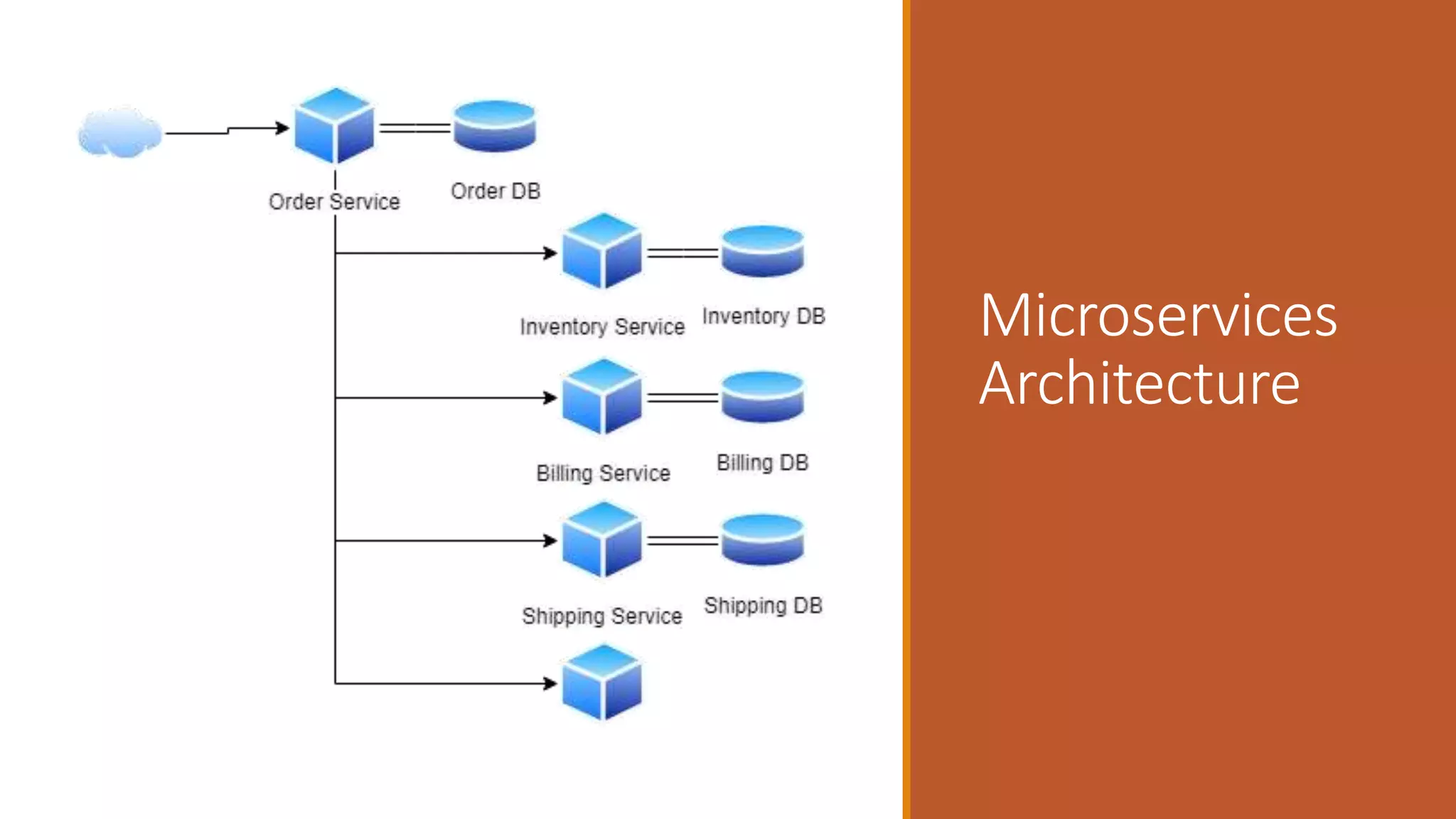
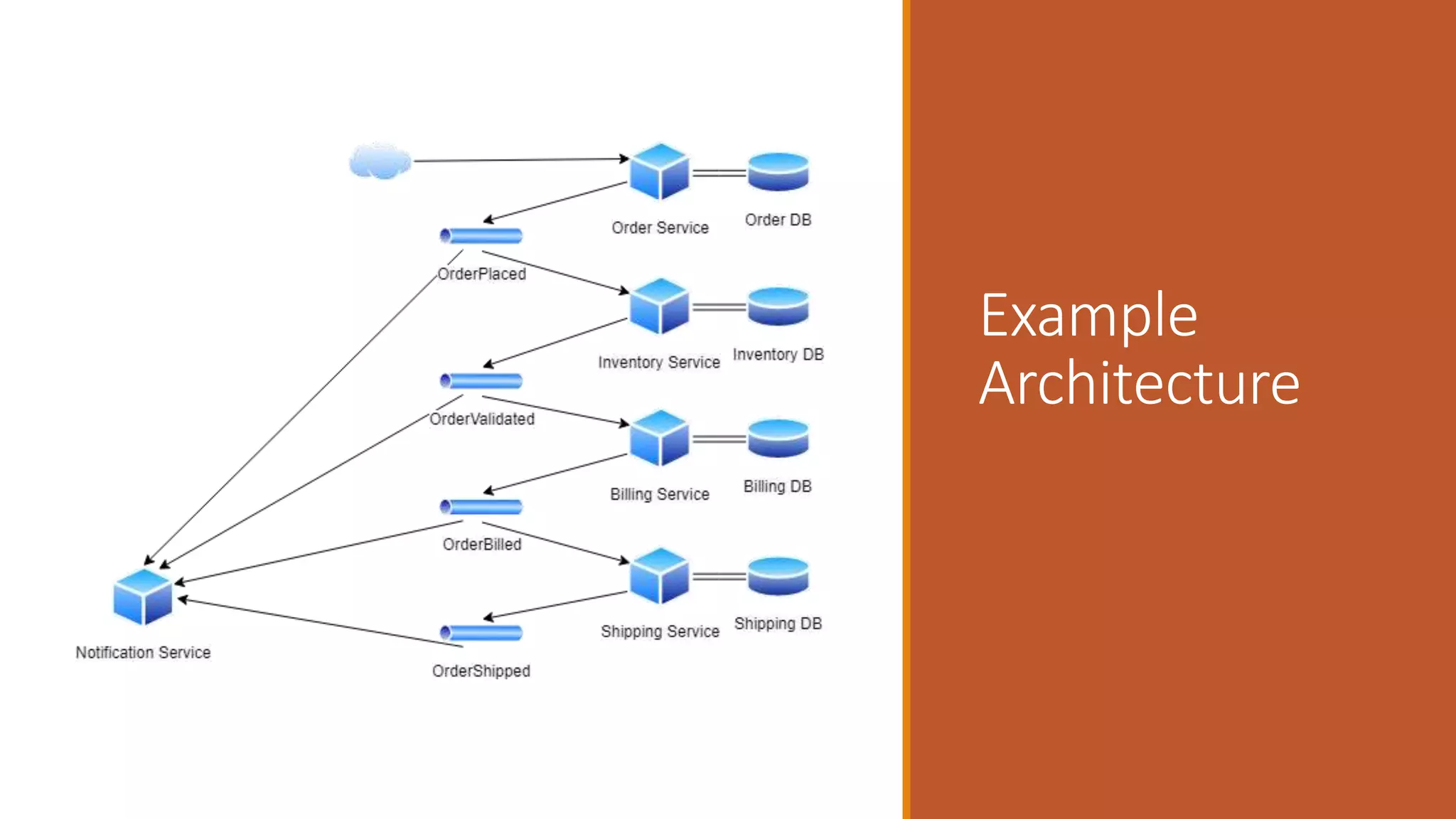
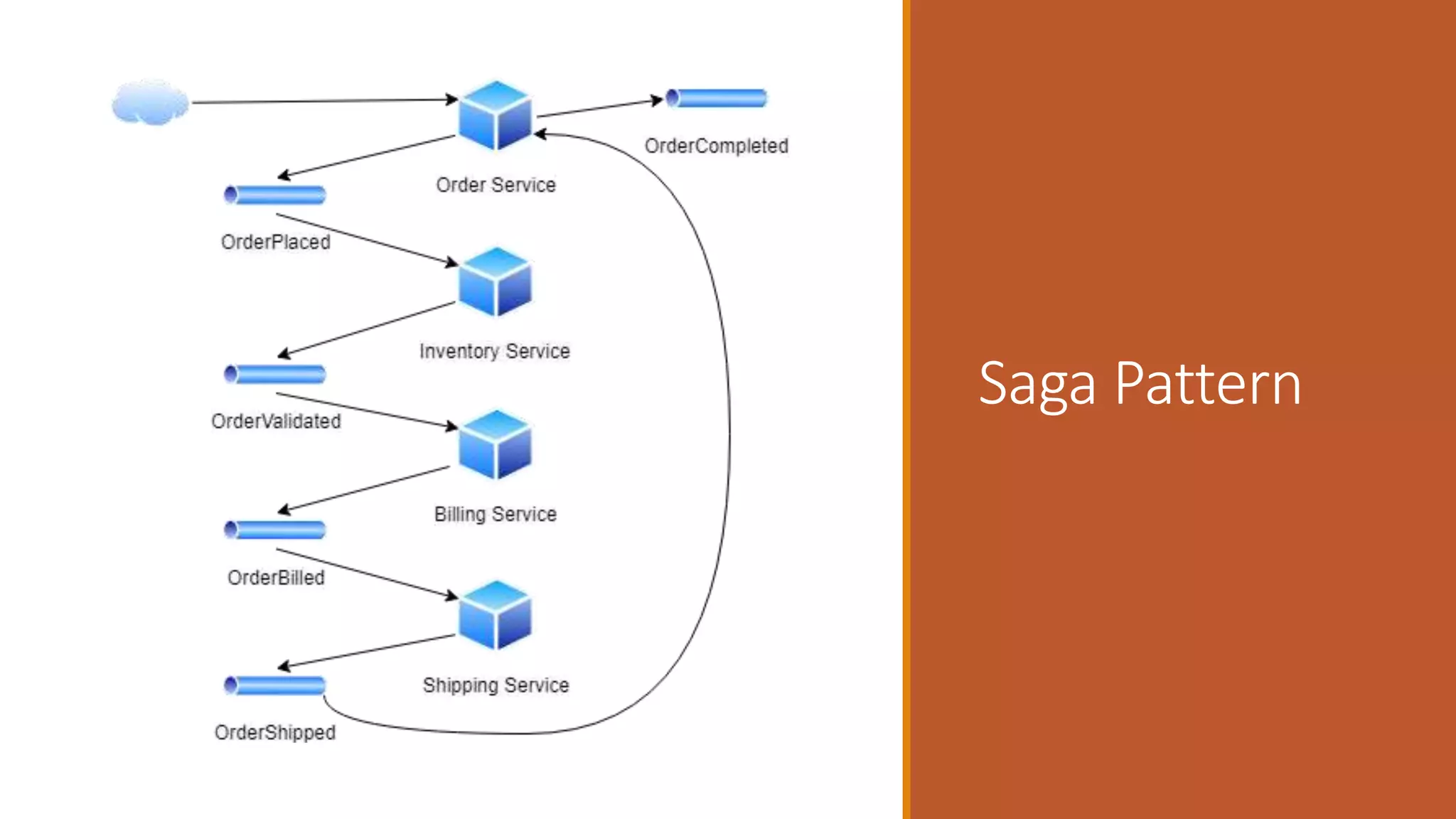
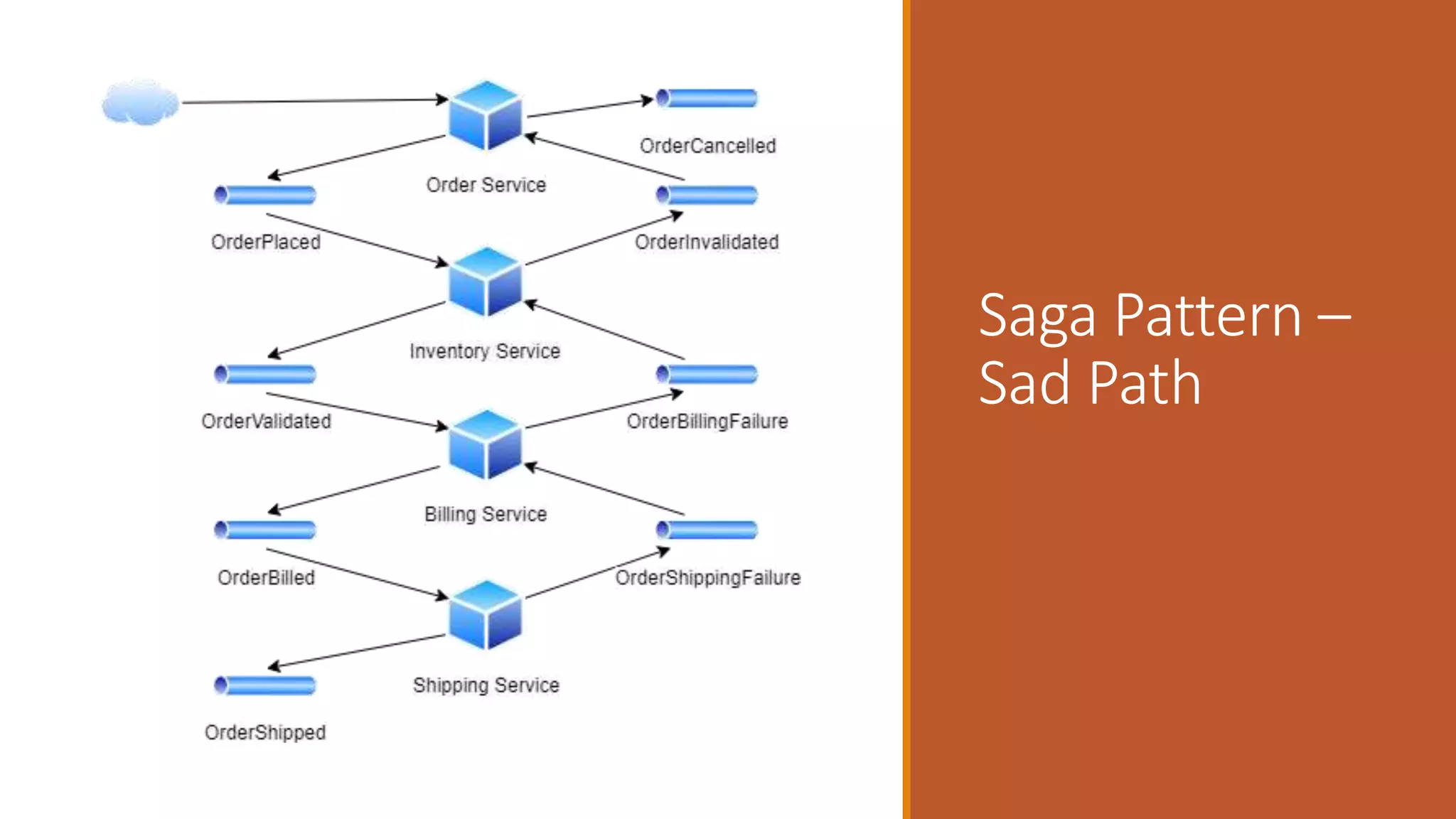
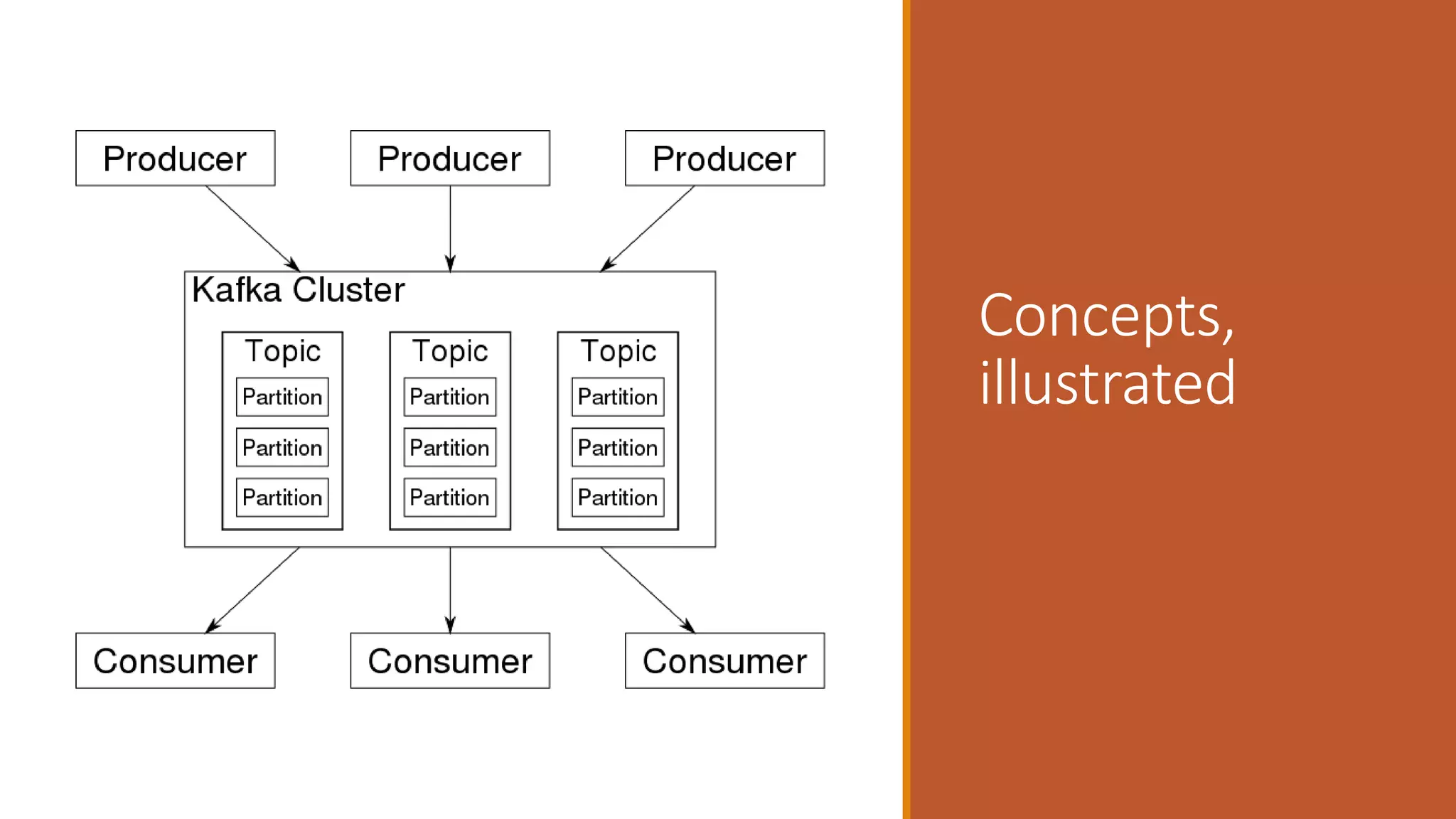
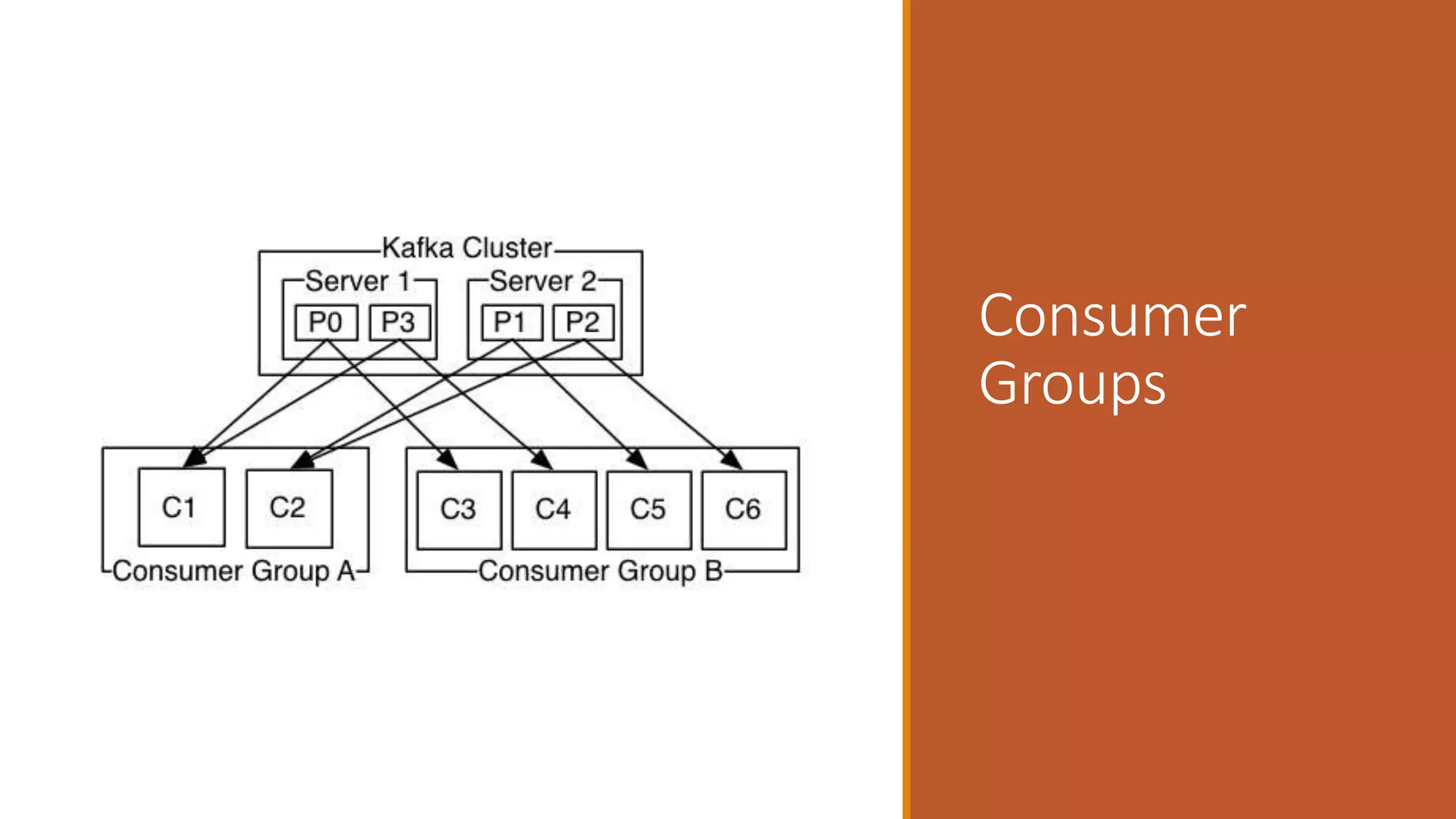
This document discusses event-driven architectures and how Apache Kafka can be used to enable them. It provides an overview of microservices architectures and the issues they can have with synchronous calls. Event-driven architectures address these issues using asynchronous messaging. Kafka is then introduced as a distributed messaging platform that allows publishing and subscribing to event streams. It describes key Kafka concepts like topics, partitions, producers, and consumers. The document argues that using Kafka for event-driven architectures solves problems around service location, load balancing, and integration of new services. It also provides durable storage and read positioning capabilities. Finally, it references additional resources and promises a demo.