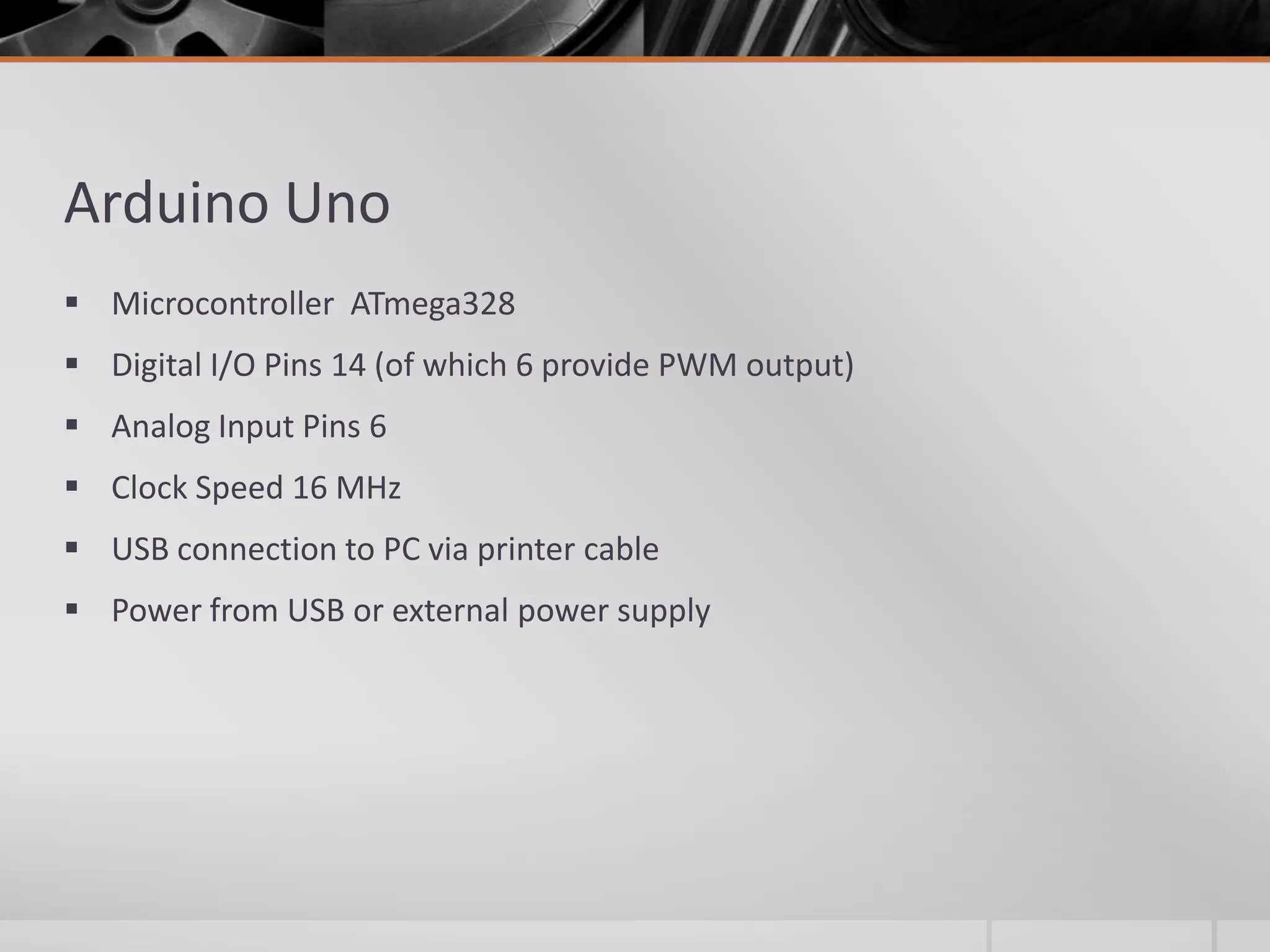
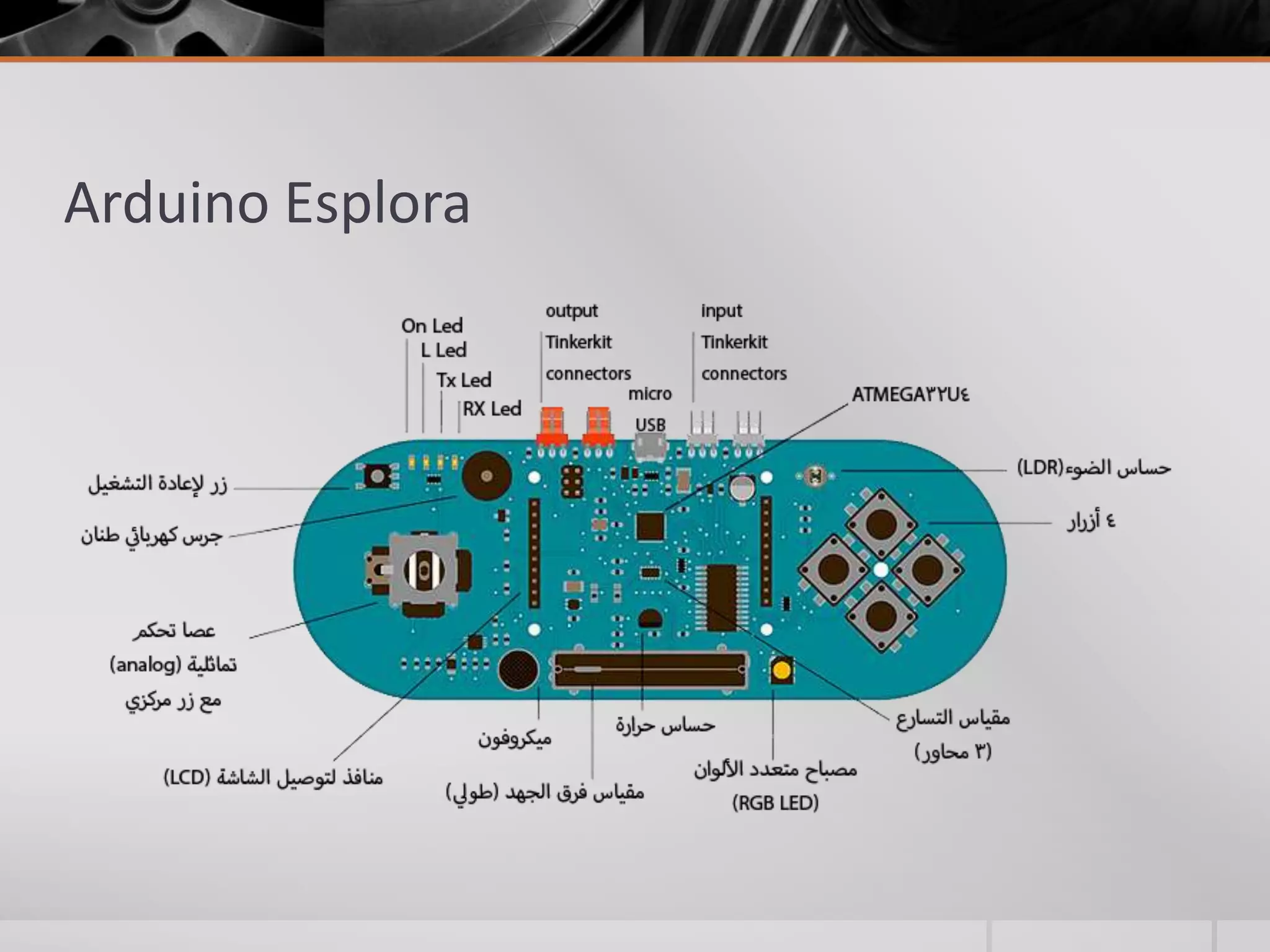
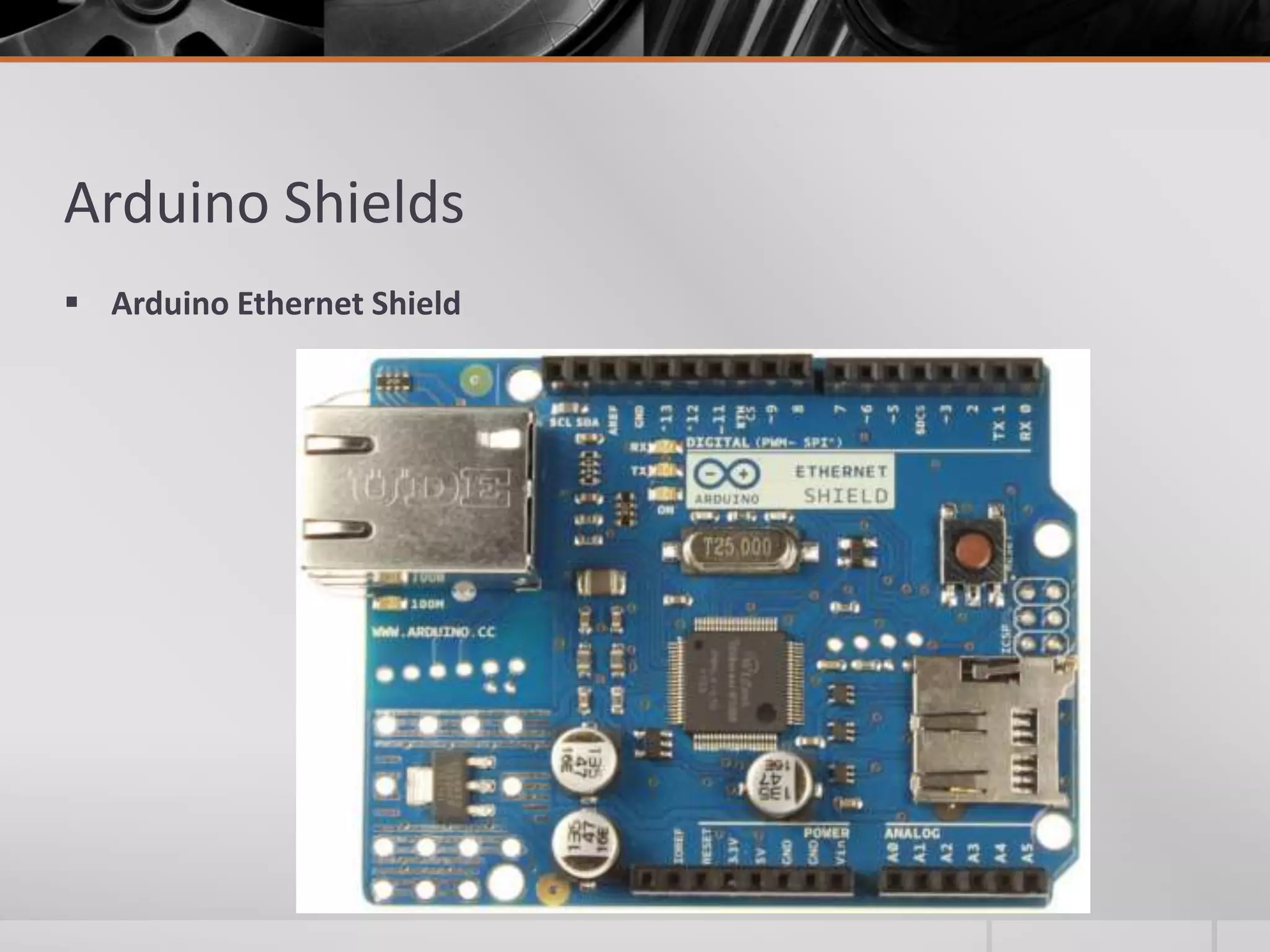
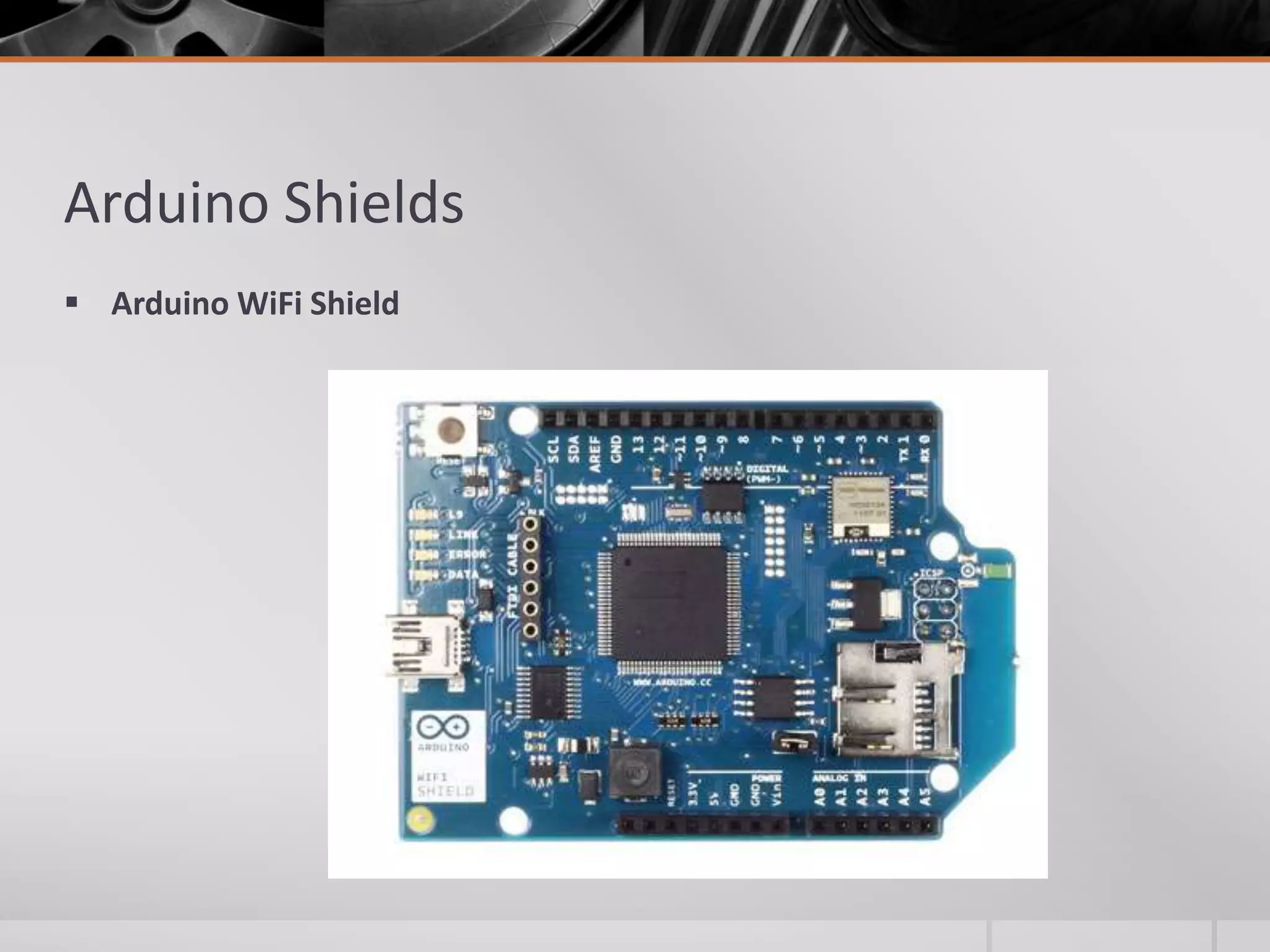
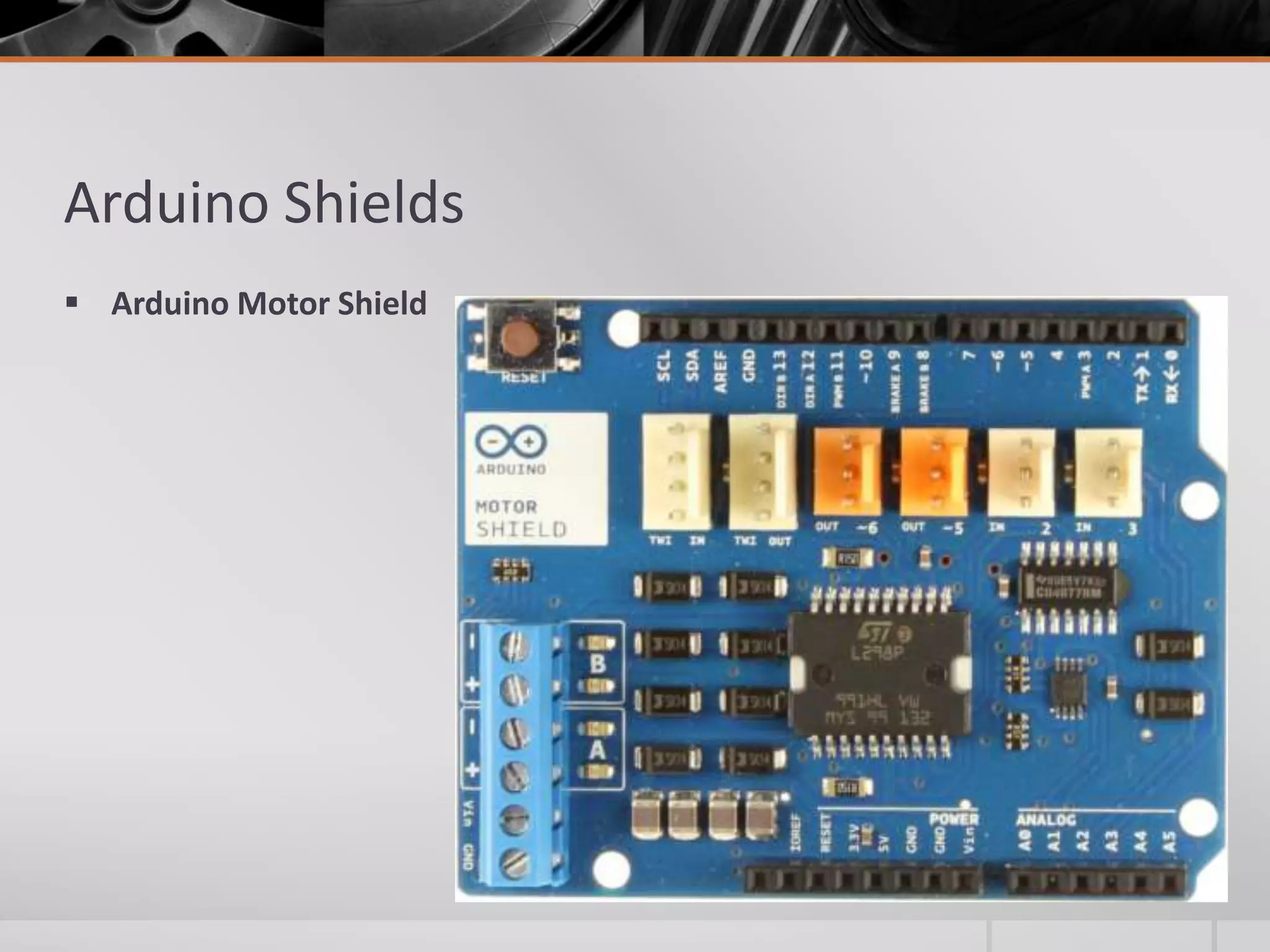
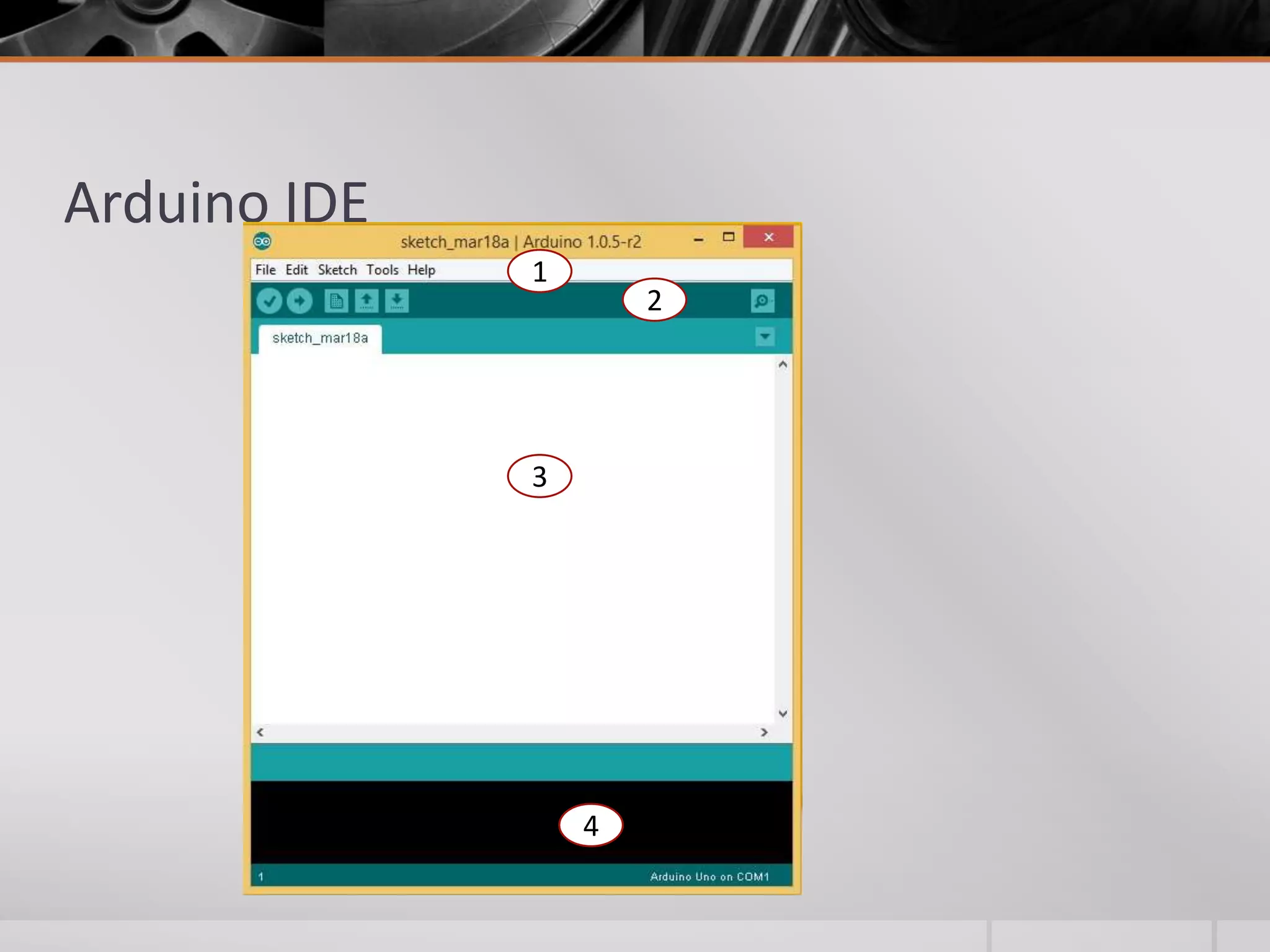
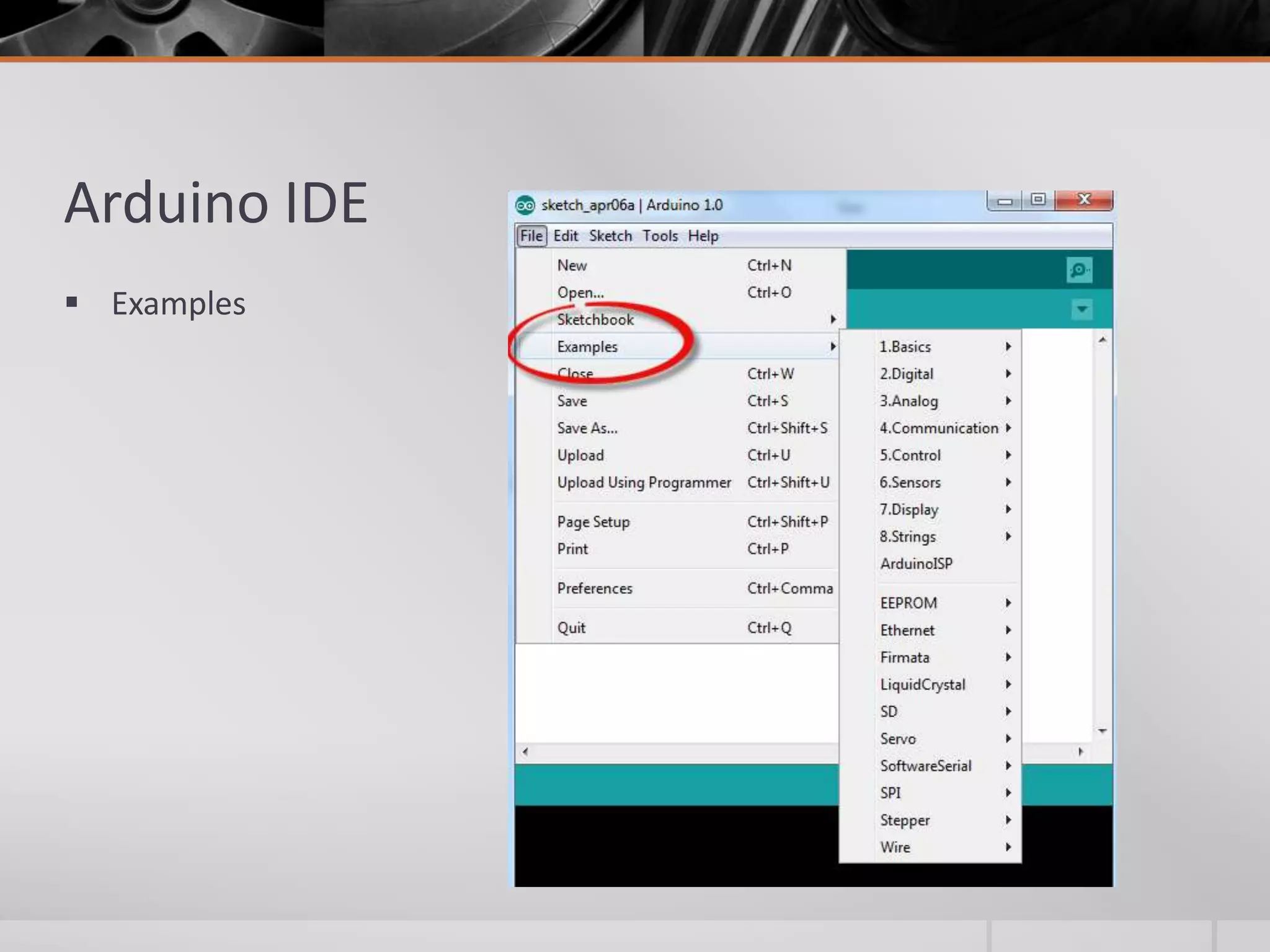
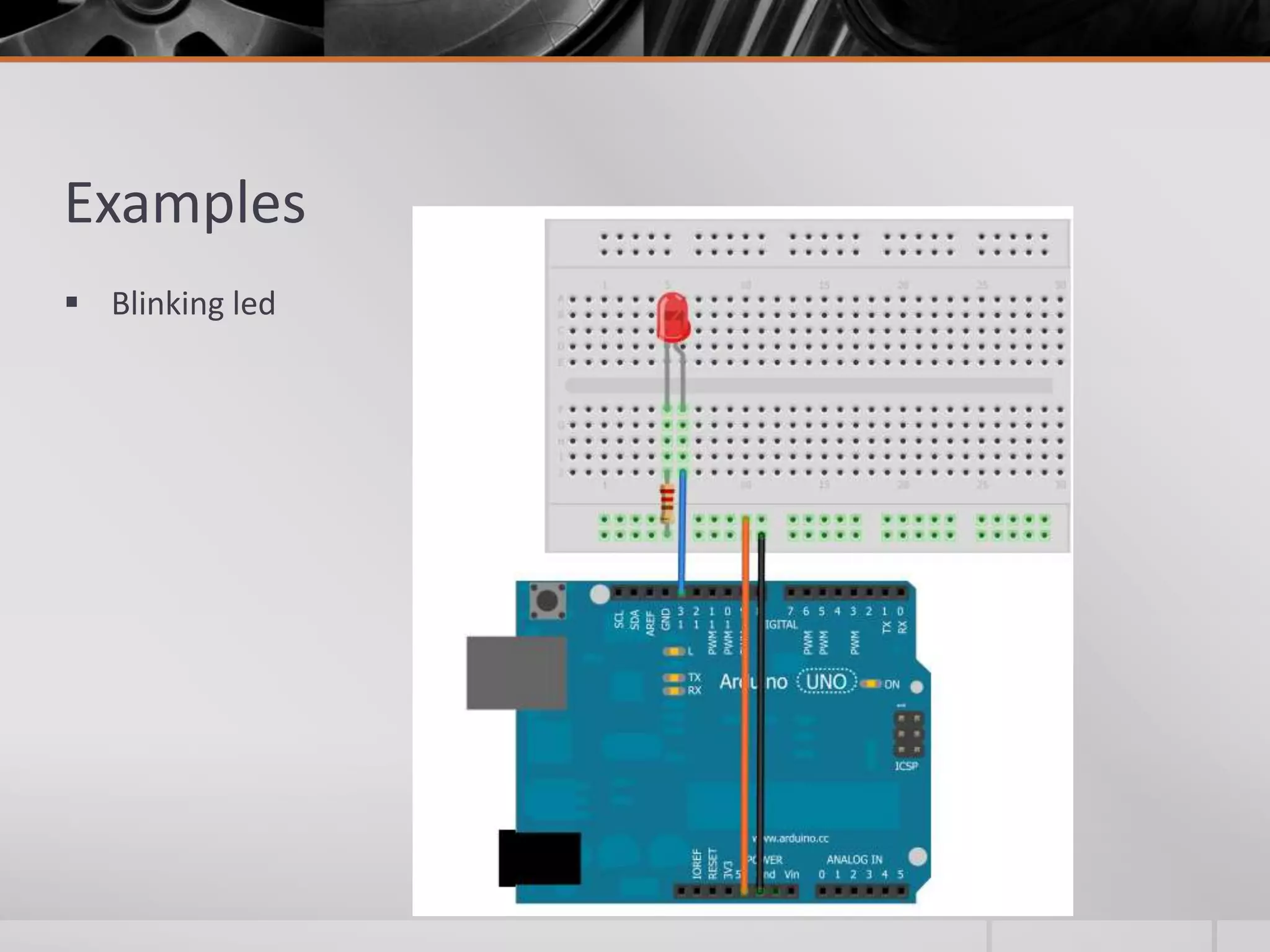
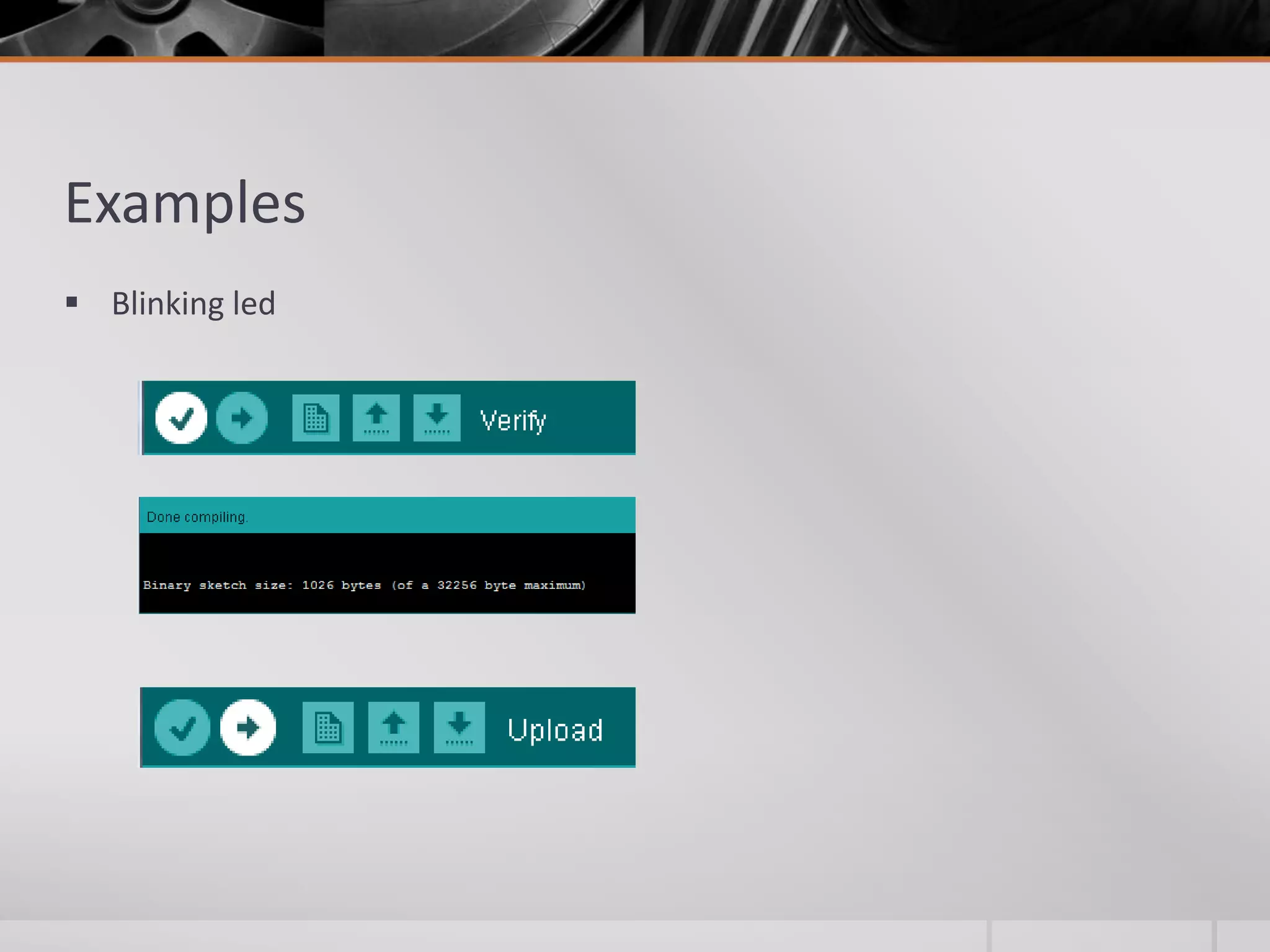
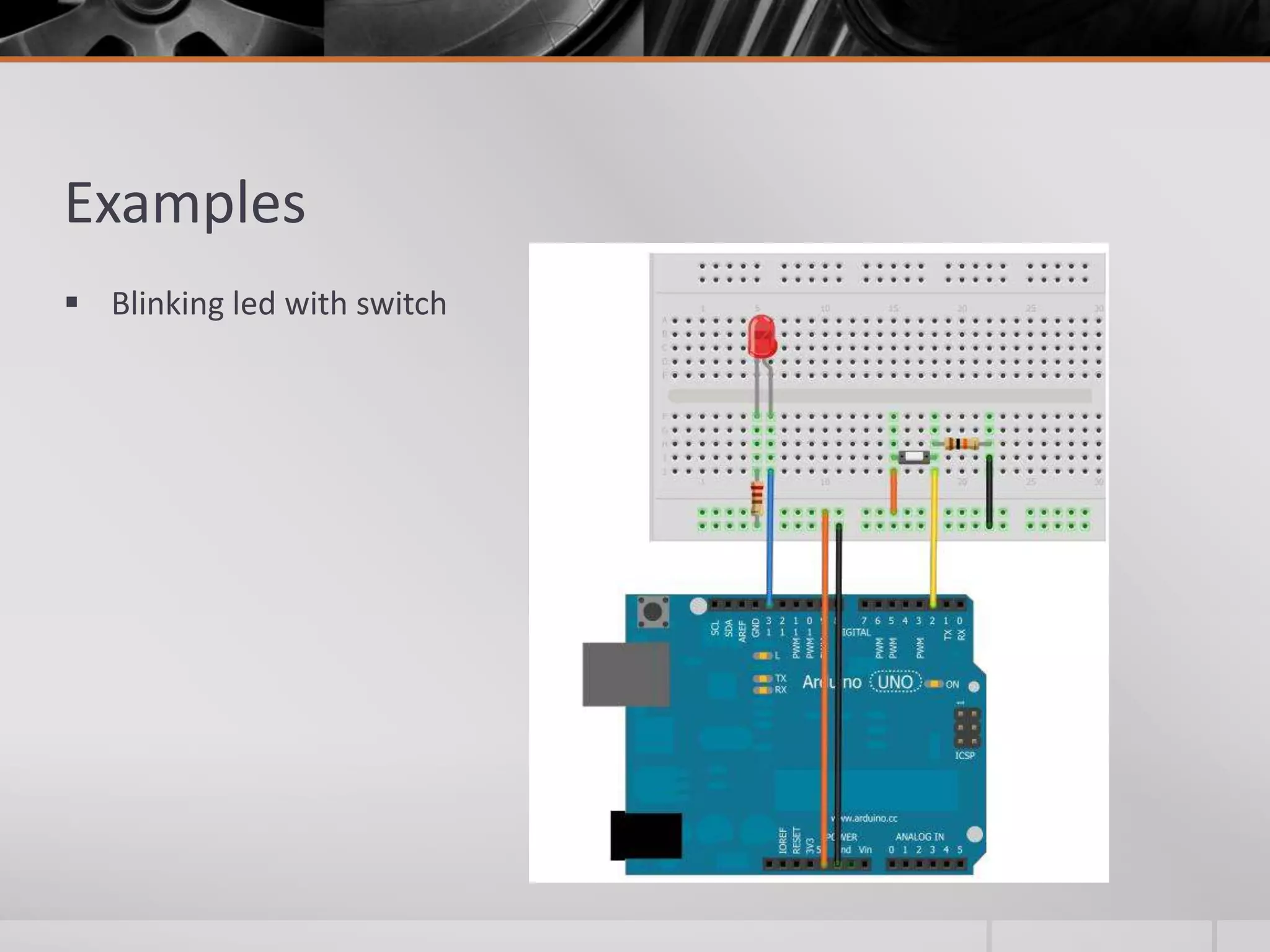
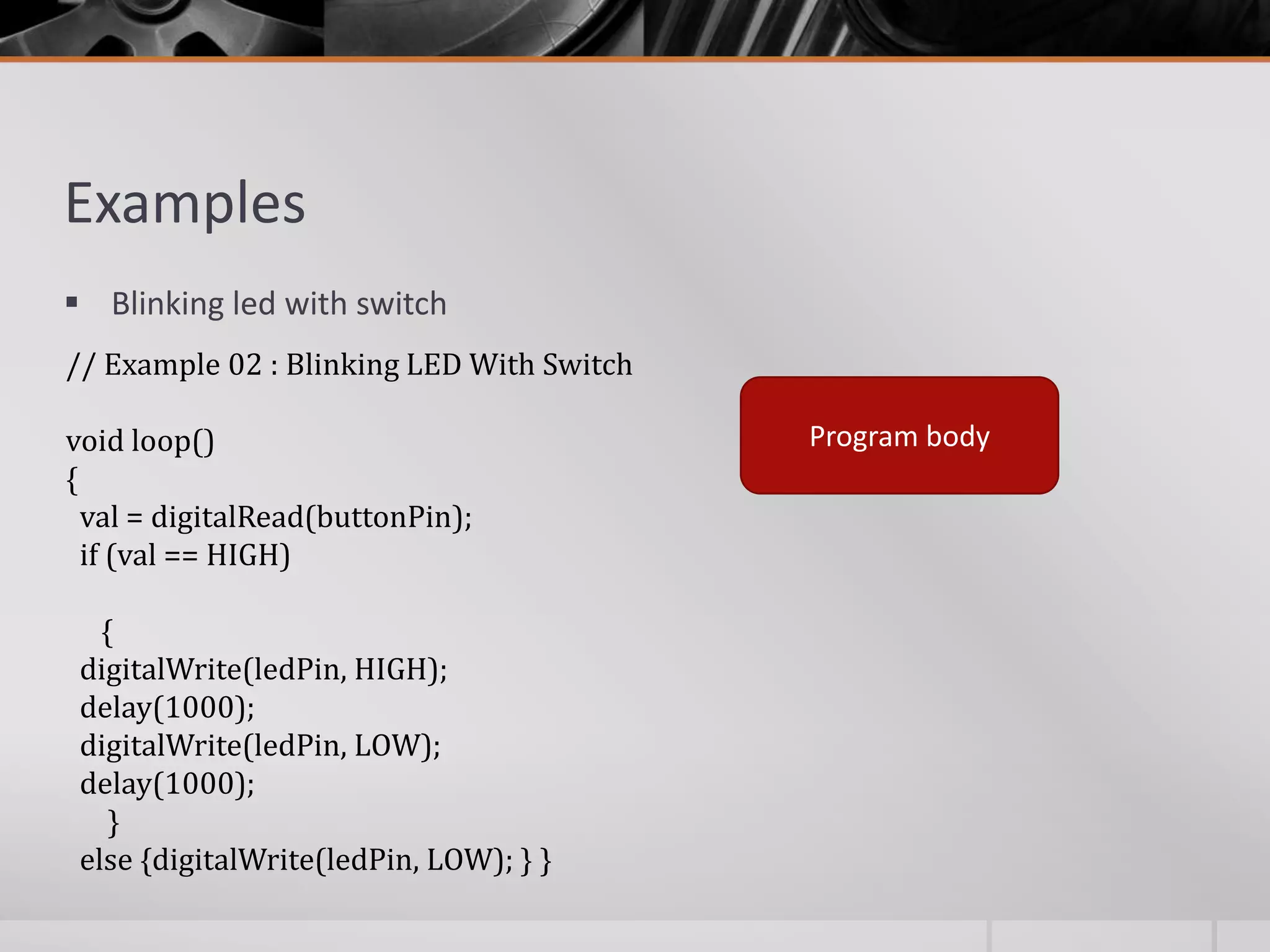
The document introduces Arduino, an open-source hardware platform for building electronics projects. Arduino consists of a programmable circuit board and IDE software. It is widely used due to its low cost, extensive documentation and community support. The document describes common Arduino boards like Uno and Mega, the Arduino programming language based on C/C++, and the Arduino IDE. It also discusses Arduino shields that extend the capabilities of the main board and provides examples of blinking LED projects.