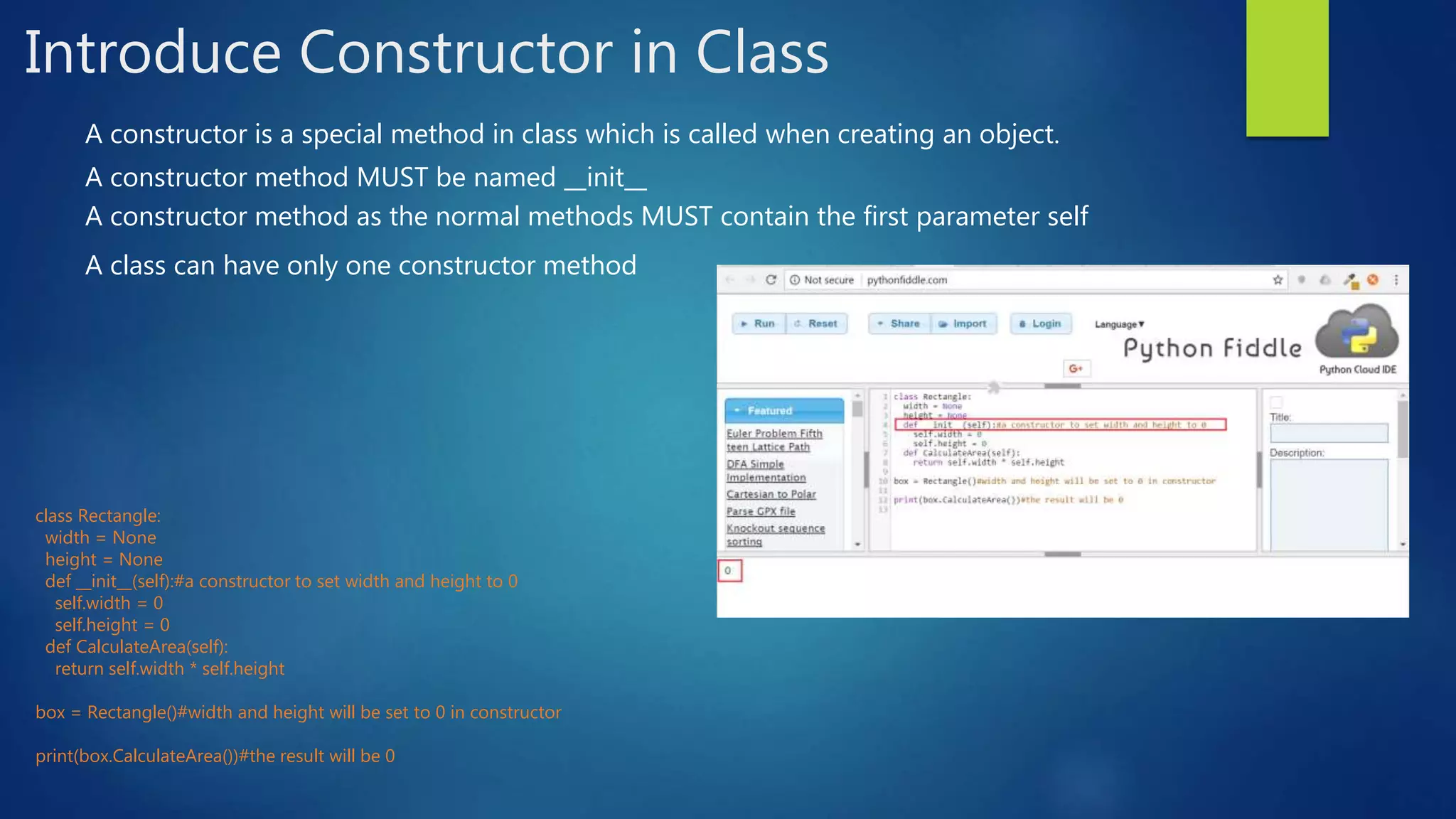
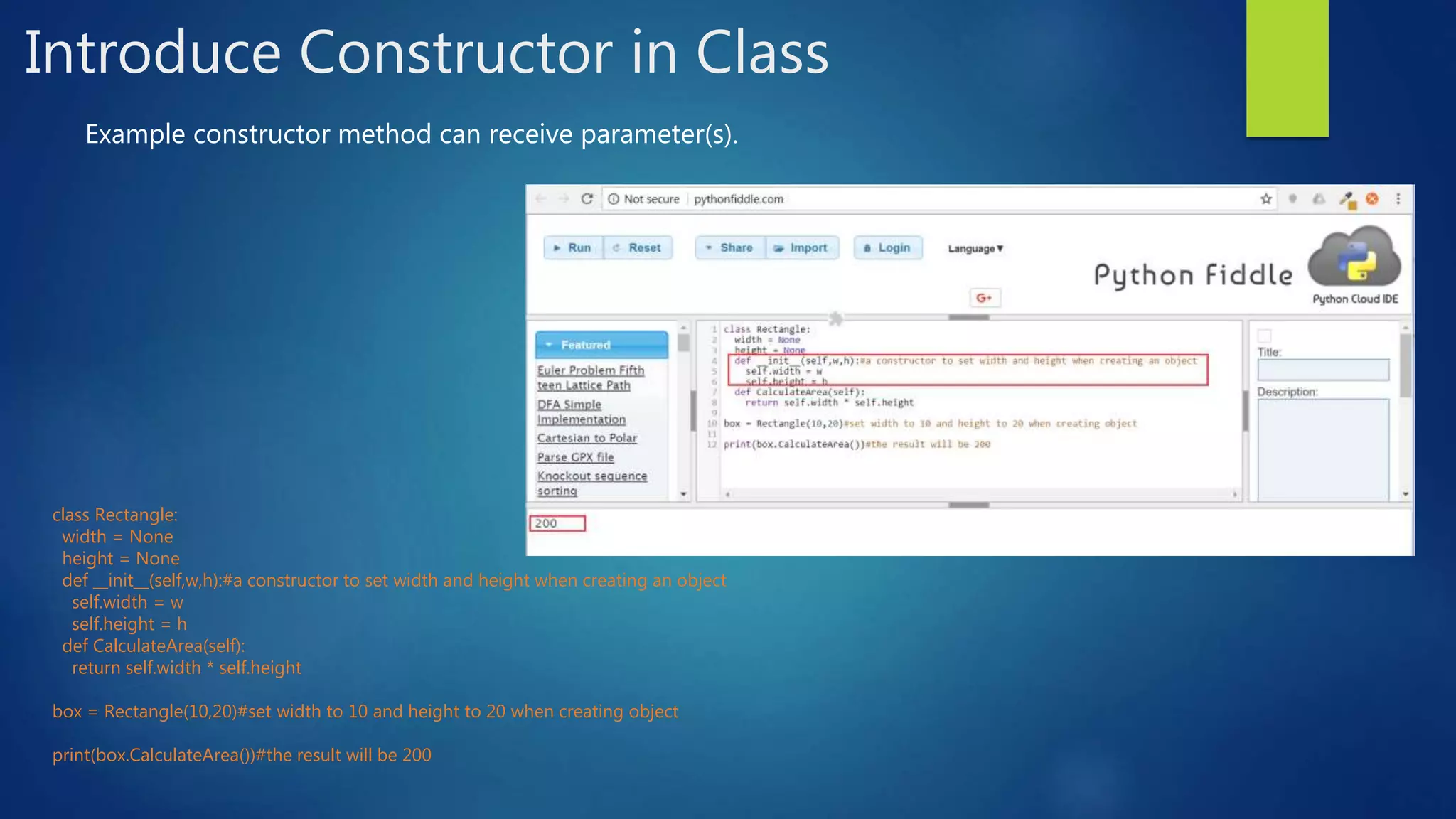
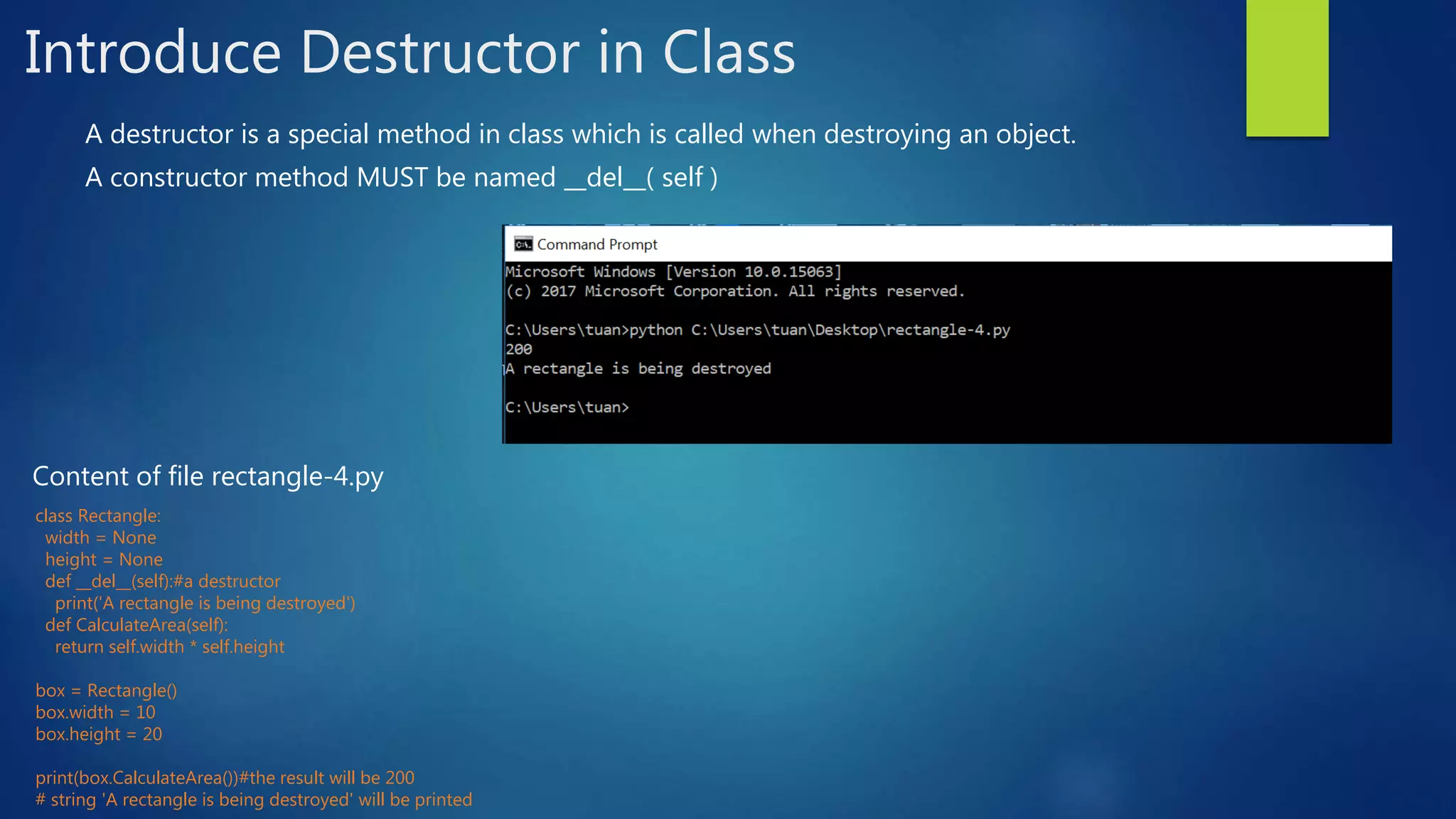
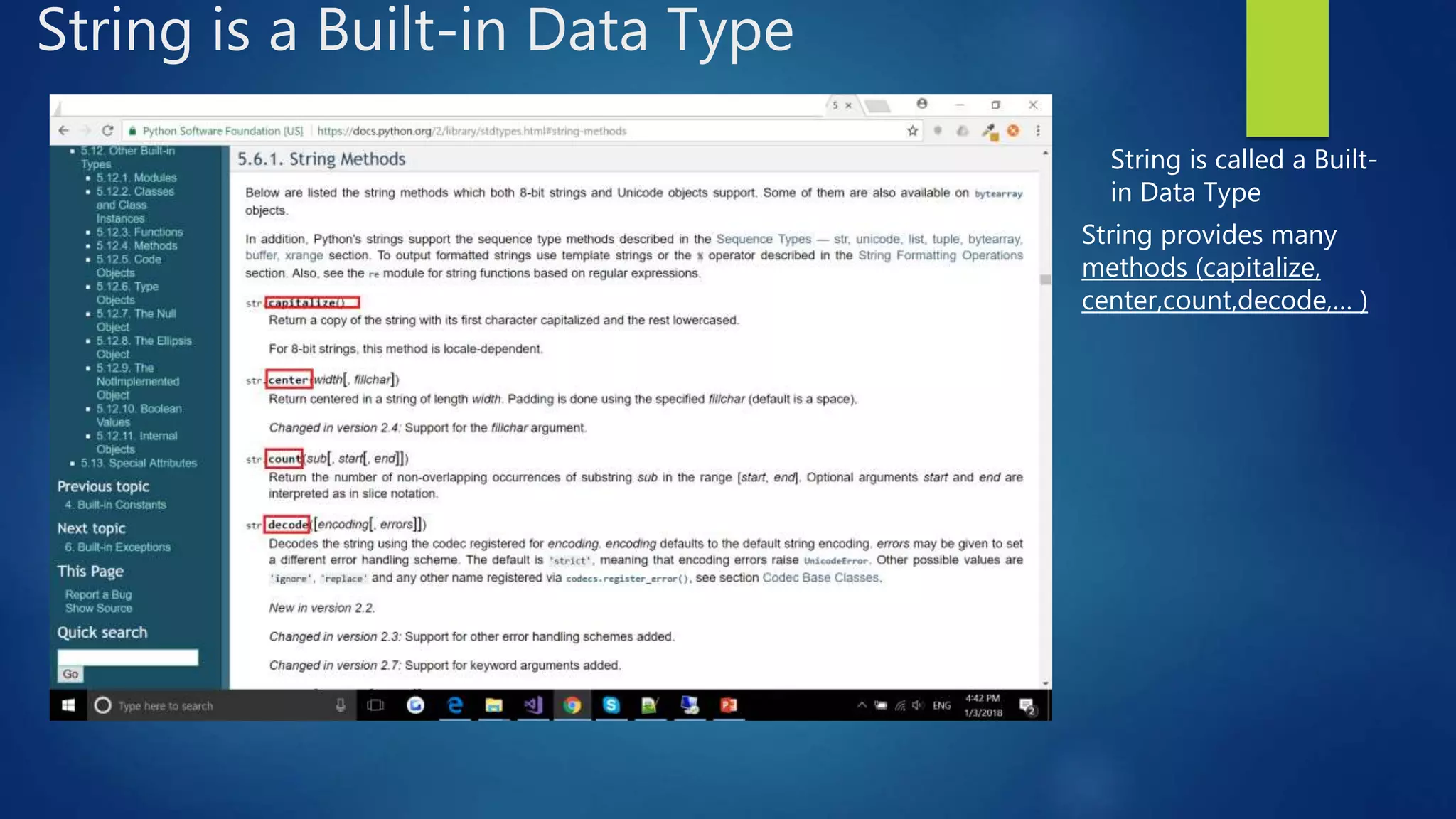
This document introduces object-oriented programming concepts in Python, including classes, objects, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. It provides examples of defining a Rectangle class with width and height attributes and a method to calculate area. Instances of Rectangle are created to demonstrate setting and getting attribute values and calling methods. The concepts of inheritance and polymorphism are demonstrated by creating subclasses of Rectangle like Cuboid that inherit attributes and can override methods. Constructors and destructors in classes are also described.



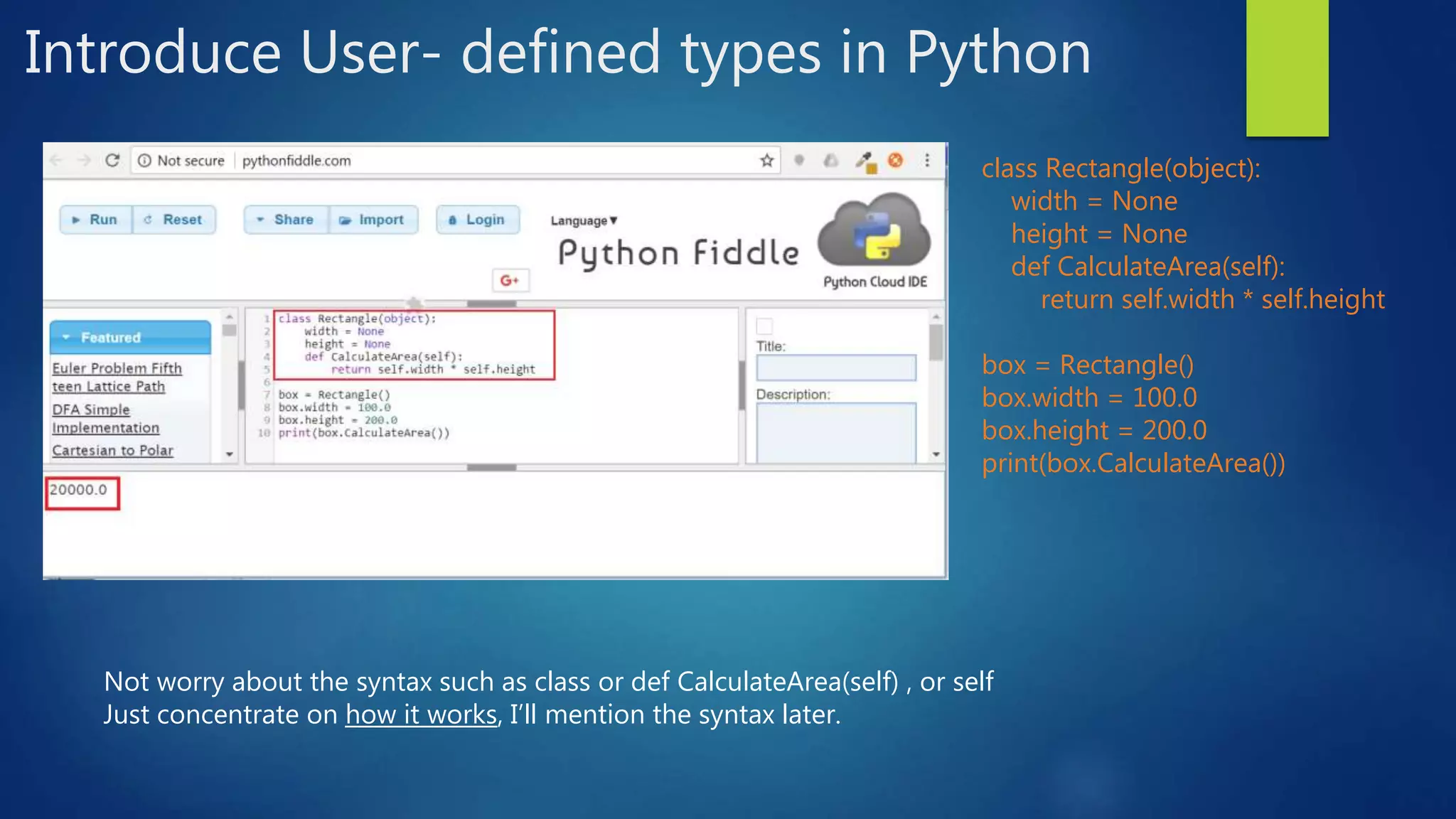



![Set of get value for attributes of an Object class Rectangle: width = None height = None def CalculateArea(self): return self.width * self.height box = Rectangle() box.width = 100.0 #set value of attribute width box.height = 200.0 #set value of attribute height print(box.width) #get value of attribute width print(box.height) #get value of attribute height The attributes of an object are sometime called properties or fields. They handle data for an object. Set value for an attribute: [NameOfObject].[NameOfAttribute] = [Value] Get value of an attribute: [NameOfObject].[NameOfAttribute] Example:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduceoopinpython-180628111716/75/Introduce-oop-in-python-11-2048.jpg)
![Call a method of an Object Note: Do not need to include self when calling the method of an instance of a class. Although the methods of a class always require the first parameter is self, but it’s not necessary to pass the parameter self to the method (this is syntax of Python ) box = Rectangle() box.width = 100.0 box.height = 200.0 print(box.CalculateArea()) It’s simple to call the method after the name of an instance and a dot. [NameOfObject].[NameOfMethod]([Parameters]) Example box.CalculateArea as below:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduceoopinpython-180628111716/75/Introduce-oop-in-python-12-2048.jpg)


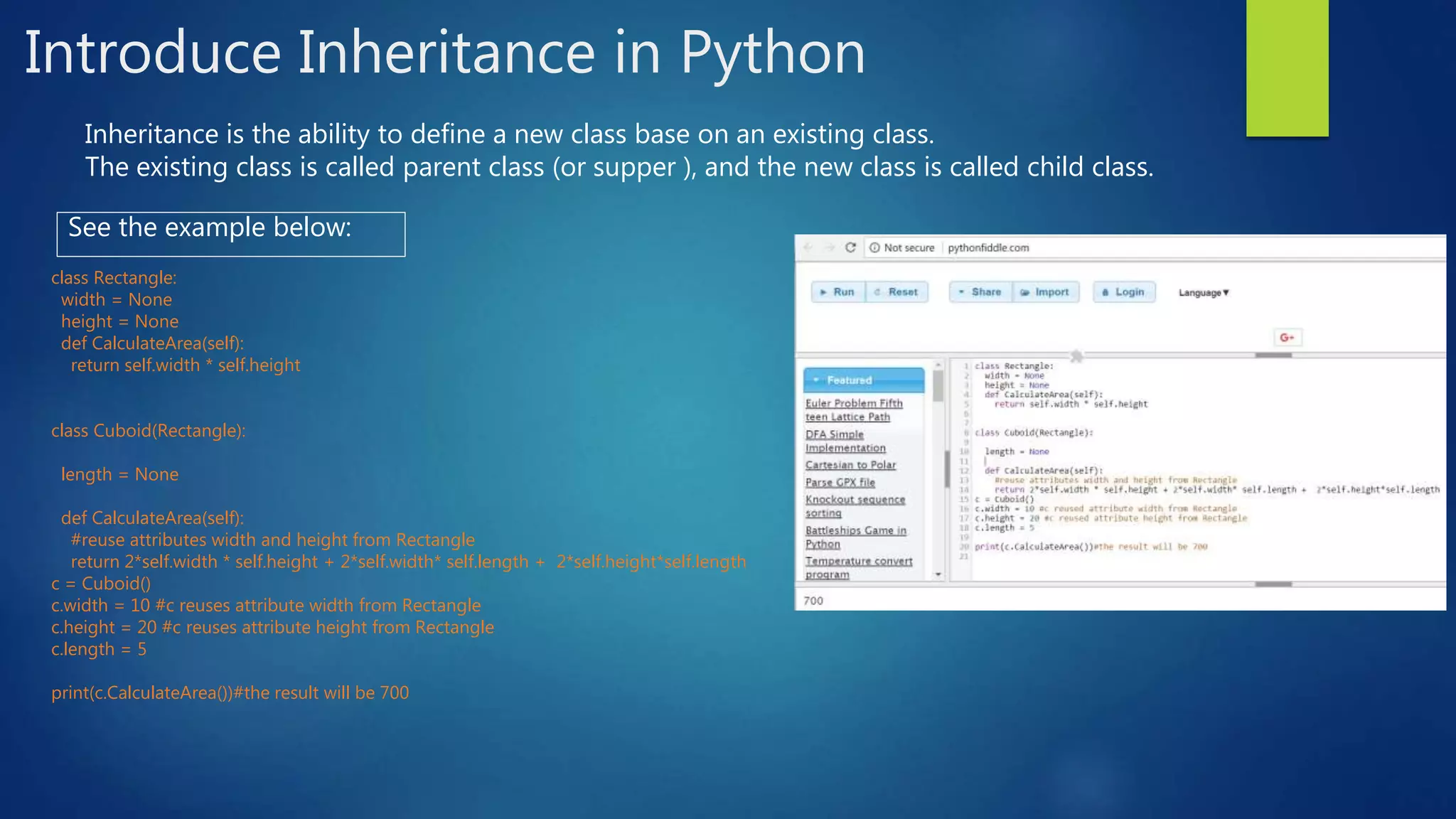
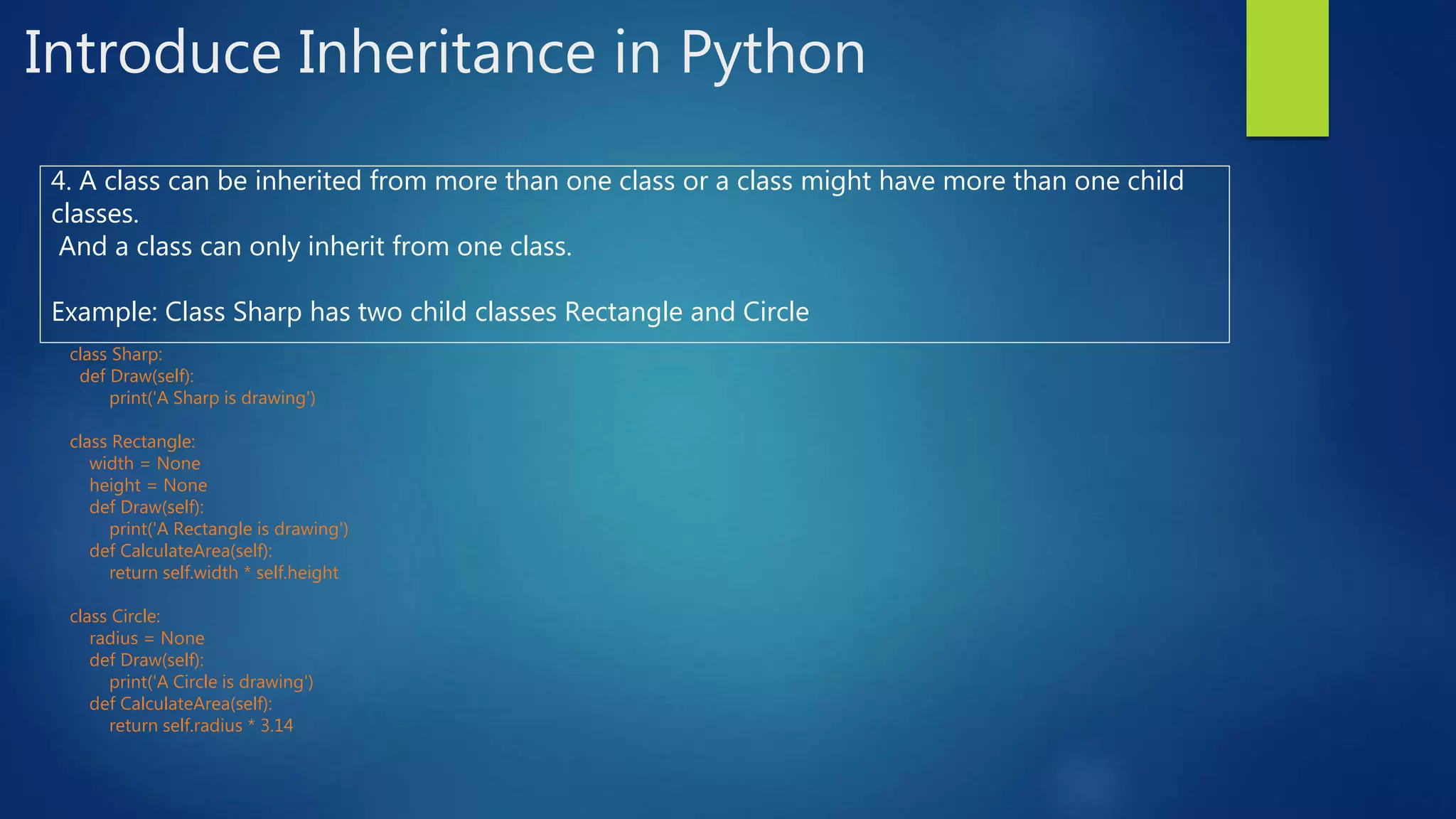
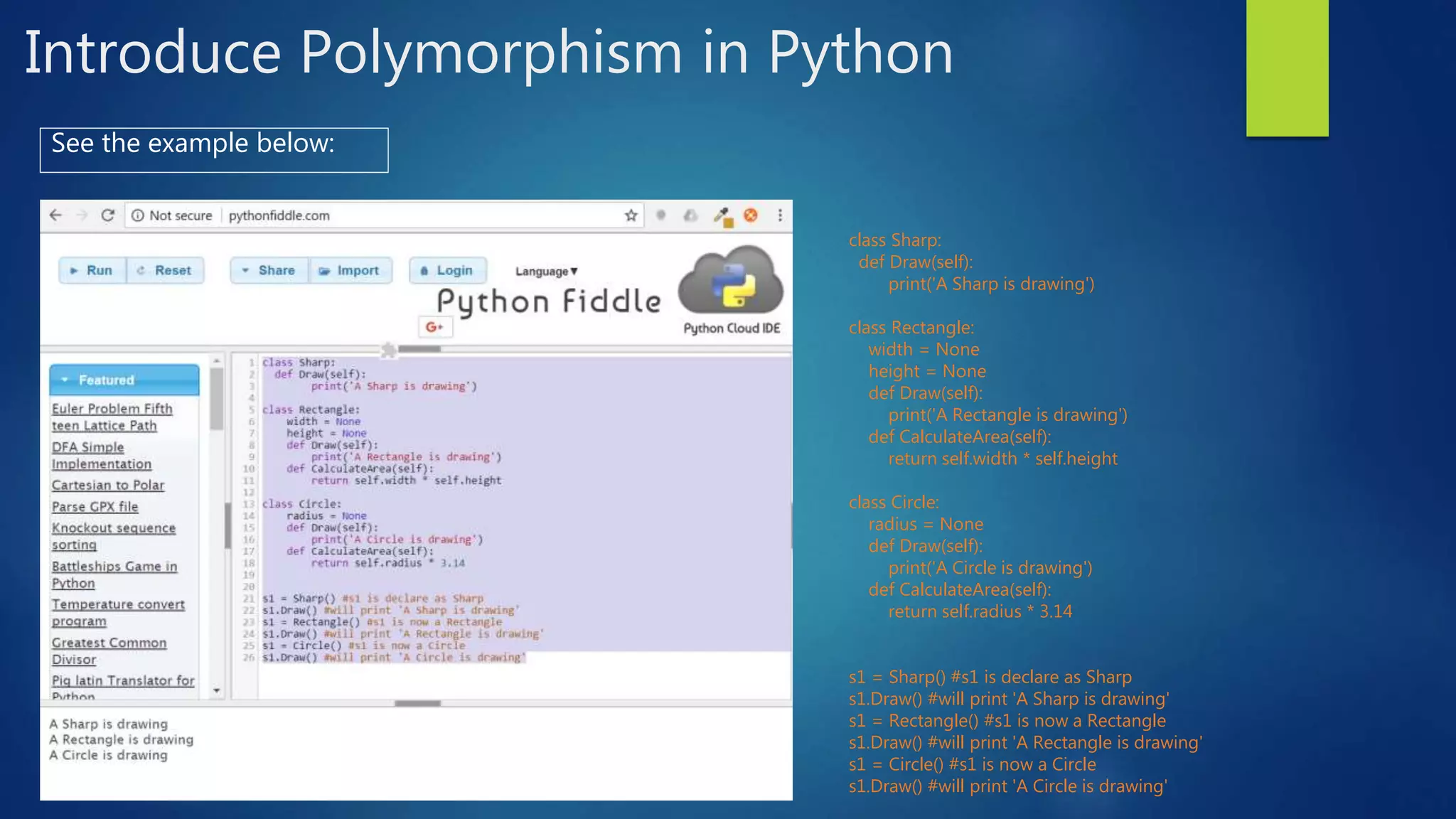
: Example: class Cuboid(Rectangle): 2. An object of the new class (child class) can use all public attributes of the existing class (supper/ parent class ) Example c = Cuboid(), c is an object of Cuboid and Cuboid is the child class of Rectangle, so c can use attributes width and height of Rectangle. 3. The child class can define a new method has the same name, same parameter(s) as the parent, this ability is called Overriding Methods. If an object of the child class calls the overriding method, then the method of the child class will execute not the method of the parent class. Example class Cuboid defines a new method CalculateArea which is defined in Rectangle, when calling c.CalculateArea() then the method CalculateArea of Cuboid is called not CalculateArea of Rectangle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduceoopinpython-180628111716/75/Introduce-oop-in-python-16-2048.jpg)