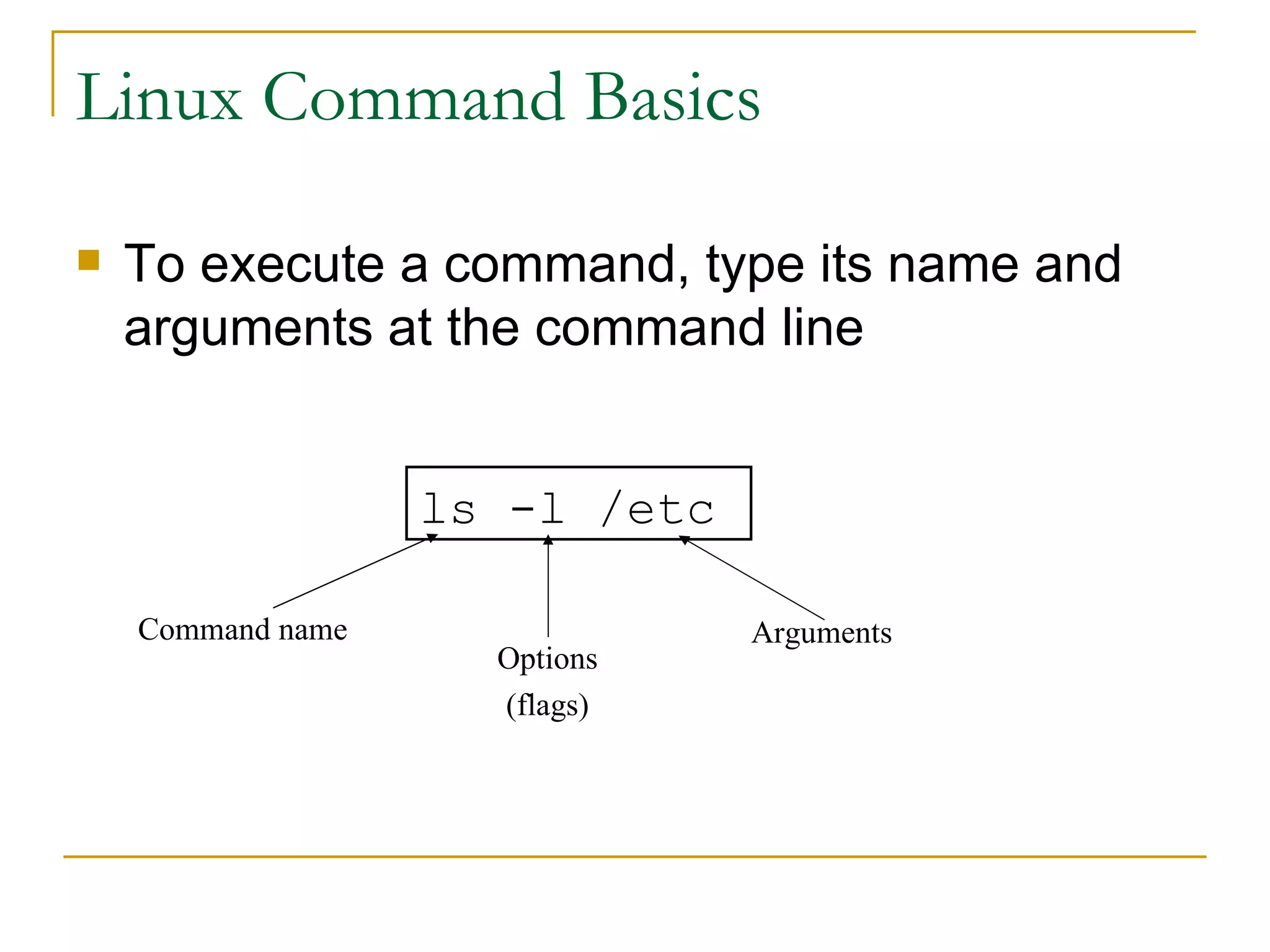
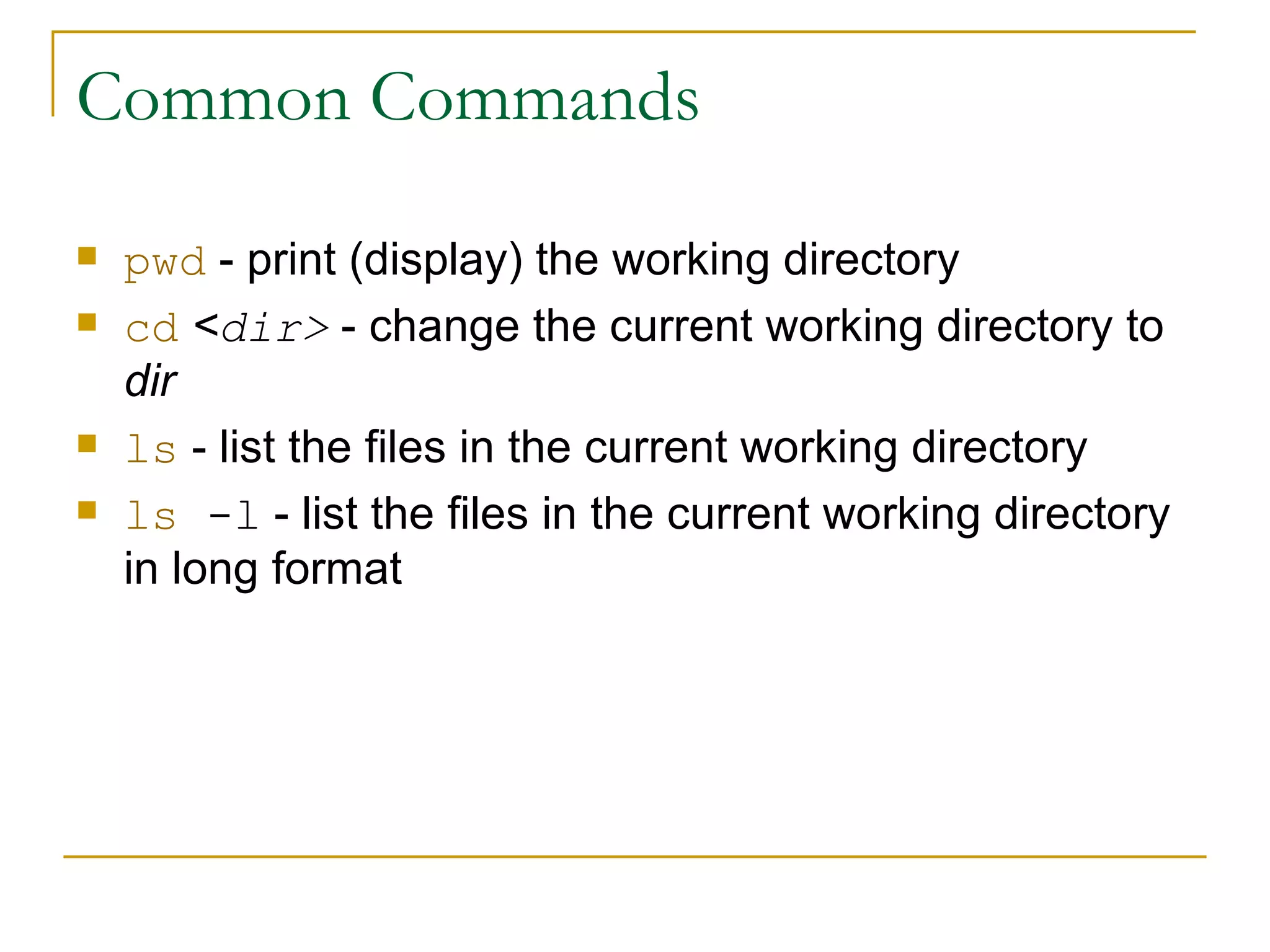
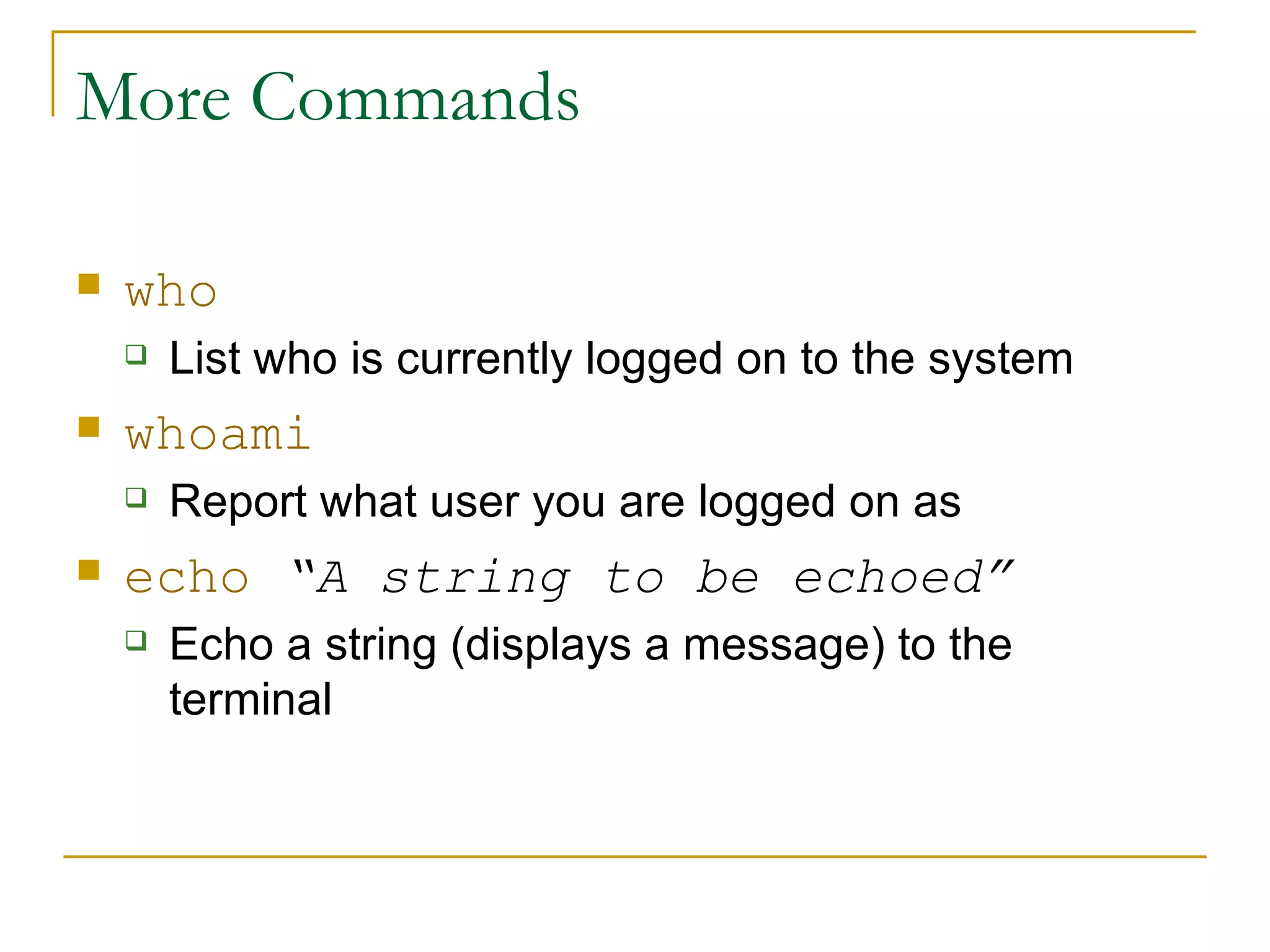
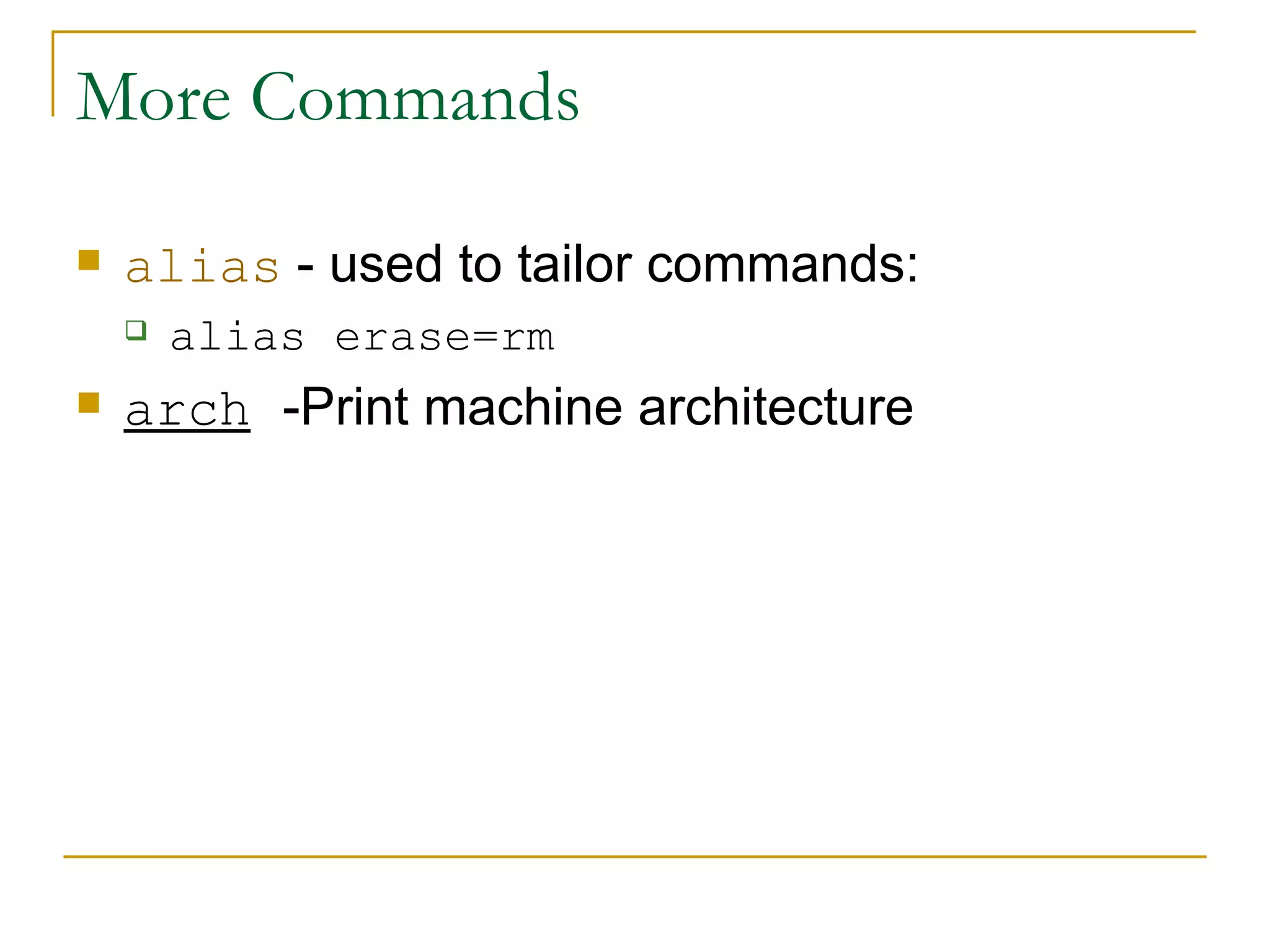
The document provides an overview of common Linux commands, including commands for executing other commands, navigating directories, listing and copying files, managing users and permissions, searching for files, processing text, managing archives, and compressing files. Examples are given for commands like ls, cd, cp, mv, rm, who, echo, alias, awk, chown, diff, grep, pushd, kill, df, cat, tar, gzip, su. Brief descriptions are provided for most commands and references are given at the end for additional Linux resources.