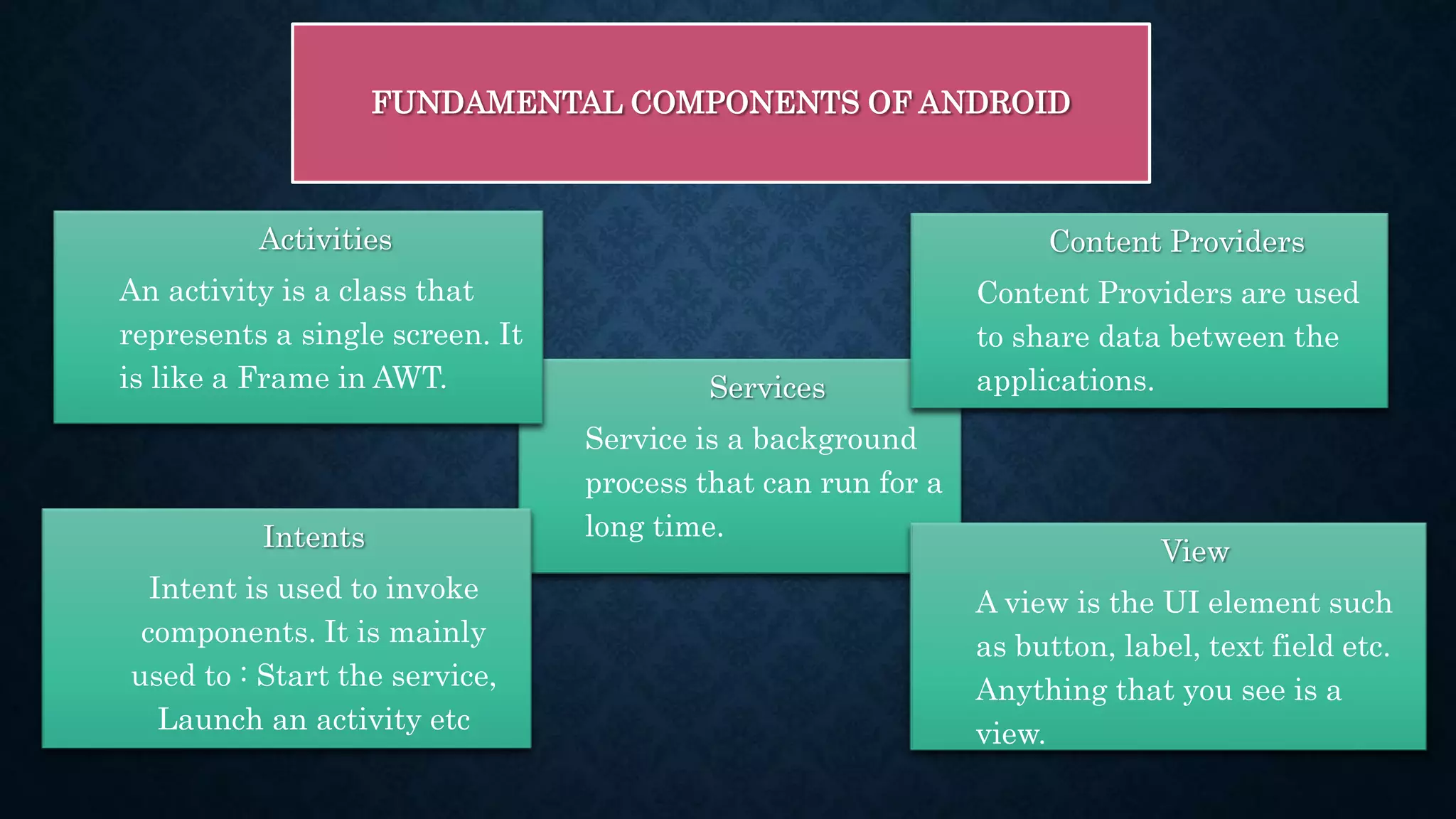
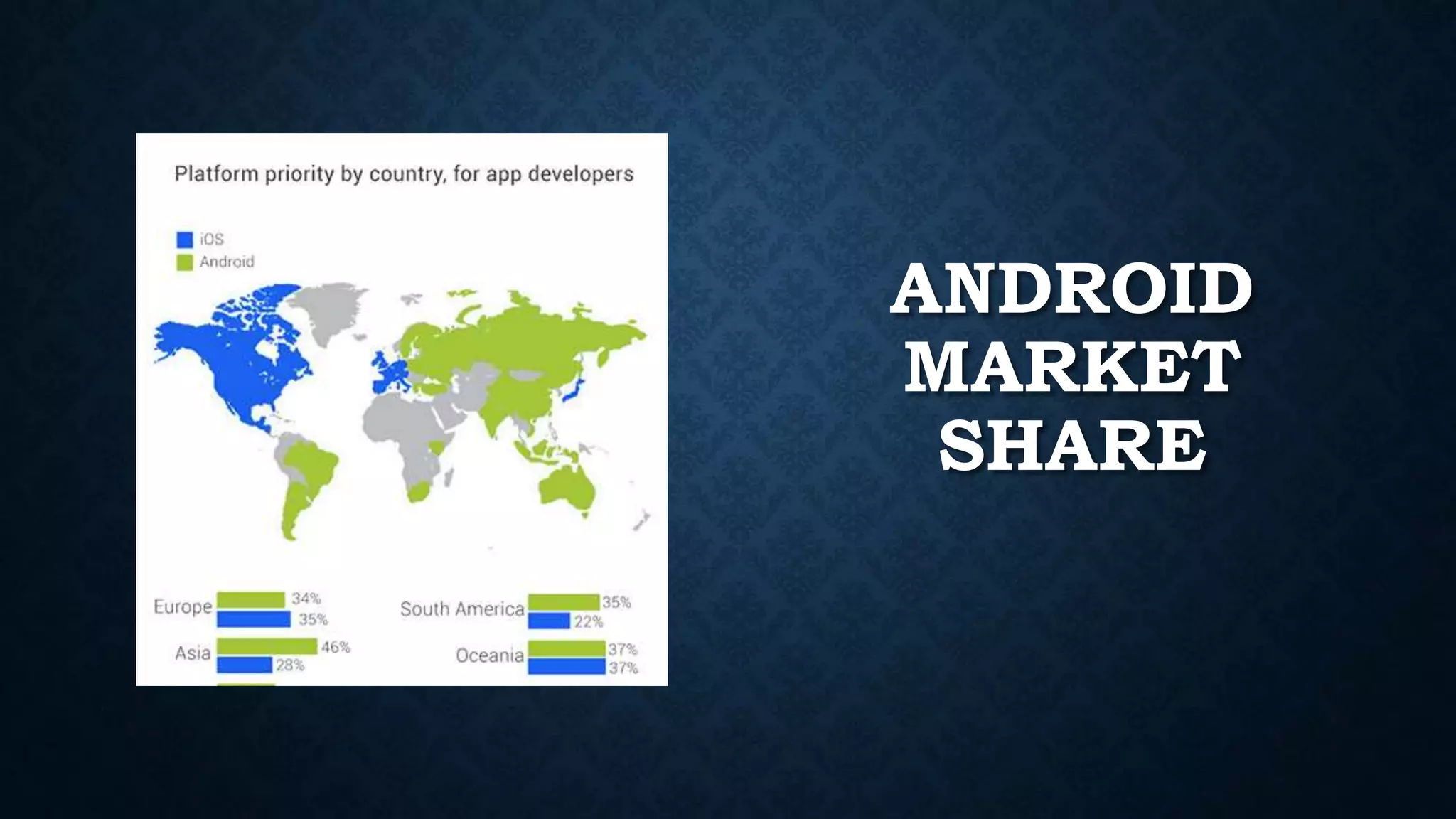
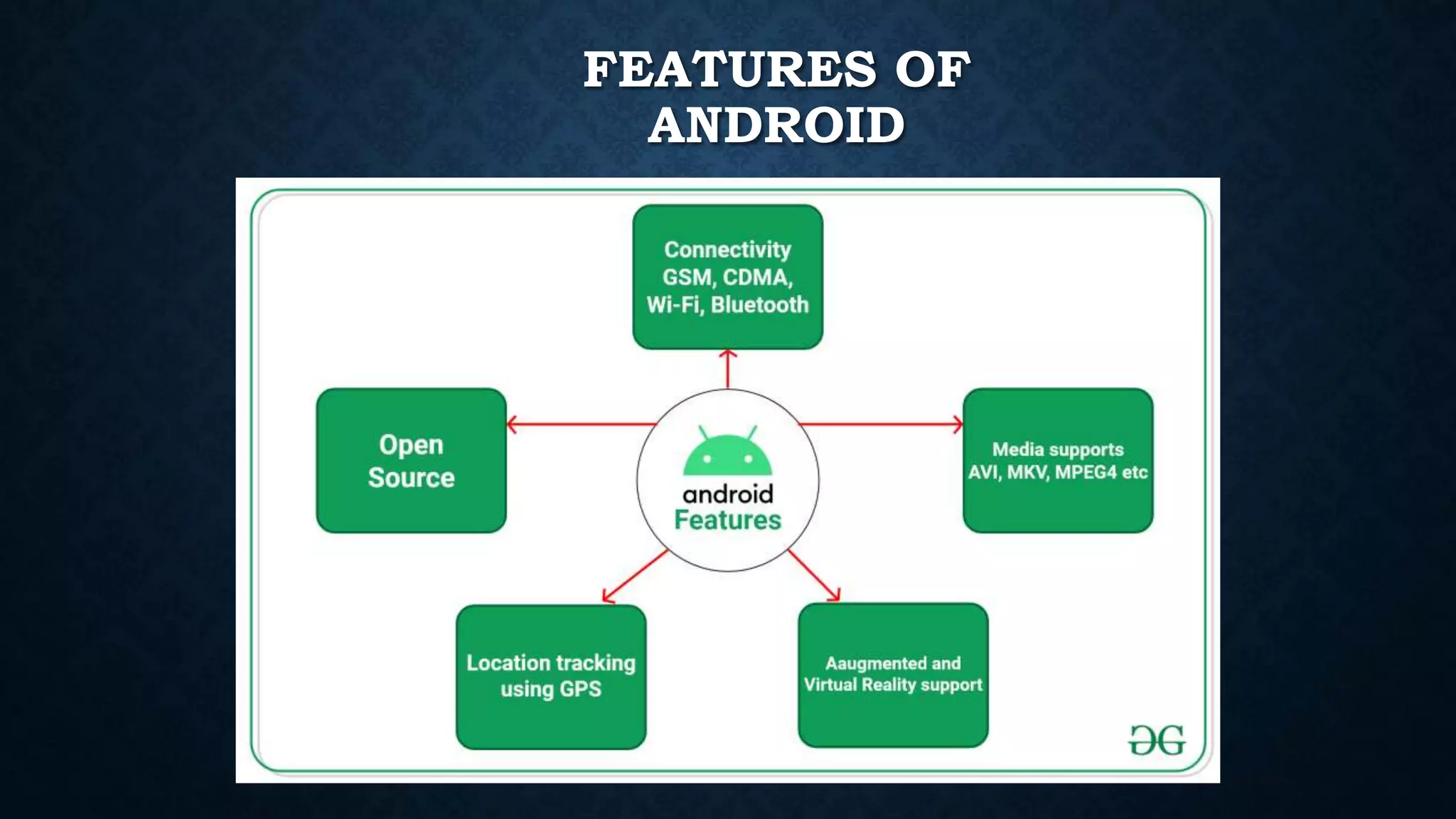
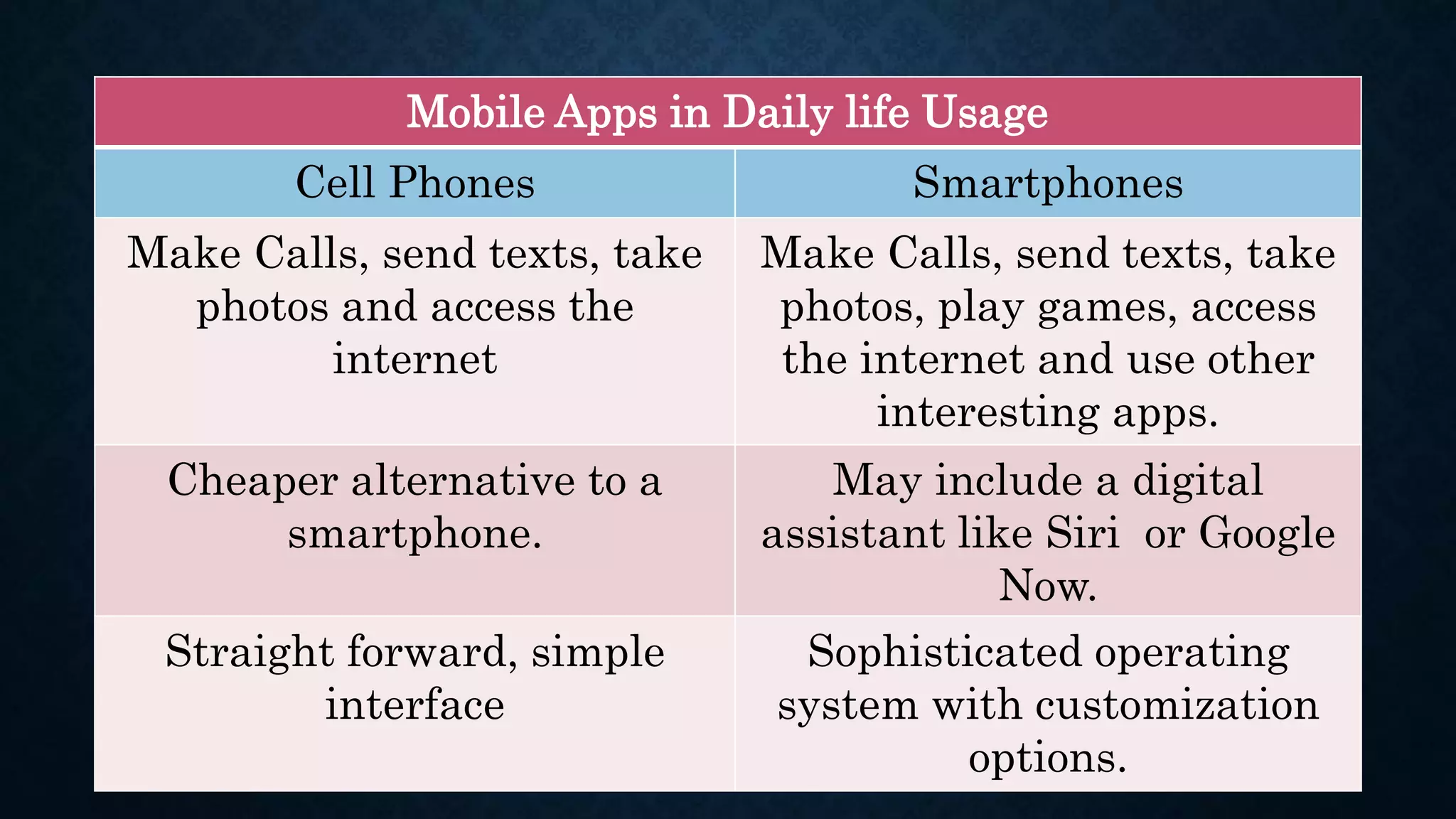
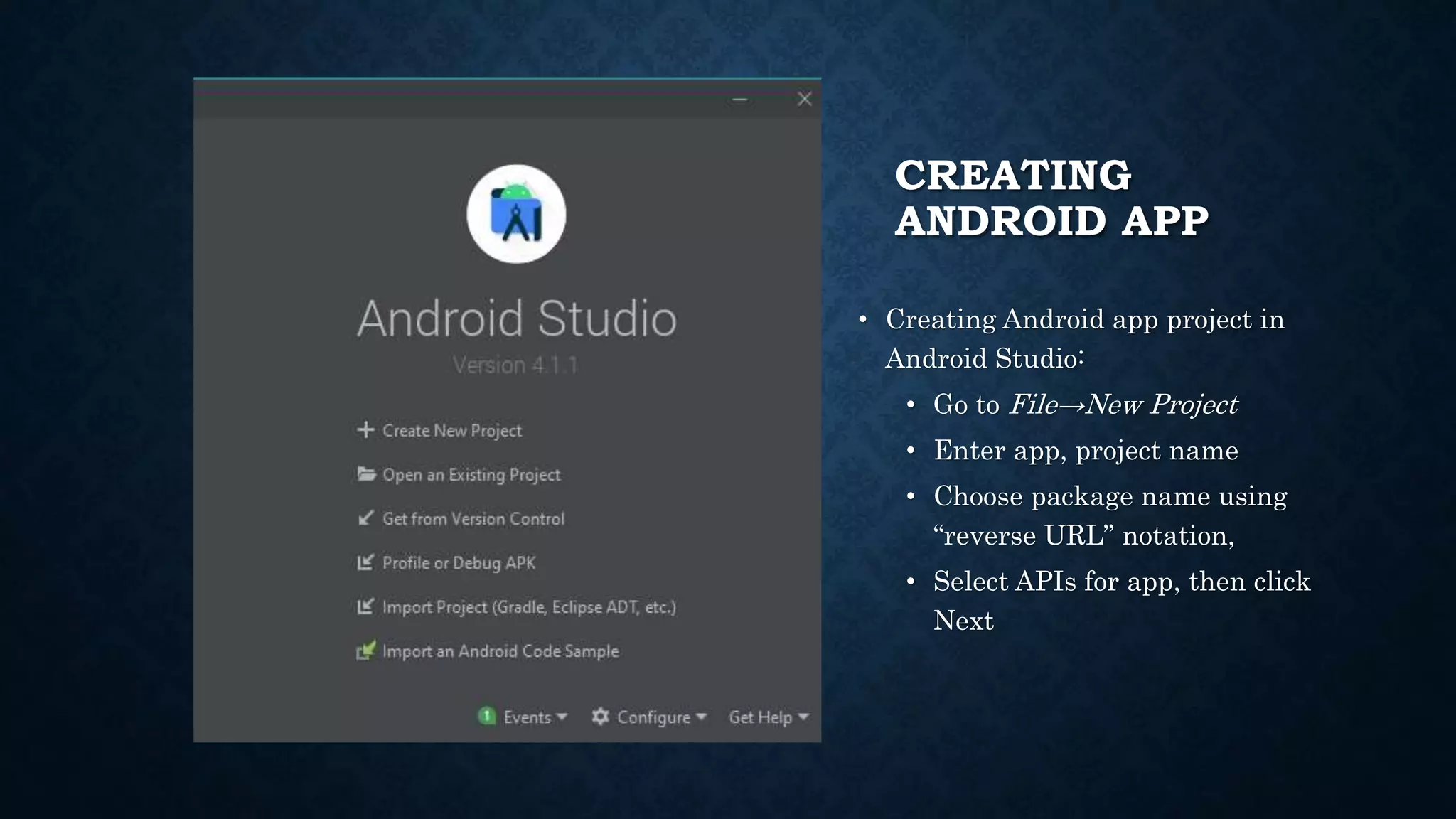
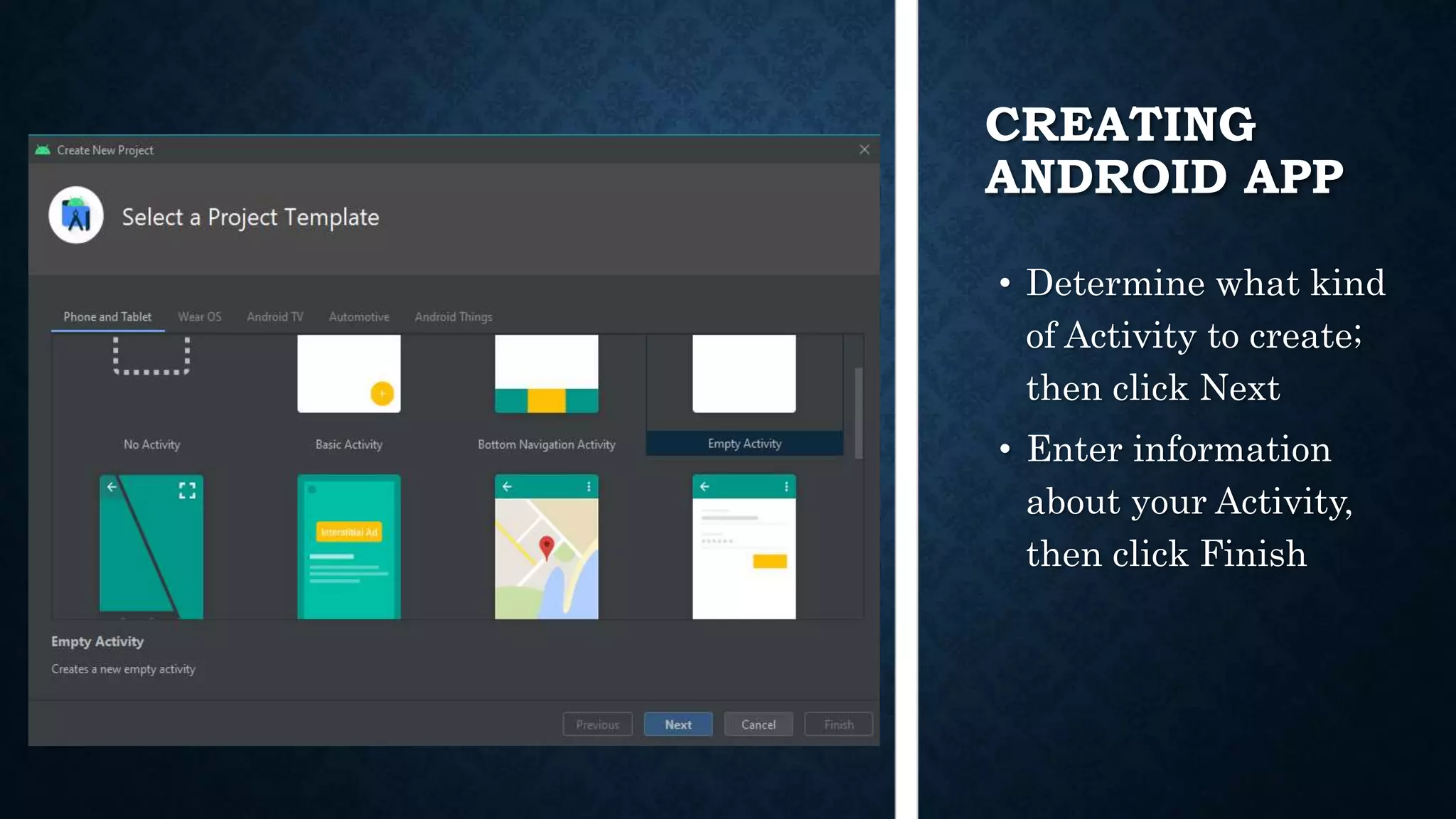
This document provides an introduction to Android and Android Studio. It discusses what Android is, its operating system components, versions and features. It also describes Android Studio as the IDE for developing Android apps, outlining its tools and how to install, create, code and deploy an Android app. The document serves as a high-level overview of getting started with Android development.