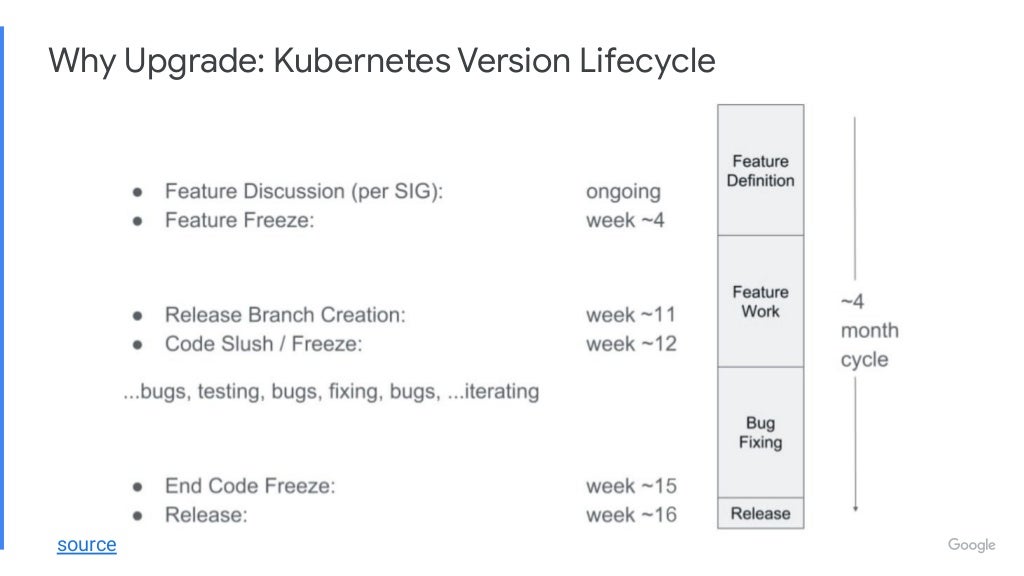
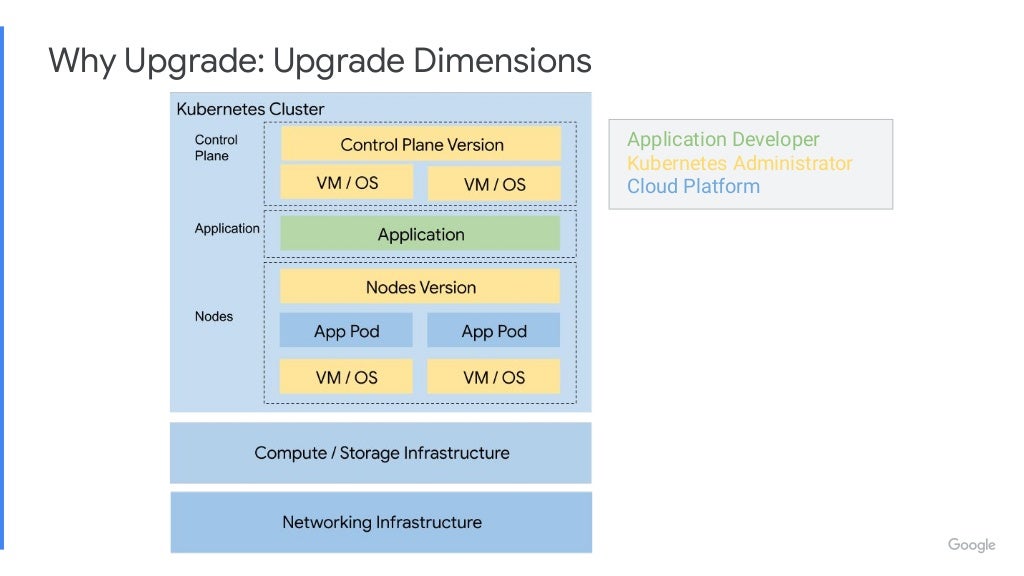
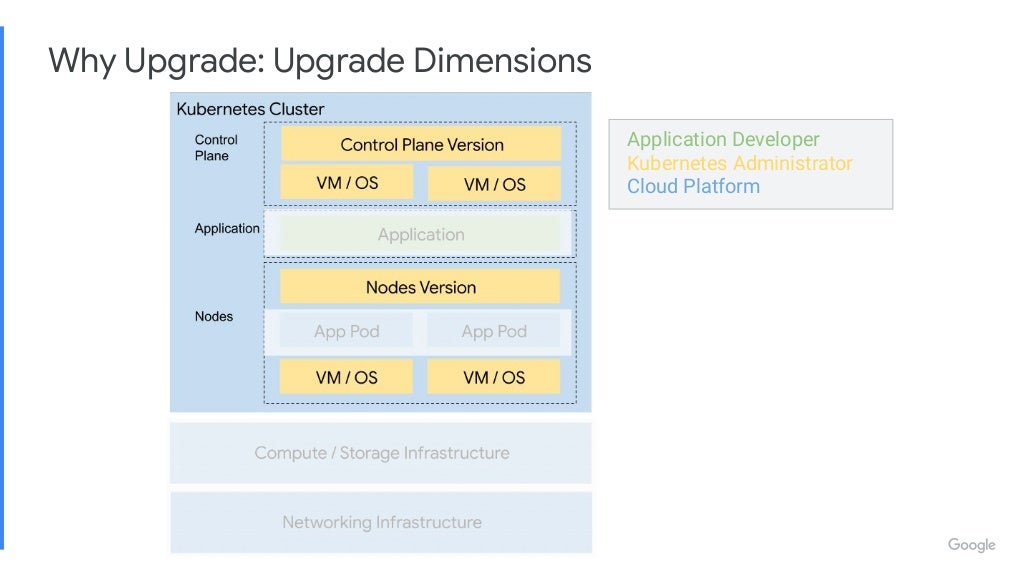
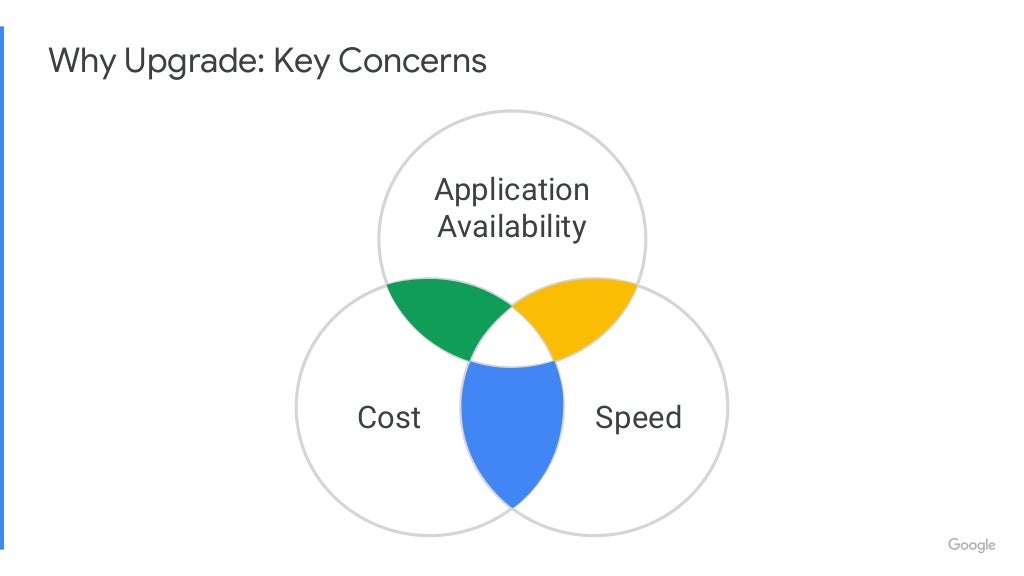
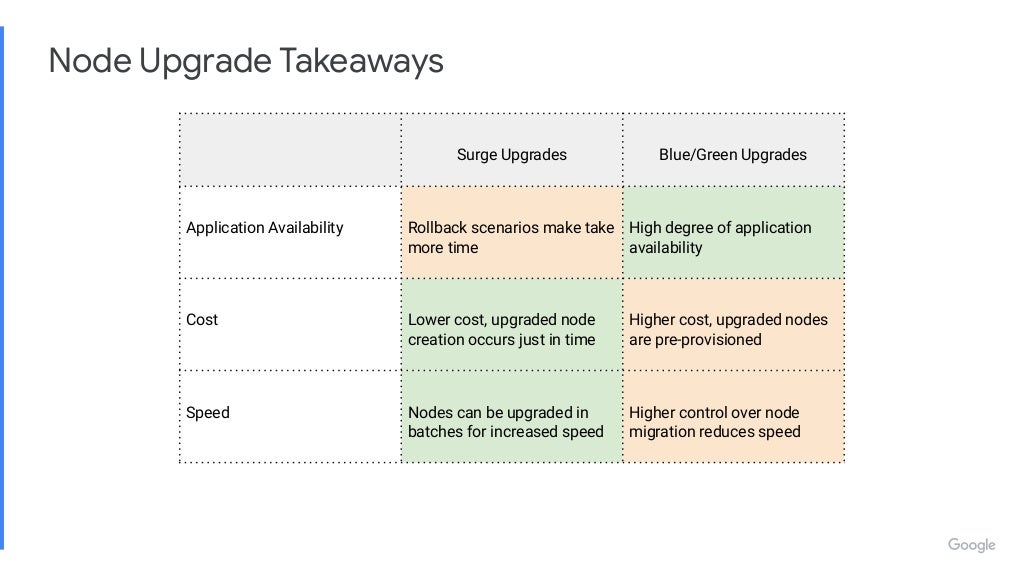
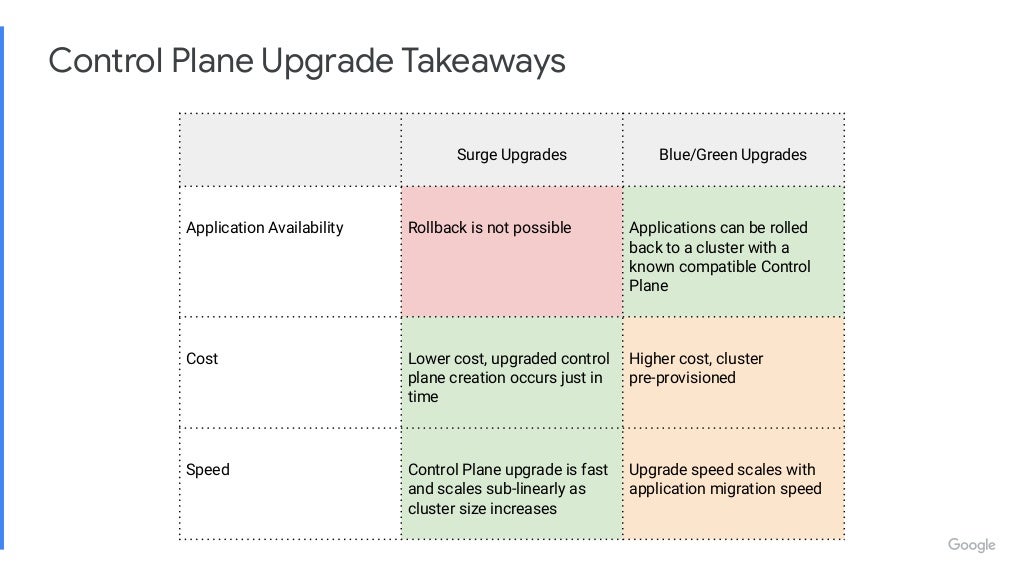
Link: https://youtu.be/qUW8LkxYayc https://go.dok.community/slack https://dok.community/ ABSTRACT OF THE TALK How do you make sure your Stateful Workloads remain available when your Kubernetes infrastructure updates? This talk will discuss different strategies of upgrading a Kubernetes cluster, and how you can manage risk for your workload. The talk will showcase demos of each upgrade strategy. BIO Peter is a Senior Software Engineer on GKE at Google. He works on improving Kubernetes for Stateful workloads. His main focus is on enhancing the Kubernetes ecosystem for high availability applications. KEY TAKE-AWAYS FROM THE TALK The mechanics of different upgrade strategies, when to apply a particular upgrade strategy depending on your Stateful workload and how to mitigate risk to your application’s availability.