The document is a comprehensive exploration of Kotlin, detailing its features, use cases, and implementation examples. It covers various aspects of the language including functions, variables, null safety, and Kotlin's interoperability with Java, while also discussing the benefits and potential drawbacks of adopting Kotlin in development. The author, Johan Haleby, shares insights from his experience evaluating Kotlin for server-side use and highlights its advantages in terms of productivity and practicality.











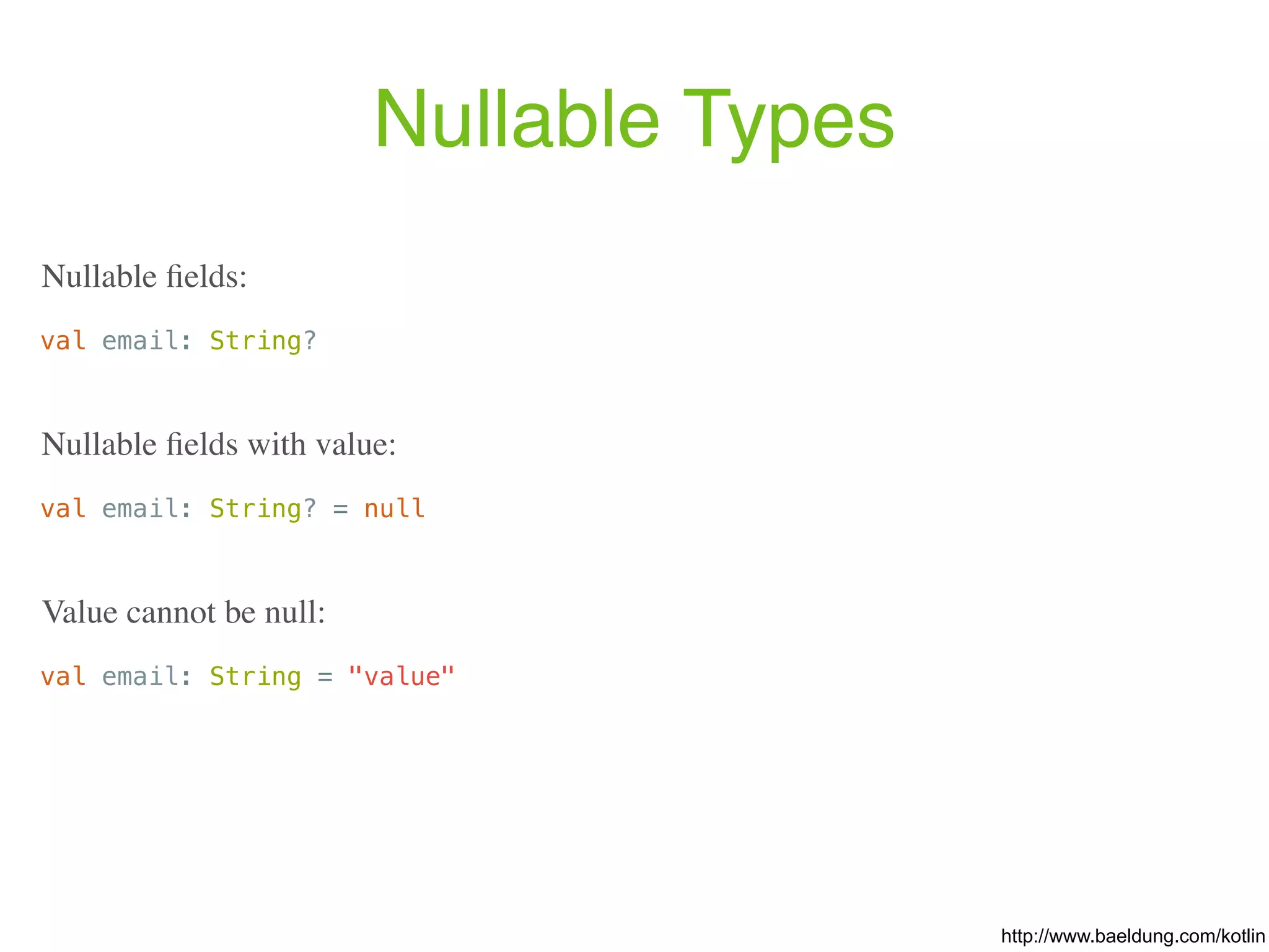

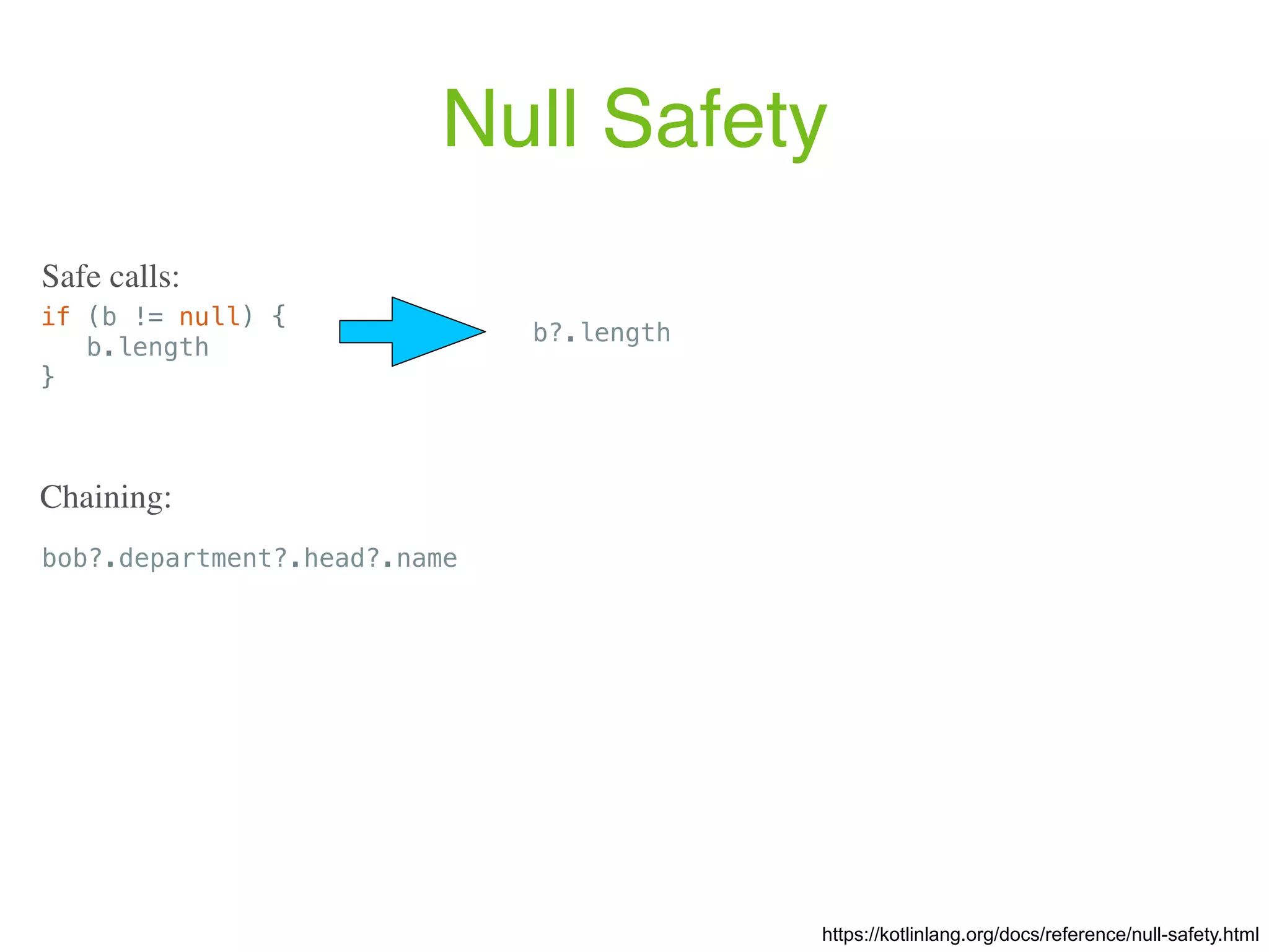
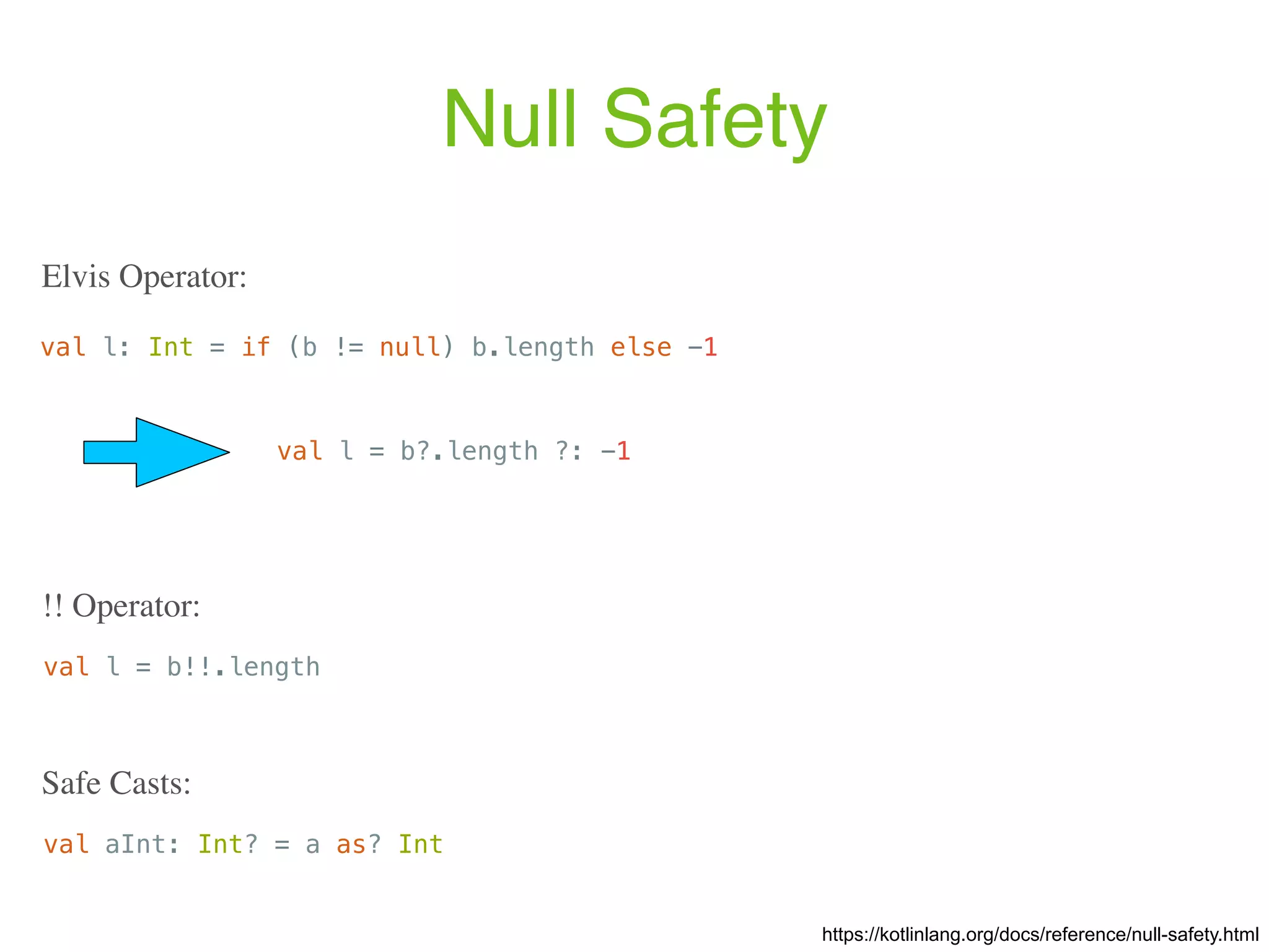








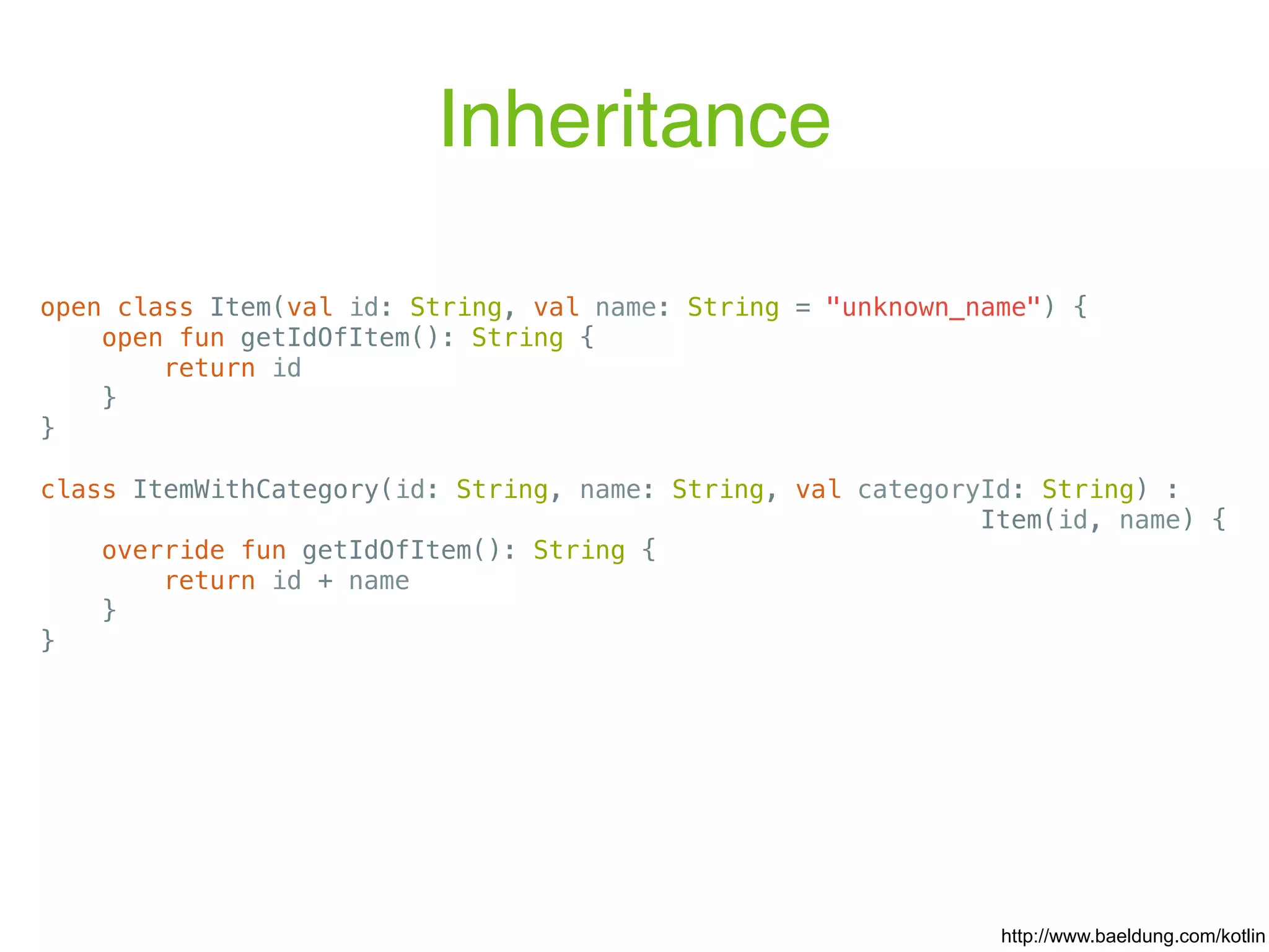


![Properties var <propertyName>[: <PropertyType>] [= <property_initializer>] [<getter>] [<setter>] var initialized = 1 // has type Int, default getter and setter val inferredType = 1 // has type Int and a default getter Examples: https://kotlinlang.org/docs/reference/properties.html The full syntax for declaring a property is: val isEmpty: Boolean get() = this.size == 0 Custom getter: // Type is inferred (since Kotlin 1.1) val isEmpty get() = this.size == 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kotlin-foo-cafe-2017-181119103810/75/Exploring-Kotlin-30-2048.jpg)


























![Sequences val fibonacci = generateSequence(1 to 1) { it.second to it.first+it.second }.map {it.first} // prints [1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55] println(fibonacci.take(10).toList()) https://agilewombat.com/2016/02/06/kotlin-sequences/ Example: Example Fibonacci: val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5) val sum = numbers.asSequence() .map { it * 2 } // Lazy .filter { it % 2 == 0 } // Lazy .reduce(Int::plus) // Terminal (eager) println(sum) // 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kotlin-foo-cafe-2017-181119103810/75/Exploring-Kotlin-64-2048.jpg)


![Looping val numbers = arrayOf("first", "second", "third", "fourth") for (i in numbers.indices) { print(numbers[i]) } https://kotlinlang.org/docs/reference/control-flow.html Loop with indices: for ((index, value) in array.withIndex()) { println("the element at $index is $value") } Value and index:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kotlin-foo-cafe-2017-181119103810/75/Exploring-Kotlin-67-2048.jpg)







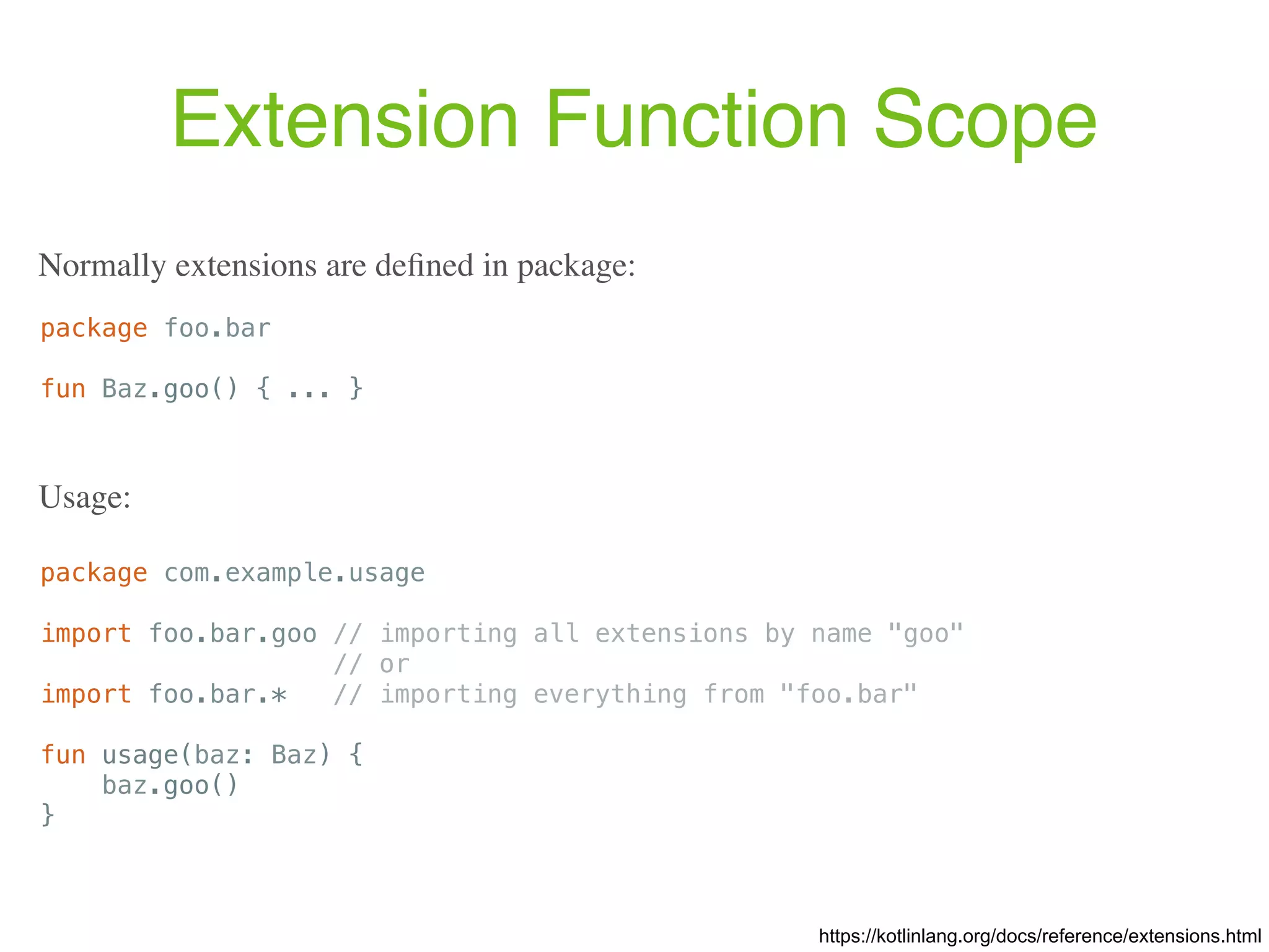
![Extension Functions fun <T> MutableList<T>.swap(index1: Int, index2: Int) { val tmp = this[index1] // 'this' corresponds to the list this[index1] = this[index2] this[index2] = tmp } https://kotlinlang.org/docs/reference/extensions.html Defining extension function: val l = mutableListOf(1, 2, 3) l.swap(0, 2) // 'this' inside 'swap()' will hold the value of 'l' Usage:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kotlin-foo-cafe-2017-181119103810/75/Exploring-Kotlin-76-2048.jpg)






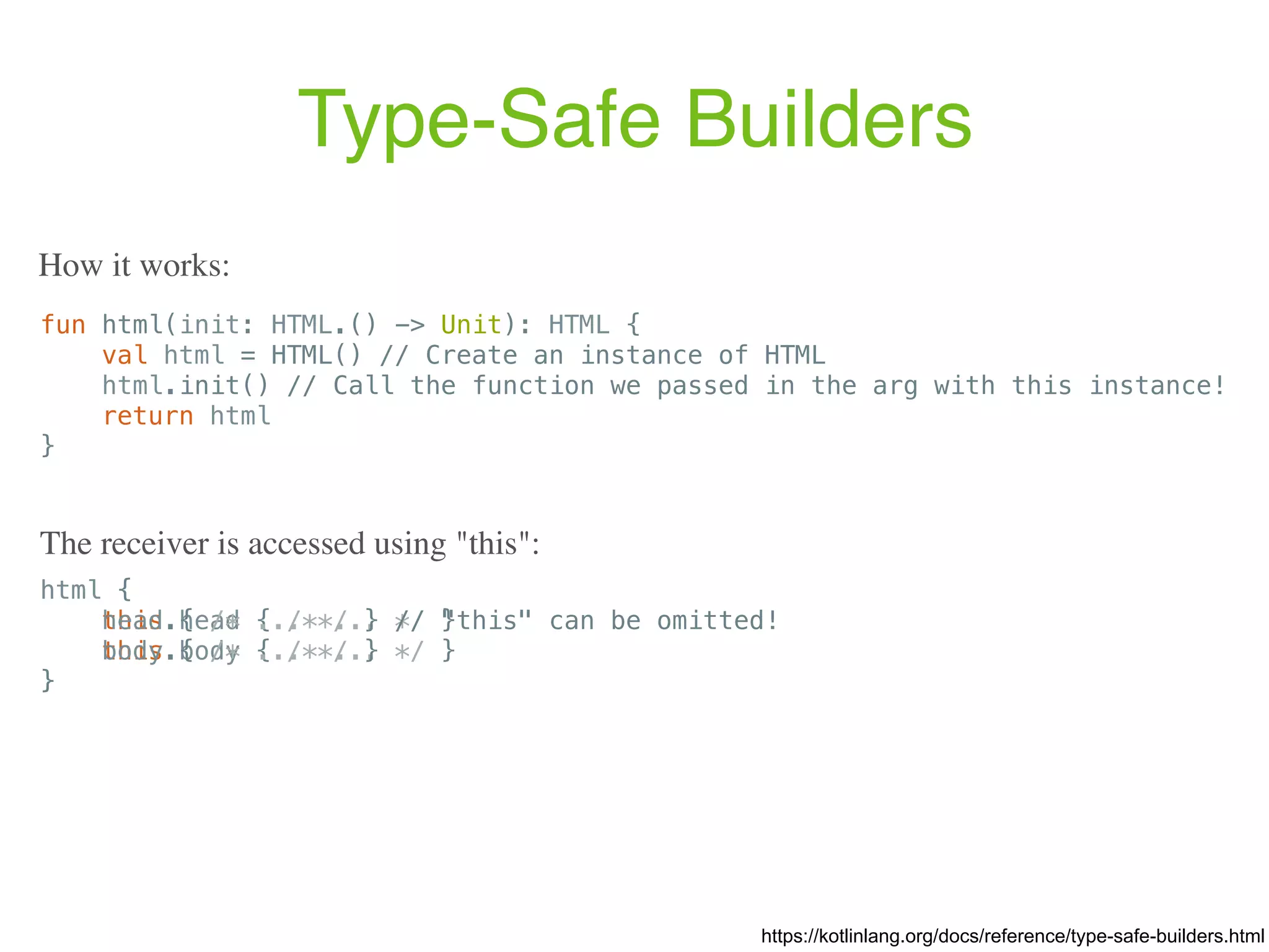




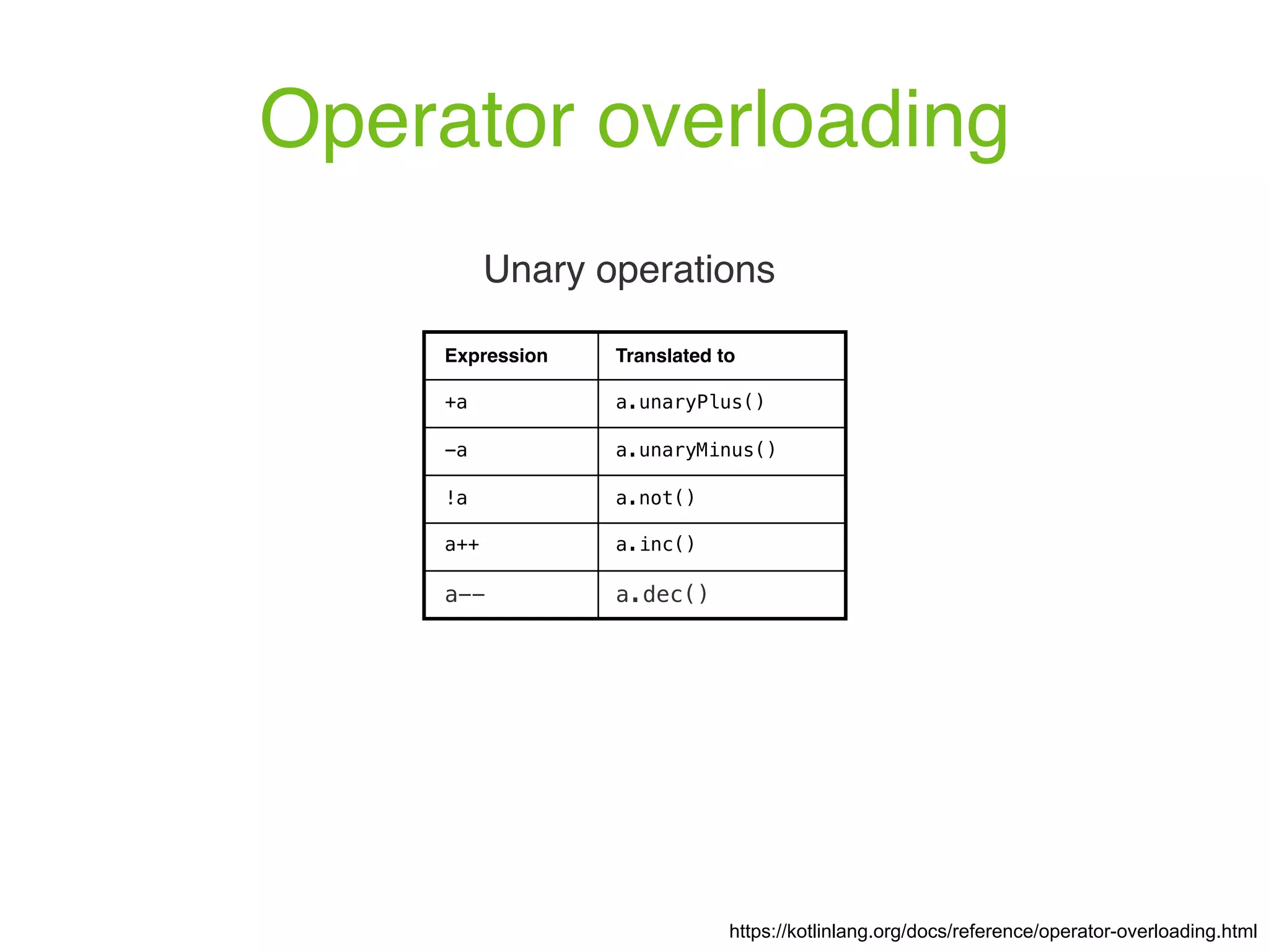

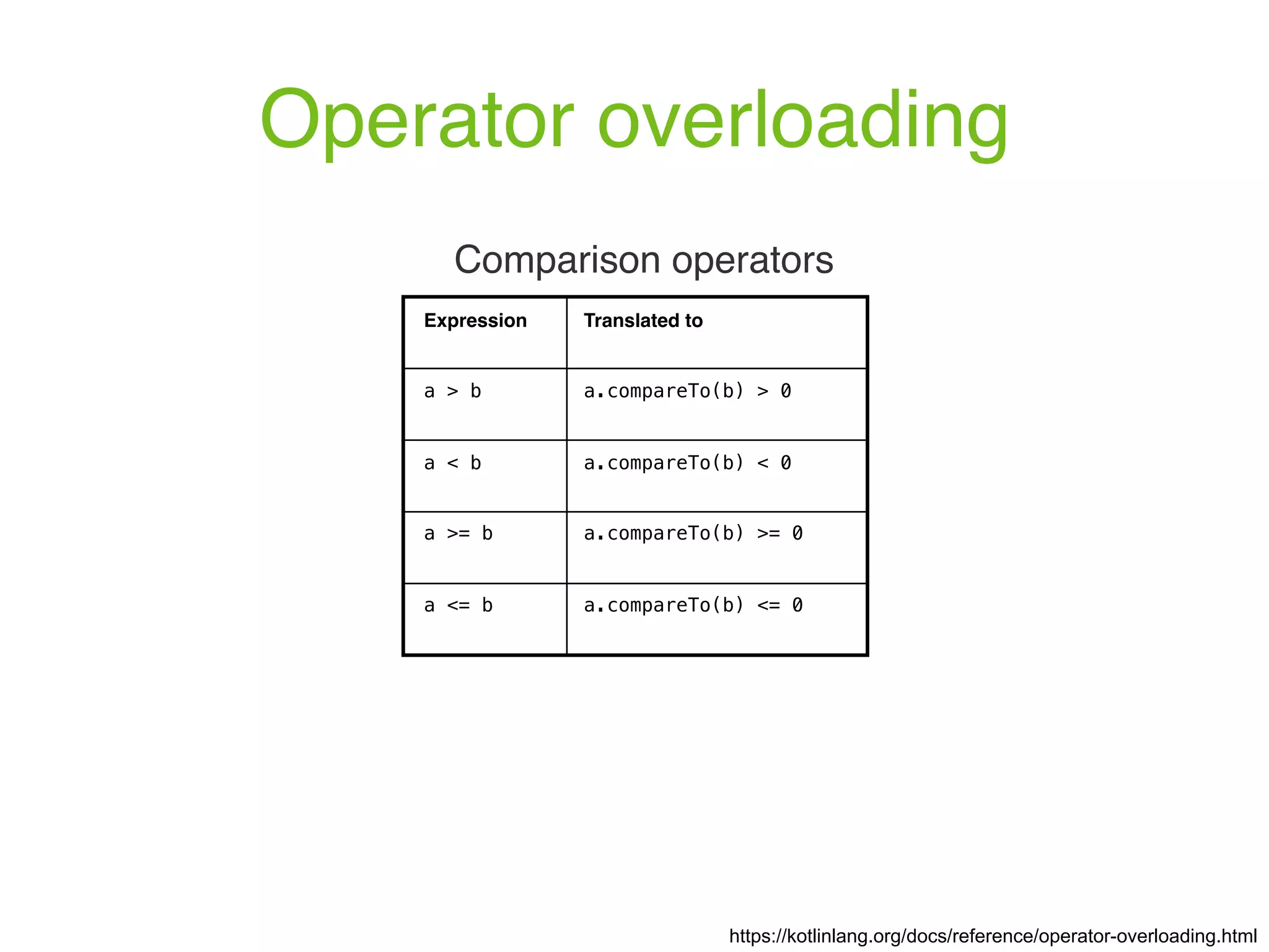
![Operator overloading https://kotlinlang.org/docs/reference/operator-overloading.html Array type operators Expression Translated to a[i] a.get(i) a[i, j] a.get(i, j) a[i_1, ..., i_n] a.get(i_1, ..., i_n) a[i] = b a.set(i, b) a[i, j] = b a.set(i, j, b) a[i_1, ..., i_n] = b a.set(i_1, ..., i_n, b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kotlin-foo-cafe-2017-181119103810/75/Exploring-Kotlin-96-2048.jpg)

![Operator overloading https://antonioleiva.com/operator-overload-kotlin/ class Employee(val id: Long, val name: String) class Company(private val employees: List) { operator fun get(pos: Int) = employees[pos] } Example: val company = Company(listOf(Employee(1235, "John"), Employee(2584, "Mike"))) val mike = company[1] // Operator "get" kicks in Usage:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kotlin-foo-cafe-2017-181119103810/75/Exploring-Kotlin-99-2048.jpg)

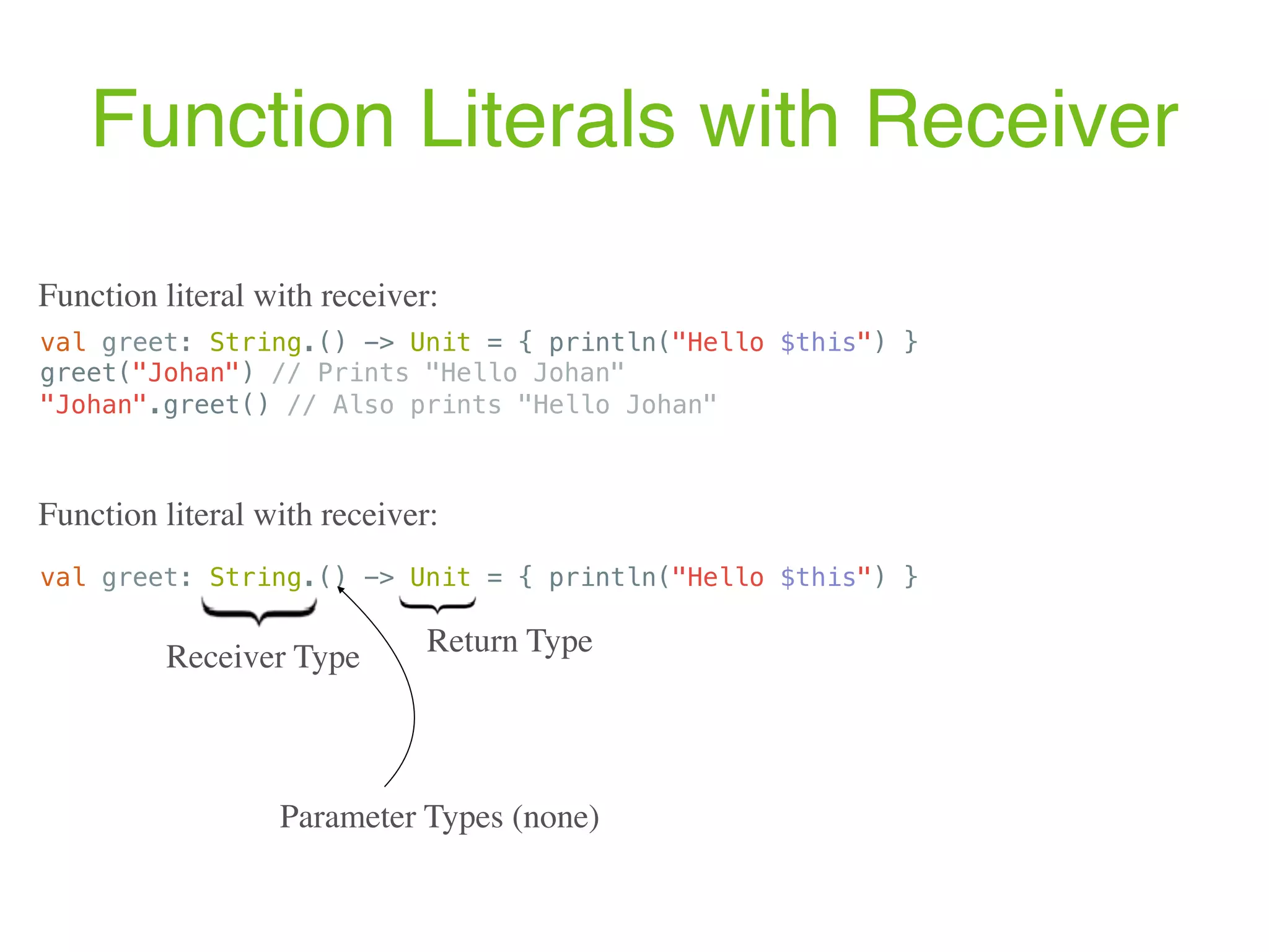
![Type Alias https://kotlinlang.org/docs/reference/type-aliases.html typealias Predicate<T> = (T) -> Boolean fun foo(p: Predicate<Int>) = p(42) fun main(args: Array<String>) { val f: (Int) -> Boolean = { it > 0 } println(foo(f)) // prints "true" val p: Predicate<Int> = { it > 0 } println(listOf(1, -2).filter(p)) // prints "[1]" } Example 1: typealias NodeSet = Set<Network.Node> typealias FileTable<K> = MutableMap<K, MutableList<File>> Example 2:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kotlin-foo-cafe-2017-181119103810/75/Exploring-Kotlin-101-2048.jpg)








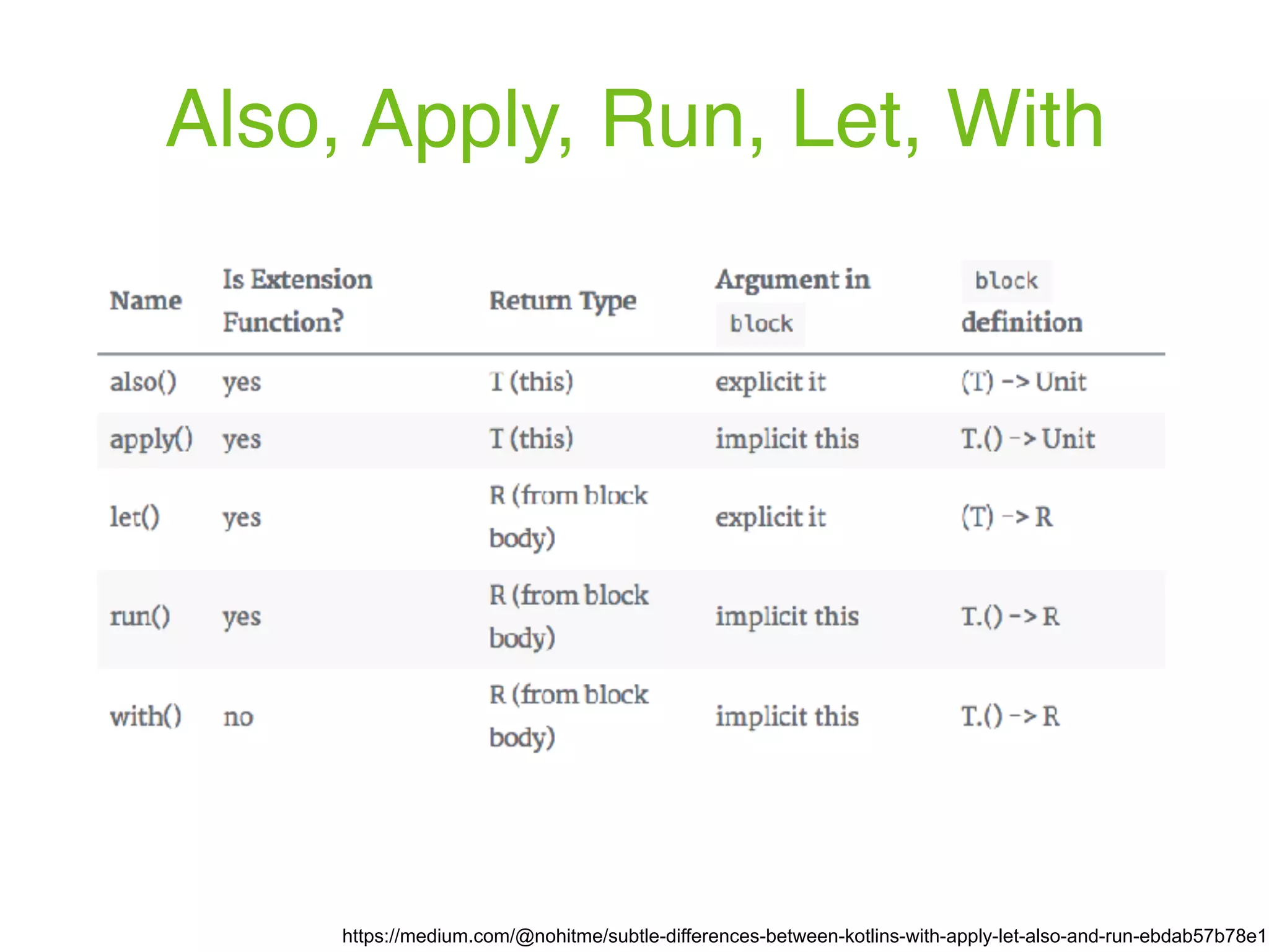






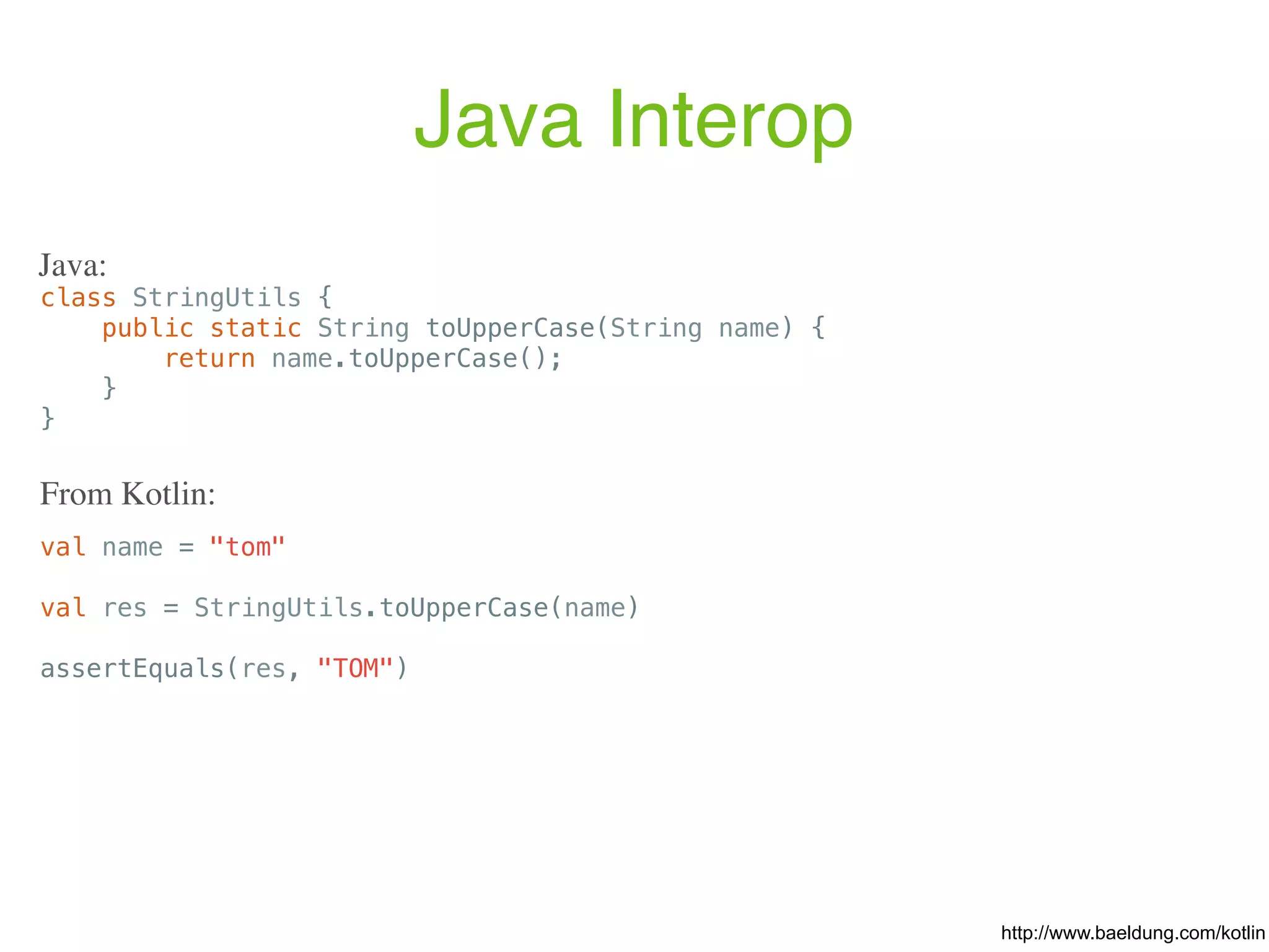
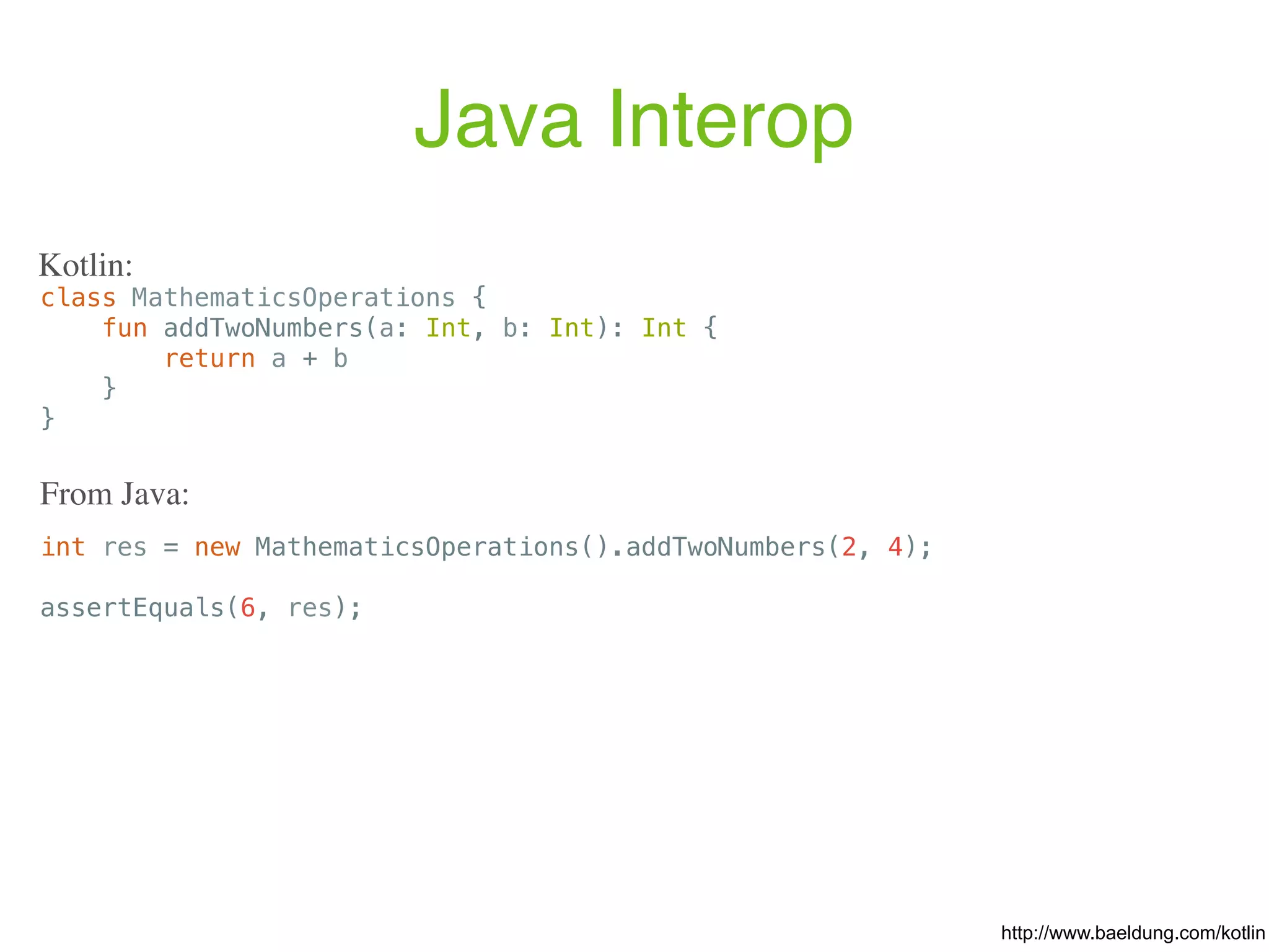








![https://github.com/JetBrains/Exposed object Users : Table() { val id = varchar("id", 10).primaryKey() // Column<String> val name = varchar("name", length = 50) // Column<String> val cityId = (integer("city_id") references Cities.id).nullable() // Column<Int?> } object Cities : Table() { val id = integer("id").autoIncrement().primaryKey() // Column<Int> val name = varchar("name", 50) // Column<String> } fun main(args: Array<String>) { Database.connect("jdbc:h2:mem:test", driver = "org.h2.Driver") transaction { create (Cities, Users) val saintPetersburgId = Cities.insert { it[name] = "St. Petersburg" } get Cities.id // .. Users.update({Users.id eq "alex"}) { it[name] = "Alexey" } (Users innerJoin Cities).slice(Users.name, Cities.name). select {(Users.id.eq("andrey") or Users.name.eq("Sergey")) and Users.id.eq("sergey") and Users.cityId.eq(Cities.id)}.forEach { println("${it[Users.name]} lives in ${it[Cities.name]}") } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kotlin-foo-cafe-2017-181119103810/75/Exploring-Kotlin-128-2048.jpg)










![Future ! Java 9 support in Kotlin 1.2 ! Could target iOS with Kotlin Native ! Collection literals ! val l: List = [ 1, 2, 3 ] ! SAM conversions for Kotlin interfaces ! Truly immutable data (persistent collections?)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kotlin-foo-cafe-2017-181119103810/75/Exploring-Kotlin-140-2048.jpg)