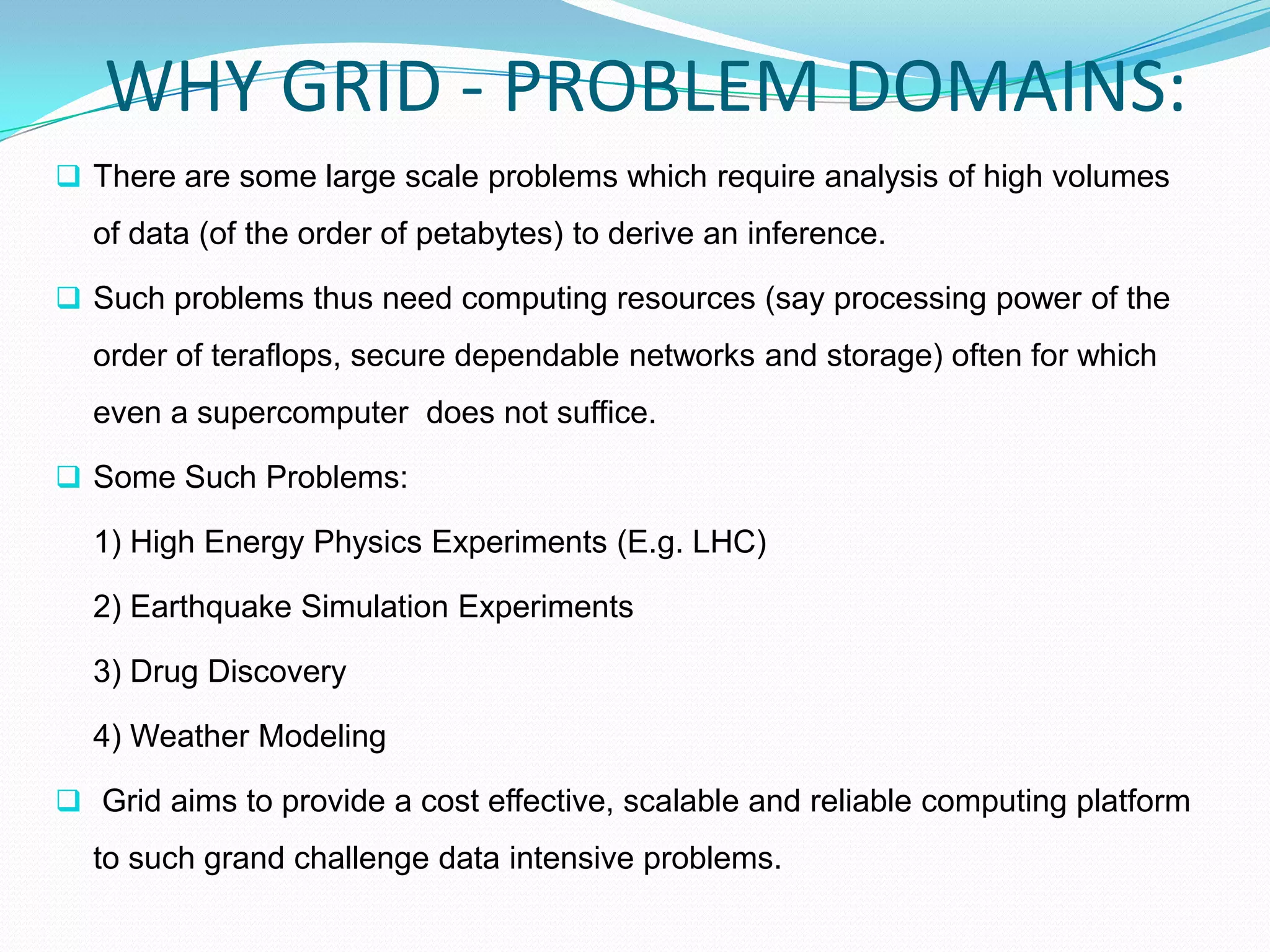
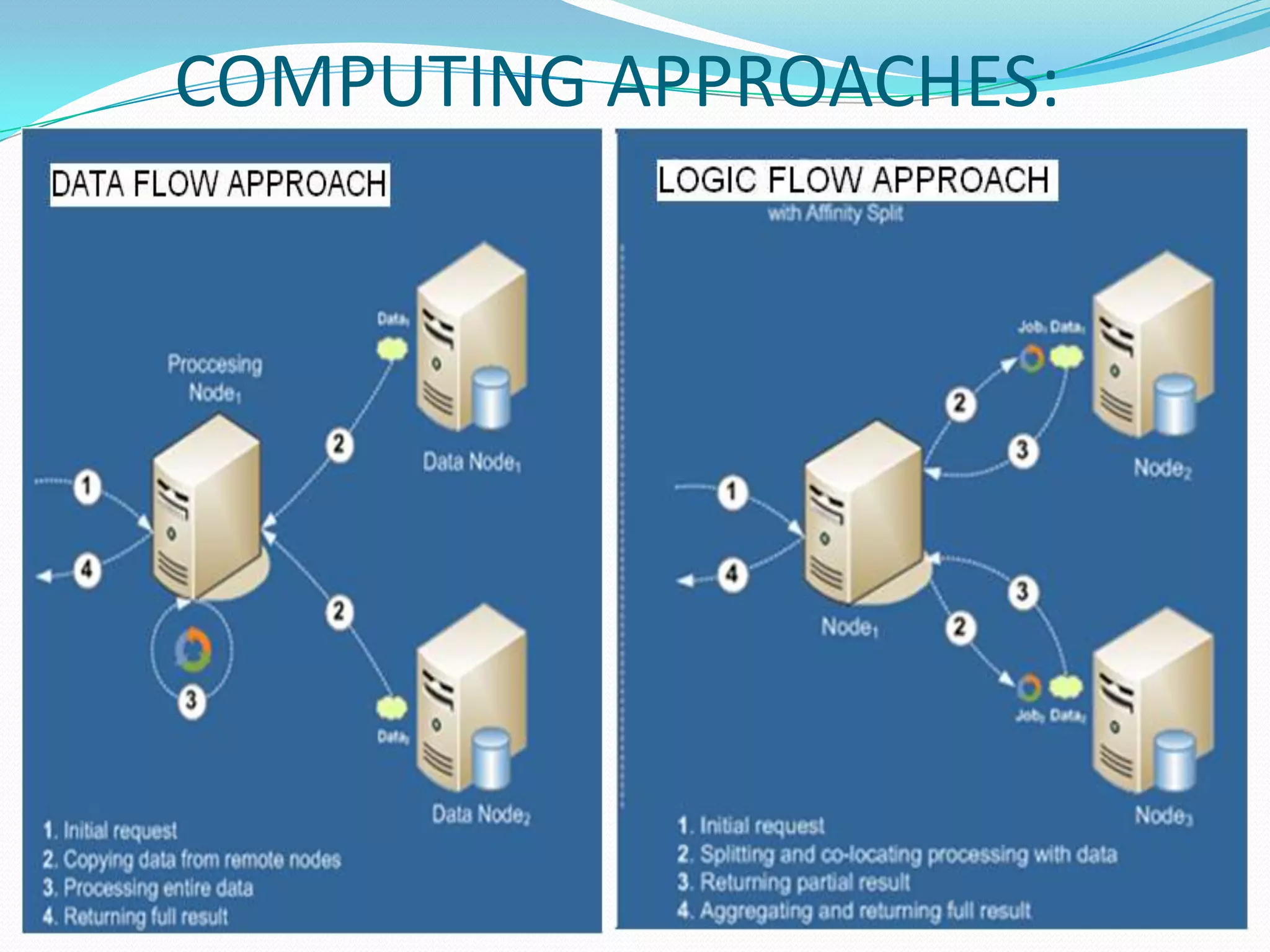
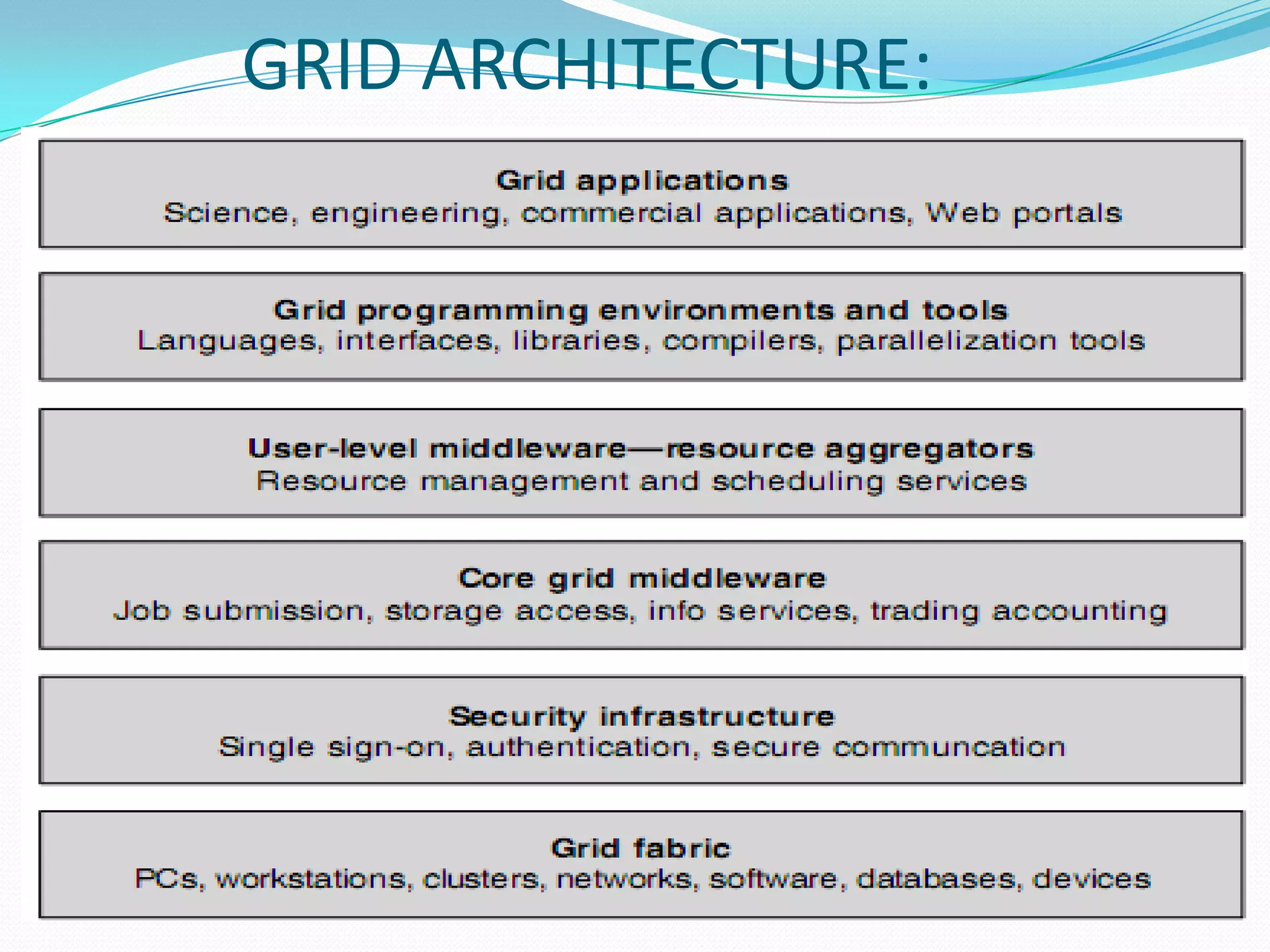
This document introduces grid computing by discussing its applications to problems requiring large-scale data analysis, such as high energy physics experiments. It defines a grid as an infrastructure involving integrated and collaborative use of computers, networks, databases, and instruments across multiple organizations. Grids allow for computational, data, and network sharing and aim to provide a cost-effective, scalable platform for data-intensive problems. Virtual organizations are dynamically formed groups that define rules for sharing resources to solve specific problems. The document outlines grid architecture and operations, including resource discovery, scheduling jobs, and accounting. Benefits of grids include exploiting underutilized resources and parallel processing capacity.