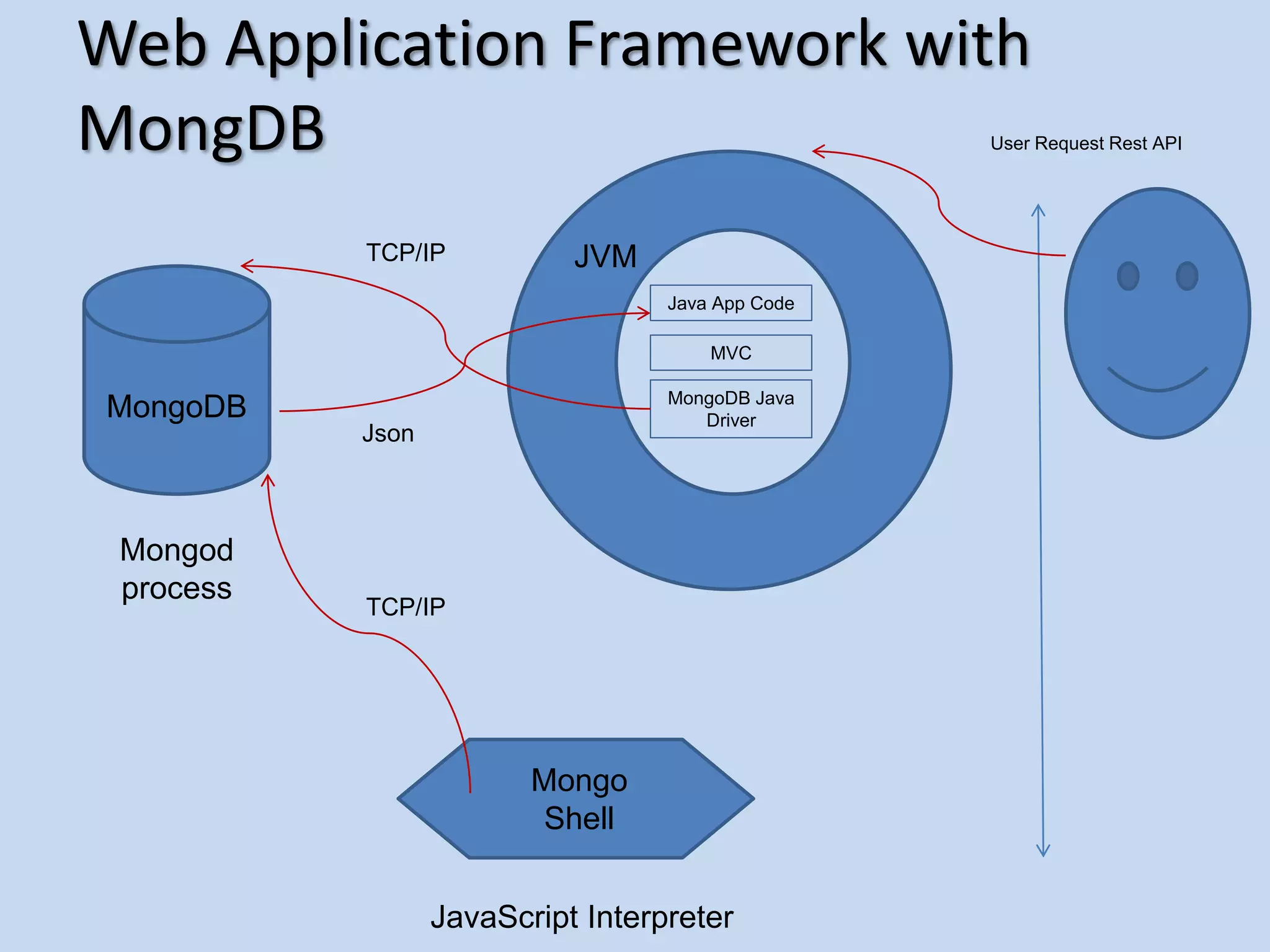
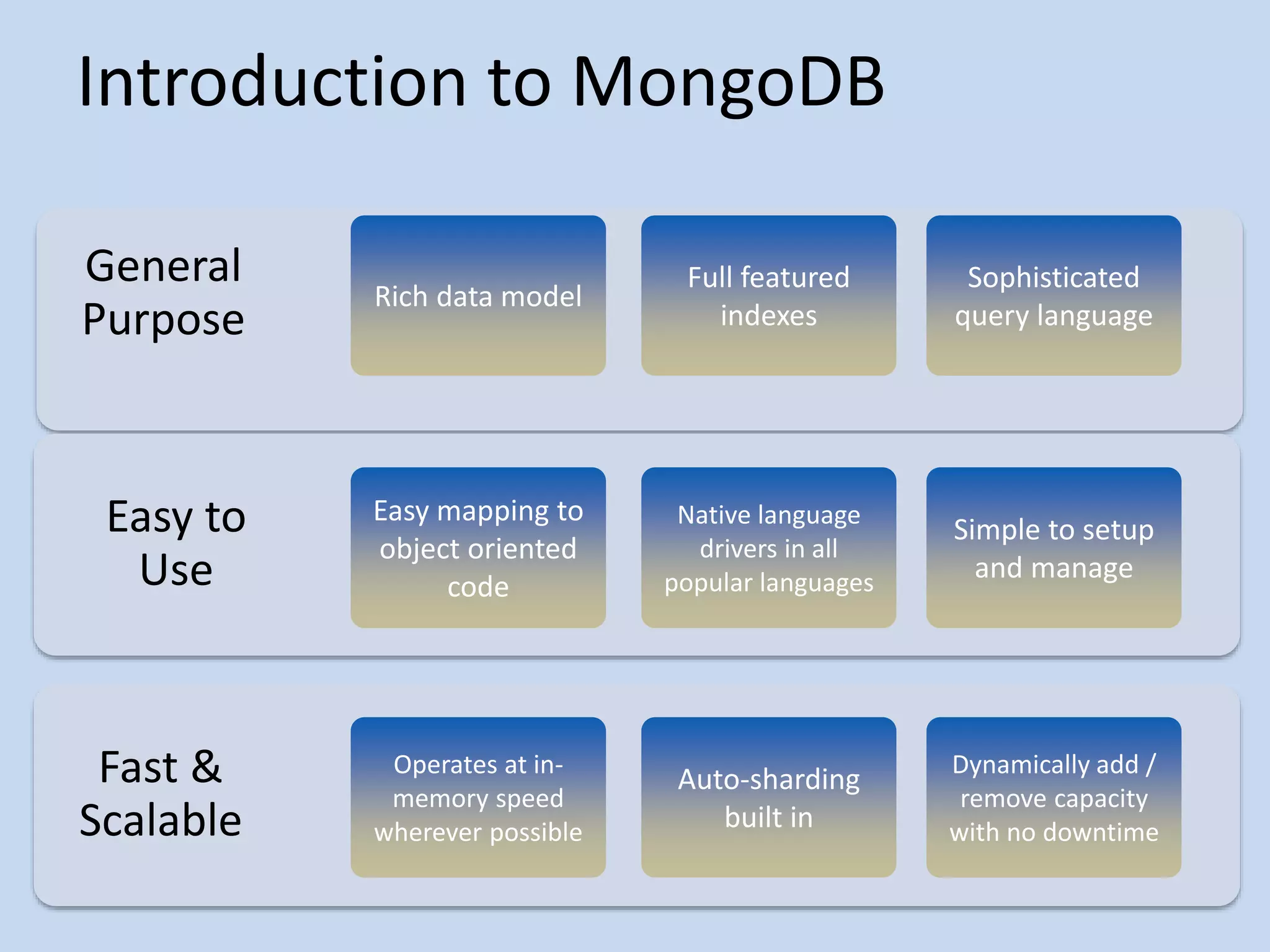
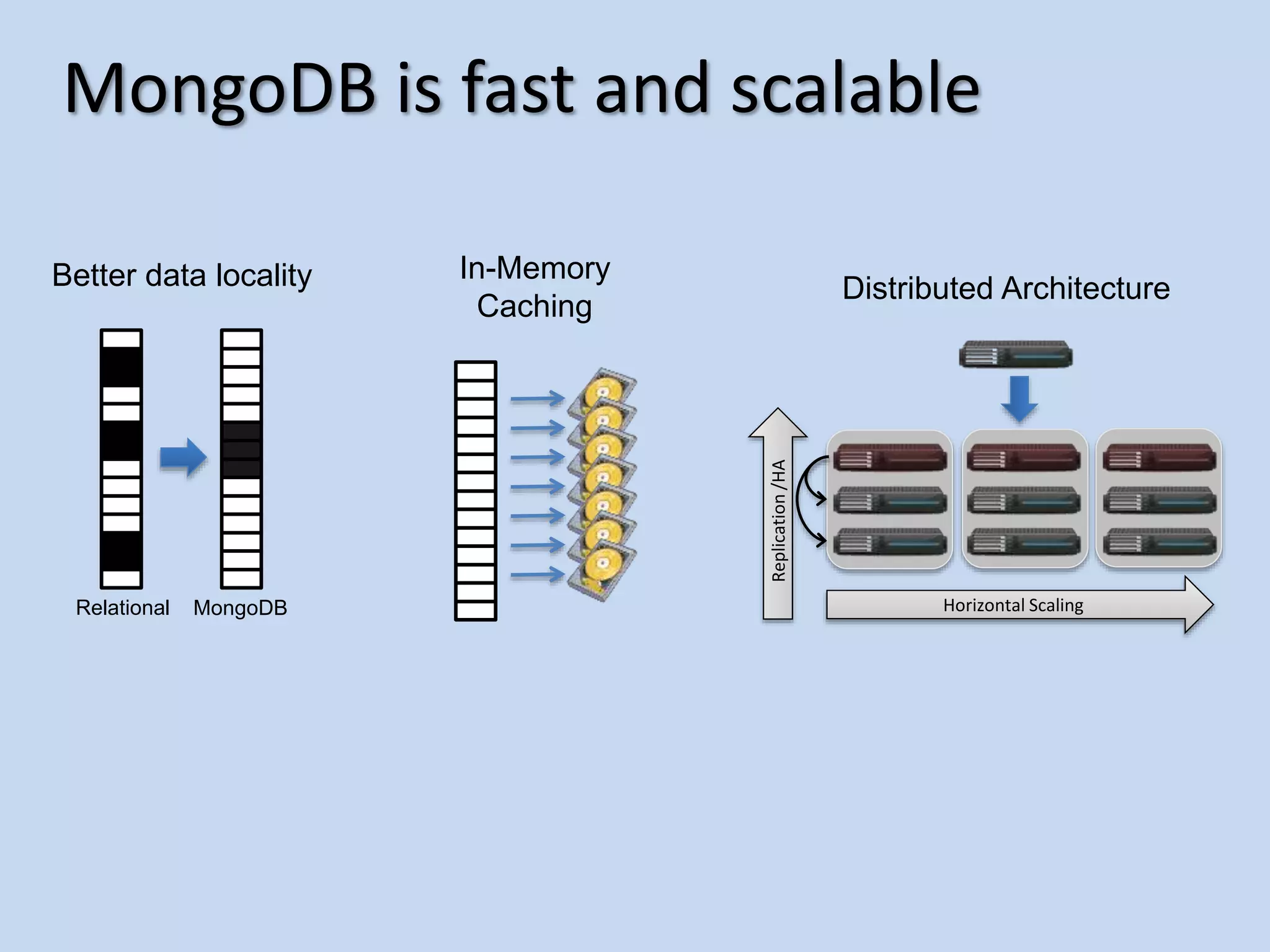
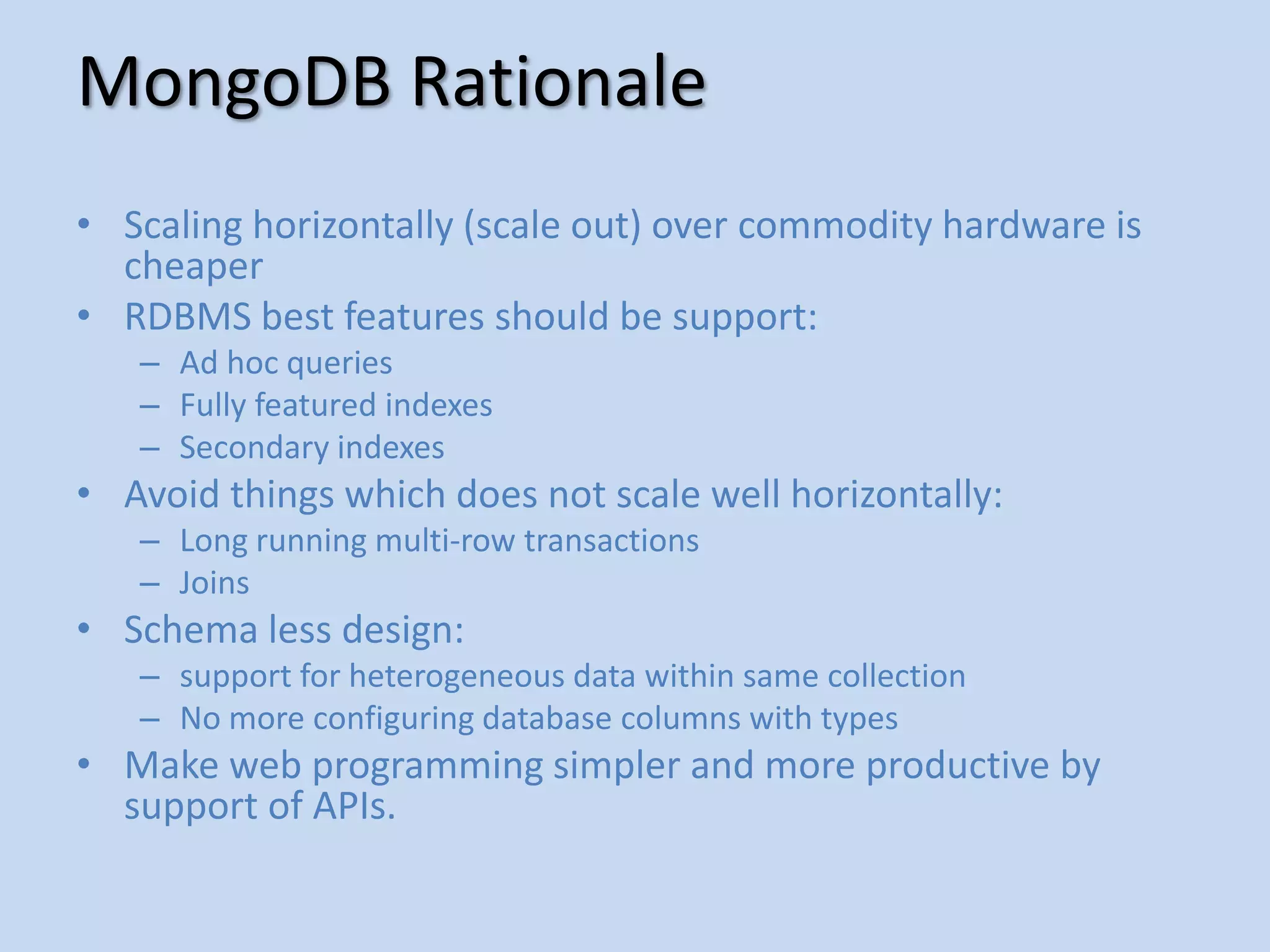
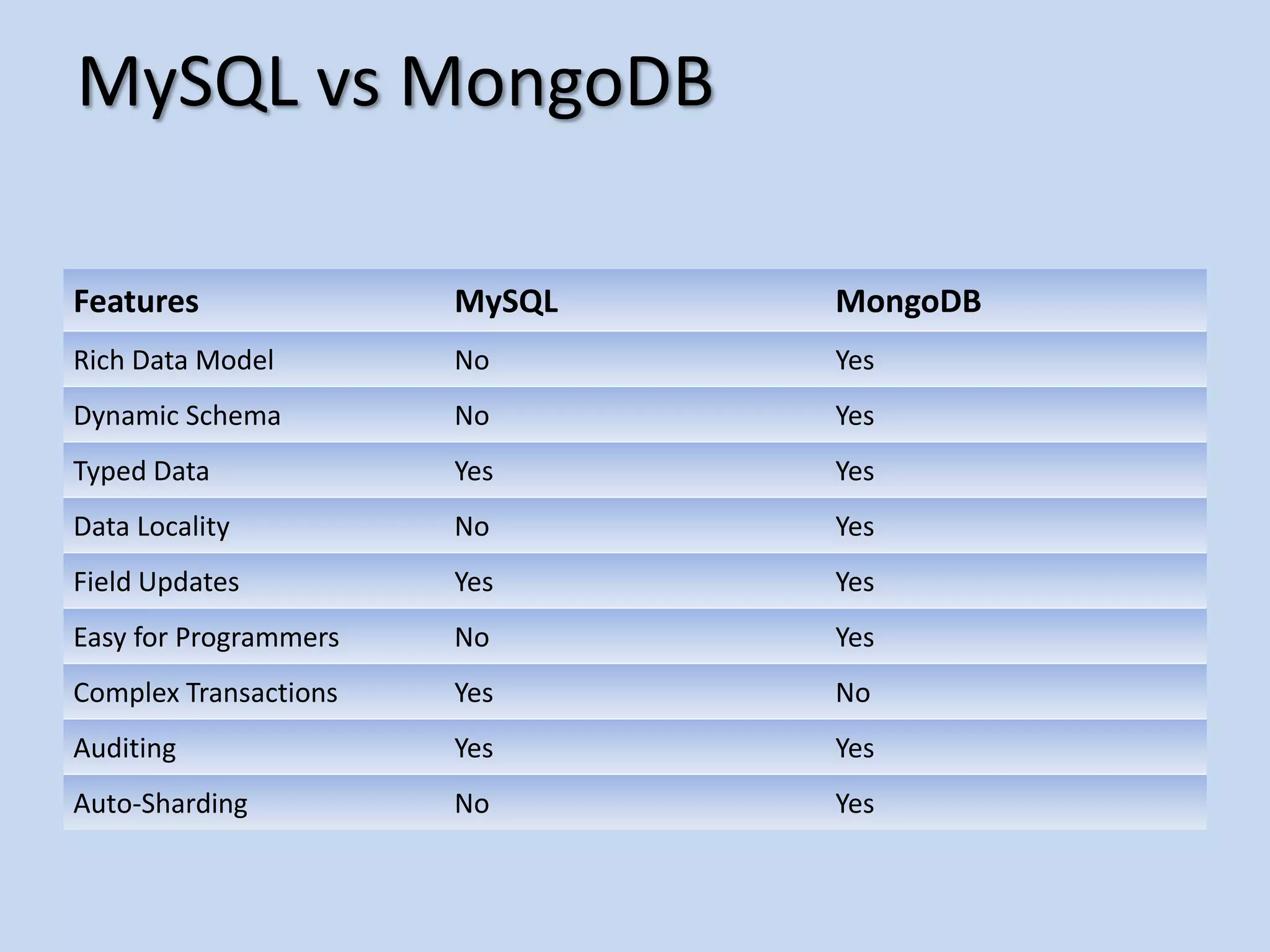
This document provides an agenda for introducing MongoDB. It discusses how MongoDB is a general purpose, document-oriented database that is easy to use, fast, scalable, and supports sophisticated queries and indexing. It compares MongoDB to relational databases and how MongoDB supports a dynamic schema and embedding of documents.



![• MongoDB does not need any pre-defined data schema • Every document could have different data! MongoDB- Schema less name: “Kartik”, color: “Red”, loc: [40.7, 73.4], Hobbies: “cycling”} {name: “Avinash”, aliases: [“Avi”]} name: “Ram”, HasHat: ”yes”} {name: “Manish”, Food: “Pasta”, height: 172, loc: [44.6, 71.3]} {name: “Rajesh, color: “blue”, birthplace: “NY”, aliases: [“Raj”, “limbo”], loc: [32.7, 63.4]}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6aa0f61a-e04e-447b-a224-b62b2659431e-150811201250-lva1-app6892/75/mongodb_Introduction-9-2048.jpg)