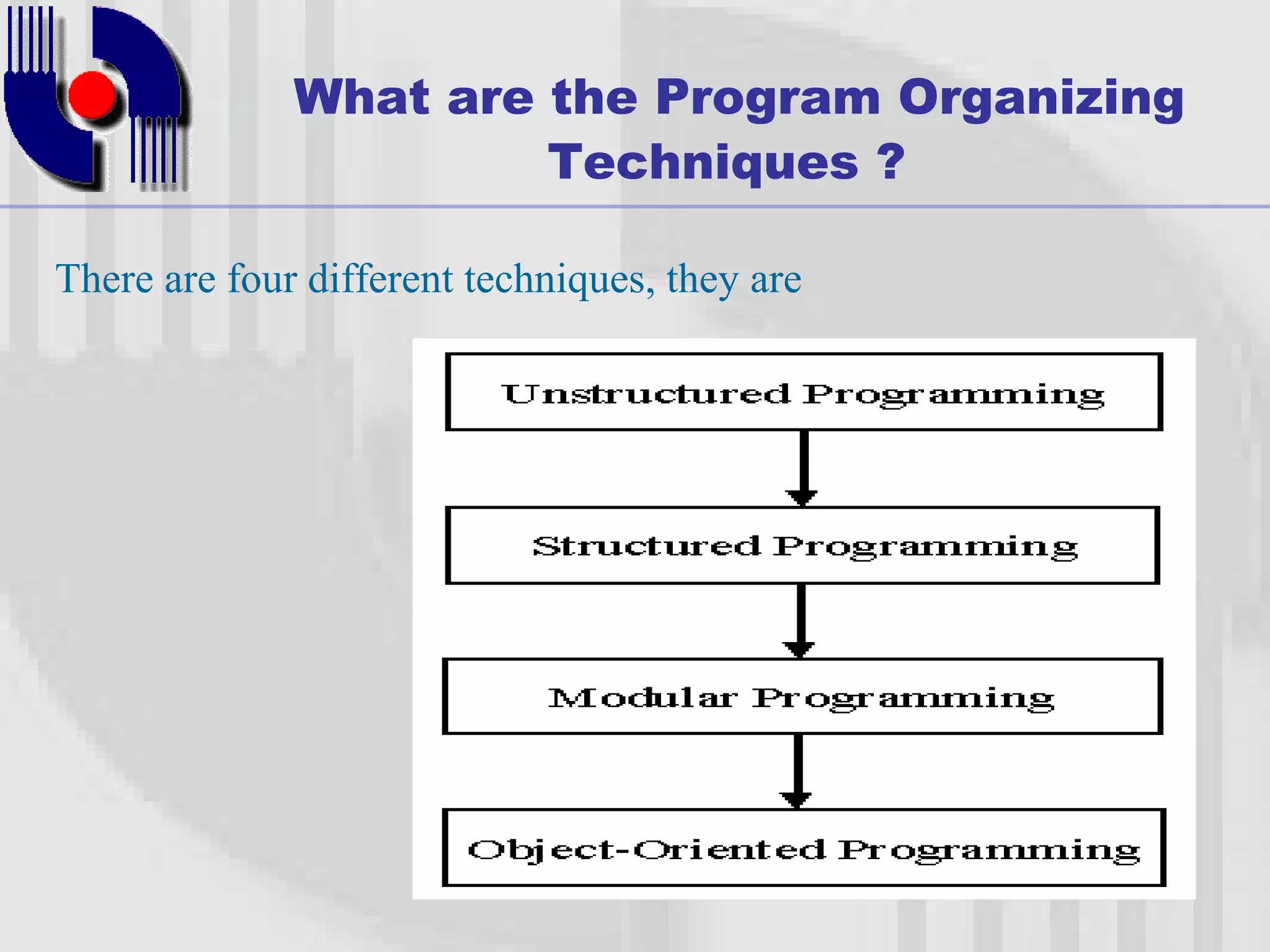
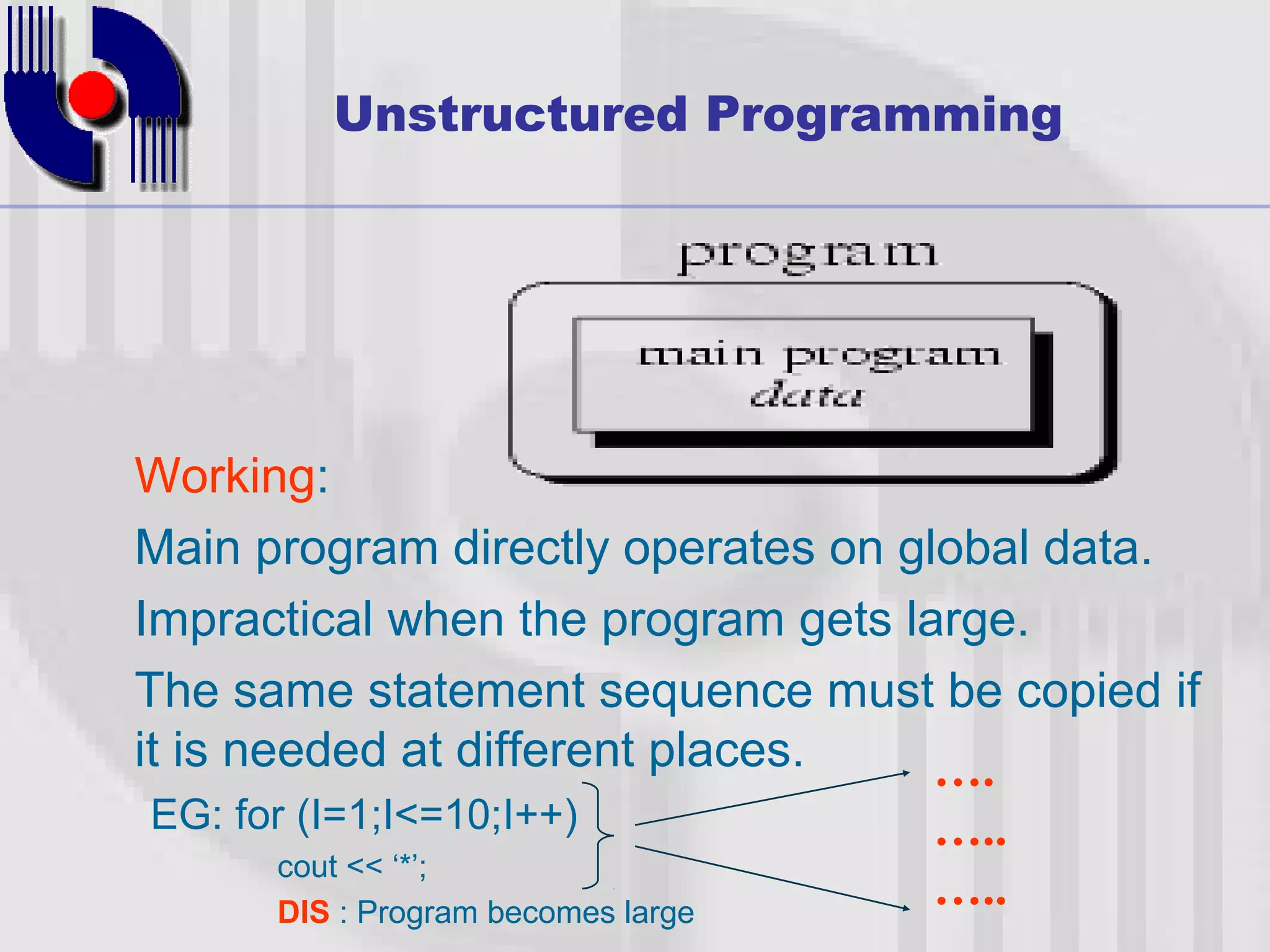
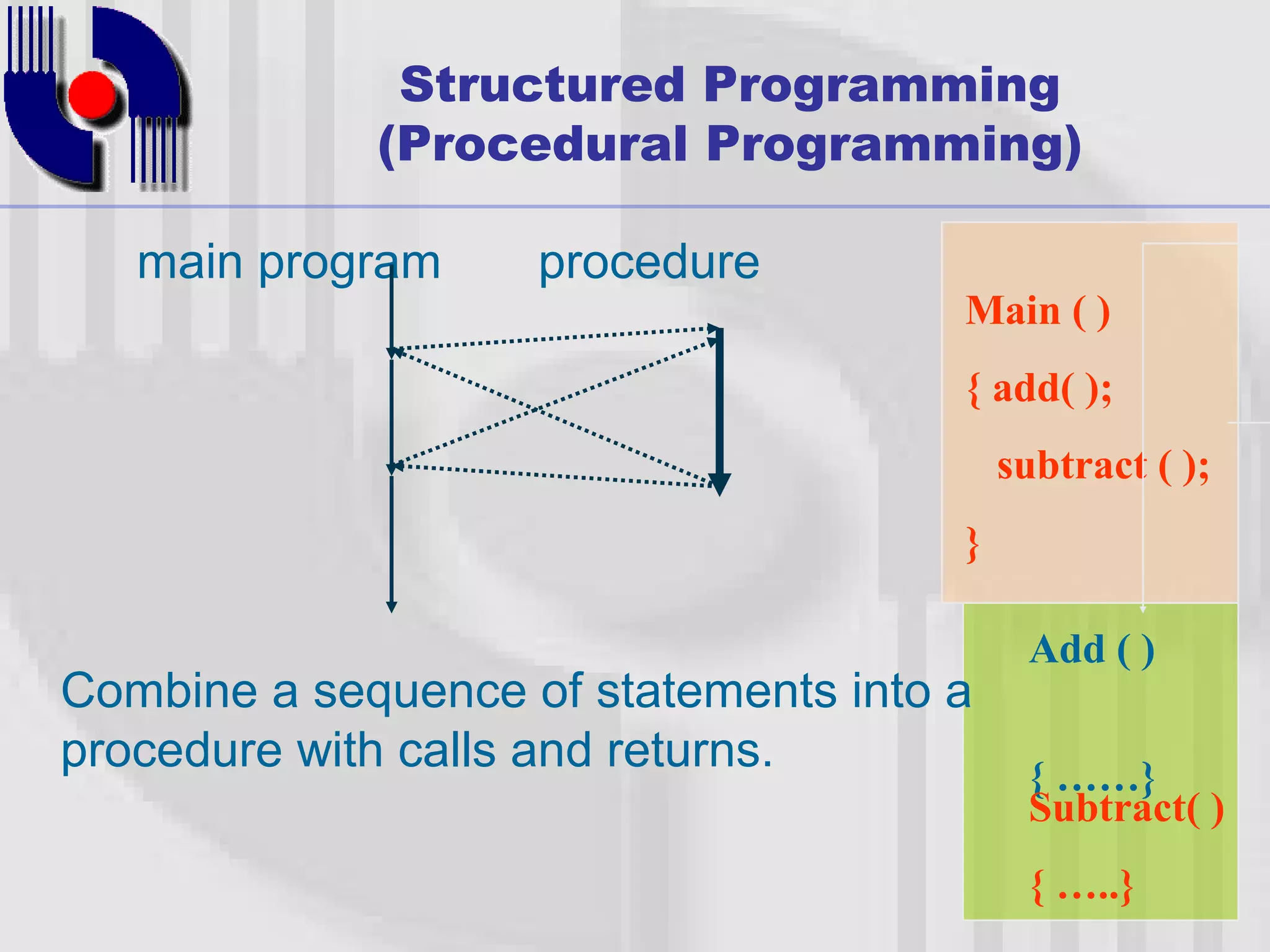
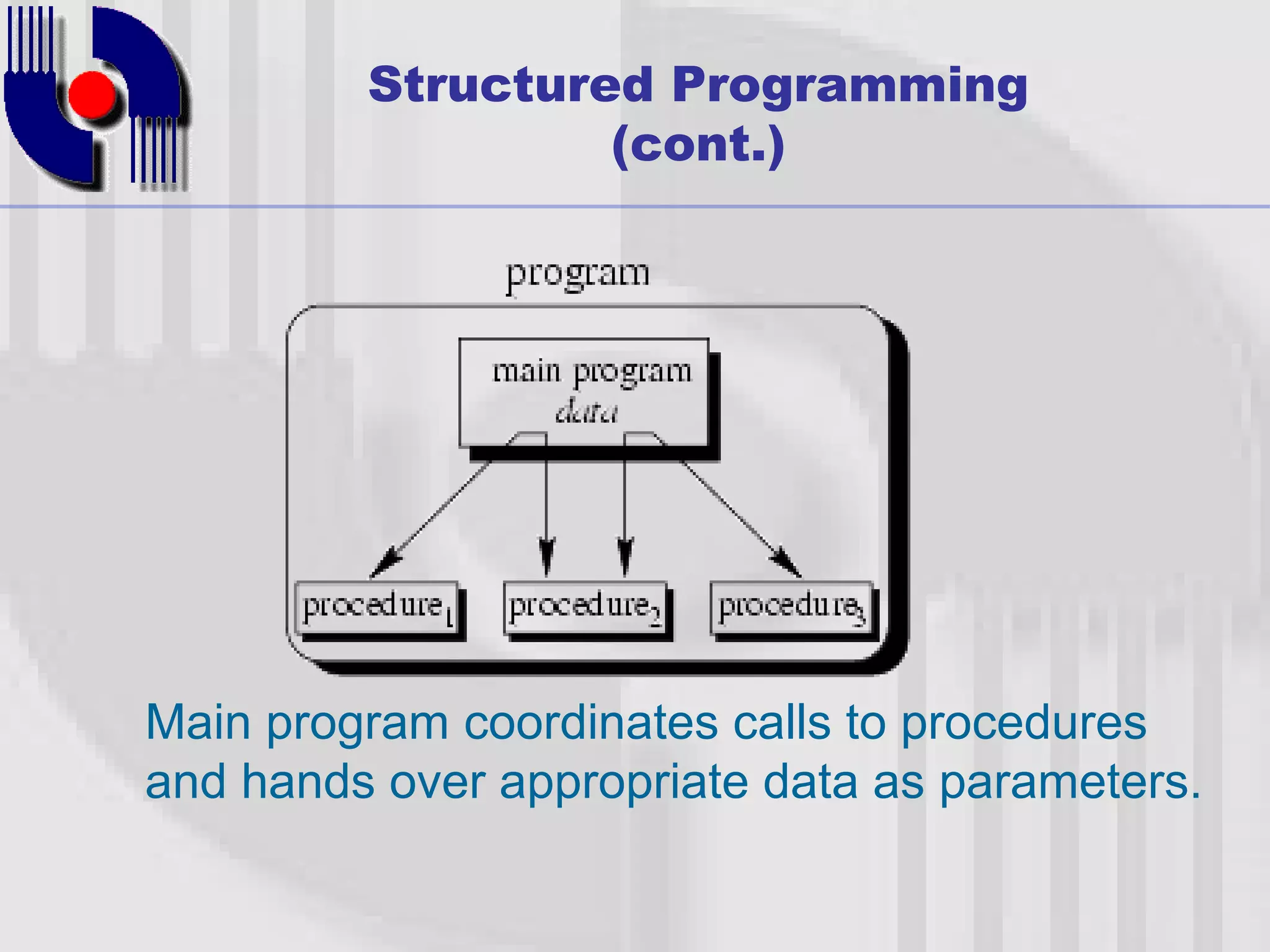
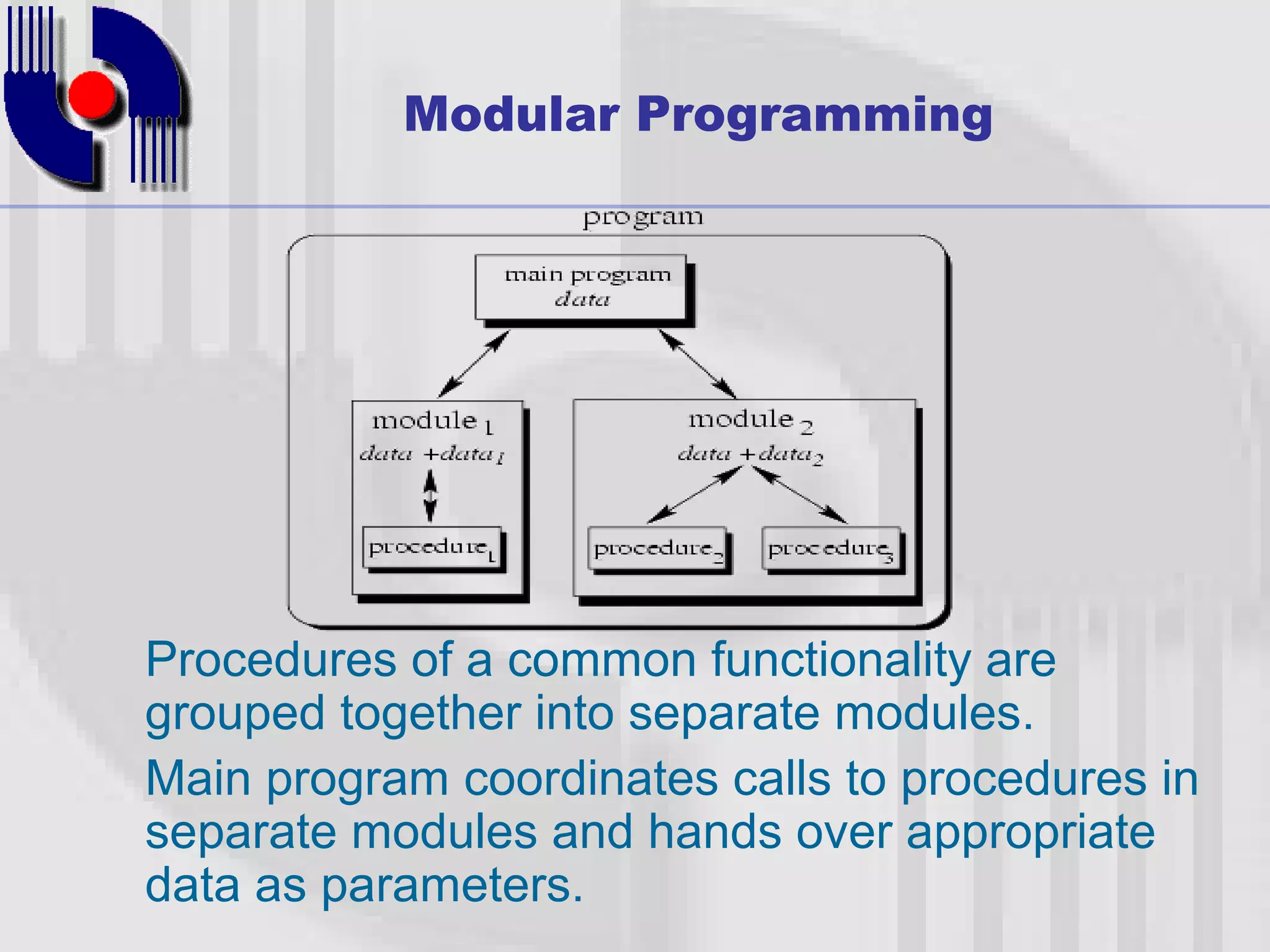
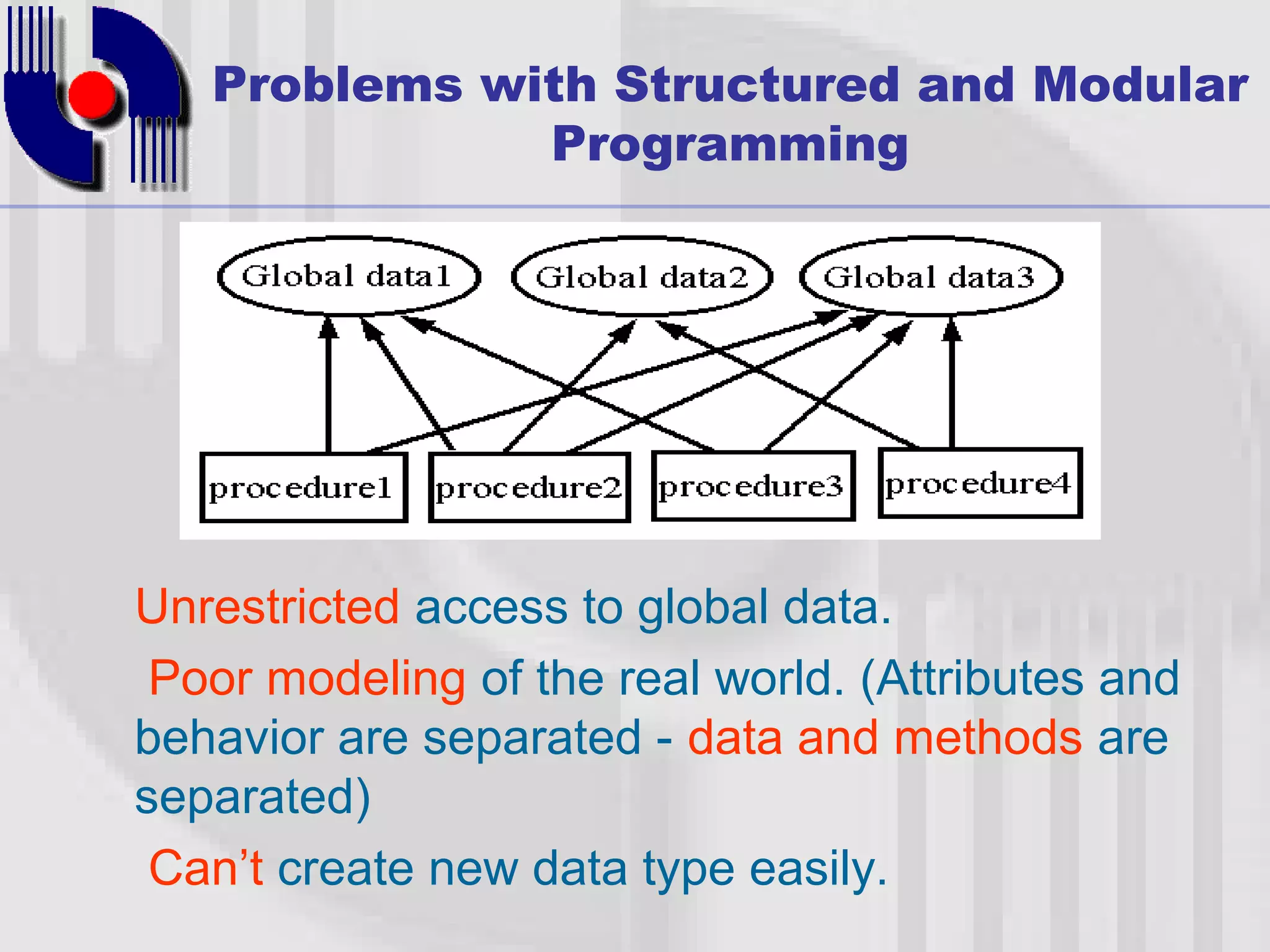
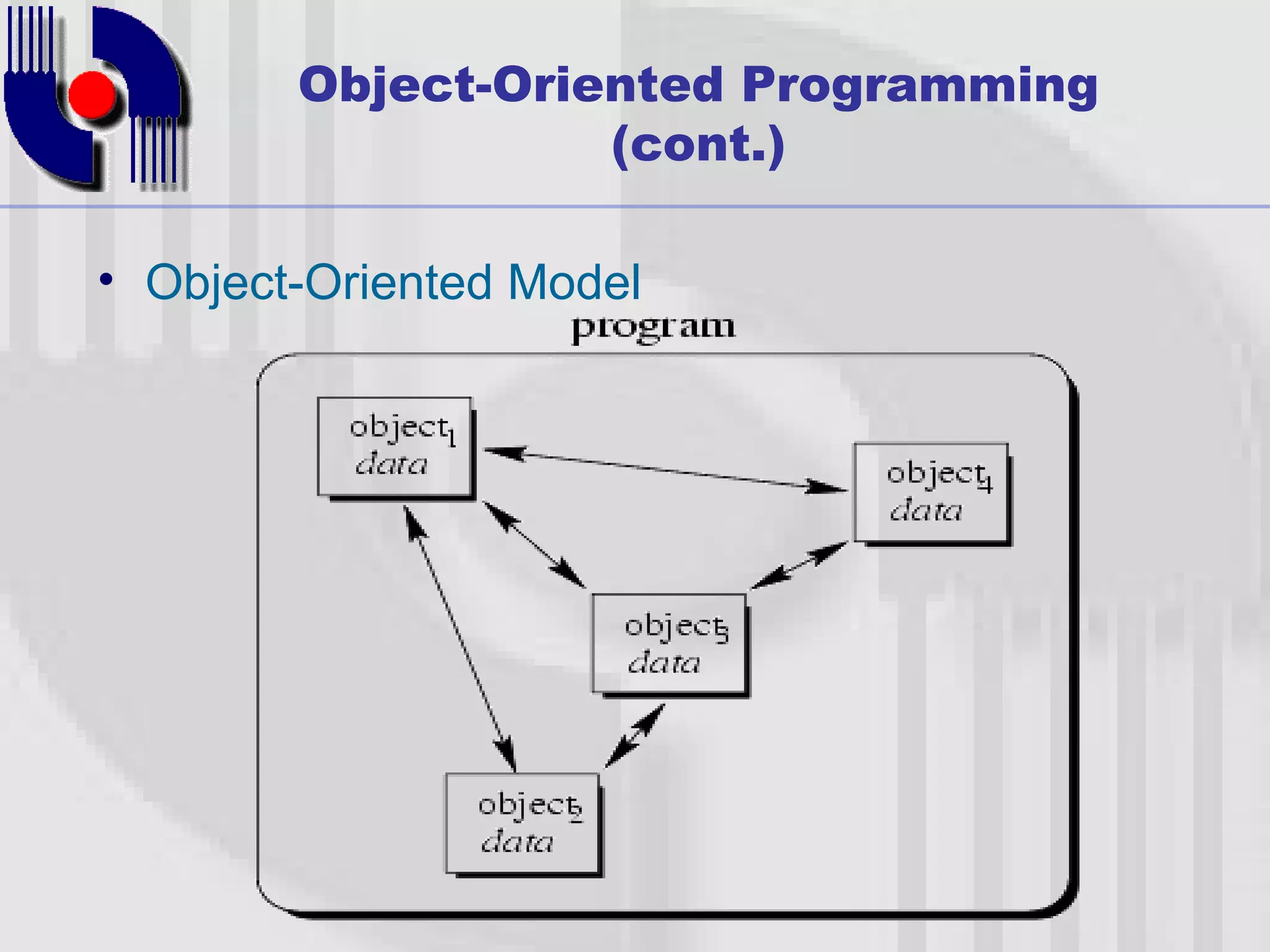
This document introduces four techniques for organizing programs: unstructured programming, structured programming, modular programming, and object-oriented programming. Structured programming involves combining statements into procedures that are called from the main program. Modular programming further groups related procedures into separate modules. Object-oriented programming combines data and functions into objects, encapsulating data and hiding it within member functions, allowing objects to interact by sending messages.