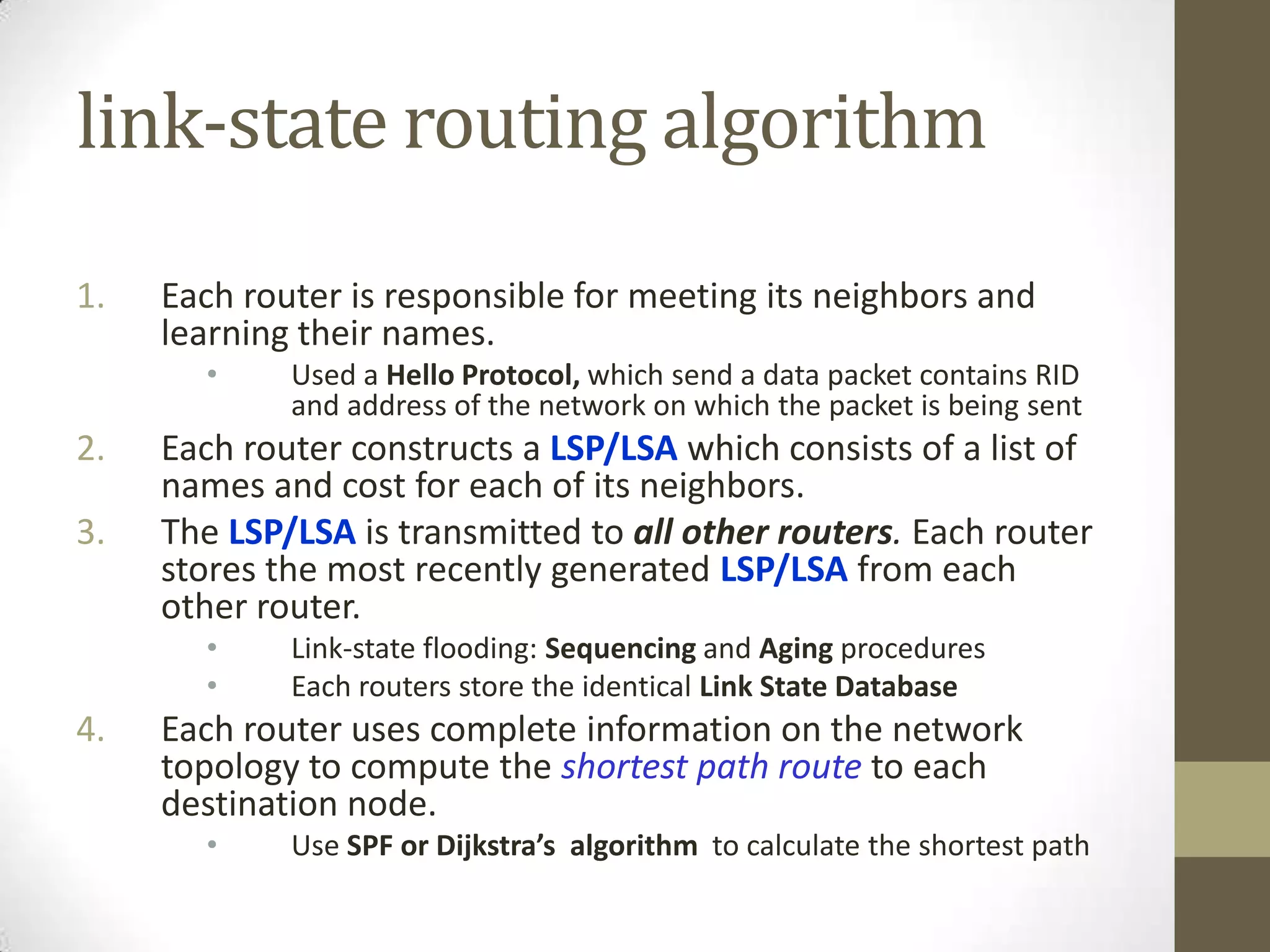
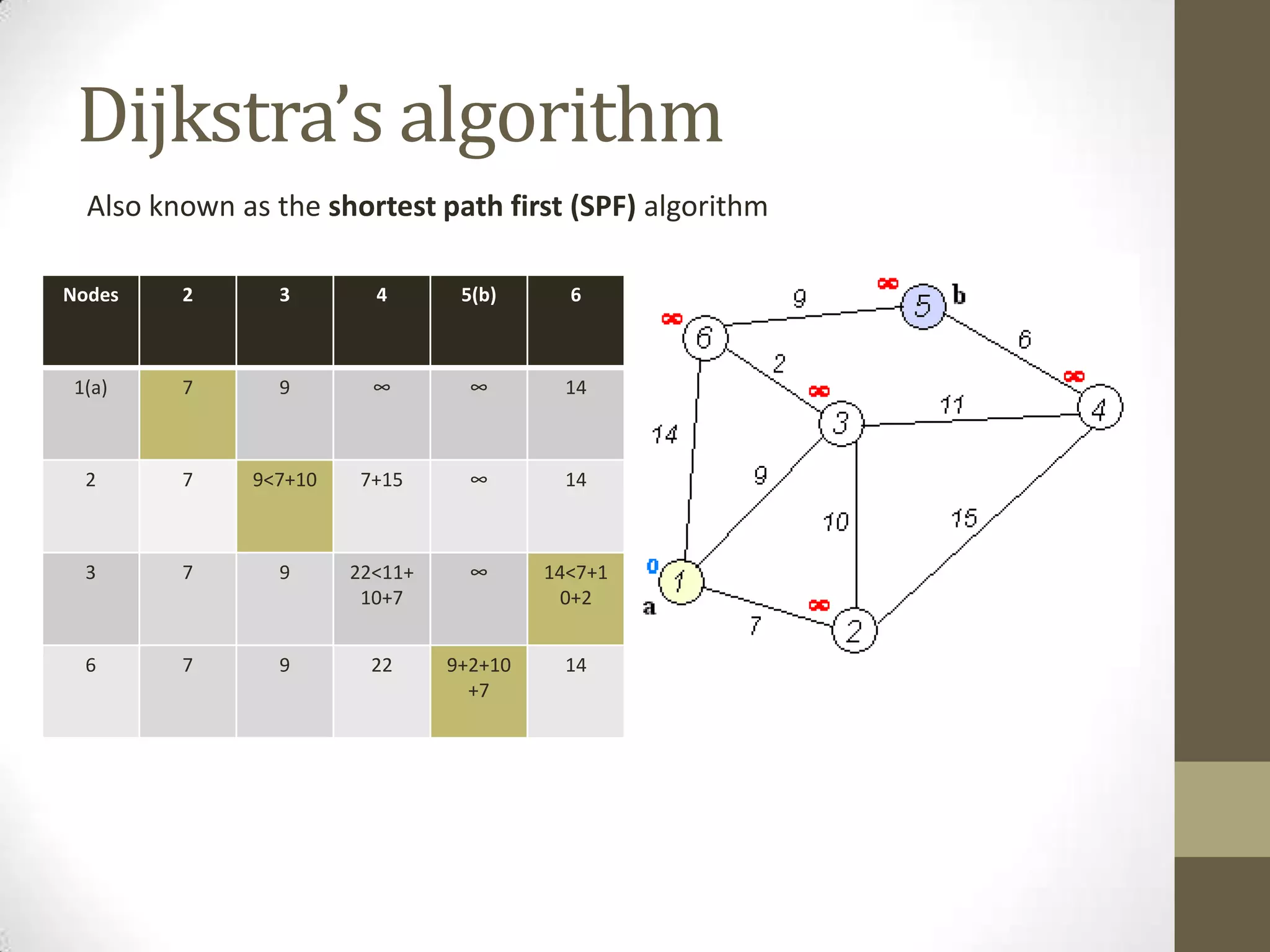
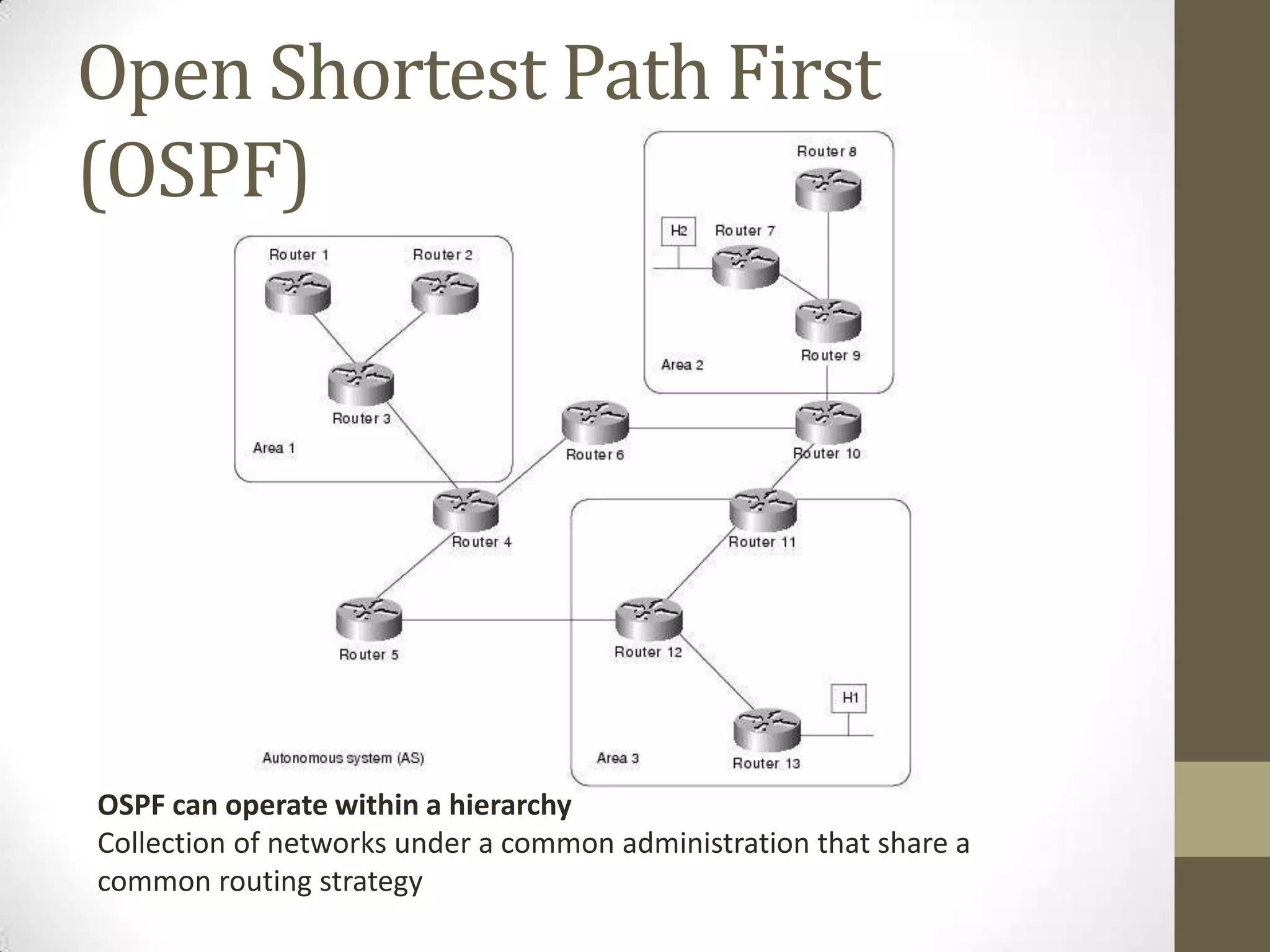
Link-state routing protocols use Dijkstra's algorithm to calculate the shortest path to all destinations based on a link-state database containing the full network topology. Each router runs the same algorithm locally to determine the optimal path. Key aspects include link-state advertisements to share connectivity information, the topological database to store network maps, and shortest path first calculations to derive routes. Common link-state protocols are OSPF and IS-IS. They provide fast convergence and scalability but require more resources than distance-vector protocols.