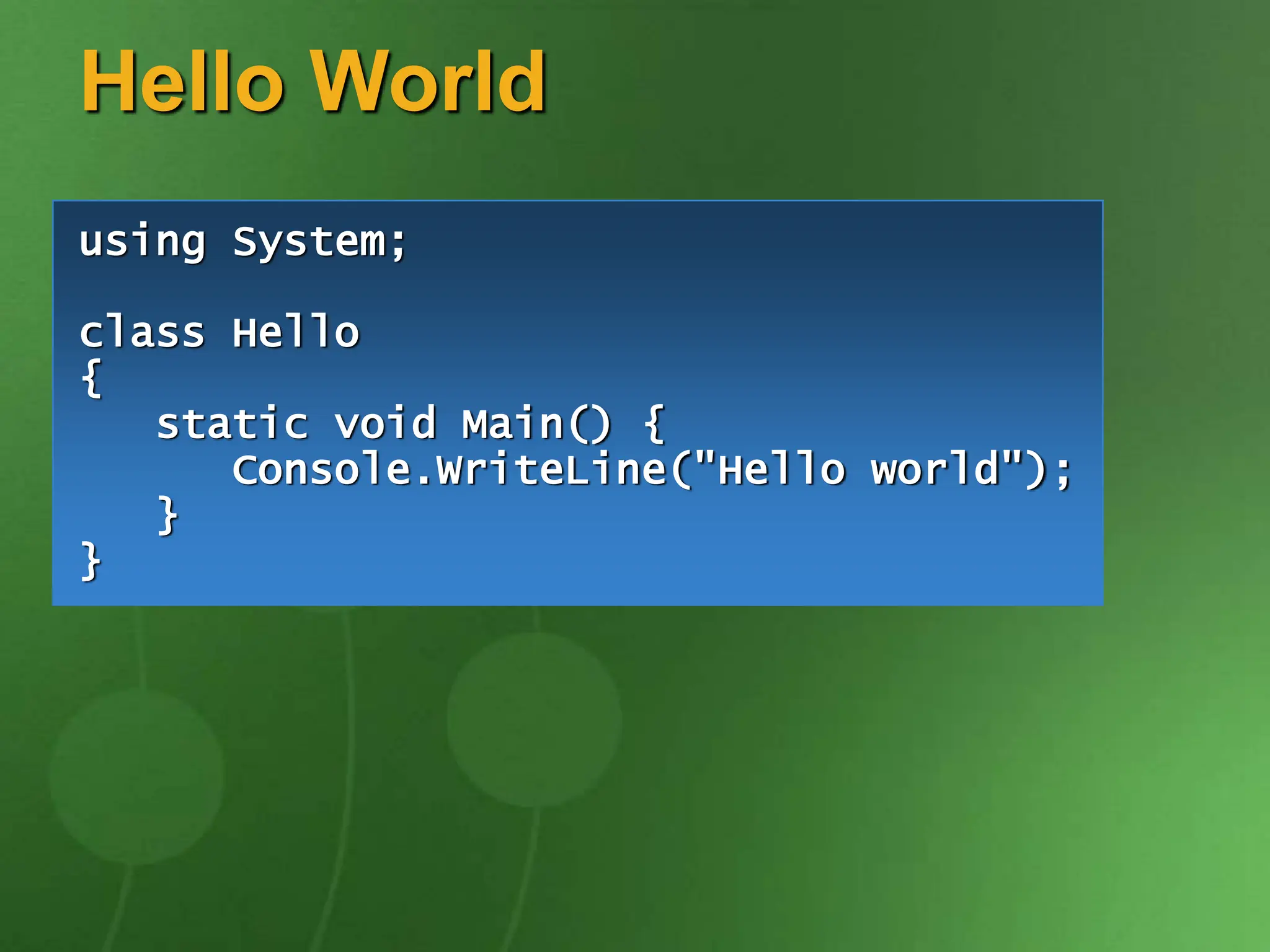
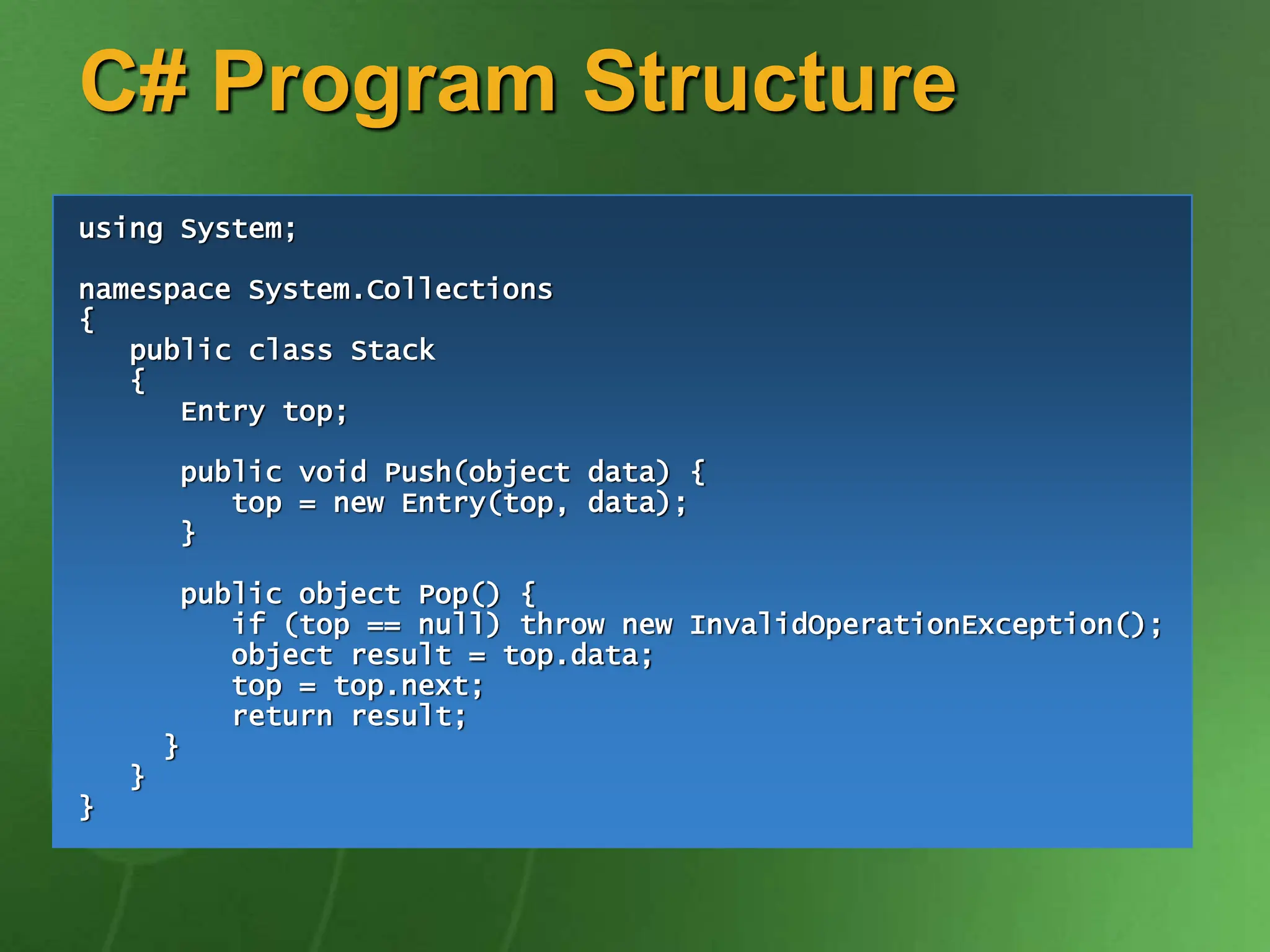
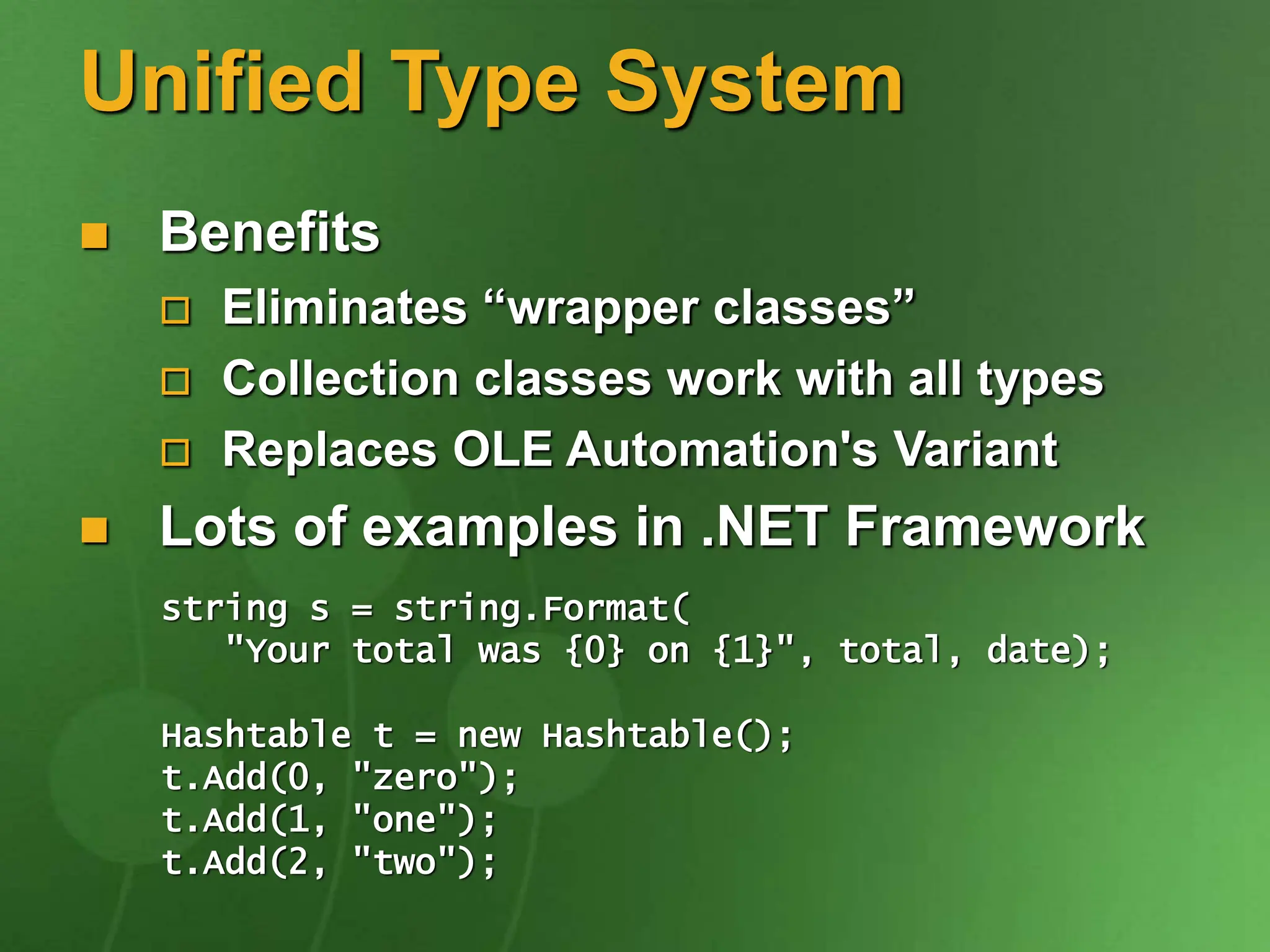
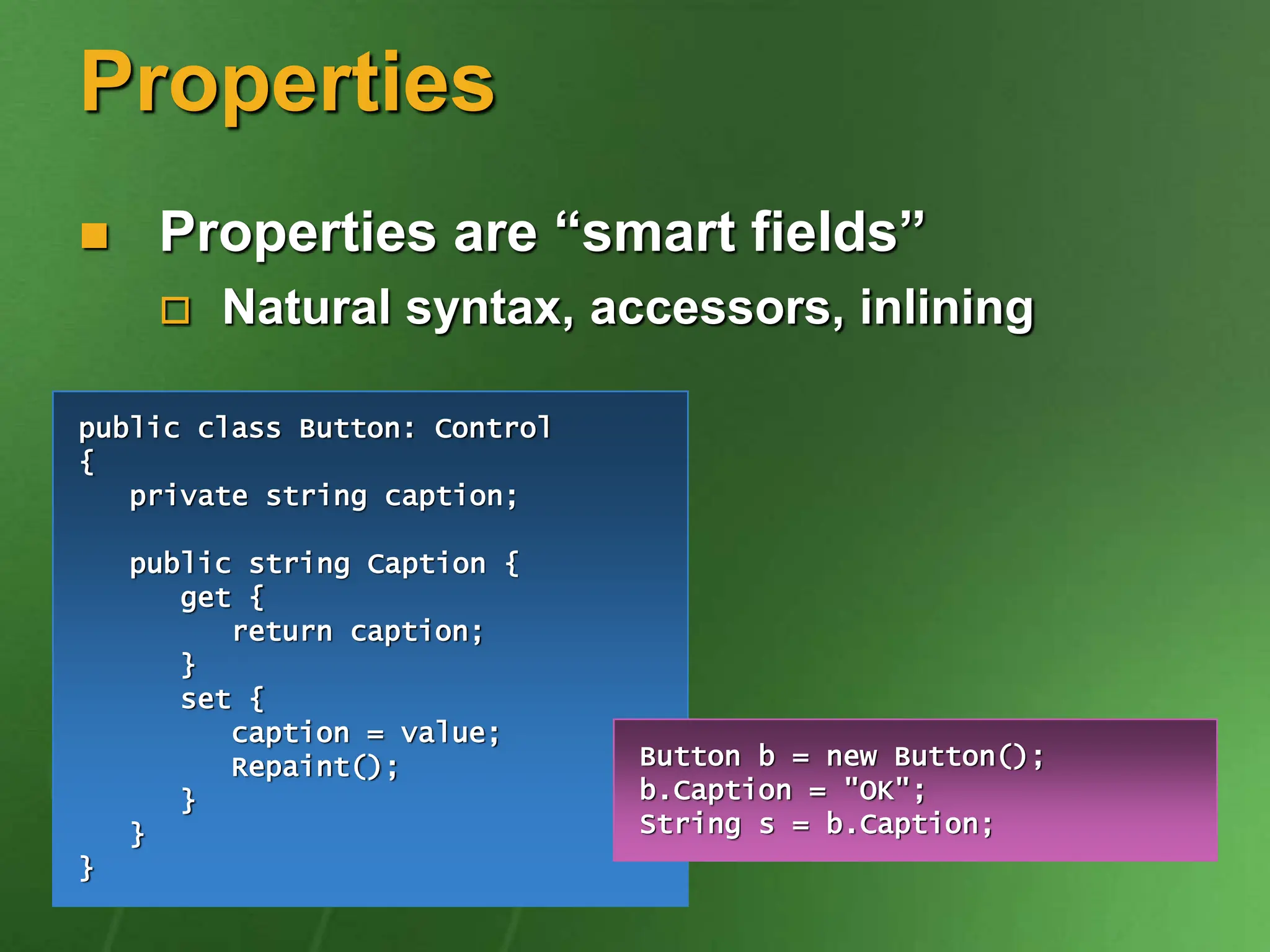
The document discusses the key ideas and features of the C# programming language. It covers C# being the first component-oriented language in the C/C++ family, that everything in C# is an object, and that C# enables robust and durable software while preserving investments in existing code and technologies. It provides examples of core C# concepts like classes, interfaces, properties, events, generics, operator overloading, and more.






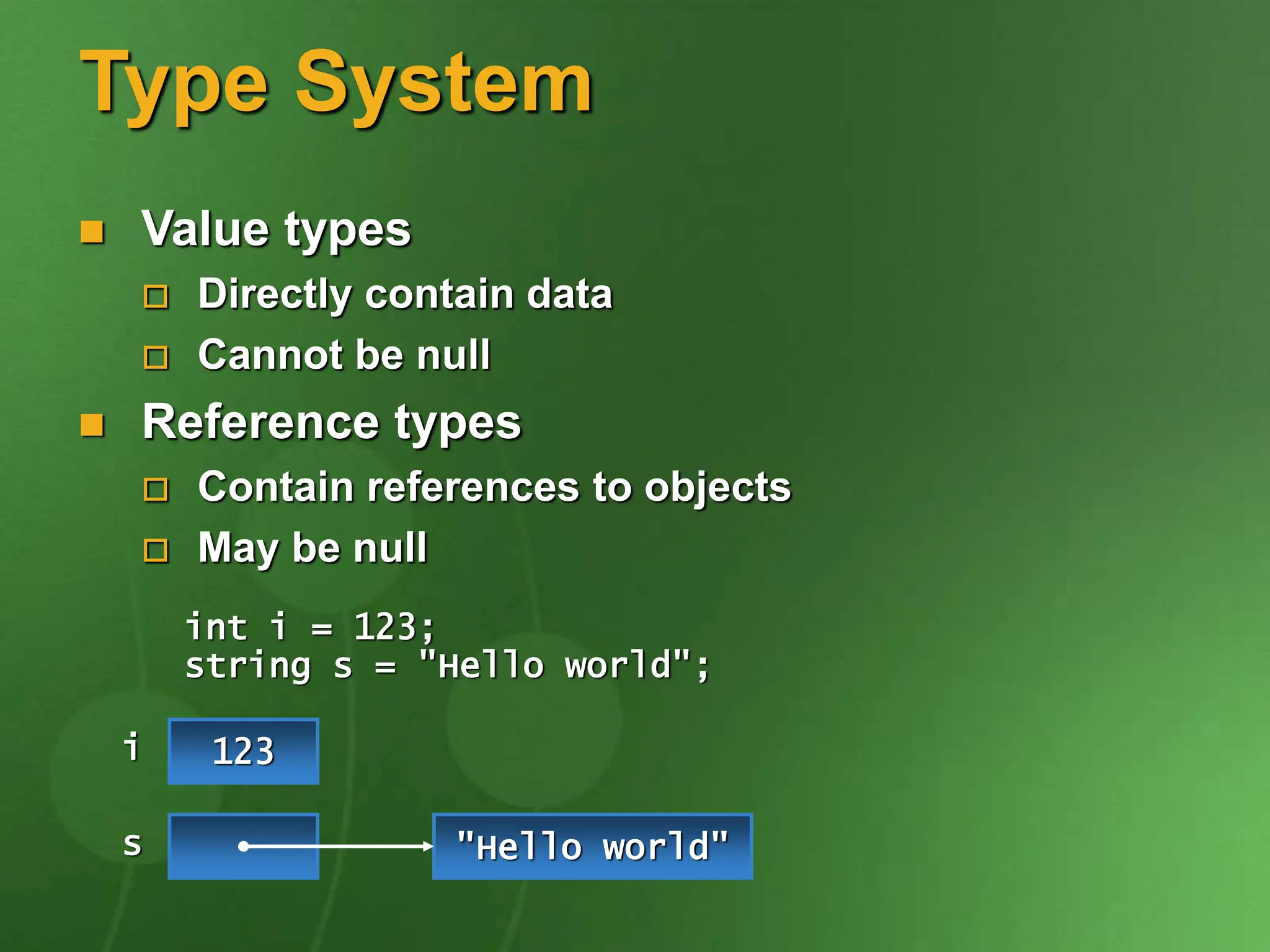
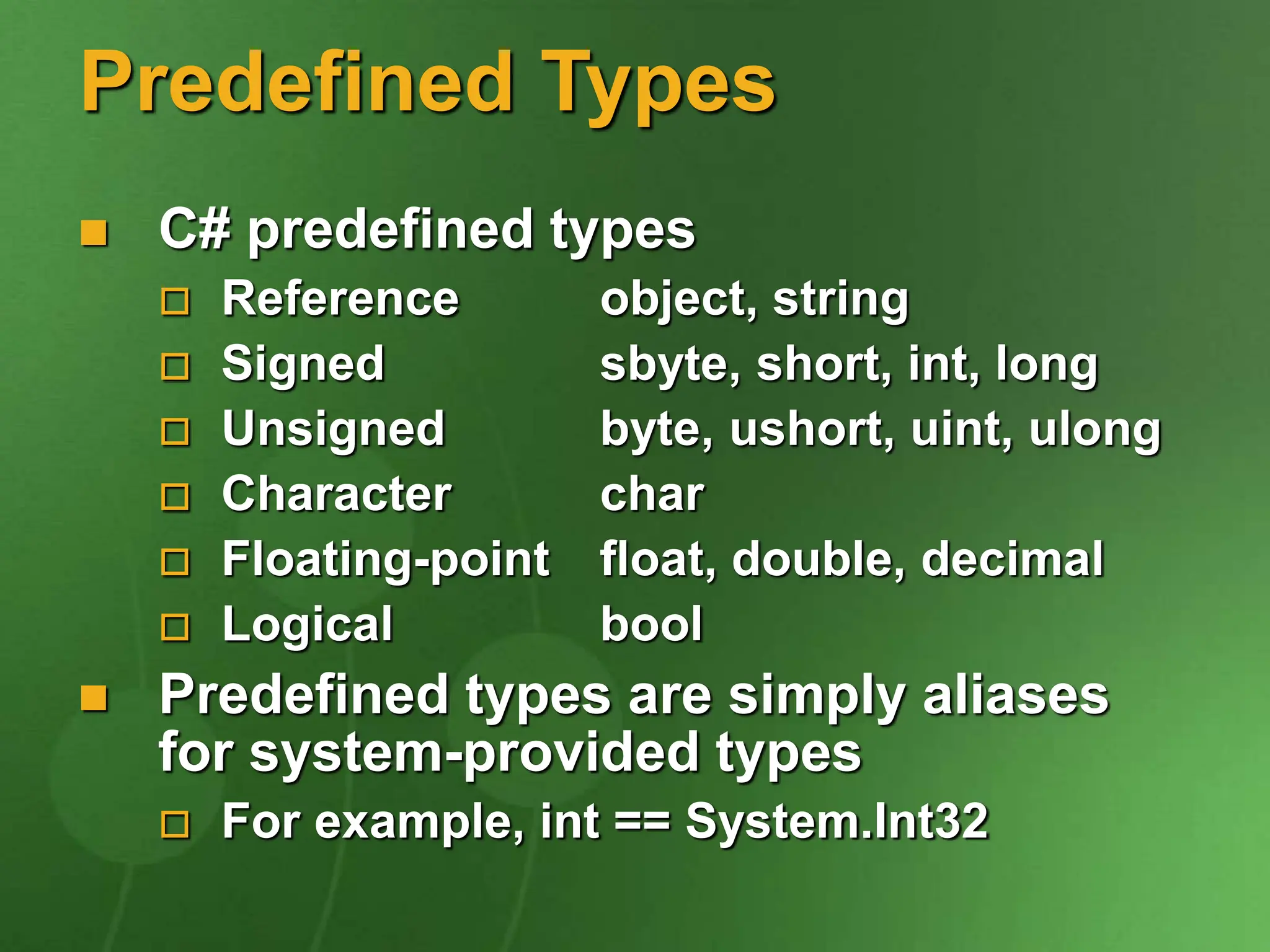
![Type System Value types Primitives int i; Enums enum State { Off, On } Structs struct Point { int x, y; } Reference types Classes class Foo: Bar, IFoo {...} Interfaces interface IFoo: IBar {...} Arrays string[] a = new string[10]; Delegates delegate void Empty();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtocsharpcode-240125130659-b53cd661/75/IntroToCSharpcode-ppt-10-2048.jpg)





![Indexers Indexers are “smart arrays” Can be overloaded public class ListBox: Control { private string[] items; public string this[int index] { get { return items[index]; } set { items[index] = value; Repaint(); } } } ListBox listBox = new ListBox(); listBox[0] = "hello"; Console.WriteLine(listBox[0]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtocsharpcode-240125130659-b53cd661/75/IntroToCSharpcode-ppt-23-2048.jpg)



![Attributes public class OrderProcessor { [WebMethod] public void SubmitOrder(PurchaseOrder order) {...} } [XmlRoot("Order", Namespace="urn:acme.b2b-schema.v1")] public class PurchaseOrder { [XmlElement("shipTo")] public Address ShipTo; [XmlElement("billTo")] public Address BillTo; [XmlElement("comment")] public string Comment; [XmlElement("items")] public Item[] Items; [XmlAttribute("date")] public DateTime OrderDate; } public class Address {...} public class Item {...}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtocsharpcode-240125130659-b53cd661/75/IntroToCSharpcode-ppt-27-2048.jpg)



![foreach Statement Iteration of arrays Iteration of user-defined collections foreach (Customer c in customers.OrderBy("name")) { if (c.Orders.Count != 0) { ... } } public static void Main(string[] args) { foreach (string s in args) Console.WriteLine(s); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtocsharpcode-240125130659-b53cd661/75/IntroToCSharpcode-ppt-31-2048.jpg)
![Parameter Arrays Can write “printf” style methods Type-safe, unlike C++ void printf(string fmt, params object[] args) { foreach (object x in args) { ... } } printf("%s %i %i", str, int1, int2); object[] args = new object[3]; args[0] = str; args[1] = int1; Args[2] = int2; printf("%s %i %i", args);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtocsharpcode-240125130659-b53cd661/75/IntroToCSharpcode-ppt-32-2048.jpg)




![Conditional Compilation #define, #undef #if, #elif, #else, #endif Simple boolean logic Conditional methods public class Debug { [Conditional("Debug")] public static void Assert(bool cond, String s) { if (!cond) { throw new AssertionException(s); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtocsharpcode-240125130659-b53cd661/75/IntroToCSharpcode-ppt-37-2048.jpg)
![Unsafe Code Platform interoperability covers most cases Unsafe code Low-level code “within the box” Enables unsafe casts, pointer arithmetic Declarative pinning Fixed statement Basically “inline C” unsafe void Foo() { char* buf = stackalloc char[256]; for (char* p = buf; p < buf + 256; p++) *p = 0; ... }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtocsharpcode-240125130659-b53cd661/75/IntroToCSharpcode-ppt-38-2048.jpg)
![Unsafe Code class FileStream: Stream { int handle; public unsafe int Read(byte[] buffer, int index, int count) { int n = 0; fixed (byte* p = buffer) { ReadFile(handle, p + index, count, &n, null); } return n; } [dllimport("kernel32", SetLastError=true)] static extern unsafe bool ReadFile(int hFile, void* lpBuffer, int nBytesToRead, int* nBytesRead, Overlapped* lpOverlapped); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtocsharpcode-240125130659-b53cd661/75/IntroToCSharpcode-ppt-40-2048.jpg)