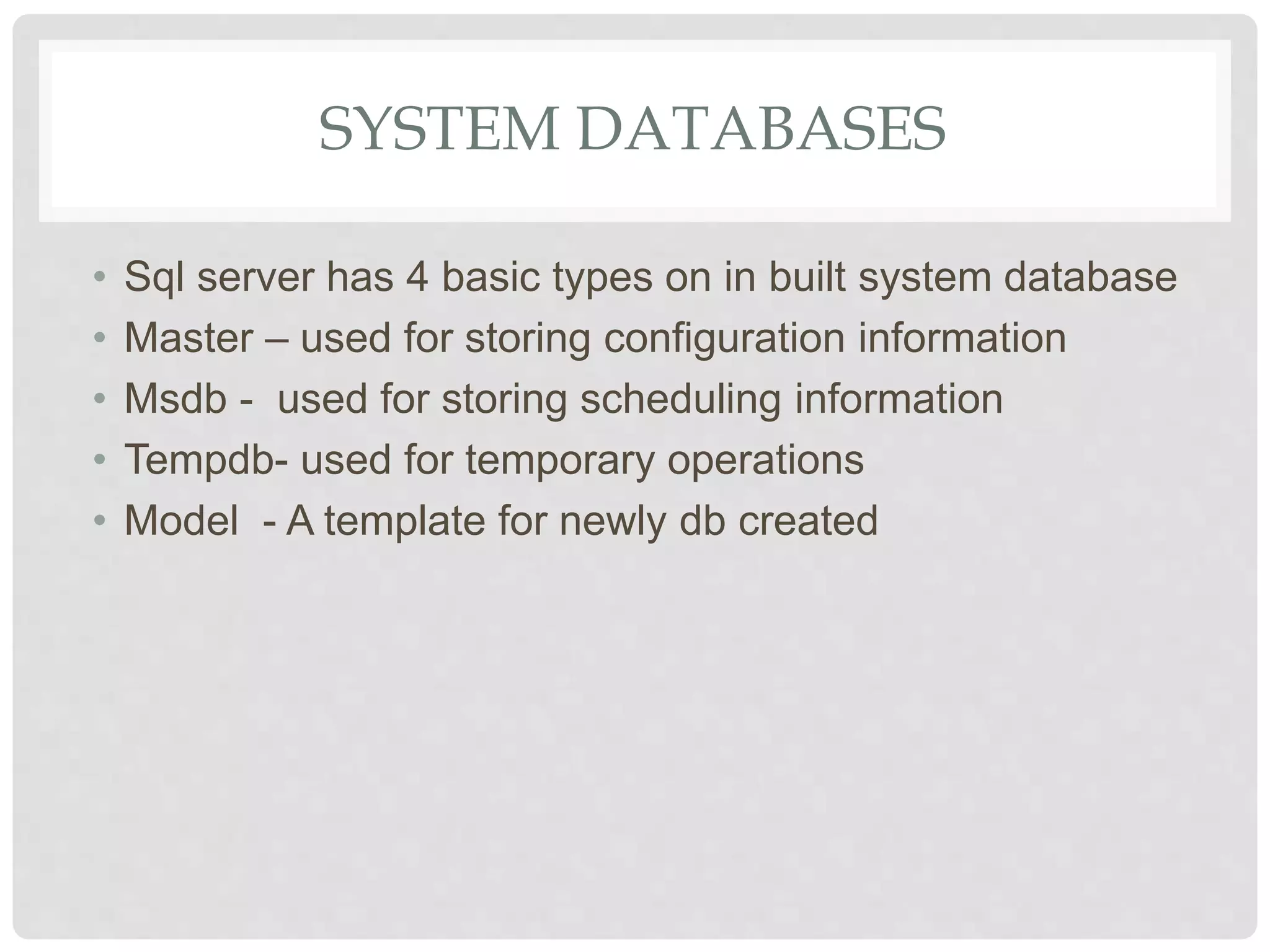
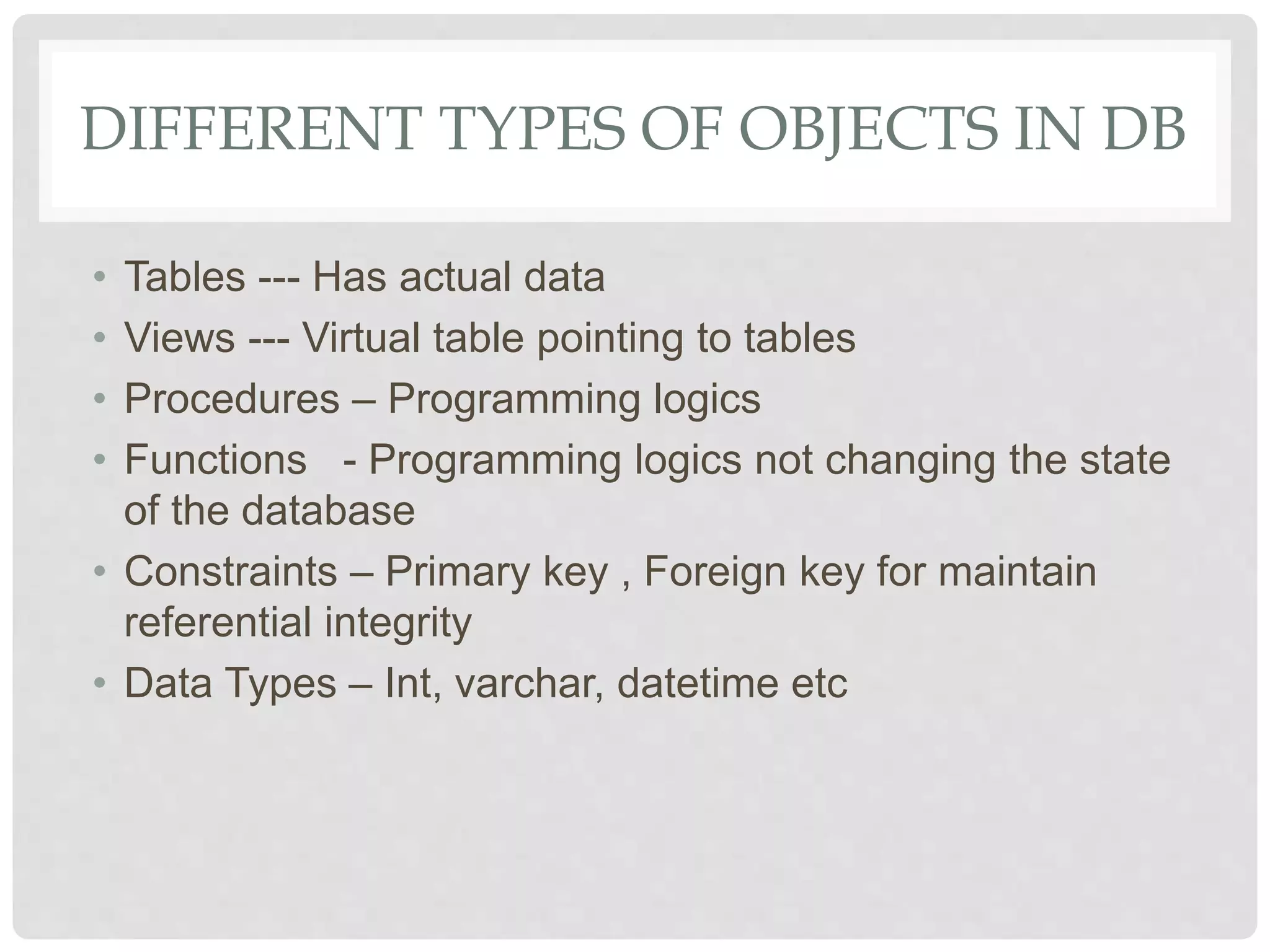
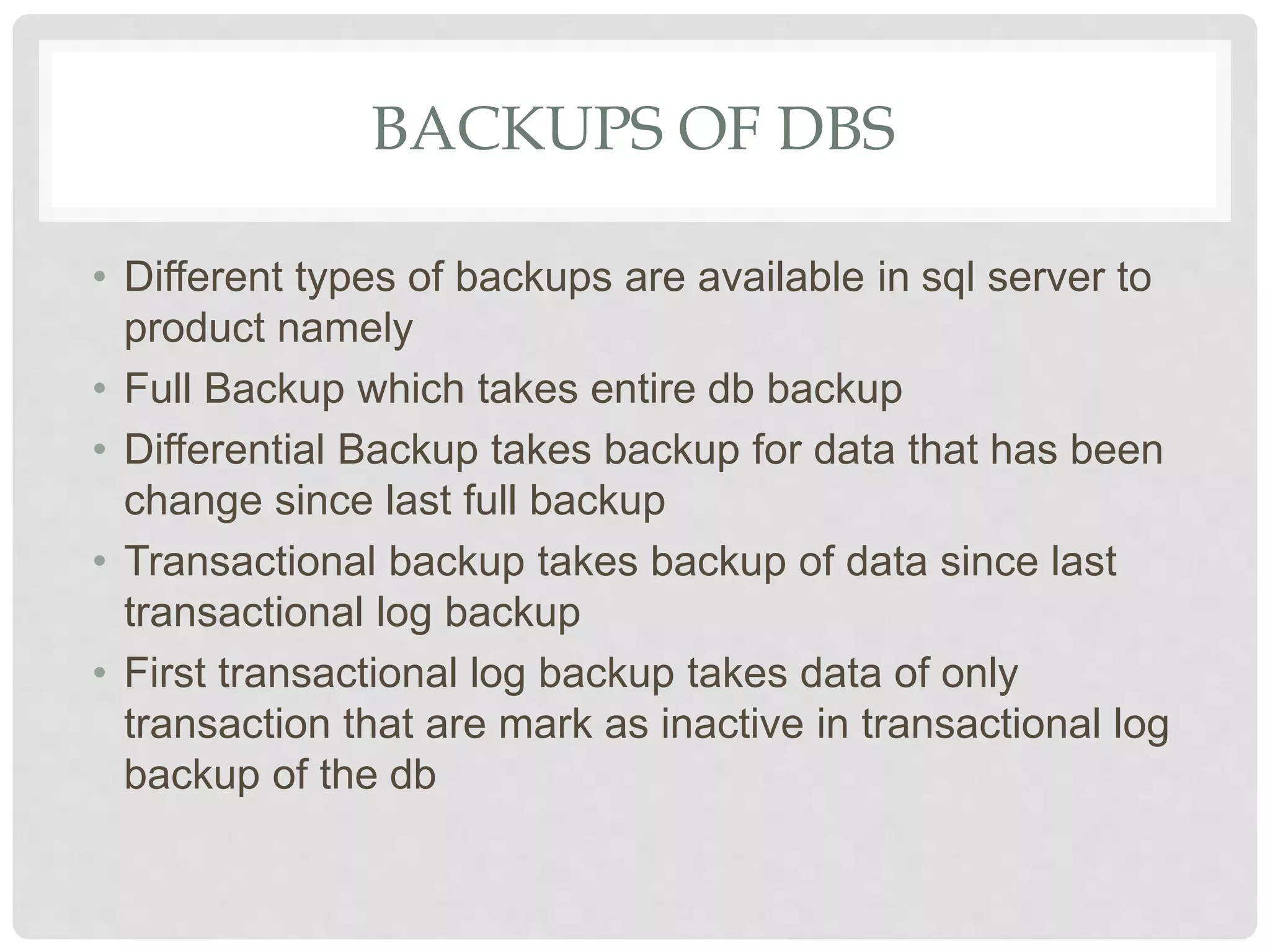
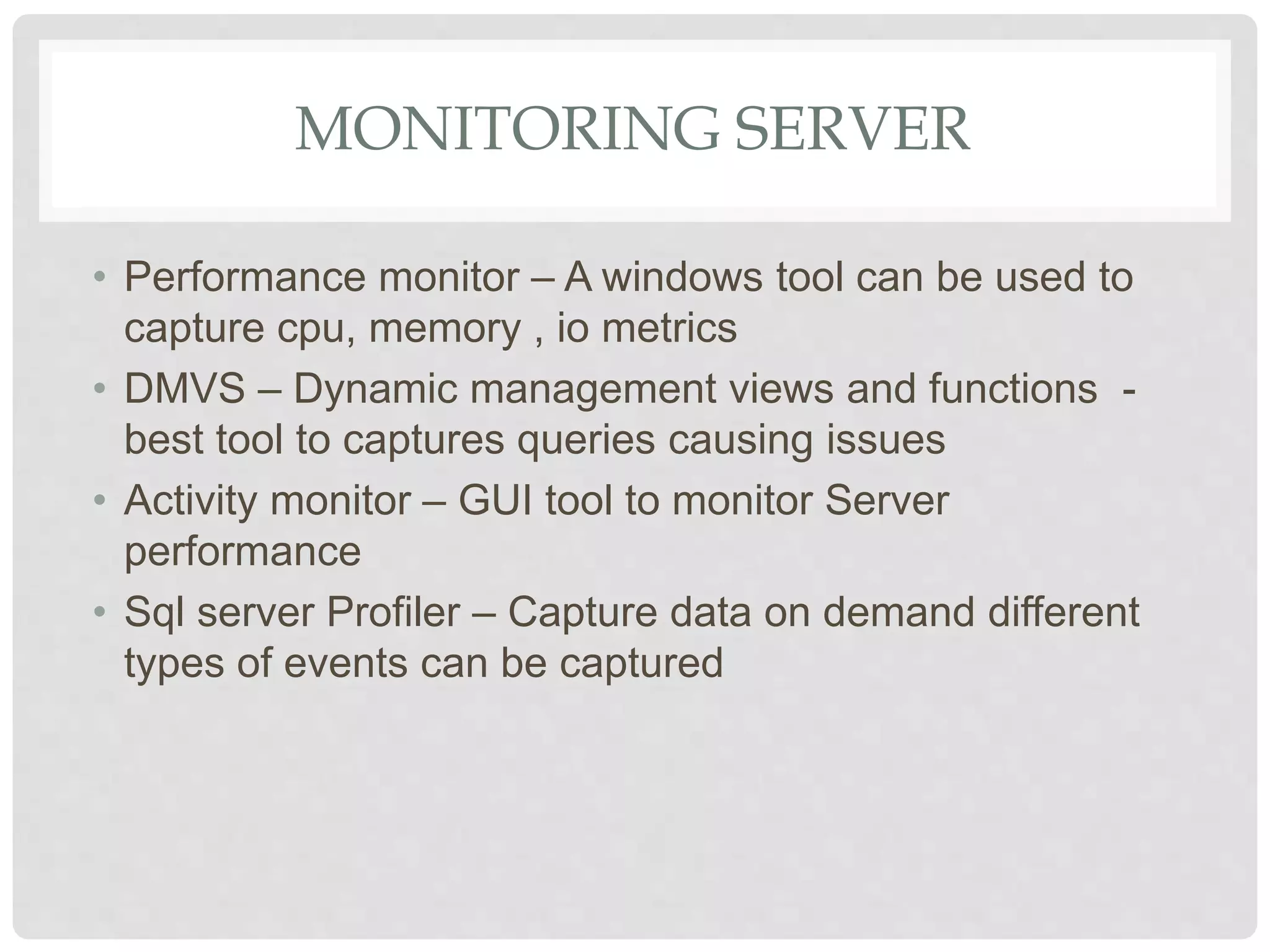
This document provides an overview of Microsoft SQL Server, including its installation, administration, and various high-availability solutions. It discusses key components such as system databases, indexing for performance, backup types, and automation of daily tasks through SQL Server Agent. Additionally, it covers monitoring tools and new features in SQL Server, enhancing performance and usability.