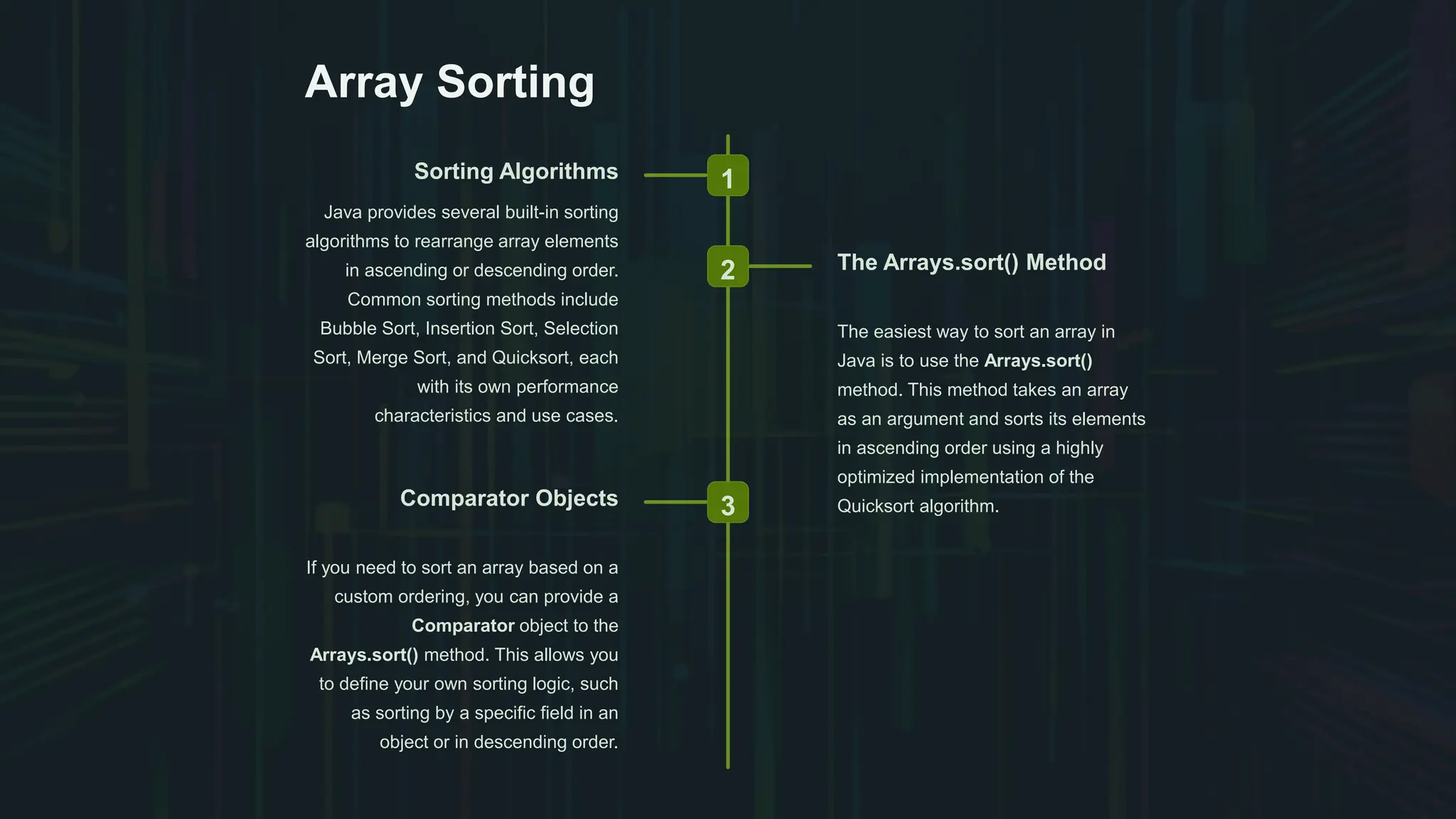
The document provides an introduction to arrays in Java, detailing their declaration, initialization, and access methods, as well as the importance of bounds checking to avoid exceptions. It discusses various ways to iterate through arrays, including for-each and traditional loops, and covers sorting and searching algorithms, such as linear and binary search. Additionally, the document explains common operations on arrays, like copying and filling, and introduces multidimensional arrays for complex data representation.

![Declaring and Initializing Arrays In Java, arrays are a fundamental data structure used to store collections of elements of the same data type. To declare an array, you specify the data type followed by square brackets []. For example, int[] myArray; declares an integer array called myArray. To initialize an array, you can use curly braces {} to enclose the elements. For instance, int[] myArray = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; creates an integer array with the values 1 through 5. Alternatively, you can use the new keyword to dynamically allocate memory for the array, such as int[] myArray = new int[5]; which creates an integer array of size 5 with all elements initialized to 0.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-arrays-in-java1-240602034416-f65108ae/75/Introduction-to-Arrays-in-Java-Exploring-array-2-2048.jpg)
![Accessing Array Elements Direct Access To access individual elements in an array, you can use the array's index, which starts at 0. For example, myArray[0] will retrieve the first element, myArray[1] the second, and so on. This direct access allows you to quickly retrieve and manipulate specific values within the array. Iterative Access Alternatively, you can use a loop to iterate through the array and access each element in turn. This is useful when you need to perform the same operation on multiple elements or when the size of the array is not known in advance. Bounds Checking It's important to ensure that you're accessing array elements within the valid range, typically from 0 to the array's length minus 1. Trying to access an element outside this range will result in an IndexOutOfBoundsException , which you should handle in your code to prevent runtime errors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-arrays-in-java1-240602034416-f65108ae/75/Introduction-to-Arrays-in-Java-Exploring-array-3-2048.jpg)



![Multidimensional Arrays Java supports multidimensional arrays, which are arrays of arrays. These allow you to represent data in a grid-like structure, such as a 2D table or a 3D volume. Multidimensional arrays are commonly used for tasks like image processing, game boards, and scientific simulations. To declare a 2D array, you can use a syntax like dataType[][] arrayName = new dataType[rows][cols];. The first set of square brackets represents the rows, and the second set represents the columns. You can access individual elements using two indices, like arrayName[row][col].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-arrays-in-java1-240602034416-f65108ae/75/Introduction-to-Arrays-in-Java-Exploring-array-7-2048.jpg)