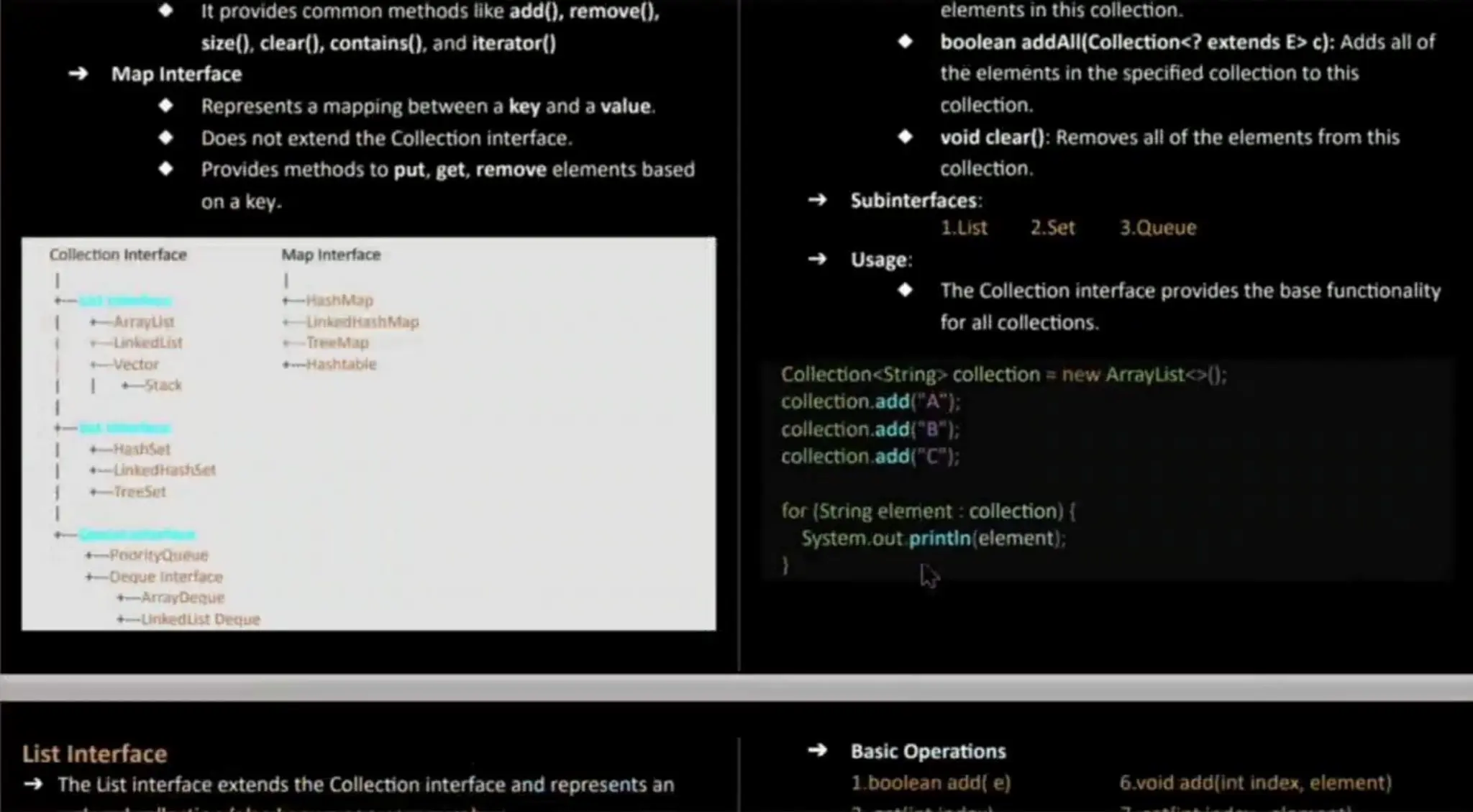
The document provides an overview of the Java Collections Framework, which offers a structured architecture for storing and manipulating groups of objects. It details various collection types such as lists, sets, queues, and maps, along with their methods and implementations, including ArrayList, LinkedList, HashSet, and HashMap. Key points include the ability of collections to dynamically resize, operations for adding and removing elements, and the significance of interfaces such as Iterator for traversing collections.


![rviousndes()' Ne ( ) No set(E) No ArrayList ArrayList is a resizable array implementation of the List interface. It is part of the Java Collections Framework and is found in the java.util package. Arraylist allows for dynamic arrays that can grow asneeded, which means it can change its size during runtime. Key Points: Unlike arrays in Java, ArrayList can grow and shrink in size dynamically. Allows duplicate elements. Provides fast random access to elements. Initial capacity is 10, but it grows automatically aselementsare added. Key Points: Doubly Linked: Each element in a LinkedList is stored in a node that contains a reference to the next and previous elements. Dynamic Size: Can grow and shrink dynamically. Allows duplicate elements. Efficient for adding or removingelementsanywhere in the list. Slowerthan ArrayList for random access (get(), as it requires traversing from the head or tail. Basic Operations: (SameasArraylist ) import java.util.: public class LinkedListExample ( public static void main(Stringl] args) { 1/Create oLinkedList LinkedList<String> linkedlist = new LinkedList<>): HAdding elements linkedList.add("Apple"); linkedList.add("Banana"); linkedList. add("Cherry" ); import java. util.Vector; public classVectorExample { public staticvoid main (String|] args) {](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaunit4-240725202854-6e239b07/75/java-unit-4-pdf-about-java-collections-5-2048.jpg)
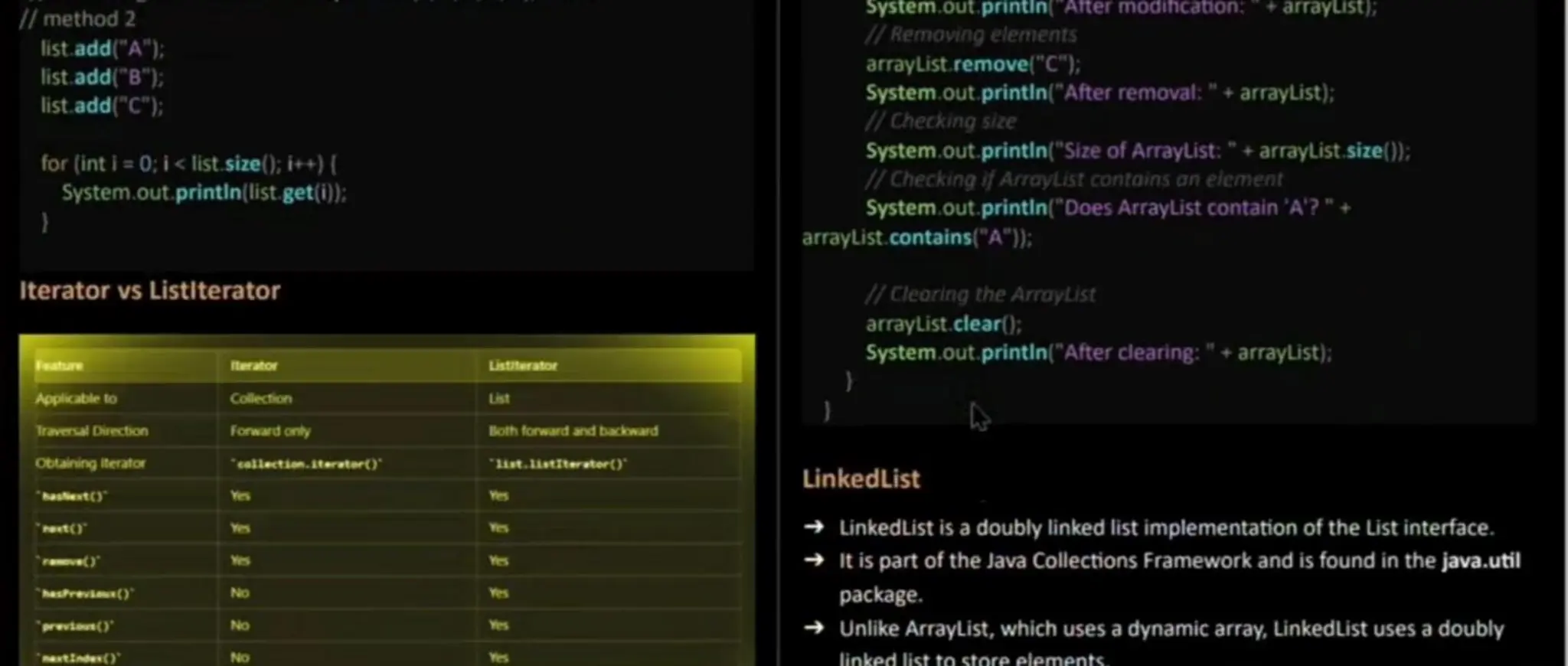
![orderedcollection (also known asa sequence). The user can access elementsby their integer index (position in the list) and search for elementsin the list. Key Points: Methods: 2.get(int index) 3. remove(int index) 4. int size() 5. booleancontains(e) set(int index, element) 8.boolean remove(e) 9. void clear() void add(int index, E element):Inserts the specified elementatthe specified position in this list. E get(int index): Returns the elementat the specified position in this list. Eset(int index, E element): Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the specified element. E remove(intindex): Removes the element at the specified position in this list. int indexOf(object o): Returns the index of the first OCcurrence of the specified element in thislist. Listiterator<E> listlterator(): Returns a list iterator over the elementsin this list. Implementations: 1.ArrayList 2. LinkedList 3. Vector 4.Stack Usage: The List interface allows for ordered collections that can contain duplicate elements. List<String> list = new ArrayList<): I/ List<integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(5. 2. 8.13):method 1 import java. util." public class ArrayListExample { public static void main(String] args) { 7/Creating on Araylist List<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); 1/Adding elements arrayList.add("A"): arraylist. add("B"): arrayList.add("C"); arrayList. add("D"); HAccessing elements System.out. printin("Element at index 2:" + arrayList. get(2)); iteroting eiements for (String element : arrayList) { System.out.printin(element); /Modifying elements arrayList.set(1, "E");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaunit4-240725202854-6e239b07/75/java-unit-4-pdf-about-java-collections-6-2048.jpg)
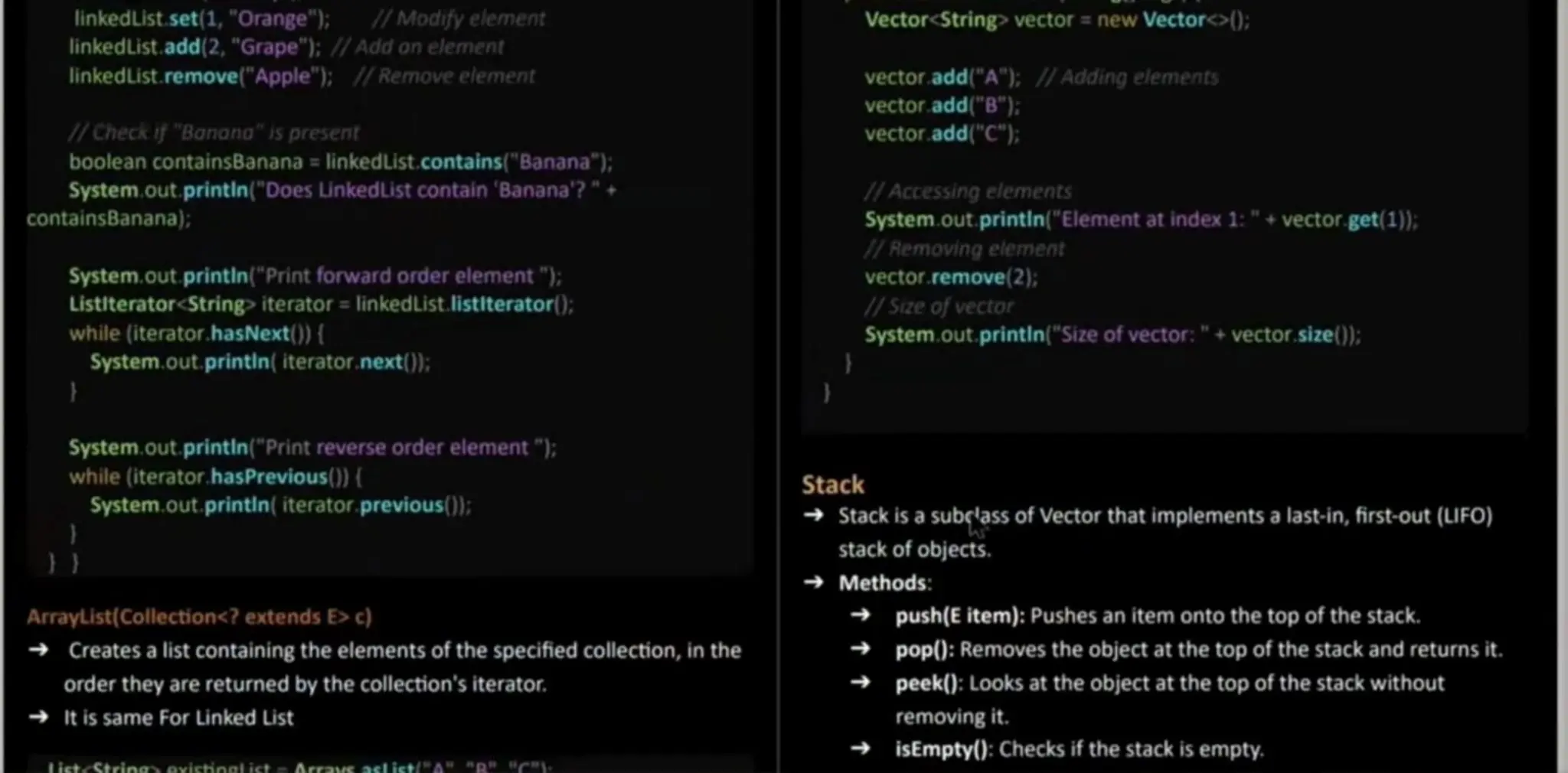
![List<String existinglist = Arrays.asList("A","B","C"); Arraylist<String> list = new ArrayList<>(existingList); System.out, printin(list): //Output: (A, B, C] LinkedList(Collection<? extendsE> ) List<String> arraylist = new ArrayListo(); arrayList.add("Apple"); arrayList.add("Banana"); arrayList.add("Cherry"); 1/ Createo Linkedist using the ArrayList elerments LinkedList<String> linkedlist= new LinkedList<>(arrayList);: import java.util.Stack; public class StackExample public static void main (String] args) { Stack<String> stack = new Stacko); 1IPushing elements stack push("A"); stack push-B"); stack.push("C"); IPeeking the top element System.out. printin ("Topelement:"+ stack.peek());](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaunit4-240725202854-6e239b07/75/java-unit-4-pdf-about-java-collections-8-2048.jpg)

![importjava.util.LinkedList; importjava.util.Queue; public class QueueExample( public staticvoid main (String|]args) { Queue<String>queue = new LinkedList<>(): IAdding elements queue.add("A"); queue.add("B"); queue.add("C"); 1/ Peeking the heod element System.out. printin ("Headelement: " + queue.peek()): 1/ inkedHashSet xample Set<String> linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet<>(); linkedHashSet.add("B"); linkedHashSet.add ("A"); linkedHashSet. add("C"); System.out. printin (" LinkedHash Set:"+ linkedHashSet): / 1TreeSet exomple Set<String treeSet = new TreeSeto); treeSet.add("B"): treeSet.add("A"); treeSet.add('C"): System.out, prhtin ("TreeSet:"+treeSet); /ABC BAC 1IPolling elements System.out. printin("Polledelement:"+ queue.poll()): 1/Checking the size System.out.printin("Size of queue:"+ queue.size(); HashSet: Fostest for basic operotions, no guaranteedorder. LinkedHashSet: Maintoins insertion order, slower thon HashSet. TreeSet: Maintains elements in sorted order, slower than HashSet ond LinkedHoshSet. Map Interface](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaunit4-240725202854-6e239b07/75/java-unit-4-pdf-about-java-collections-10-2048.jpg)

![LinkedHash Set Extends HashSetand maintains a doubly-linked list of entries to preserve the insertion order. Iterates over elementsin insertion order. Slowerthan HashSet for basic operations due to maintaining order. Allows null elements. SortedSet Interface public class HashMapExample public static void main(Stringl] args) ( Map<String,Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); hashMap.put("One",1); hashMap.gt("Two", 2); hashMap.put("Three", 3); System.out, printin ("HashMap:" + hashMap); Extends Set and maintains elements in sorted order defined by their natural ordering or a comparator. Provides methods for accessing elementsby their position in the sorted set. LinkedHashMap Class Evtende HachMan and maintainc incortion order of kove](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaunit4-240725202854-6e239b07/75/java-unit-4-pdf-about-java-collections-12-2048.jpg)
![Set. Implementations include TreeSet. TreeSet ImplementsSortedSet using a tree structure (red-black tree). Maintains elementsin sorted order (ascending by default or basedon a custom comparator). Slowerperformancefor basic operations compared to HashSetand LinkedHashSet. Does not allow null elements. Example Of All Sets interface import java.util."; public class SetExamples{ public static void main(Stringl] args) { 1/HashSetexomple Set<String> hashSet =new HashSet<>(); hashSet.add("B"); hashSet.add("A"); hashSet.add("C"); System.out.printin (" Hash Set:" +hashSet); /CB A Extends HashMap and maintains insertion order of keys. Iterates over elementsin the order they were inserted. Slowerperformancefor basic operations compared to HashMap due to maintaining order. Allows null values and one null key. import java.util. LinkedHashMap; importjava.util.Map; public class LinkedHashMapExample { public staticvoid main(Stringl] args) { Map<String, Integer> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(): linkedHashMap.put (One", 1); linkedHashMap.put(" Two",2);: linkedHashMap.put("Three", 3): System.out. printin("LinkedHashMap:" +linkedHashMap);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaunit4-240725202854-6e239b07/75/java-unit-4-pdf-about-java-collections-13-2048.jpg)
![HoshMop:Fastest for basic operotions, no order guarantee. LinkedHashMap: Maintoins insertion order, inherits from HoshMap. TreeMap: Maintains keys in sorted order, slower for basic operotions due to sorting.* Hashtable Class The Hashtable class in Java provides a basic implementation of a hash table, which maps keys to values. It inherits from the Dictionary class and implementsthe Map interface, making it similar to HashMap but with some differences: Hashtable is synchronized, Neither keys nor values can be nul import java.util.Hashtable; int[] nums = (5, 2,8, 1, 3}; Arrays.sort(nums); //Sorts nums array in ascending order Sorting Collections 1.Collections.sort():Sorts collections such aslists using natural ordering (if elementsimplement Comparable)or a specified Comparator. List<String> names =new ArrayList<>); names.add("Alice" );: names.add("Bob"); Collectils.sort(names); //Sorts olphobetically (notural order) 2.Sorting with Comparator: ascending order use: Comparator.naturalOrder() and descending order use: Comparator.reverseOrder() public class HashtableExample( public staticvoid main(Stringl] args) { /Using Hoshtable HachtabloStrinalntoGArhachtablo noM Hachtahlocs List<String> names = new ArrayList<>(); names.add("Alice"): names.add("Bob"); Collections.sort(names, Comparator.reverse Order(): //Sorts in](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaunit4-240725202854-6e239b07/75/java-unit-4-pdf-about-java-collections-14-2048.jpg)
![System.out. printin("Hashtable:" + hashtable); Iterators used in Map and Set import java. util."; Comparable Interface Comparable is an interface in the java.lang package. It declares one method compareTo()which compares the current object (this) with anotherobject of the same type. Classes that implement Comparable can be sorted automatically using methods like Arrays.sort() or Collections.sort(). public class SetMaplterationExample { public static void main(Stringl] args) ( 7Create a HashSet Set<String> set = new HashSetc>); HAdd elements to the Set set.add("Apple"); set.add("Banana"); set.add("Orange"); 1/terating over the Setusing for-eoch loop System.out. printin("Elements in the Set:"); for (String element : set) ( System.out. printin(element); public interface Comparable<T>{ public int compareTo(T o); Example of Comparable InterFace public class Student implementsComparable<Student>{ private String name; private int age; 1H Constructor public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = rtome; this.ageage; 1/Create oHashMop Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<o);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaunit4-240725202854-6e239b07/75/java-unit-4-pdf-about-java-collections-15-2048.jpg)
![public int compareTo(Student other) ( /Compore students based on age return Integer.compare(this.age, other.age): 7Exomple usoge in moin method public staticvoid main(String [] args) { List<Student> students =new ArrayList<> (): students.add(new Student("Alice", 20)); students.add(newStudent ("Bob", 18); students.add(new Student("Charlie", 22)); /Sorting using Collections.sort) (usesComparable) Collections.sort(students); /Printing sorted students System.out.printin ("Sorted Studentsby Age:"); for (Student student: students) ( System.out. printin (student); Properties Class Properties stores key-value pairs where both keys and values are strings. It supportsloading from and saving to files using load() and store() methods. Default values can be set and queried if a property is not found in the current instance. Java system properties (System-getProperties()) are accessible through a Properties object. Exampleusage involves setting, saving to file, loading, and accessing properties. lIt provides persistence for application settings like database connectionsand Ul configurations. methods : setProperty(String key, String value): Sets a key-value pair in the Properties object. getProperty(String key): Retrieves the value associated with a specified key. store(OutputStream out, String comments): Saves properties to an output stream, with optional comments.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaunit4-240725202854-6e239b07/75/java-unit-4-pdf-about-java-collections-16-2048.jpg)
![Comparator Interface The Comparator interface in Java is located in the java.util package. It defines two methods:compare(T o1,T o2)and equals(Object obi). You typically create an instance of Comparatoreither asan anonymous class. Comparator is commonly used with sorting methods like Collections.sort() for lists or Arrays.sort() for arrays to define the order in which elementsshould be sorted. Example of Comparator Interface import java.util.; public class Student { private String name; private int age, public Student (String name, int age) ( this.name = name; this. age = age, int getAge() (return this. age;) load(InputStream in): Loads properties from an input stream. stringPropertyNames(): Returns keys where both the key and value are strings. import java.io."; import java.util.; public class Student( public staticvoid main(String[] args) ( Properties prop = new Properties(); /Setting properties prop.setProperty( "database.url", "jdbc:mysql:/ localhost:3306/mydb"); prop.setProperty( "database. user", "root"); p. setProperty "database. password","password");: prop. /Soving properties to afile try (OutputStreamoutput = new FileOutputStream("config. properties") ( prop.store(output, "DatabaseConfiguration"); System.out.printin ("Properties saved successfully."); } catch (1OException e) ( e.printStackTrace(): nuhlic staticunid mainLStrinalLarc)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaunit4-240725202854-6e239b07/75/java-unit-4-pdf-about-java-collections-17-2048.jpg)
![public static void main(Stringl] args) { List<Student>students new ArrayListo: students.add(new Student("Alice,20): students.add (new Student("Bob", 18)): students.add(new Student(" Charlie", 22): HUsing Comporotor to sort by oge in descending order Comparator<Student> ageComparator a new Comparator<Student>() Override public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) ( return integer.compare(s2 getAge), s1 getAge()l: //Descending order /Looding properties from ofile try (InputStream input = new FileinputStream("config properties") { prop.load(input); System.out, printin("Propertiesloaded successfully."); /Display properties prop.forEach(key, value) -> ( System.out. printin (key +";"+value); 7 Sorong sTudents hst using ogeCormporotor Collections. sort(students, ageComparator); 1/ Accessing individuol property String dblUrl = prop.getProperty(" database. url"); System.out. printin ("Database URL:"+ dbUri);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaunit4-240725202854-6e239b07/75/java-unit-4-pdf-about-java-collections-18-2048.jpg)