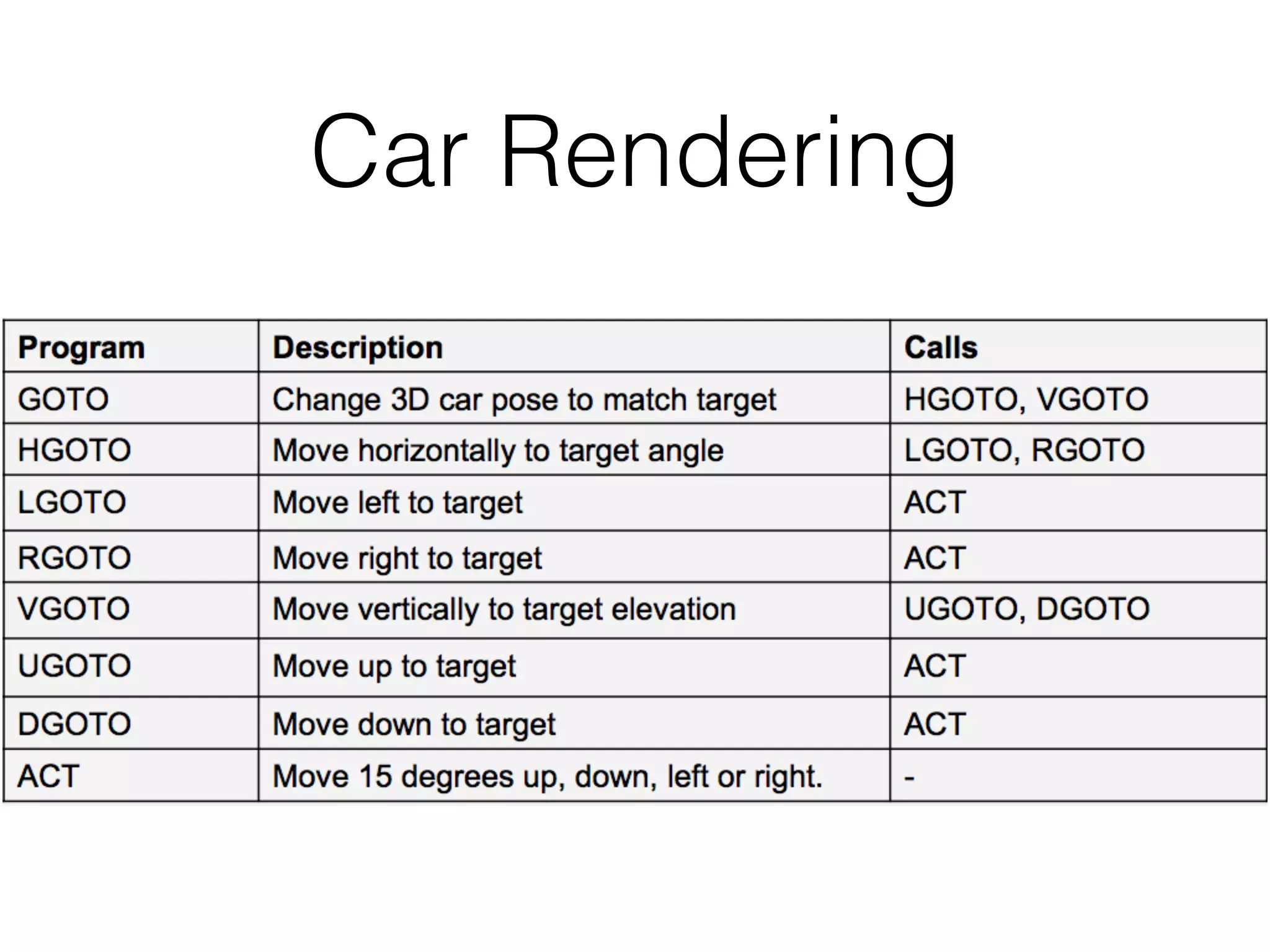
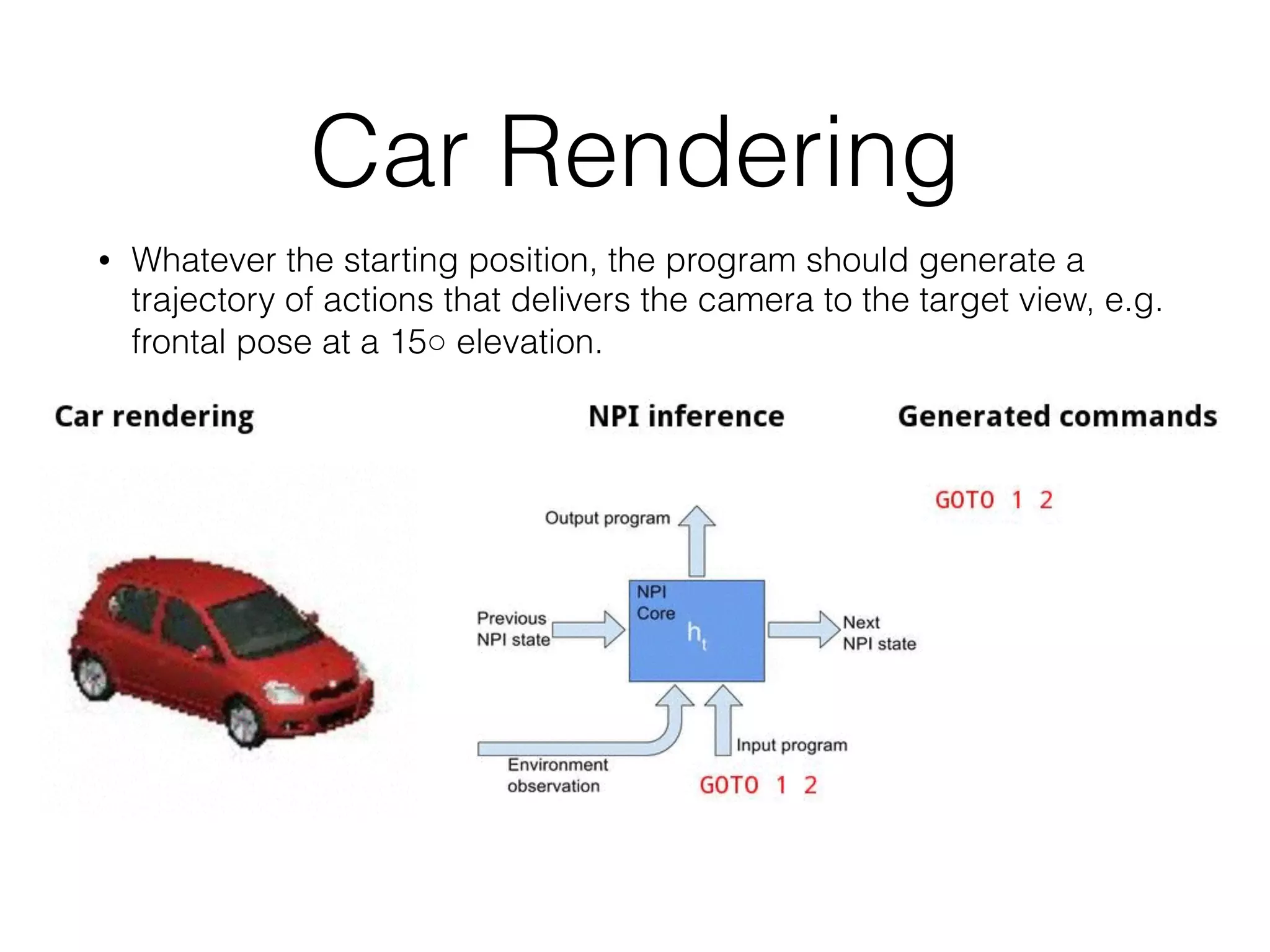
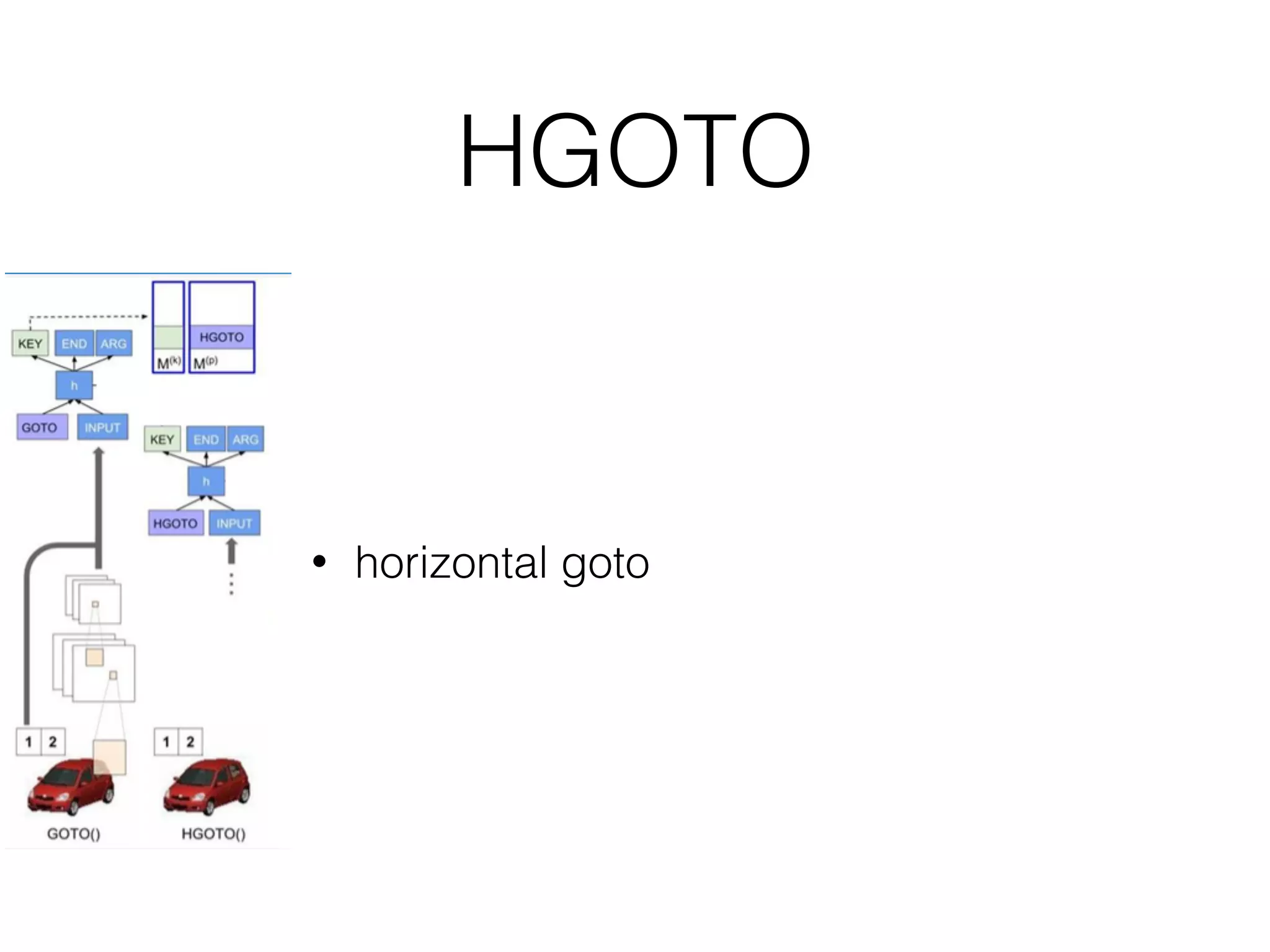
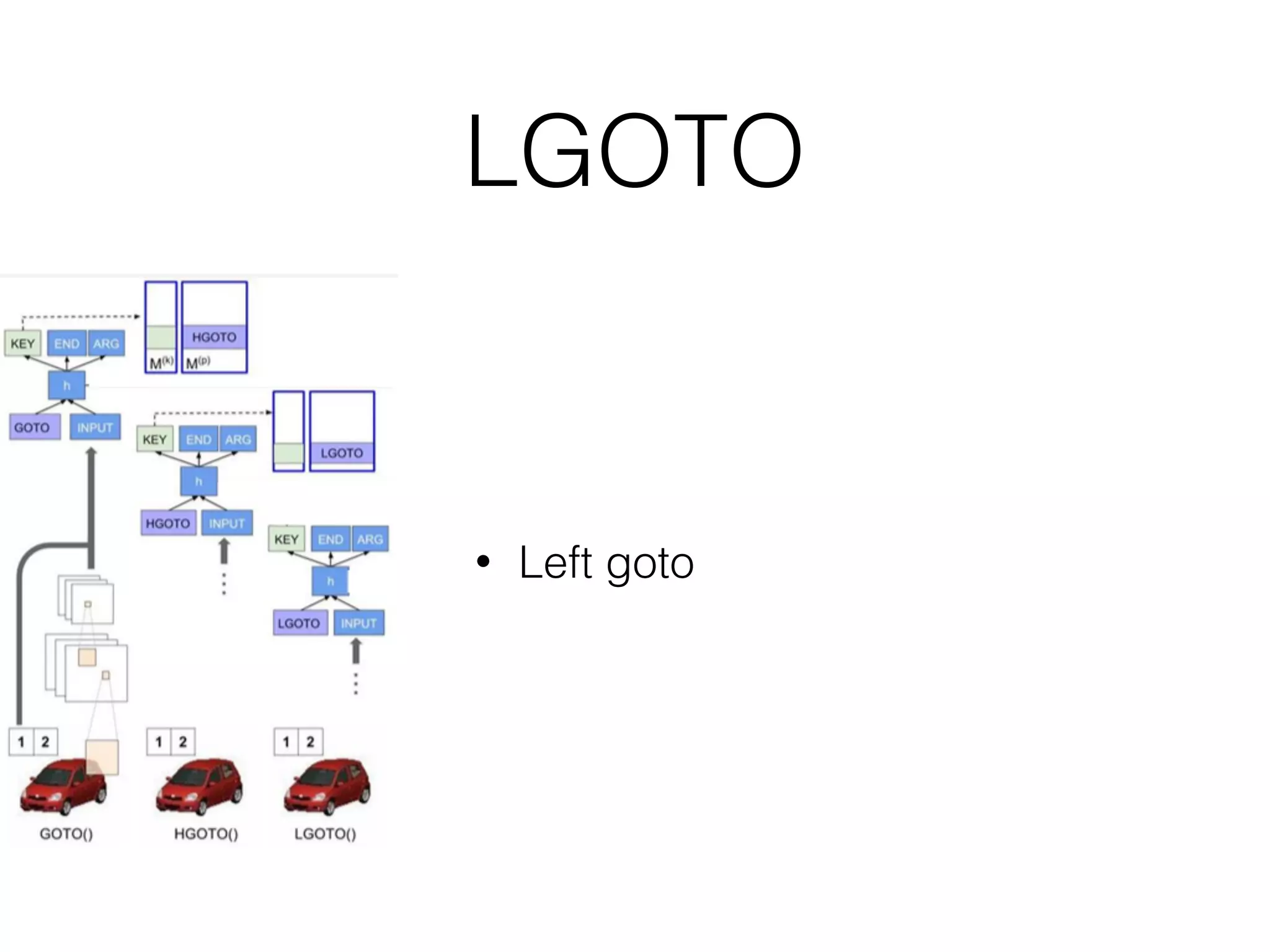
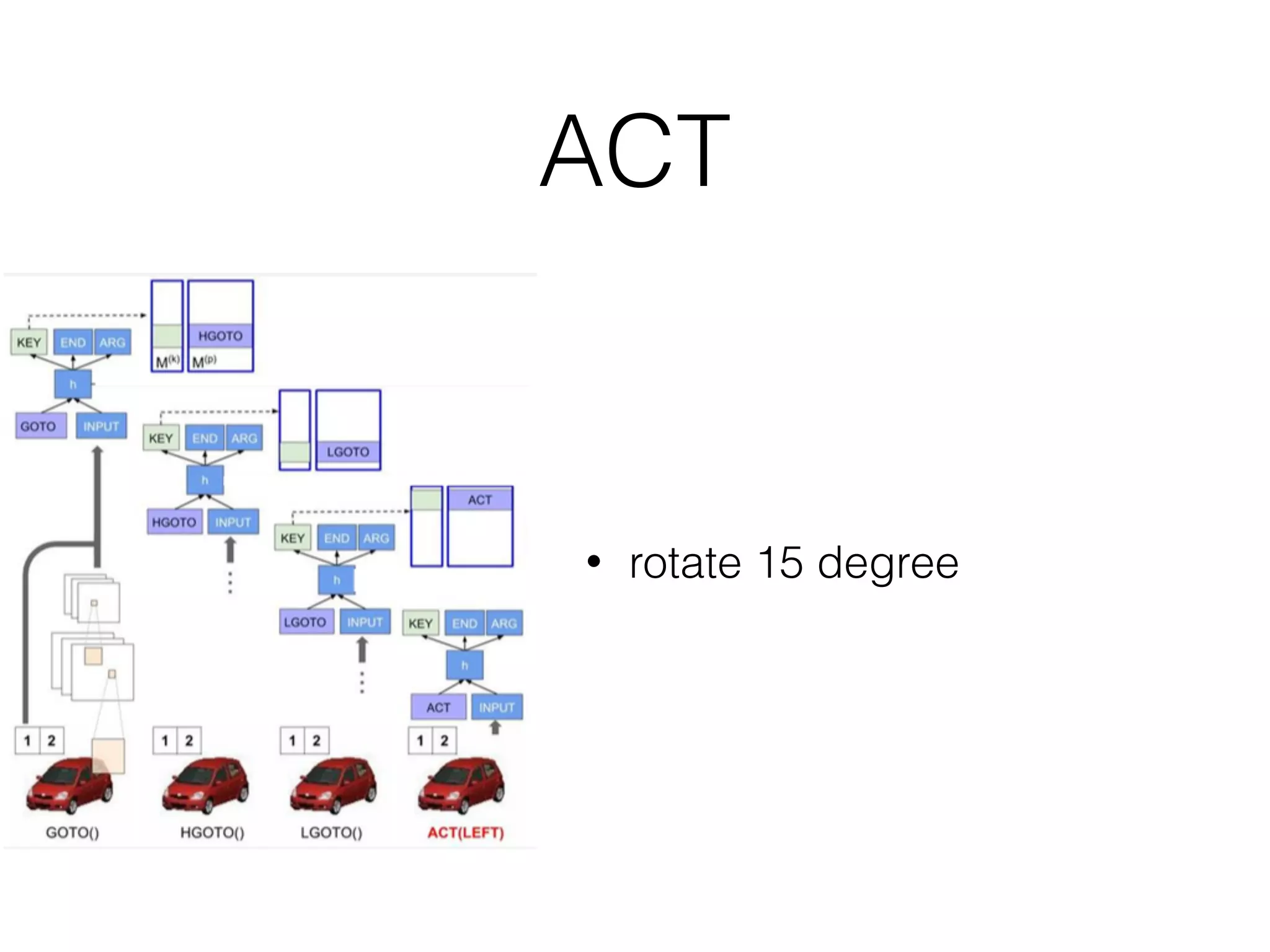
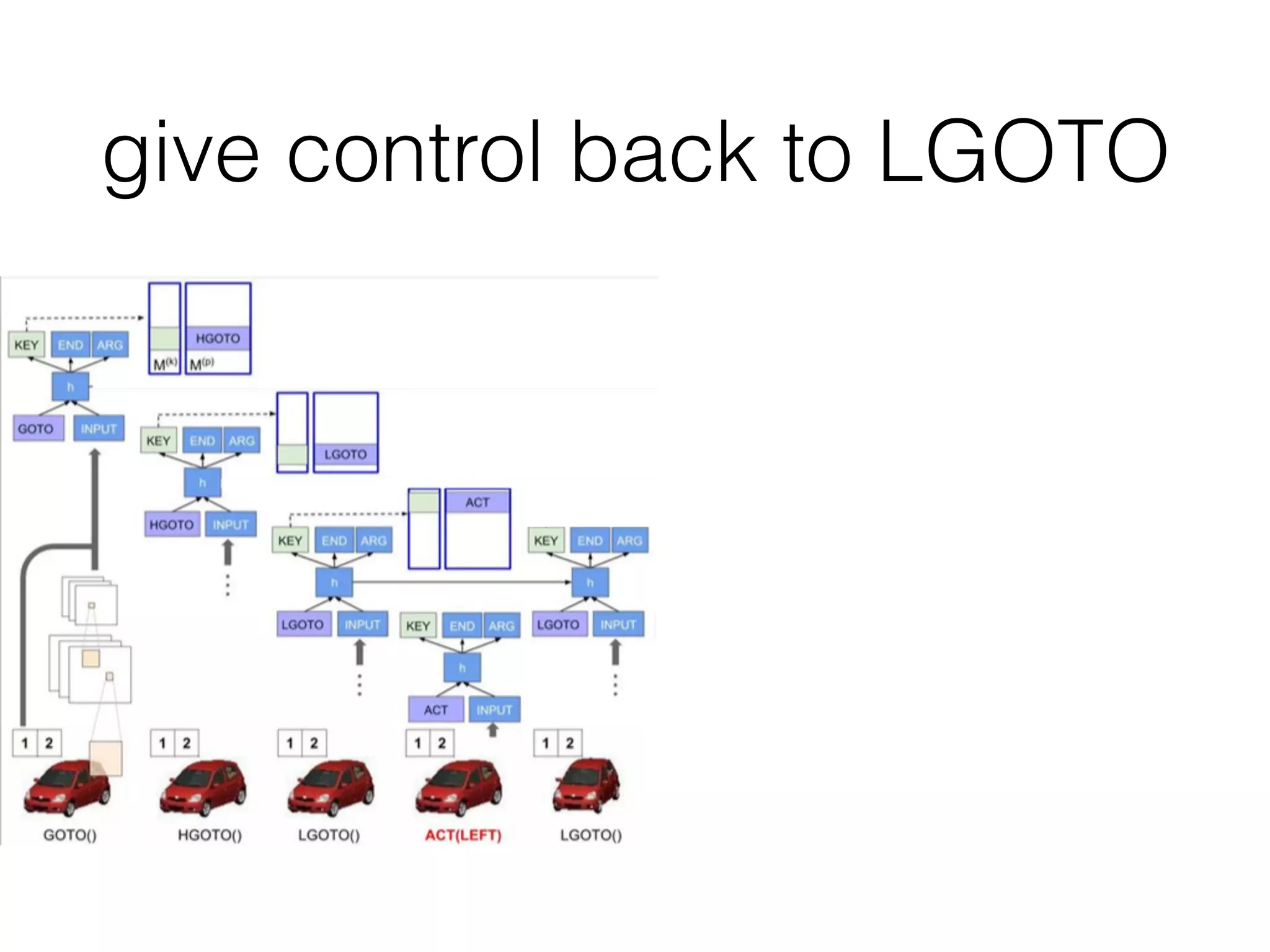
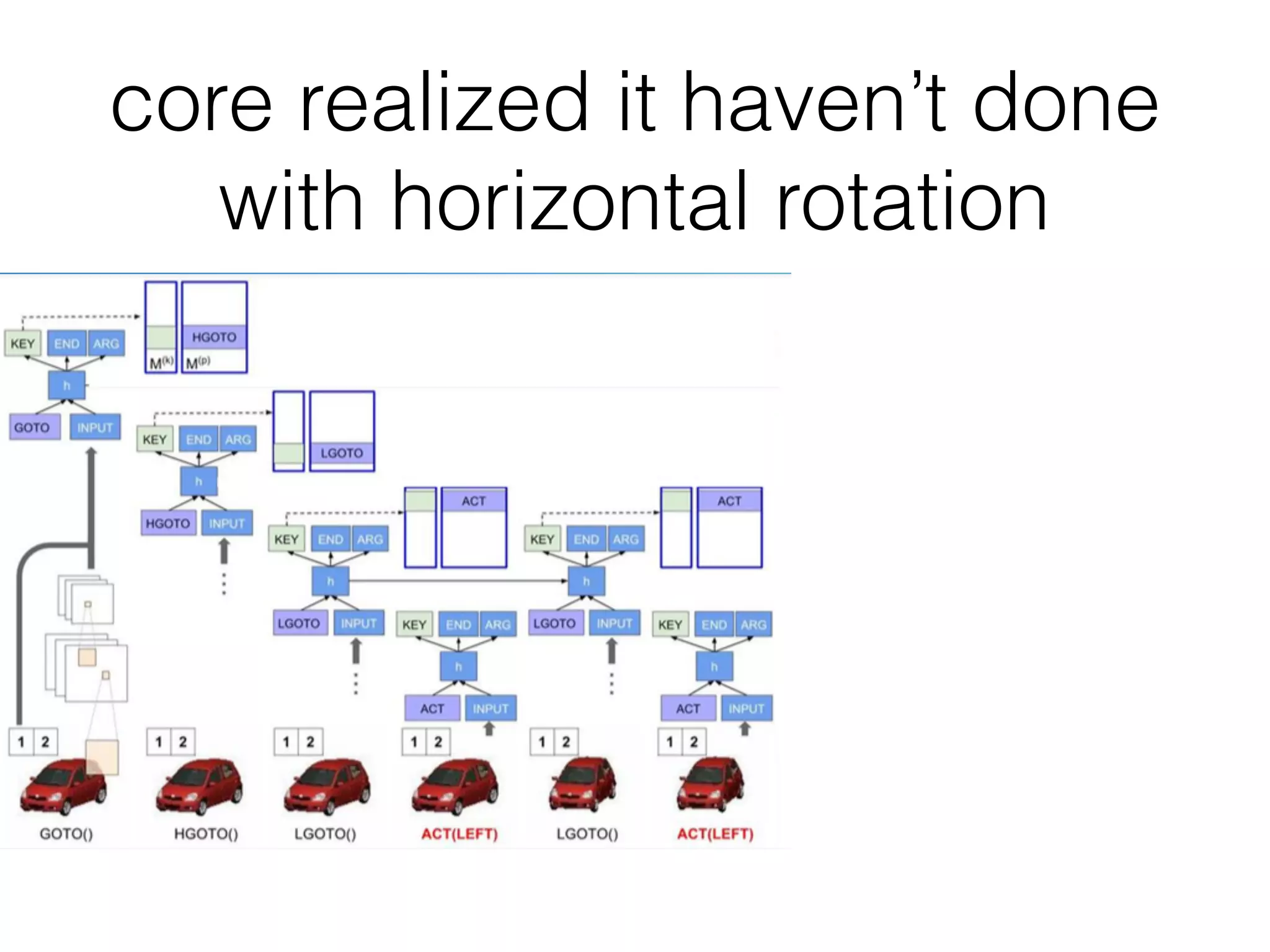
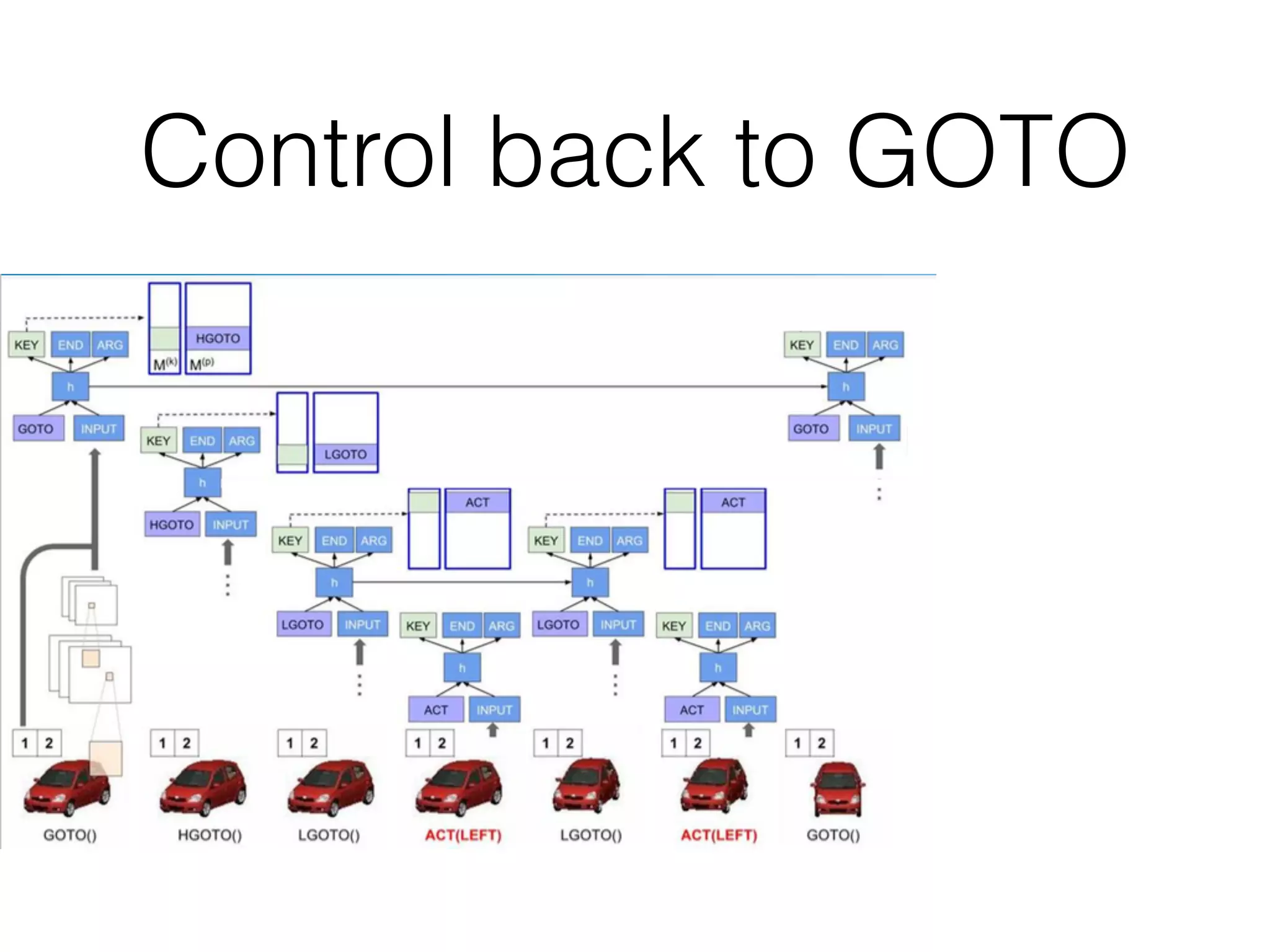
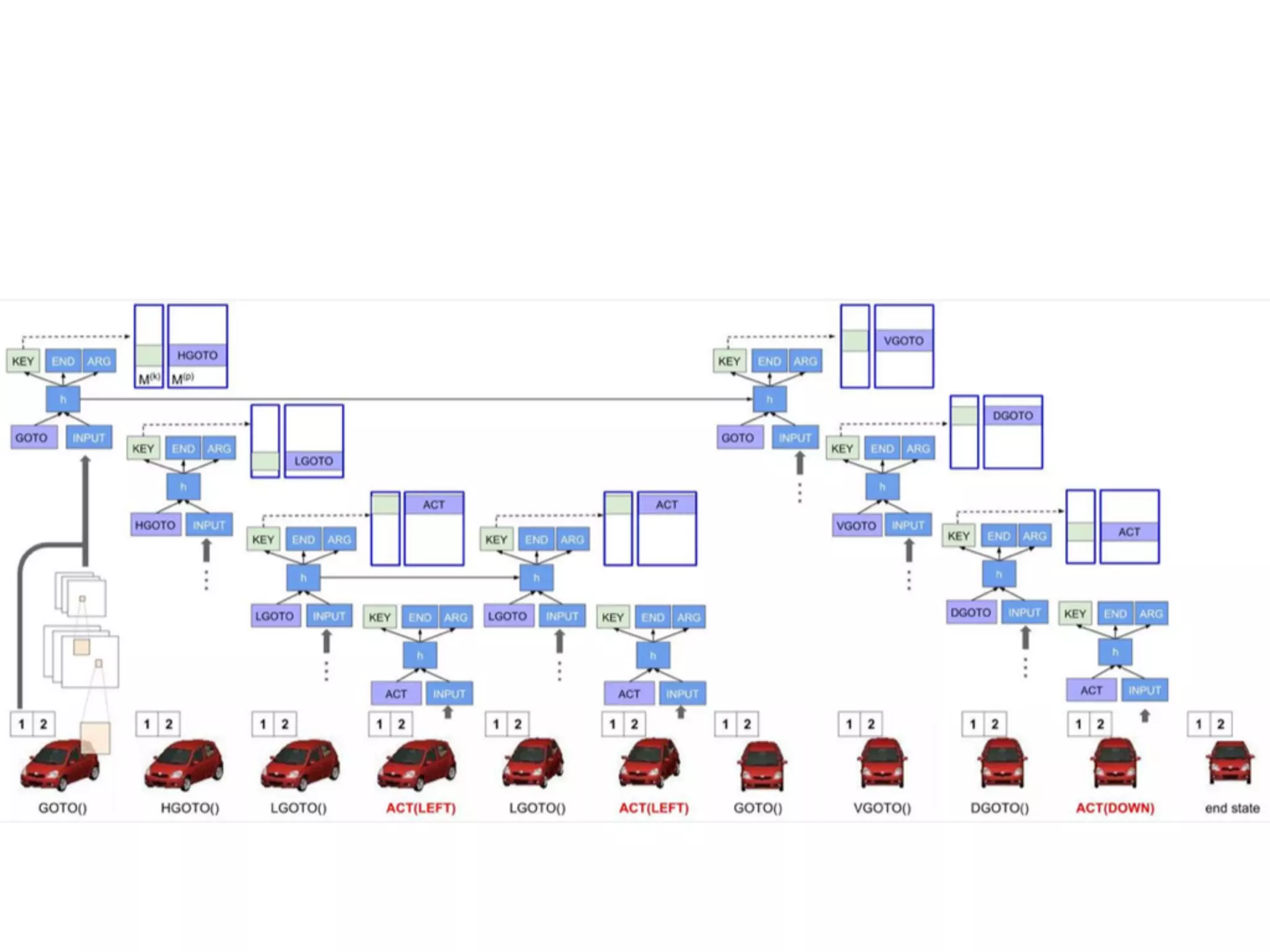
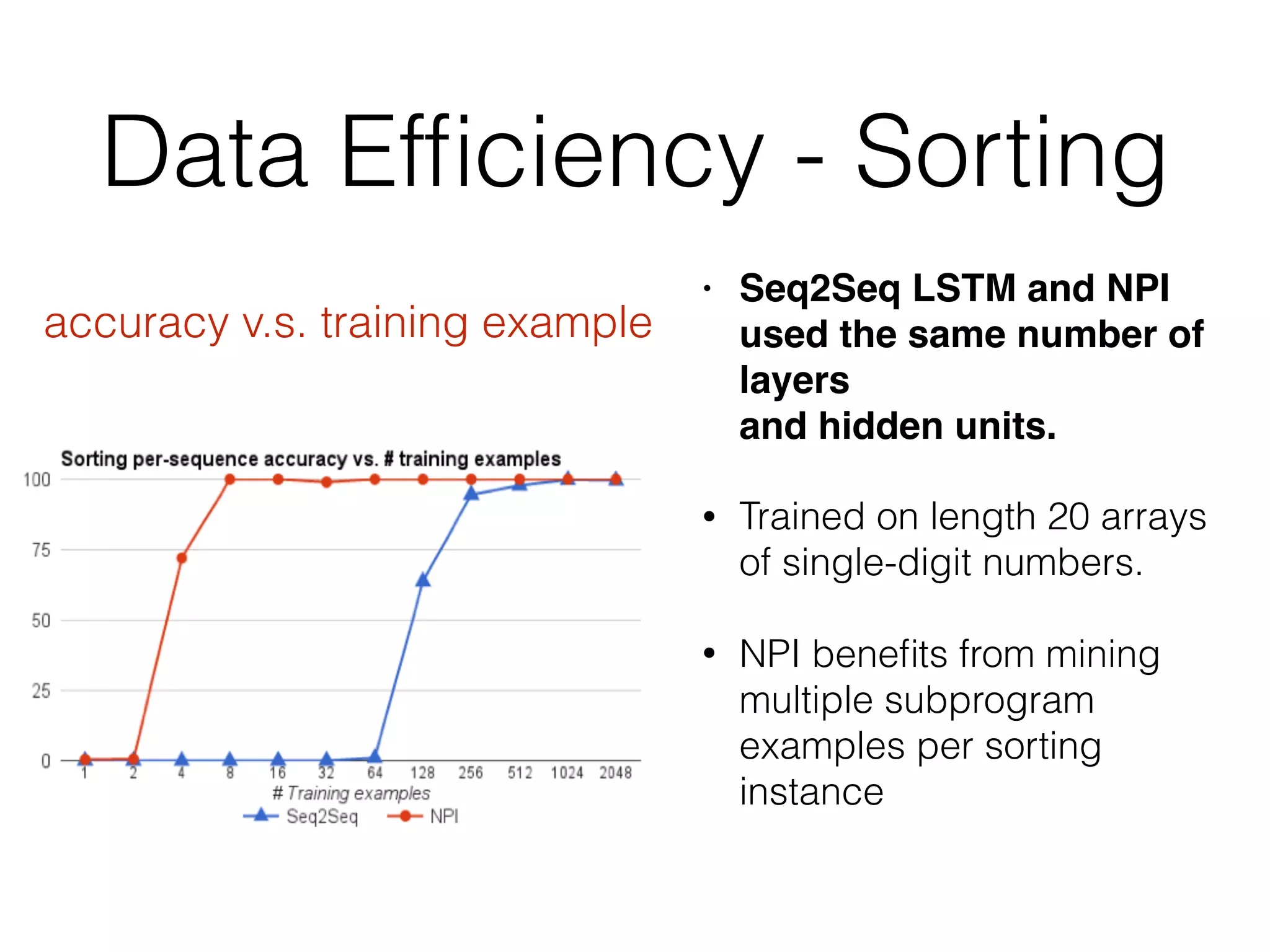
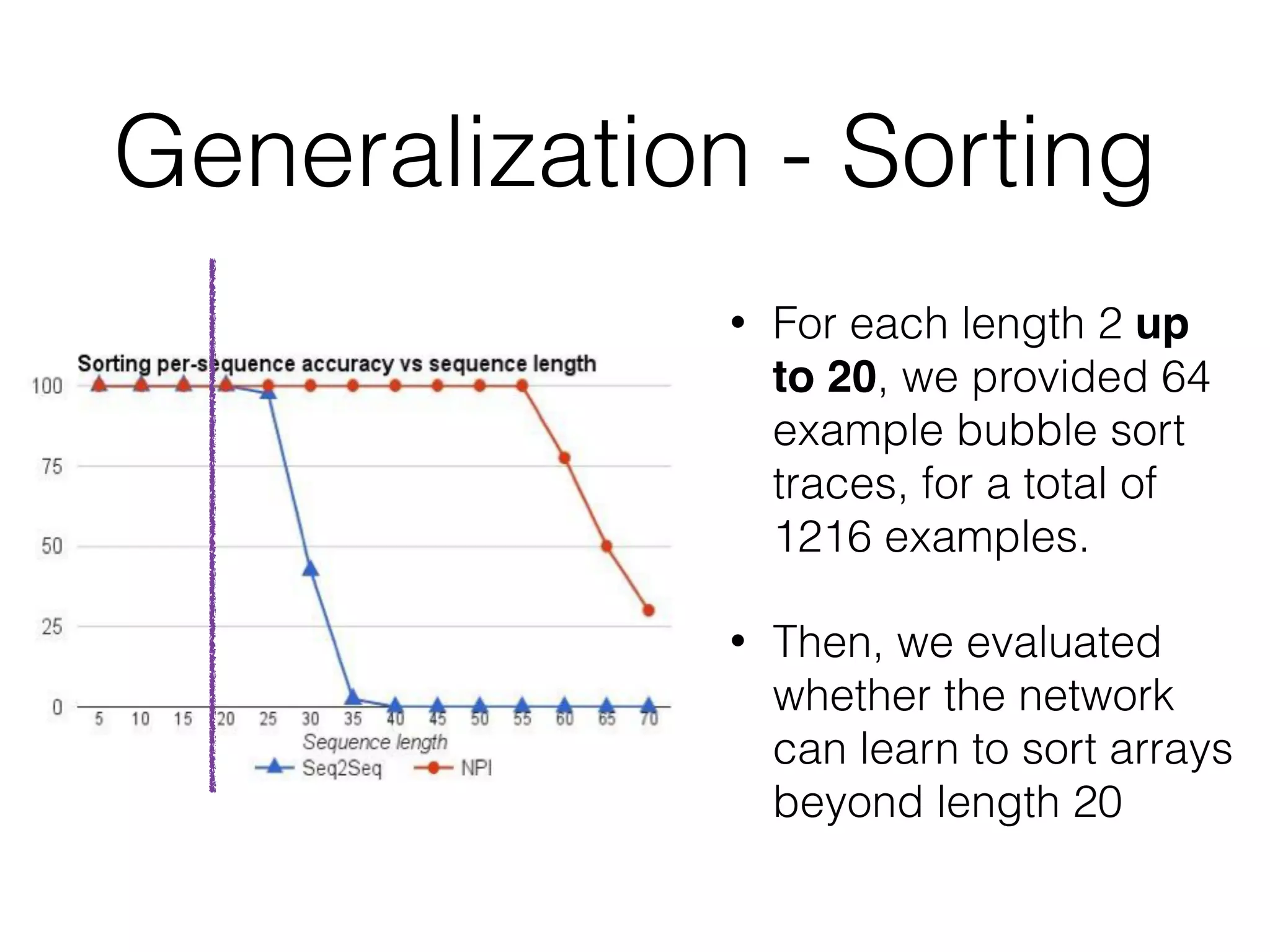
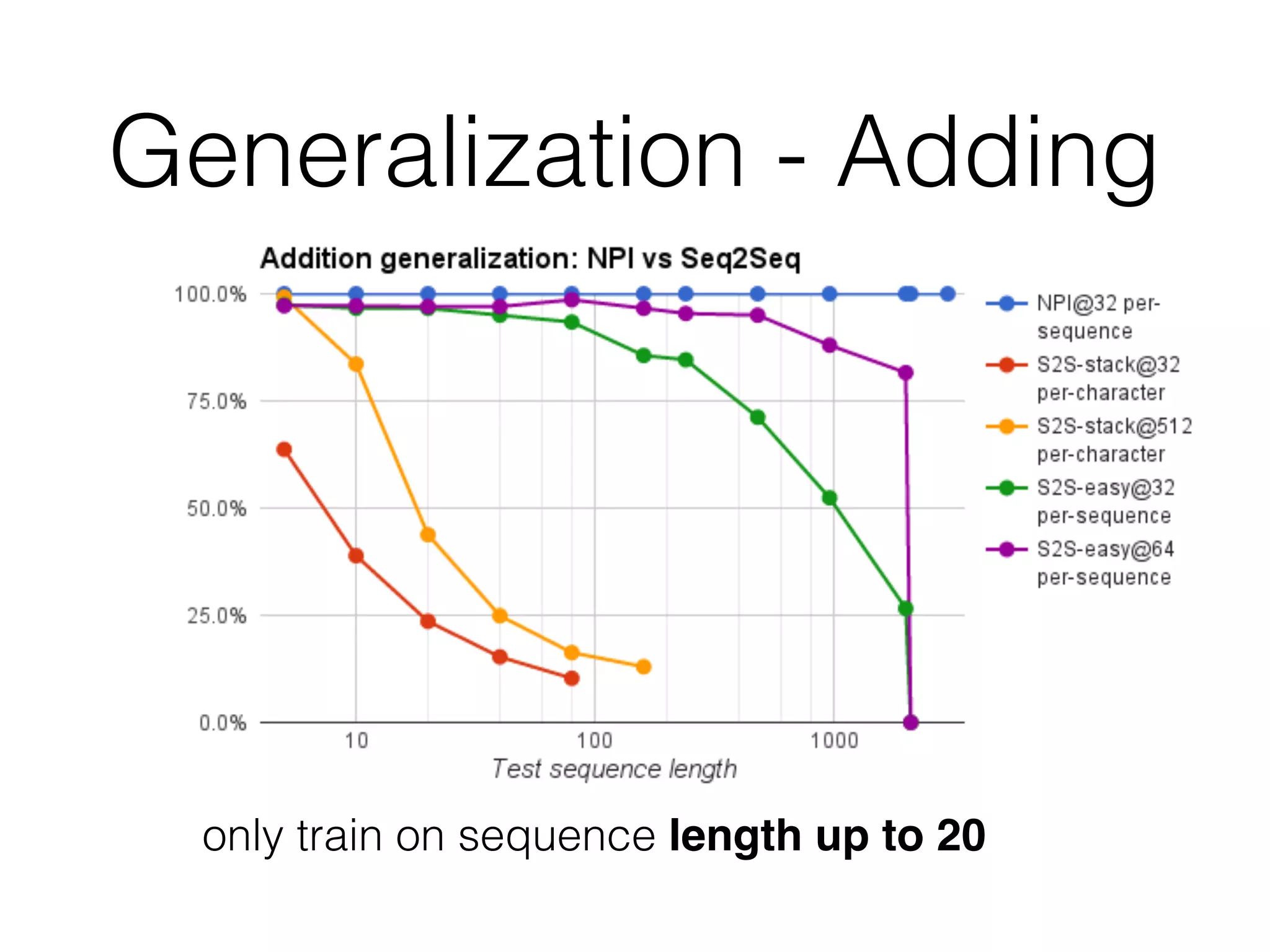
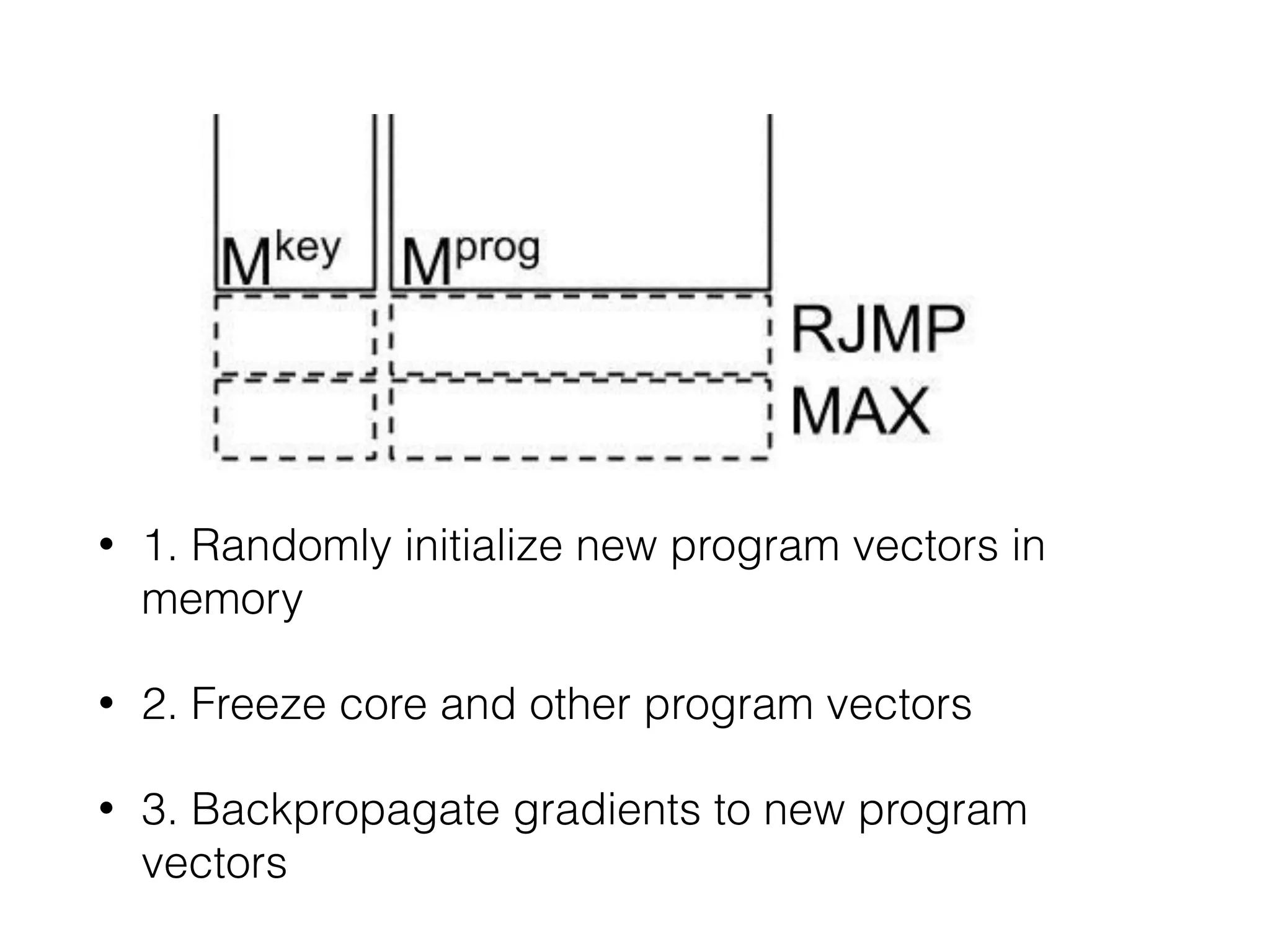
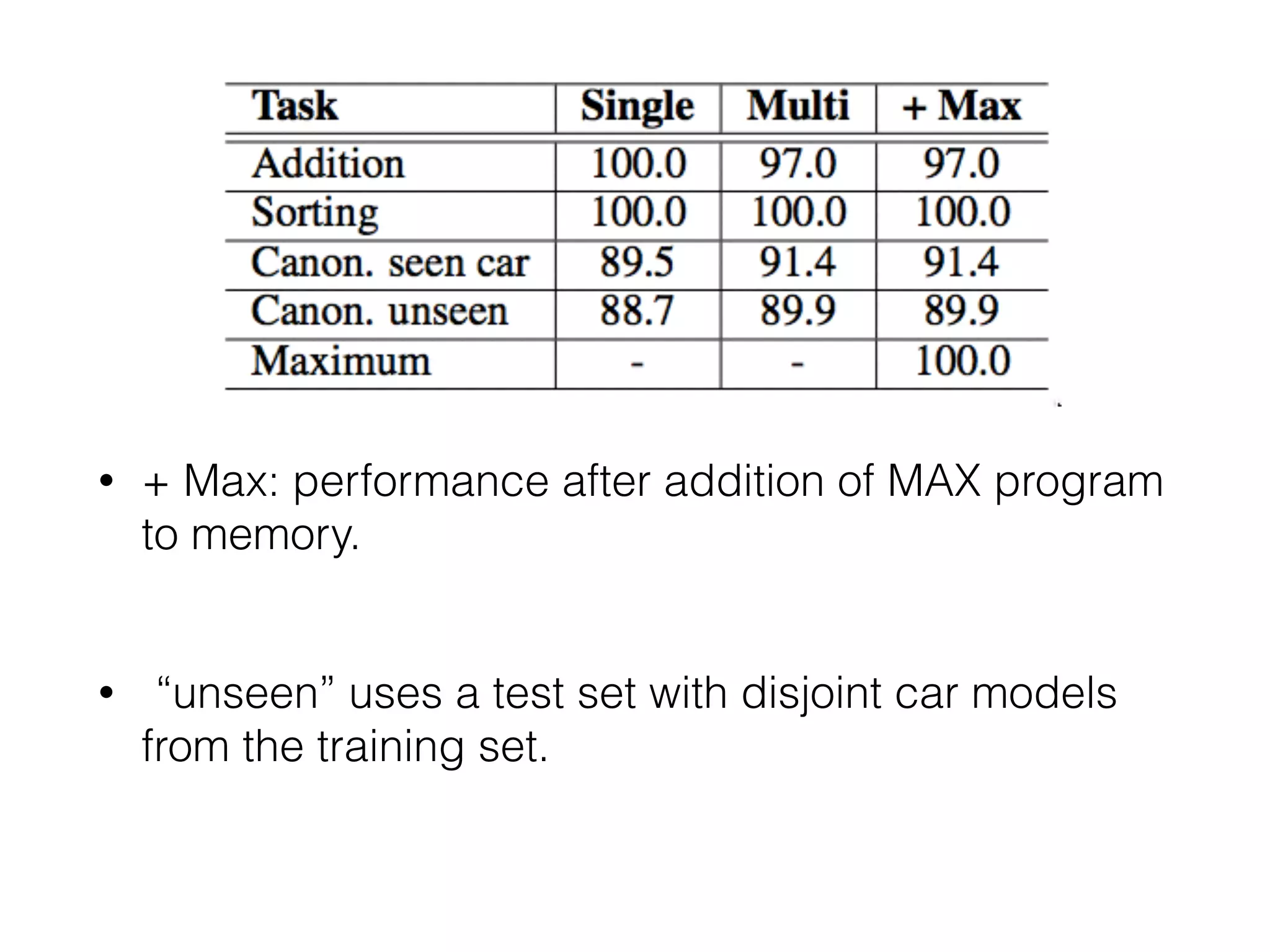
Neural Programmer-Interpreters (NPI) is a neural network model that can learn programs from small amounts of training data and generalize to new situations. It has a core LSTM module that acts as a router between learned programs. In experiments, NPI outperformed sequence-to-sequence models in data efficiency and generalization when learning tasks like adding numbers and sorting arrays. It was also able to learn new programs like finding the maximum value by composing existing programs, without forgetting previous tasks. The authors conclude that NPI is better able to exploit compositional structure in tasks compared to sequence models.