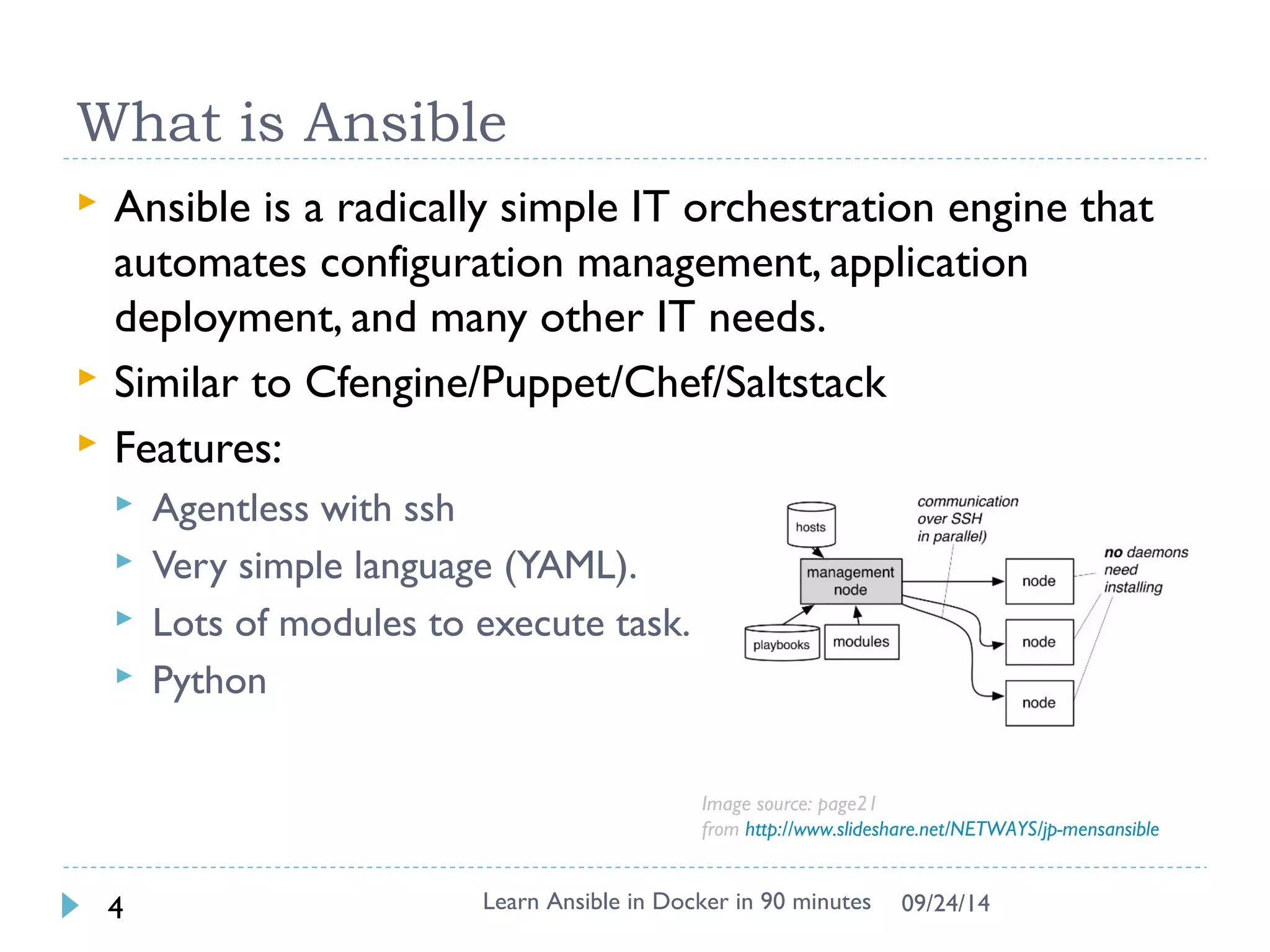
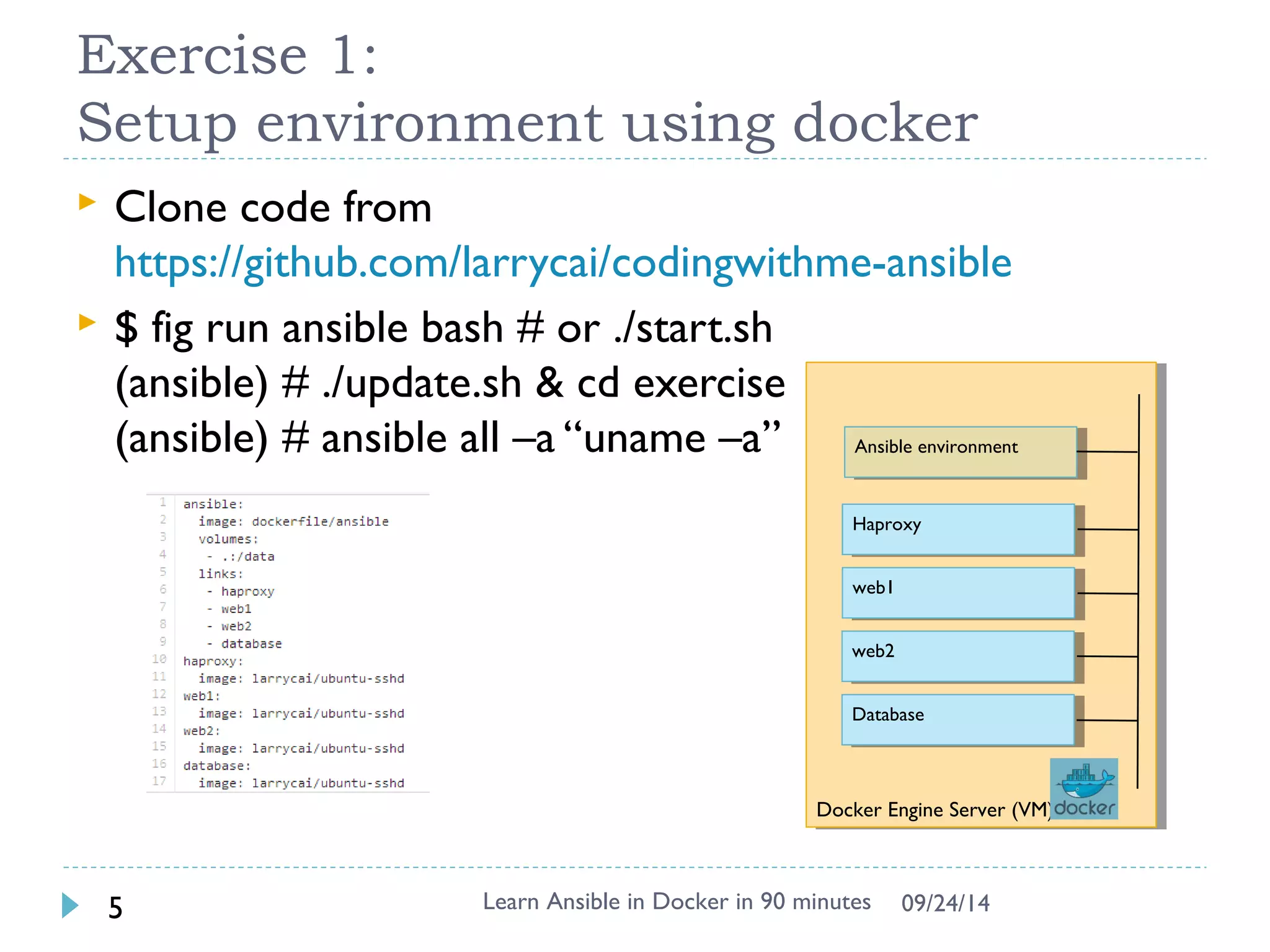
The document outlines an 90 minute introduction to Ansible using Docker. It discusses setting up the environment with Docker, using ad-hoc commands and playbooks to automate tasks like installing Apache and configuring variables. Exercises demonstrate inventory management, templating configurations with Jinja2, and other core Ansible concepts. The document provides an overview but does not cover more advanced topics like dynamic inventory, roles, writing custom modules, or Ansible Tower.




![Inventory & ad-hoc command hosts: Inventory is host list ansible.cfg: define An ad-hoc command is something that you might type in to do something really quick, but don’t want to save for later. $ ansible <host patterns> [options] $ ansible web –m command –a “uname –a” -m module name, default is command -I inventory name, defaults is set in ansible.cfg or /etc/ansible/hosts -a module args See http://docs.ansible.com/intro_adhoc.html Learn Ansible 7 in Docker in 90 minutes 09/28/14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learnbasicansibleusingdocker-140924040706-phpapp01/75/Learn-basic-ansible-using-docker-7-2048.jpg)